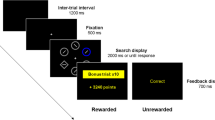
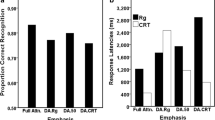
Abstract
Many previous studies observed that higher retrospective confidence ratings about memory performance were associated with shorter response times in memory test. Researchers often interpret response time as a measure of retrieval fluency which is an important cue utilized in confidence formation process. However, the drift diffusion model (DDM) indicates that response time in recognition memory test includes both a decision component representing memory retrieval, and a non-decision component unrelated to retrieval process. Few previous studies have investigated whether retrospective confidence in recognition test is related to the speed of both retrieval and non-decision processes. To address this question, the current study first analyzed data from six published experiments, and found that higher retrospective confidence ratings were associated with both higher drift rate (indicating retrieval fluency) and shorter non-decision time in DDM. Then we manipulated the ease of perception in two new experiments, and the results consistently indicated that difficulty in stimulus perception increased non-decision time in recognition test, which affected retrospective confidence. Furthermore, the documented results also suggest drift rate could partly account for the positive relationship between confidence and memory performance, while the reliance of confidence on non-decision time negatively affected confidence accuracy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In the Confidence Database, there are also experiments with study materials other than single words (e.g., word pairs or pictures). However, fitting the Bayesian model to data in each experiment was computationally expensive (see below). Here we only analyzed the experiments asking participants to learn single words, which are one of the most commonly used materials in recognition test and also used in the two experiments of the current study.
The transformation of confidence scale implemented here was based on a simplified assumption that participants considered the intervals between neighboring scale points were equal across the whole scale. Some studies provided evidence against this assumption (Hanczakowski, Zawadzka, et al., 2013; Zawadzka & Higham, 2015), which might be considered in future studies.
Although many previous studies on metamemory use Gamma correlation to measure confidence accuracy (for a review, see Masson & Rotello 2009), there are some studies using Kendall’s τb (Dougherty et al., 2018; Robey et al., 2017). Here we use Kendall’s τb as the measure of confidence accuracy because it is easy to compute semi-partial Kendall’s τb correlation.
The Kendall’s τb correlation could not be computed in hard-to-perceive condition for one participant in Experiment 1b, because all of the trials were correctly answered in recognition test.
References
Ackerman, R. (2014). The diminishing criterion model for metacognitive regulation of time investment. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General (143 vol., pp. 1349–1368). American Psychological Association. 3https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035098
Anderson, J. R. (1981). Interference: The relationship between response latency and response accuracy. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 7(5), 326–343. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.7.5.326
Brown, S. D., & Heathcote, A. (2008). The simplest complete model of choice response time: Linear ballistic accumulation. Cognitive Psychology, 57(3), 153–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COGPSYCH.2007.12.002
Busey, T. A., Tunnicliff, J., Loftus, G. R., & Loftus, E. F. (2000). Accounts of the confidence-accuracy relation in recognition memory. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 7, 26–48. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03210724
Chang, M., & Brainerd, C. J. (2022). Association and dissociation between judgments of learning and memory: A Meta-analysis of the font size effect. Metacognition and Learning, 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11409-021-09287-3
Coltheart, M. (1981). The MRC psycholinguistic database. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 33(4), 497–505. https://doi.org/10.1080/14640748108400805
Cousineau, D. (2005). Confidence intervals in within-subject designs: A simpler solution to Loftus and Masson’s method. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 1(1), 42–45. https://doi.org/10.20982/tqmp.01.1.p042
Diemand-Yauman, C., Oppenheimer, D. M., & Vaughan, E. B. (2011). Fortune favors the bold (and the italicized): Effects of disfluency on educational outcomes. Cognition, 118(1), 111–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2010.09.012
Dougherty, M. R., Scheck, P., Nelson, T. O., & Narens, L. (2005). Using the past to predict the future. Memory & Cognition, 33(6), 1096–1115. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193216
Dougherty, M. R., Robey, A. M., & Buttaccio, D. (2018). Do metacognitive judgments alter memory performance beyond the benefits of retrieval practice? A comment on and replication attempt of Dougherty, Scheck, Nelson, and Narens (2005). Memory & Cognition, 46(4), 558–565. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-018-0791-y
Enders, C. K., & Tofighi, D. (2007). Centering Predictor Variables in Cross-Sectional Multilevel Models: A New Look at an Old Issue. Psychological Methods, 12(2), 121–138. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.12.2.121
