Abstract
Training interventions for self-regulated learning foster the use of strategies and skills as well as their transfer to new learning tasks. Because cognitive strategies or motivation regulation strategies are task-specific, their transfer is limited. In contrast, metacognitive skills are task-general and transferable to a wide variety of learning tasks. Questions arise, therefore, as to whether students transfer metacognitive skills spontaneously and how to support metacognitive skill transfer. Previous research shows that hybrid training, which addresses both metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies, supports near transfer. However, it is not clear whether hybrid training also fosters far transfer of metacognitive skills. In investigating this research question, 233 fifth-grade students were randomly assigned to six different conditions: two hybrid-training conditions (metacognitive skills and one out of two cognitive strategies), two non-hybrid training conditions (“only” one out of two cognitive strategies), and two control training conditions (neither metacognitive skills nor cognitive strategies). After 15 weeks of training, transfer of metacognitive skills to learning tasks similar to training tasks (near transfer) was tested. In the following 15 weeks, all students received a second, non-hybrid training involving a new cognitive strategy. Far transfer of metacognitive skills to the new cognitive strategy was tested afterward. The results show that hybrid training, compared to non-hybrid and control training, improved both students’ near and far transfer of metacognitive skills. Moreover, cognitive strategy use increased in at least one of the hybrid-training conditions. However, since the level of metacognitive skills use remained low, further means to support transfer are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Modern communication and information technologies, new forms of work, and rapid obsolescence affecting acquired knowledge and skills raise the question of what competencies students need for lifelong learning (Kirschner and Stoyanov 2018). For example, students are required to control their own learning processes in a wide variety of learning contexts (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 2016). Self-regulated learning (SRL) promises an effective approach to handle such control in all areas of life. Research on SRL has successfully evaluated different kinds of training interventions (e.g., Paris and Paris 2001; Perels et al. 2005; Stoeger and Ziegler 2008; Zimmerman et al. 2002). However, all the training interventions to date have used concrete learning tasks, requiring students to regulate their learning within specific learning contexts (e.g., Dignath et al. 2008). Whether students have the ability to transfer their acquired knowledge and skills to all types of learning contexts and learning-related tasks remains an open question in most training evaluations as well as in research on SRL (Veenman et al. 2006). Some training interventions affect different though relatively similar learning tasks (“near transfer”; e.g., Aghaie and Zhang 2012) or problem-solving tasks (e.g., van Meeuwen et al. 2018). However, no empirical study to date has shown transfer of SRL in learning tasks that differ substantially from the training tasks in the study (“far transfer”). The present study intends to fill this gap by investigating the effects of an SRL training approach on fostering the transfer of SRL to both similar and highly different learning tasks. Accordingly, the purpose of this study was to examine the extent to which near and far transfer can be developed in the context of SRL training.
The role of metacognitive skills in self-regulated learning
Within SRL, “learners set goals for their learning and then attempt to monitor, regulate and control their cognition, motivation and behavior, guided and constrained by their goals and the contextual features of the environment” (Pintrich 2000, p. 453). Accordingly, SRL is an active and constructive process in which the interaction of three essential components – cognition, motivation, and metacognition – serves to govern learning (Schraw et al. 2006). In considering the transfer of SRL, a core question arises concerning which of these components are task-specific, and which are not. Task-specificity is crucial to considering whether a component can be used in only one specific set of learning tasks or if it is transferable to different learning contexts and tasks (Neuenhaus et al. 2011; Veenman et al. 1997; Veenman et al. 2006).
Cognition includes cognitive strategies, problem-solving strategies, and critical thinking skills (Schraw et al. 2006). Cognitive strategies, which are conducive to rehearsing, organizing, and elaborating information (Weinstein et al. 2000), are task-specific because they directly address particular kinds of information processing that must suit a given learning task (e.g., Donker et al. 2014). For example, a student will ideally read a nonfiction text with the goal of understanding the topic as effectively as possible. Text highlighting offers one appropriate cognitive strategy to begin this task, directly addressing the specific kind of information processing needed: selecting relevant information while reading (Mayer 1996). Other cognitive strategies – for example, the variable control strategy that can be used when conducting experiments – do not fit the learning task of reading a nonfiction text.
Motivation represents beliefs and attitudes that influence the use and development of cognition and metacognition (Schraw et al. 2006). Motivation regulation strategies directly address specific motivational problems: for example, if a task is too difficult or boring for a student (Engelschalk et al. 2016; Wolters and Rosenthal 2000). Accordingly, motivation regulation strategies are task-specific (e.g., Donker et al. 2014) because they always focus on a particular motivational problem (Wolters and Rosenthal 2000). For example, for a student who has a motivation problem due to the large scope of a task, an effective strategy would be to set and track proximal goals (Latham and Seijts 1999; Schwinger et al. 2009). However, a self-rewarding strategy would not work near as good in this case (Wolters 1998).
Metacognition enables students to take control of their own cognitive and motivational processes. According to Schraw et al. (2006), metacognition comprises two main components: metacognitive knowledge and metacognitive skills. The former includes knowledge about oneself as a learner (declarative), strategies (procedural), and why and when to use a particular strategy in a specific learning context (conditional; e.g., Brown 1978). Since metacognitive knowledge contains a repertoire of specific strategies such as note-taking or summarizing the main ideas of a nonfiction text, it can be defined as task-specific (Schraw et al. 2006). Using metacognitive knowledge assists learners as they are adjusting to the changing situational demands of a specific learning task, thus directly addressing information processing.
Metacognitive skills, also referred to as metacognitive strategies, can be subclassified in planning, monitoring, and evaluating (Flavell et al. 2002; Jacobs and Paris 1987; Schraw & Dennison 1994). Such skills represent higher-order strategies because they serve to regulate cognitive or motivational strategies within all varieties of learning tasks (Schraw 2001; Veenman et al. 2006). These skills, which do not directly address information processing or motivational problems, ensure that learners’ applications of cognitive or motivation regulation strategies are of high quality (e.g., Leopold and Leutner 2015). Therefore, metacognitive skills are positively related to learning performance and achievement (e.g., Veenman et al. 2005) or motivation (e.g., Zepeda et al. 2015). Additionally, research has shown metacognitive skills to enhance performance across several domains (e.g., Carretti et al. 2014; Ohtani and Hisasaka 2018; Zepeda et al. 2019). Thus, metacognitive skills are task-general (e.g., Donker et al. 2014; Schraw et al. 1995; Schraw and Nietfeld 1998; Veenman et al. 1997; Veenman and Verheij 2003). They can be applied to many different learning contexts and tasks, and once learned (e.g., in an SRL training), they can transfer to new contexts and tasks. For example, metacognitive skills are effective for reading a nonfiction text as well as for conducting experiments.