Fleming, S. M., Ryu, J., Golfinos, J. G., & Blackmon, K. E. (2014). Domain-specific impairment in metacognitive accuracy following anterior prefrontal lesions. Brain, 137(10), 2811–2822. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu221
Geller, J., & Peterson, D. (2021). Is this going to be on the test? Test expectancy moderates the disfluency effect with sans forgetica. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. https://doi.org/10.1037/XLM0001042
Gelman, A., & Rubin, D. B. (1992). Inference from Iterative Simulation Using Multiple Sequences. Statistical Science, 7(4), 457–472. https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177011136
Hanczakowski, M., Pasek, T., Zawadzka, K., & Mazzoni, G. (2013a). Cue familiarity and ‘don’t know’ responding in episodic memory tasks. Journal of Memory and Language, 69(3), 368–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JML.2013a.04.005
Hanczakowski, M., Zawadzka, K., Pasek, T., & Higham, P. A. (2013b). Calibration of metacognitive judgments: Insights from the underconfidence-with-practice effect. Journal of Memory and Language, 69(3), 429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JML.2013b.05.003
Hayes, A. F., & Rockwood, N. J. (2020). Conditional Process Analysis: Concepts, Computation, and Advances in the Modeling of the Contingencies of Mechanisms. American Behavioral Scientist, 64(1), 19–54. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002764219859633
Hu, X., Liu, Z., Chen, W., Zheng, J., Su, N., Wang, W. … Luo, L. (2017). Individual differences in the accuracy of judgments of learning are related to the gray matter volume and functional connectivity of the left mid-insula. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00399
Hu, X., Luo, L., & Fleming, S. M. (2019). A role for metamemory in cognitive offloading. Cognition, 193, 104012. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COGNITION.2019.104012
Kantner, J., & Lindsay, D. S. (2014). Cross-situational consistency in recognition memory response bias. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(5), 1272–1280. https://doi.org/10.3758/S13423-014-0608-3
Kelley, C. M., & Lindsay, D. S. (1993). Remembering Mistaken for Knowing: Ease of Retrieval as a Basis for Confidence in Answers to General Knowledge Questions. Journal of Memory and Language, 32(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1006/JMLA.1993.1001
Kim, S. (2015). ppcor: An R Package for a Fast Calculation to Semi-partial Correlation Coefficients. Communications for Statistical Applications and Methods, 22(6), 665–674. https://doi.org/10.5351/CSAM.2015.22.6.665
Koriat, A. (1997). Monitoring one’s own knowledge during study: A cue-utilization approach to judgments of learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 126(4), 349–370. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.126.4.349
Koriat, A., Bjork, R. A., Sheffer, L., & Bar, S. K. (2004). Predicting one’s own forgetting: The role of experience-based and theory-based processes. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 133(4), 643–656. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.133.4.643
Koriat, A., Nussinson, R., Bless, H., & Shaked, N. (2008). Information-based and experience-based metacognitive judgments: Evidence from subjective confidence. In J. Dunlosky & R. A. Bjork (Eds.), Handbook of Metamemory and Memory (pp. 117–135). https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203805503
Koriat, A., & Ackerman, R. (2010). Choice latency as a cue for children’s subjective confidence in the correctness of their answers. Developmental Science, 13(3), 441–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1467-7687.2009.00907.X
Lee, M. D., & Wagenmakers, E. J. (2013). Bayesian cognitive modeling: A practical course. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139087759
Masson, M. E., & Rotello, C. M. (2009). Sources of bias in the Goodman-Kruskal gamma coefficient measure of association: implications for studies of metacognitive processes. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 35(2), 509–527. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014876
McCurdy, L. Y., Maniscalco, B., Metcalfe, J., Liu, K. Y., de Lange, F. P., & Lau, H. (2013). Anatomical coupling between distinct metacognitive systems for memory and visual perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(5), 1897–1906. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1890-12.2013
Metcalfe, J., & Finn, B. (2008). Evidence that judgments of learning are causally related to study choice. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 15(1), 174–179. https://doi.org/10.3758/PBR.15.1.174
Metcalfe, J., & Kornell, N. (2005). A Region of Proximal Learning model of study time allocation. Journal of Memory and Language, 52(4), 463–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2004.12.001
Mueller, M. L., Dunlosky, J., Tauber, S. K., & Rhodes, M. G. (2014). The font-size effect on judgments of learning: Does it exemplify fluency effects or reflect people’s beliefs about memory? Journal of Memory and Language, 70, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2013.09.007
Mueller, M. L., & Dunlosky, J. (2017). How beliefs can impact judgments of learning: Evaluating analytic processing theory with beliefs about fluency. Journal of Memory and Language, 93, 245–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2016.10.008