Within SRL, cognition, motivation, and metacognitive knowledge are non-transferable, task-specific components, directly addressing specific information processing or motivational problems. In contrast, metacognitive skills are transferable and task-general, regulating cognitive and motivational strategies within all kinds of learning tasks.
Supporting the transfer of metacognitive skills in self-regulated learning
Varying types of interventions support the development and use of metacognitive skills, such as metacognitive questions (e.g., King 1991; Kramarski et al. 2002; Lee et al. 2018), metacognitive judgment training (e.g., Händel et al. 2020; Mihalca et al. 2017; Miller and Geraci 2011; Nietfeld et al. 2005; Roelle et al. 2017), or complex SRL training interventions that combine metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies (hybrid training; e.g., Desoete et al. 2003; Leopold and Leutner 2015; Souvignier and Mokhlesgerami 2006; Zepeda et al. 2015). According to Zepeda et al. (2019), such interventions can differ in metacognitive content, meaning the type of knowledge (declarative, procedural, conditional) and skills (planning, monitoring, evaluating) that are supported, as well as the kind of metacognitive delivery (how the support was delivered).
In terms of metacognitive content, previous research has shown that hybrid training is more beneficial than non-hybrid training in terms of the quality of cognitive strategy application (e.g., Leopold and Leutner 2015) and for learning performance in general (e.g., Dignath and Büttner 2008). Within a hybrid-training approach (see Fig. 1), students learn to use metacognitive skills to regulate a particular cognitive or motivation regulation strategy. In contrast, students undergoing non-hybrid training “only” learn a particular cognitive, motivation regulation, or metacognitive strategy. In hybrid training interventions, students acquire metacognitive skills and learn how to increase the quality of the use of a cognitive or a motivation regulation strategy by employing their metacognitive skills. Moreover, students can learn to use their metacognitive skills to increase the quality of any cognitive or motivation regulation strategy employed in any learning task. Increasing the quality of any strategy use always requires planning, monitoring, and evaluating the strategy use.
Hybrid-training approach. (Adapted from Leopold & Leutner (2015)).
Regarding metacognitive delivery, Zepeda et al. (2019) distinguished between metacognitive manner and metacognitive framing. In the context of metacognitive manner, instructional support can include directive instruction, prompting, or modeling. From directive instruction to modeling, the teacher’s influence on the learners’ behavior decreases. In line with the cognitive apprenticeship approach, SRL training should be structured in such a way that direct strategy instruction becomes increasingly redundant (Collins et al. 1989; Palinscar and Brown 1984). This approach allows students the opportunity to independently solve new tasks and apply the acquired strategies.
Metacognitive framing refers to how specifically or generally the support is framed. SRL training should be based on the principle of specific-to-general. Following the hybrid-training approach, metacognitive skills must be initially trained with a cognitive strategy on a specific training task. As training continues, metacognitive skills must be transferred to various cognitive strategies, finally resulting in a more general framing. This process is associated with transfer because it might be easy to recognize coherences between tasks (Engle et al. 2012). In terms of the transfer of metacognitive skills, learners must recognize that metacognitive skills remain the same, while cognitive strategies change across training and learning tasks.
Transfer of metacognitive skills in self-regulated learning
As O’Sullivan and Pressley (1984) acknowledged several decades ago, students struggle when it comes to transfer (Scharff et al. 2017) – especially with the transfer of strategies that have been taught to them, a trend that remains to this day. At the time they conducted their research, the authors suspected that the nonexistent transfer was due to lack of knowledge about the strategy (metacognitive knowledge; O’Sullivan and Pressley 1984). From the perspective of the discussion so far, the nonexistent transfer could also result from a lack of metacognitive skills.
Transfer occurs when learning in one context improves performance in a different learning context (Perkins and Salomon 1989). Transfer-related research shows that the similarity between two tasks can have a conducive effect on transfer (Gentner et al. 1993). The more similar the characteristics of two tasks, the more likely transfer is to occur. According to Noam Chomsky (1957), tasks can be differentiated in terms of their surface and depth structure. The features or properties of the task, such as the topic, characterize the surface structure of tasks. The depth structure of tasks describes the relationship between the elements of a task that are relevant to the processing and the solution of the task. Transfer occurs when learners recognize the depth structure of the source area.
According to Perkins and Salomon (1988), two types of transfer are possible. Near transfer occurs when tasks are similar in depth structure, while far transfer refers to a depth-structural dissimilarity between tasks. In the context of SRL training, depth-structural similarity between training and learning tasks means that both tasks can be processed using the identical cognitive strategy. Thus, near transfer occurs when both metacognitive skills and a particular cognitive strategy can be transferred from training to learning tasks. For instance, this concept may apply when students have learned metacognitive skills with a cognitive mapping strategy while acquiring information from a nonfiction text within a hybrid training intervention. Accordingly, a near-transfer task can be solved with the same metacognitive and cognitive strategies, even when the content of the text differs between the training and learning task (see Fig. 2). Some evidence already suggests that hybrid training could enhance near transfer in SRL (e.g., Aghaie and Zhang 2012; Souvignier and Mokhlesgerami 2006) and problem-solving (e.g., Kim and Pedersen 2011; Mayer 1998; van Meeuwen et al. 2018). For example, Aghaie and Zhang (2012) examined the impact of hybrid training on reading comprehension, performance, and strategy transfer in second-language acquisition. The hybrid-training group applied metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies to learning tasks in the language to be learned (training task) as well as in their mother tongue (near transfer).