Murayama, K., Usami, S., & Sakaki, M. (2020). Summary-statistics-based power analysis: A new and practical method to determine sample size for mixed-effects modelling. https://doi.org/10.31219/OSF.IO/6CER3
Nelson, T. O., & Narens, L. (1990). Metamemory: A theoretical framework and new findings. In H. B. Gordon (Ed.), Psychology of Learning and Motivation: Vol. Volume 26 (pp. 125–173). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-7421(08)60053-5
Nunez, M. D., Vandekerckhove, J., & Srinivasan, R. (2017). How attention influences perceptual decision making: Single-trial EEG correlates of drift-diffusion model parameters. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 76, 117–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMP.2016.03.003
Palmer, E. C., David, A. S., & Fleming, S. M. (2014). Effects of age on metacognitive efficiency. Consciousness and Cognition, 28, 151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2014.06.007
Palser, E. R., Fotopoulou, A., & Kilner, J. M. (2018). Altering movement parameters disrupts metacognitive accuracy. Consciousness and Cognition, 57, 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CONCOG.2017.11.005
Patel, D., Fleming, S. M., & Kilner, J. M. (2012). Inferring subjective states through the observation of actions. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279(1748), 4853–4860. https://doi.org/10.1098/RSPB.2012.1847
Plummer, M. (2003). JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing, 20–22. https://doi.org/10.1.1.13.3406
Rahnev, D., Desender, K., Lee, A. L. F., Adler, W. T., Aguilar-Lleyda, D., Akdoğan, B. … Zylberberg, A. (2020). The Confidence database. Nature Human Behaviour, 4(3), 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-019-0813-1
Ratcliff, R. (1978). A theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review, 85(2), 59–108. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.85.2.59
Ratcliff, R., McKoon, G., & Gomez, P. (2004). A Diffusion Model Account of the Lexical Decision Task. Psychological Review, 111(1), 159–182. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.111.1.159
Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2008). The Diffusion Decision Model: Theory and Data for Two-Choice Decision Tasks. Neural Computation, 20(4), 873–922. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO.2008.12-06-420
Ratcliff, R., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2002). Estimating parameters of the diffusion model: Approaches to dealing with contaminant reaction times and parameter variability. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(3), 438–481. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196302
Ratcliff, R. (2013). Parameter variability and distributional assumptions in the diffusion model. Psychological Review, 120(1), 281–292. https://doi.org/10.1037/A0030775
Ratcliff, R., Smith, P. L., Brown, S. D., & McKoon, G. (2016). Diffusion Decision Model: Current Issues and History. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(4), 260–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TICS.2016.01.007
Robey, A. M., Dougherty, M. R., & Buttaccio, D. R. (2017). Making Retrospective Confidence Judgments Improves Learners’ Ability to Decide What Not to Study. Psychological Science, 28(11), 1683–1693. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797617718800
Robey, A. M., Castillo, C., Ha, J., Kerlow, M., Tesfa, N., & Dougherty, M. (2021). Generalizing the effect of type of metacognitive judgment on restudy decisions. Metacognition and Learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-021-09274-8
Robinson, M. D., Johnson, J. T., & Herndon, F. (1997). Reaction time and assessments of cognitive effort as predictors of eyewitness memory accuracy and confidence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82(3), 416–425. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.82.3.416
Rosner, T. M., Davis, H., & Milliken, B. (2015). Perceptual blurring and recognition memory: A desirable difficulty effect revealed. Acta Psychologica, 160, 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTPSY.2015.06.006
Sadeghi, S., Ekhtiari, H., Bahrami, B., & Ahmadabadi, M. N. (2017). Metacognitive deficiency in a perceptual but not a memory task in methadone maintenance patients. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06707-w
Schmidt, C., Reyes, G., Barrientos, M., Langer, Á. I., & Sackur, J. (2019). Meditation focused on self-observation of the body impairs metacognitive efficiency. Consciousness and Cognition, 70, 116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2019.03.001
Siedlecka, M., Skóra, Z., Paulewicz, B., Fijałkowska, S., Timmermans, B., & Wierzchoń, M. (2019). Responses improve the accuracy of confidence judgements in memory tasks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 45(4), 712–723. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000608
Singmann, H., & Kellen, D. (2020). An introduction to mixed models for experimental psychology. In D. H. Spieler, & E. Schumacher (Eds.), New Methods in Cognitive Psychology. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429318405-2
Smith, R. L., Ager, J. W., & Williams, D. L. (1992). Suppressor Variables in Multiple Regression/Correlation. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 52(1), 17–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316449205200102
Su, Y. S., & Yajima, M. (2021). R2jags: Using R to Run ‘JAGS’’. R package version 0.7-1.’ https://cran.r-project.org/package=R2jags