In the context of SRL training, a depth-structural dissimilarity exists between the training and learning task when both tasks are to be processed with metacognitive skills – but not with the identical cognitive strategy. In this case, far transfer occurs when metacognitive skills can be transferred from training to learning tasks but the cognitive strategy cannot. An example of this situation would be where students have learned metacognitive skills with a cognitive mapping strategy when learning from a nonfiction text within a hybrid training. In a far-transfer task, metacognitive skills would be helpful for processing this learning task, but the cognitive mapping strategy would not. In this case, a variable control strategy for conducting experiments might be helpful. Thus, the cognitive strategy acquired in hybrid training is useless for the far-transfer task (see Fig. 2). Previous research in the context of strategy training has not yet proven the possibility of far transfer. Carretti et al. (2014) showed that students who learned metacognitive skills and a cognitive reading strategy in hybrid training improved performance in both reading and listening comprehension. However, the authors did not demonstrate that the superiority of the hybrid-trained group was due to the transfer of metacognitive skills.
Research question and hypotheses
Considering SRL from a transfer perspective, focusing on metacognitive skills appears to offer a promising approach. These task-general skills (e.g., Donker et al. 2014; Veenman et al. 2006) lead to a quality improvement of cognitive or motivation regulation strategy application in different domains (e.g., Leopold and Leutner 2015; Schraw 2001). In contrast to other components of SRL, metacognitive skills are not task-specific, allowing learners to transfer metacognitive skills from one learning task to another. However, whether learners transfer their metacognitive skills, and which instructional training approaches support this kind of transfer, are not yet known. A hybrid-training approach, in which metacognitive skills are used to regulate metacognitive knowledge about a particular cognitive strategy, has an increased potential for promoting transfer through SRL training. Previous research showed that hybrid training could facilitate near transfer (e.g., Aghaie and Zhang 2012; van Meeuwen et al. 2018). However, empirical studies on far-transfer processes involved in hybrid training are few. In this context, the question arises regarding whether hybrid training fosters students’ transfer of metacognitive skills and thus improves the quality of their cognitive strategy application.
To investigate this research question, we conducted an experimental study assessing hybrid training, non-hybrid training, and control group training for fifth-grade students. We expected that students receiving hybrid training would use their metacognitive skills more often in a near-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training or control group training (Hypothesis 1, near transfer). Furthermore, we expected that students receiving hybrid training would use their metacognitive skills oftener in a far-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training or control group training (Hypothesis 2, far transfer). Beyond this, we expected that students receiving hybrid training would use cognitive strategies, considering all steps of the strategy, more often in a far-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training or control group training (Hypothesis 3, improvement of cognitive strategy application).
Method
Participants
The sample consisted of 243 fifth-grade students from two German secondary schools (122 females; M = 10.5 years, SD = 0.49; Min = 11, Max = 16). Both schools participated in a school development project for all-day schools and deliberately chose to participate in the training study. We conducted a power analysis with α = .05, an acceptable power of 1-β = .80, and an effect size of f = .25 in G*Power 3.1.9.4 (Faul et al. 2007), resulting in a minimum required sample size of N = 211. Due to non-compliance, N = 10 students had to be excluded from the analysis, resulting in a final sample size of N = 233. Since not all students were present at all times of measurement, the analyses include different sample sizes. Missing data occurred due to student absence because of illness, school organizational incidents, or a fire alarm during one measurement period. Participating students did not receive any reward for their participation since the training study was part of everyday school life. Written informed consent was obtained from all students.
Design
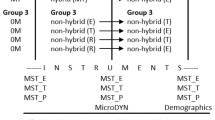
The study lasted one full school year. For the first half of the school year, students were randomly assigned to one of six conditions within a between-subject design. Two conditions represented hybrid training, a combination of both metacognitive skills and a particular cognitive learning strategy. Two conditions fulfilled the definition of non-hybrid training, involving a particular cognitive learning strategy only. Lastly, two conditions embodied control training, a reading motivation training addressing neither metacognitive skills nor a particular cognitive learning strategy. The two hybrid-training conditions as well as the two non-hybrid training conditions differed in the particular cognitive learning strategy (text highlighting or conducting experiments) that students learned in the training sessions.
In the second half of the school year, all students received a second training intervention that encompassed one of the two non-hybrid training conditions. Students who had received hybrid or non-hybrid training addressing the cognitive strategy “conducting experiments” in the first half of the school year received non-hybrid training addressing the cognitive learning strategy “text highlighting” in the second half of the school year, and vice versa (Table 1). The two control conditions were randomly assigned to one of the two non-hybrid training schemes in the second half of the school year. Notably, in the second half of the school year, none of the training conditions in any of the six conditions addressed metacognitive skills.
This design resulted in the following training versions: ME was a hybrid training in which metacognitive skills were used to regulate a cognitive strategy for conducting experiments. E was a non-hybrid training in which students were trained in a cognitive strategy for conducting experiments. MT was a hybrid training in which metacognitive skills were used to regulate a cognitive strategy for text highlighting. T was a non-hybrid training in which students were trained in a cognitive strategy for text highlighting. R was a control group training aiming to foster reading motivation without practicing any metacognitive or cognitive strategies. Since each student received two training interventions, the groups were distributed among the training interventions as follows: Group 1 (ME/T) received the hybrid training ME first, followed by the non-hybrid training T (N = 39). Group 2 (E/T) received the non-hybrid training E first, followed by the non-hybrid training T (N = 39). Group 3 (MT/E) received the hybrid training MT first, followed by the non-hybrid training E (N = 40). Group 4 (T/E) received the non-hybrid training T first, followed by the non-hybrid training E (N = 40). Group 5 (R/E) received the control group training R first, followed by the non-hybrid training E (N = 38). Group 6 (R/T) received the control group training R first, followed by the non-hybrid training T (N = 37). No differences existed between the groups across any demographic variables or prior knowledge, including students’ gender, cognitive abilities (KFT, Heller et al., 2000), grade point average, and application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies (all ps ≥ .101). Regarding metacognitive strategy application, all groups scored 0 at T1 (see Table 2). Accordingly, the data revealed no variation for T1. This outcome can probably be attributed to the high level of difficulty of the test instrument used.
Researchers administered all training conditions while observed by additional researchers in order to keep the intervention fidelity high (Gearing et al. 2011). Lessons took place in the classrooms of the schools to which the students belonged. Before the beginning of the training, all fifth-grade students from each school were randomly allocated to one of the different training conditions (see Table 1). Accordingly, instead of being taught in their regular classes, the students received instruction in the groups created for the training study. Participation in the training did not involve canceling regular lessons for the participating students. In order to implement the training conditions, a time slot of 90 min was blocked in the students’ regular timetable.
Training
Each student received a first and second training (see Table 1). The first training comprised approximately 15 sessions of 90 min each and lasted for the first half of the school year. Instruction consisted of either hybrid (ME/MT), non-hybrid (E/T), or control group training (R).
In the second half of the school year, students received a second training (approximately 15 sessions of 90 min each). In this segment of the intervention, all six groups received non-hybrid training (E/T). The cognitive strategy was new to the students, allowing them to apply metacognitive skills learned in the first training. The following section describes the different hybrid, non-hybrid, and control group training conditions in more detail.
Hybrid training
The hybrid trainingFootnote 1 was based on the theoretical assumption of the task generality of metacognitive skills (e.g., Donker et al. 2014; Veenman et al. 2006) and their potential to regulate cognitive strategies to a high level (Leopold and Leutner 2015), resulting in higher learning performance (e.g., Dignath and Büttner 2008). Students were taught to apply metacognitive skills in combination with a particular cognitive strategy. Whereas metacognitive skills included planning, monitoring, and evaluating (e.g., Schraw et al. 2006), cognitive strategies involved either a strategy for conducting experiments (ME) or a text-highlighting strategy for reading expository science texts (MT). In line with Klahr and Dunbar (1988), the strategy for conducting an experiment consisted of three steps:
-
1.
Derive a hypothesis.
-
2.
Check the hypothesis by conducting an experiment using the control-of-variables strategy (CVS; Tschirgi 1980). This strategy requires students to systematically change one variable at a time while all others remain constant. Such strategic behavior is seen as the most relevant for succeeding in scientific tasks (Fischer et al. 2012; Lotz 2018).
-
3.
Draw a conclusion.
Similarly, the text-highlighting strategy comprised three steps, through which students learned to select relevant information from texts (Leopold and Leutner 2015):
-
1.
Read a section.
-
2.
Formulate questions about the content of the section.
-
3.
Highlight parts of the text that answer the formulated questions
By identifying the main ideas in the text and selecting significant text information, this text-highlighting strategy aims at active information processing (Weinstein and Mayer 1986). Consequently, this cognitive strategy is associated with fostering deep text comprehension (e.g., Glenberg et al. 1987).
In accordance with the abovementioned hybrid training approach, metacognitive skills and one of the two cognitive strategies were combined. Each step of the employed cognitive strategy was regulated by applying all three metacognitive skills. The following description provides an example of how the process works. To begin, a student wants to check a hypothesis by conducting an experiment using the CVS (Step 2 of the cognitive strategy of conducting experiments). Therefore, the student sets a goal of conducting an experiment in which only one variable in two runs is manipulated (planning). The next step is to conduct the experiment. Occasionally, the student stops and monitors experimental progress, asking: Did I manipulate only one variable in two experimental runs? Am I doing everything right (monitoring)? Lastly, the student evaluates the learning process and reacts if unsatisfied with the experiment (evaluating).
In line with Zepeda et al.’s (2019) categories of metacognitive delivery, the hybrid training was designed to reduce teachers’ influence on students’ behavior (metacognitive manner) and to progress from explicit training of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies to a more general framing (in other words, metacognitive framing). In the first learning sequence of both hybrid training conditions, the students learned the basics of learning (why is SRL important, and how does it work?), rules for classroom behavior, and basic forms of cooperative learning. Subsequently, the students were introduced to metacognitive skills combined with cognitive strategies to either conduct experiments (ME) or perform text highlighting (MT; explicit training). Both hybrid training conditions continued with an application training sequence that included various experiments (strategy to conduct experiments) or different kinds of expository texts (text-highlighting strategy). This sequence was intended to lead students to practice metacognitive skills and a cognitive strategy in combination. Both hybrid training conditions ended with a transfer lesson in which students applied metacognitive skills (general framing) to everyday life situations. A reflection phase accompanied each lesson, allowing students to reflect on their learning process by means of a questionnaire.
Non-hybrid training
Within both non-hybrid training conditions, students were taught either the specified cognitive strategy for conducting experiments (E) or the text-highlighting strategy (T). The three steps of these cognitive strategies were identical to the steps of the cognitive strategies in the hybrid training. In both non-hybrid training conditions (T and E), the cognitive strategy was taught without referring to metacognitive skills, leaving more time to practice the cognitive strategy. In line with the procedure for hybrid training, the students experiencing non-hybrid training learned the basics of learning, rules for classroom behavior, and basic forms of cooperative learning. Subsequently, the students were introduced to a cognitive strategy for conducting experiments (E) or performing text highlighting (T), followed by an application training sequence that included the same experiments or kinds of expository texts as those presented in the hybrid training. The transfer lesson from the hybrid training was replaced by more time to conduct experiments (E) or practice text highlighting (T). A reflection phase, in which students reflected on their learning process with a questionnaire, accompanied each lesson.
Control group training
Students in the control groups participated in a training intervention in which they were given different opportunities to read. This step was performed to foster reading motivation (R). In line with the procedure for hybrid training, students in the control group training learned rules for classroom behavior and basic forms of cooperative learning but no basics of learning. Subsequently, the participants practiced various methods to increase reading motivation, such as creating one’s own radio play based on a fictional text. In this training, students were not instructed or trained in any metacognitive skill or cognitive strategy.
Test instruments
Spontaneous recall and application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies were assessed using a multi-strategy test (MST; Stebner et al. 2015). In the form of a vignette, the MST outlines a fictitious learning situation in which students are asked to describe their intended approach to process the given learning task. The students’ descriptions, provided in an open-response format, are analyzed using a category system to detect how many metacognitive skills in combination with each step of the respective cognitive strategy have been mentioned. The number of correctly described intended metacognitive skills in this fictitious task is seen as an indicator of the spontaneous application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies in real learning situations, as strategy knowledge has to be spontaneously retrieved to suit the learning task and must be adapted to the specific circumstances of the learning situation. A high-quality cognitive strategy application means that all steps of a cognitive strategy are regulated by all metacognitive skills (planning, monitoring, and evaluation; Schraw et al. 2006) and no skill/strategy step is omitted. That is, the more skills/strategy steps in the MST are recalled, the more effectively the cognitive strategy may be executed.