Sungkhasettee, V. W., Friedman, M. C., & Castel, A. D. (2011). Memory and metamemory for inverted words: Illusions of competency and desirable difficulties. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 18(5), 973–978. https://doi.org/10.3758/S13423-011-0114-9/FIGURES/3
Susser, J. A., & Mulligan, N. W. (2015). The effect of motoric fluency on metamemory. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 22, 1014–1019. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0768-1
Susser, J. A., Panitz, J., Buchin, Z., & Mulligan, N. W. (2017). The motoric fluency effect on metamemory. Journal of Memory and Language, 95, 116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JML.2017.03.002
Thompson, V. A., Turner, J. A. P., Pennycook, G., Ball, L. J., Brack, H., Ophir, Y., & Ackerman, R. (2013). The role of answer fluency and perceptual fluency as metacognitive cues for initiating analytic thinking. Cognition, 128(2), 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COGNITION.2012.09.012
Turner, W., Angdias, R., Feuerriegel, D., Chong, T. T. J., Hester, R., & Bode, S. (2021). Perceptual decision confidence is sensitive to forgone physical effort expenditure. Cognition, 207, 104525. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COGNITION.2020.104525
Undorf, M., Zimdahl, M. F., & Bernstein, D. M. (2017). Perceptual fluency contributes to effects of stimulus size on judgments of learning. Journal of Memory and Language, 92, 293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2016.07.003
Voss, A., Rothermund, K., & Voss, J. (2004). Interpreting the parameters of the diffusion model: An empirical validation. Memory & Cognition, 32(7), 1206–1220. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196893
Voss, A., Voss, J., & Lerche, V. (2015). Assessing cognitive processes with diffusion model analyses: a tutorial based on fast-dm-30. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 336. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYG.2015.00336
Vuorre, M., & Bolger, N. (2018). Within-subject mediation analysis for experimental data in cognitive psychology and neuroscience. Behavior Research Methods, 50(5), 2125–2143. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0980-9
Vuorre, M., & Metcalfe, J. (2021). Measures of relative metacognitive accuracy are confounded with task performance in tasks that permit guessing. Metacognition and Learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11409-020-09257-1. Advance online publication
Wabersich, D., & Vandekerckhove, J. (2014). Extending JAGS: A tutorial on adding custom distributions to JAGS (with a diffusion model example). Behavior Research Methods, 46(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.3758/S13428-013-0369-3
Wang, Z., Yang, C., Zhao, W., & Jiang, Y. (2020). Perceptual Fluency Affects Judgments of Learning Non-analytically and Analytically Through Beliefs About How Perceptual Fluency Affects Memory. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 552824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.552824
Weidemann, C. T., & Kahana, M. J. (2016). Assessing recognition memory using confidence ratings and response times. Royal Society Open Science, 3, 150670. https://doi.org/10.1098/RSOS.150670
Whelan, R. (2008). Effective Analysis of Reaction Time Data. The Psychological Record, 58, 475–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395630
Wiecki, T. V., Sofer, I., & Frank, M. J. (2013). HDDM: Hierarchical Bayesian estimation of the Drift-Diffusion Model in Python. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNINF.2013.00014
Yang, C., Huang, T. S. T., & Shanks, D. R. (2018). Perceptual fluency affects judgments of learning: The font size effect. Journal of Memory and Language, 99, 99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2017.11.005
Yang, C., Yu, R., Hu, X., Luo, L., Huang, T. S. T., & Shanks, D. R. (2021). How to assess the contributions of processing fluency and beliefs to the formation of judgments of learning: methods and pitfalls. Metacognition and Learning, 16, 319–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-020-09254-4
Yoon, H. D., Shin, M., & Jeon, H. A. (2021). The critical role of interference control in metaphor comprehension evidenced by the drift–diffusion model. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98351-8
Yue, C. L., Castel, A. D., & Bjork, R. A. (2013). When disfluency is-and is not-a desirable difficulty: The influence of typeface clarity on metacognitive judgments and memory. Memory and Cognition, 41(2), 229–241. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-012-0255-8
Zawadzka, K., & Higham, P. A. (2015). Judgments of learning index relative confidence, not subjective probability. Memory and Cognition, 43(8), 1168–1179. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-015-0532-4
Zhang, Z., Zyphur, M. J., & Preacher, K. J. (2009). Testing multilevel mediation using hierarchical linear models: Problems and solutions. Organizational Research Methods, 12(4), 695–719. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428108327450
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (32171045, 32000742).
Data and code availability.
Data and analysis code for the current study are available at Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/kd3f8/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Yang, C. & Luo, L. Retrospective confidence rating about memory performance is affected by both retrieval fluency and non-decision time. Metacognition Learning 17, 651–681 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-022-09303-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-022-09303-0