Two versions of the MST were used to measure the spontaneous recall and intended application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies while working on an experimentation task (MST_E) or a text-highlighting task (MST_T).
The term MST_E describes a learning task that could have occurred in the ME or the E training. The task was presented as follows: “At school, you are dealing with plants. With the help of an experiment, you want to find out what plants need to grow. What possibilities do you have to work on this task?” The category system for coding the students’ descriptions contained three categories, one for each step of the cognitive strategy (Klahr and Dunbar 1988). These steps included (a) deriving a hypothesis, (b) checking a hypothesis by conducting an experiment using CVS, and (c) drawing a conclusion. In each category, 3 points were awarded for three specific quality characteristics of each cognitive strategy step. In addition, for each category, 3 points were given for metacognitive skills (planning, monitoring, and evaluating) to reflect that each cognitive strategy step was regulated by all three metacognitive skills. Accordingly, students were able to achieve a total of 9 points for metacognitive skills (meta) and 9 points for the cognitive strategy to conduct experiments (cog). For example, regarding the second cognitive strategy step of conducting experiments, 1 point was given in each case if students actually conducted an experiment (cog) or manipulated only one variable (cog) in two experimental runs (cog). These actions reflect the specific quality characteristics of the cognitive strategy step “checking hypothesis by conducting an experiment using CVS.” For metacognitive skills, 1 point was given in each case if students mentioned setting a goal to conduct an experiment (meta), monitoring the progress of the experiment (meta), and evaluating the experimenter’s satisfaction with the experiment (meta). Students received 0 points if they did not mention any of the strategy steps.
The term MST_T describes a learning task that could have occurred in the MT or the T training. The task was presented as follows: “For homework, you have to read a multi-page article from a magazine and tell your classmates tomorrow what the article is about. How do you proceed to solve the task?” As for MST_E, the category system for coding students’ descriptions contained three categories, one for each step of the cognitive strategy for highlighting texts. In each category, up to 3 points were given for metacognitive skills, along with up to 3 points for the steps of the cognitive strategy of text highlighting. The coding was identical to that for MST_E. Therefore, the evaluation of both MST versions resulted in one score signifying the application of metacognitive skills and a second score for the cognitive strategy.
Double-coding a subsample of student descriptions (N = 60) helped determine the inter-rater reliability for both MST versions. This subsample corresponded to about 25% of the total sample. Inter-rater reliability was good, with an average Cohen’s ƙ = .91 (.75 ≤ ƙ < 1.0).
The MST constitutes an economic and scenario-based measure of learning strategies (for further information about scenario-based measures, see Händel et al. 2014). Compared to established learning strategy questionnaires (e.g., MSLQ; Pintrich et al. 1993), vignette tests represent a promising means to increase the validity of measures of learning strategies (Su & Steiner 2018). Moreover, in comparison to think-aloud protocols (e.g., Swanson 1990), analyzing vignettes with a coding scheme is less time-consuming. Previous scenario-based measures aiming to capture predominantly metacognitive knowledge have provided good reasons for investing effort in developing and using these tools (e.g., Händel et al. 2014; Maag Merki et al. 2013; Neuenhaus et al. 2011).
Procedure
First, all students completed a pretest before the first training (T1). Students received either hybrid training, non-hybrid training, or control group training for half the school year. In the middle of the school year, the participating students completed a posttest after the first training ended (T2). Following the posttest, all students received the second training, which involved non-hybrid training. After the second training ended (T3), the students completed a third test at the end of the school year. Researchers conducted all training conditions in school. Additional researchers observed the teaching researchers to ensure treatment fidelity. Furthermore, the researchers took turns leading the training group after 2 weeks (first week observing, second week teaching) in order to prevent teacher effects (Fig. 3).
At each measurement time point, both versions of the MST (MST_E and MST_T) were administered. At T1, both versions of the MST were used to measure students’ prior knowledge about the intended application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies while working on an experimental task (MST_E) or a reading task (MST_T). Regarding the transfer of metacognitive skills, the MST performance at T2 and T3 of both hybrid training groups (ME/T; MT/E) are of interest because both groups learned metacognitive skills combined with a cognitive strategy in the first training. For Group 1 (ME/T), MST_E served as a near-transfer task at T2 and T3, since the training and learning task were structurally similar and could be successfully processed with the same metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies that students had previously learned within hybrid training ME. In contrast, MST_T served as a far-transfer task, being structurally dissimilar to the training task in hybrid training ME and requiring the application of another cognitive strategy that students had not previously learned in the hybrid training (see Fig. 4). For Group 3 (MT/E), the MST_T served as a near-transfer task at T2 and T3, while the MST_E served as a far-transfer task.
Results
This section presents the findings related to our three hypotheses concerning the differences between the hybrid, non-hybrid, and control groups with respect to metacognitive skill application in a near-transfer task (H1) and a far-transfer task (H2), as well as cognitive strategy application in a far-transfer task (H3).
Table 2 provides descriptive statistics for both MST versions at all three measurement points. An α-level of .05 was used for all statistical analyses. For F-tests, we report partial η2 as effect size measure. In line with Cohen (1988), 0.01 is considered small, 0.06 is medium, and 0.14 is a large effect size.
To test the effect of the training condition on performance at T2 and T3, we conducted analyses of covariance (ANCOVA), controlling for students’ prior application of metacognitive skills and/or cognitive strategies regarding the given transfer task. Although we planned to include application of metacognitive skills within the analysis, the variable was not considered due to zero variance. However, the cognitive strategy application could be considered. Furthermore, we calculated planned contrasts, which are recommended as a means to test the hypotheses in intervention studies (Wilkinson & the Task Force on Statistical Inference 1999). We contrasted the hybrid to the non-hybrid training condition, including the control group condition (contrast weights assigned to experimental conditions: 1 for hybrid training, −1 for non-hybrid training, and 0 for the control group). Furthermore, we contrasted the hybrid and non-hybrid training conditions against the control group training (contrast weights assigned to experimental conditions: 1 for hybrid training, 1 for non-hybrid training, and −2 for the control group). Even though Kolmogorow-Smirnov tests revealed that the assumption of normality was violated (all ps ≤ .05), we present the results of ANCOVA as those are considered relatively robust despite the violation of the normal distribution (Glass et al. 1972).
Application of metacognitive skills in a near-transfer task
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (ME) more often applied metacognitive skills in a near-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training (E), we looked at the results of the MST_E at T2, controlling for the application of cognitive strategy MST_E score at T1. The covariate cognitive strategy application at T1 did not correspond significantly to the metacognitive strategy application at T2, F(1, 177) = 0.03, p > .05, partial η2 = .00). A significant effect of training condition on metacognitive strategy application appeared at T2 after controlling for the effect of the cognitive strategy application at T1, F(5,177) = 11.72, p < .01, partial η2 = .26. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (ME) significantly increased the metacognitive strategy application at T2, compared to receiving non-hybrid training (E), t(99) = 4.63, p < .01, η2 = .03, as well as compared to receiving the control group training (R), t(99) = 2.59, p < .05, η2 = .01.
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (MT) more often applied metacognitive skills in a near-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training (T), we scrutinized the results of the MST_T at T2, controlling for cognitive strategy MST_T score at T1. The covariate cognitive strategy application at T1 was not significantly related to the metacognitive skill application at T2, F(1, 175) = 0.94, p > .05, partial η2 = .01. A significant effect of training condition on metacognitive skill application was observable at T2 after controlling for the effect of cognitive strategy application at T1, F(5,175) = 48.74, p < .01, partial η2 = .59. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (MT) significantly increased the metacognitive strategy application at T2 compared to receiving non-hybrid training (T), t(92) = 12.67, p < .01, η2 = .41, as well as compared to receiving the control group training (R), t(92) = 7.24, p < .01, η2 = .13.
Application of metacognitive skills in a far-transfer task
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (ME) more often applied metacognitive skills in a far-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training (E), we examined the results of the MST_E at T3. A significant effect of training condition on metacognitive skill application could be seen at T3, F(5,205) = 6.32, p < .01, partial η2 = .09. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (ME) significantly increased metacognitive skill application at T3 compared to receiving non-hybrid training (E), t(108) = 2.67, p < .01, η2 = .01 but not compared to receiving the control group training (R), t(108) = 1.52, p > .05, η2 = .00.
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (MT) more often applied metacognitive skills in a far-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training (T), we considered the results of the MST_T at T3. A significant effect of the training condition on metacognitive skill application showed at T3, F(5,162) = 17.13, p < .01, partial η2 = .35. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (MT) significantly increased metacognitive skill application at T3 compared to receiving non-hybrid training (T), t(71) = 4.86, p < .01, η2 = .06, as well as compared to receiving the control group training (R), t(71) = 2.94, p < .01, η2 = .01.
Application of cognitive strategy in a far-transfer task
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (ME) more often applied cognitive strategies in a far-transfer task than students receiving non-hybrid training (E), we assessed the results of the MST_T at T3, controlling for cognitive strategy application at T2. The covariate cognitive strategy application at T2 was not significantly related to the cognitive strategy application at T3, F(1, 155) = 0.68, p > .05, partial η2 = .01. A significant effect of the training condition on cognitive strategy application at T3 could be observed after controlling for the effect of the cognitive strategy application at T2, F(5,155) = 3.53, p < .01, partial η2 = .11. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (ME) significantly increased cognitive strategy application at T3 in comparison to receiving the control group training (R), t(108) = 3.00, p < .01, η2 = .00, but not when compared to receiving non-hybrid training (E), t(108) = 0.50, p > .05, η2 = .01.
To investigate whether students receiving hybrid training (MT) more often applied cognitive strategies in a far-transfer task than students who received non-hybrid training (T), we analyzed the results of the MST_E at T3, controlling for cognitive strategy application at T2. The covariate, cognitive strategy application at T2 was not significantly related to the cognitive strategy application at T3, F(1, 162) = 1.38, p > .05, partial η2 = .01. We found a significant effect of the training condition on cognitive strategy application at T3, F(5,162) = 58.84, p < .01, partial η2 = .66. Planned contrasts revealed that receiving hybrid training (MT) significantly increased cognitive strategy application at T3 compared to receiving non-hybrid training (E), t(71) = 7.71, p < .01, η2 = .21, as well as in comparison to receiving the control group training (R), t(71) = 6.15, p < .01, η2 = .12.
Discussion
Our study contributes to SRL research regarding transfer. In light of the results, a hybrid training approach revealed promising potential for promoting transfer. When task-general metacognitive skills (e.g., Donker et al. 2014; Veenman et al. 2006) are trained together with task-specific cognitive strategies, students may transfer those metacognitive skills to other cognitive strategies. However, these far-transfer processes have not yet been shown empirically, in contrast to near-transfer processes (e.g., Aghaie and Zhang 2012).
Our findings showed overall that hybrid training generally proved the most effective approach to improving students’ application of skills. First, our results showed that hybrid training, in comparison to non-hybrid and control group training, improved students’ application of metacognitive skills in a near-transfer task. Second, hybrid training was more effective in terms of application of metacognitive skills in a far-transfer task compared to non-hybrid and control group training. Third, in terms of cognitive strategy application, one type of hybrid training (MT) was more effective than non-hybrid and control group training. The other type (ME) was not.
Theoretical considerations
From a theoretical perspective, our findings may serve to confirm the previous research and bring new insights regarding far-transfer processes within SRL and relating to task generality or specificity of metacognitive skills.
For example, our results replicate Leopold and Leutner’s (2015) assertion classifying hybrid training, compared to non-hybrid training, as more beneficial to fostering cognitive strategy application. Additionally, our findings confirm previous evidence that hybrid training improves near-transfer performance (e.g., Aghaie and Zhang 2012). Since the hybrid approach helps students learn to regulate a particular cognitive or motivational strategy, the quality of strategy use via application of metacognitive skills may increase (e.g., Leopold & Leutner 2015).
Moreover, our study can be understood as the first evidence that hybrid training fosters even far transfer within SRL. This result satisfies the vital demand to compare metacognitive skills across tasks and domains (Veenman et al. 2006). However, the hybrid training approach should be explored more broadly in future. Metacognitive skills should also be combined with other aspects of metacognitive knowledge: for example, motivational strategies (Wolters 2010) or resource management strategies (Claessens et al. 2007). A systematic variation of tasks and domains to prove the transfer of metacognitive skills to new learning tasks and situations is urgently needed.
Furthermore, our results can be understood as evidence for the task generality of metacognitive skills (planning, monitoring, and evaluation; Schraw 2001), in contrast to the task-specific nature of metacognitive knowledge about cognitive and motivational strategies. Only task-general components of metacognition can be transferred to new tasks (e.g., Veenman et al. 2006). Therefore, this study can contribute important insights to the unresolved discussion of the extent to which metacognitive skills are general or specific (Schraw et al. 1995; Schraw and Nietfeld 1998; Veenman et al. 1997; Veenman et al. 2006). In light of these results, we recommend paying more attention to strategy transfer in SRL. Because students often fail to transfer trained strategies (e.g., O’Sullivan and Pressley 1984), and benefits of teaching self-regulated learning are therefore doubtful (Sweller and Paas 2017), this aspect of metacognitive knowledge should be incorporated in established models of SRL (Boekaerts 1996; Efklides 2011; Hadwin et al. 2017; Pintrich 2000; Winne 2017; Winne and Hadwin 1998; Zimmerman and Moylan 2009).
Somewhat surprisingly, performance in the cognitive strategy application of a far-transfer task seems to depend on the respective cognitive strategy itself. Our results revealed far transfer that connected to the far-transfer task MST_T (cognitive strategy of text highlighting), but not for the MST_E (cognitive strategy to conduct experiments). This outcome may be due to students’ greater familiarity with (several) reading strategies, having already learned them in (primary) school, while they might not have previously encountered a cognitive strategy for conducting experiments. Transfer might be dependent on task-general as well as task-specific aspects. Although, statistically, no prior knowledge differences were found, descriptive results also reveal that students were more familiar with the cognitive strategy for conducting experiments than with the text-highlighting strategy.
Methodological implications
From a methodological perspective, the present study aimed to measure students’ intended application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies with a newly developed instrument called MST (Stebner et al. 2015). A fictitious learning situation was presented in the form of a vignette, and students had to describe their learning process in an open-response format. The MST is an economic and scenario-based means to measure the application of metacognitive skills and cognitive strategies along with transfer. However, the students made only limited mention of metacognitive skills.
First, this outcome may reflect the difficulty of operationalizing the application of metacognitive skills. Established learning questionnaires (e.g., Pintrich et al. 1993) provide students with strategies or procedures, asking them to indicate whether and/or how often they apply the respective strategies. In contrast, the MST requires students to spontaneously recall skills or strategy steps without any specific prompts. The intended application of a strategy is recorded in a fictitious learning situation, increasing the validity of strategy measurement (e.g., Händel et al. 2014). However, this approach results in only few mentions of metacognitive skills, since only conscious strategy knowledge can be named and recorded. Nevertheless, the MST does not measure actual strategy application. Instead, it assesses the intended skill/strategy application in a fictitious yet concrete learning situation. The extent to which the intended strategy application in a fictitious learning situation reflects the actual strategy application of students in a real learning situation remains a topic for future research to investigate.
Second, research on SRL is generally faced with the challenge of defining and operationalizing metacognition (Dinsmore et al. 2008). The fact that many studies describe the same metacognitive processes using different terms renders the comparability of study findings even more elusive. Third, transfer is generally difficult to measure. Valid instruments for measuring transfer distances are still pending. Transfer measures always have the difficulty of operationalizing the distance between the training and learning task (Robertson, 2000). The transfer distance is likely to be closely related to the likelihood of occurred transfer.
One vital limitation of this study concerns the instruction of MST_E and MST_T, due to their differences. While the MST_E instruction encourages students to write down all possibilities, the MST_T requires students to “simply” list what they would do. Correspondingly, students might have mentioned more strategies in MST_E than in MST_T. However, this problem was solved by coding. Even when students described several experiments, the same score was given for naming the skills/strategies. In other words, instead of rating several possibilities describing an experiment as better, we coded the naming of skills and strategies. Additionally, the MST instructions caused students to write down as many strategies as possible. Coding is based on a quantitative approach (Wirth and Leutner 2008): the more points, the better the application of skills/strategies. These results might have been influenced by the amount of text that the students had produced. Some people simply write less than others. This aspect should be included as a covariate in statistical analyses as well as mentioned in future research.
Another limitation concerns the dependent variable. The study did not report on content knowledge. However, we captured content knowledge regarding the cognitive strategy to conduct experiments with a computer-based measure (MicroDYN; Greiff and Funke 2009). The results of Stebner et al. (2015) showed that hybrid-trained groups performed better than non-hybrid and control groups. However, one weakness of the present study is that the results relate only to the transfer of metacognitive skills. Since this was a first attempt to investigate far transfer within SRL using an experimental study design in schools, we will seek to expand on this topic in future studies.
Practical implications for schools
The results of the present study may support the demand for the development of concepts that focus on using metacognitive skills in different learning contexts at school since students are able to transfer metacognitive skills combined with various cognitive and motivational strategies. Our experiment was conducted in the form of an SRL training intervention alongside regular classes in school, which enabled us to meet quality standards of experimental research studies, including various groups and random allocation of participants to groups (Spörer and Glaser 2010). Furthermore, intervention fidelity was sustained by having researchers from the university administer and observe the training conditions while rotating between the training conditions. This practice can be seen as a strength of the present study in that field interventions are generally more difficult to implement than interventions under laboratory conditions (Hulleman and Cordray 2009). Future research should consider applying metacognitive skills, for instance, in regular school classes and in various school subjects in the sense of a holistic concept of SRL in school (Boekaerts 1999). In order to achieve this aim, teachers would have to be trained to encourage students to apply metacognitive skills combined with cognitive and/or motivational strategies in their regular classes. Equipping teachers with evaluated material, which can be used in regular classes, and providing them with metacognitive knowledge and skills could be beneficial in terms of implementing SRL at school (Dignath et al. 2008; Stebner et al. 2019). Therefore, investigating potential determinants of teachers’ promotion of SRL in their classrooms could be a promising means to help teachers to support SRL in their classrooms (Dignath-van Ewijk 2016).
Conclusions
Overall, our findings provide interesting, innovative insights into the transfer of metacognitive skills within SRL training. The results indicate that hybrid training can improve near and far transfer of metacognitive skills, leading in the end to a higher quality of cognitive strategy application. On the one hand, these findings suggest that students’ ability to self-regulate their learning can be trained and transferred to far-transfer tasks to enhance their learning performance. However, in line with Sweller and Paas (2017), we call for future research regarding the demonstration of differential learning performance by using effectively acquired metacognition skills (planning, monitoring, and evaluating). Further experimental studies are needed to establish whether our results can be replicated with other performance measures, such as acquired content knowledge. On the other hand, the present research offers a starting point for developing effective and practical concepts for SRL at school. Future research should incorporate studies in which the role of metacognitive skills in various learning environments, topics, and subjects is examined. For example, one promising approach might be to implement metacognitive skills through a combination of direct and indirect training in regular school classes in order to support students’ transfer performance (Schuster et al. 2018). Since in direct strategy training, metacognitive skills are directly trained, indirect training comprises a skill-improving learning environment such as using implementation intentions (Stalbovs et al. 2015). Indirect training intervention might help to overcome a so-called production deficit – that is, a developmental stage in which students do not spontaneously use strategies even though they know the respective strategy and are able to use it (Hasselhorn 1995). Continuously triggering the use of strategies via indirect training enhances the automation of strategies learned in direct training. Therefore, a combined hybrid training approach is presumably the most effective way to promote metacognitive knowledge and skills at school (e.g., Paris and Paris 2001).
Notes
The learning material of all learning conditions was presented in German.
References
Aghaie, R., & Zhang, L. J. (2012). Effects of explicit instruction in cognitive and metacognitive reading strategies in Iranian EFL students’ reading performance and strategy transfer. Instructional Science, 40, 1063–1081.
Boekaerts, M. (1996). Self-regulated learning at the junction of cognition and motivation. European Psychologist, 2, 100–112.
Boekaerts, M. (1999). Self-regulation learning. Where are we today. International Journal of Educational Research, 31, 445–457.
Brown, A. L. (1978). Knowing when, where, and how to remember: A problem of metacognition. In R. Glaser (Ed.), Advances in instructional psychology (Vol. 1, pp. 77–165). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Carretti, B., Caldarola, N., Tencati, C., & Cornoldi, C. (2014). Improving reading comprehension in reading and listening settings: The effect of two training programmes focusing on metacognition and working memory. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84, 194–210.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Logical structures in language. American Documentation, 8, 284–291.
Claessens, B. J. C., van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36, 255–276.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Collins, A., Brown, J. S., & Newman, S. E. (1989). Cognitive apprenticeship: Teaching the crafts of reading, writing, and mathematics. In L. B. Resnick (Ed.), Knowing, learning, and instruction: Essays in honor of Robert Glaser (pp. 453–494). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Desoete, A., Roeyers, H., & De Clercq, A. (2003). Can offline metacognition enhance mathematical problem solving? Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 188–200.
Dignath, C., & Büttner, G. (2008). Components of fostering self-regulated learning among students. A meta-analysis on intervention studies at primary and secondary school level. Metacognition Learning, 3, 231–264.
Dignath, C., Büttner, G., & Langfeldt, H.-P. (2008). How can primary students learn self-regulated learning strategies most effectively? A meta-analysis on self-regulation training programs. Educational Research Review, 3, 101–129.
Dignath-van Ewijk, C. (2016). Which components of teacher competence determine whether teachers enhance self-regulated learning? Frontline Learning Research, 4, 83–105.
Dinsmore, D. L., Alexander, P. A., & Loughlin, S. M. (2008). Focusing the conceptual lens of metacognition, self-regulation, and self-regulated learning. Educational Psychology Review, 20, 391–409.
Donker, A., de Boer, H., Kostons, D., Dignath-van Ewijk, C., & van der Werf, M. (2014). Effectiveness of self-regulated learning strategies on academic performance: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 11, 1–26.
Efklides, A. (2011). Interactions of metacognition with motivation and affect in self-regulated learning: The MASRL model. Educational Psychologist, 46, 6–25.
Engelschalk, T., Steuer, G., & Dresel, M. (2016). Effectiveness of motivational regulation: Dependence on specific motivational problems. Learning and Individual Differences, 52, 72–78.
Engle, R. A., Lam, D. P., Meyer, X. S., & Nix, S. E. (2012). How does expansive framing promote transfer? Several proposed explanations and a research agenda for investigating them. Educational Psychologist, 47, 215–231.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A.-G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioural, and biomedical sciences. Behaviour Research Methods, 39, 175–191.
Fischer, A., Greiff, S., & Funke, J. (2012). The process of solving complex problems. The Journal of Problem Solving, 4, 20–42.
Flavell, J. H., Miller, P. H., & Miller, S. A. (2002). Cognitive development (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Gearing, R. E., El-Bassel, N., Ghesquiere, A., Baldwin, S., Gillies, J., & Ngeow, E. (2011). Major ingredients of fidelity: A review and scientific guide to improving quality of intervention research implementation. Clinical Psychology Review, 31, 79–88.
Gentner, D., Rattermann, M. J., & Forbus, K. D. (1993). The roles of similarity: Separating retrievability from inferential soundness. Cognitive Psychology, 25, 524–575.
Glass, G. V., Peckham, P. D., & Sanders, J. R. (1972). Consequences of failure to meet assumptions underlying the fixed effects analyses of variance and covariance. Review of Educational Research, 42, 237–288.
Glenberg, A. M., Meyer, M., & Lindem, K. (1987). Mental models contribute to foregrounding during text comprehension. Journal of Memory and Language, 26, 69–83.
Greiff, S., & Funke, J. (2009). Measuring complex problem solving: The MicroDYN approach. In F. Scheuermann & J. Björnsson (Eds.), The transition to computer-based assessment. New approaches to skills assessment and implications for large-scale testing (pp. 157–163). Luxemburg: European Communities.
Hadwin, A., Järvelä, S., & Miller, M. (2017). Self-regulation, co-regulation, and shared regulation in collaborative learning environments. In D. H. Schunk & J. A. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 83–106). New York: Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Händel, M., Lockl, K., Heydrich, J., Weinert, S., & Artelt, C. (2014). Assessment of metacognitive knowledge in students with special educational needs. Metacognition and Learning, 9, 333–352.
Händel, M., Harder, B., & Dresel, M. (2020). Enhanced monitoring accuracy and test performance: Incremental effects of judgment training over and above repeated testing. Learning and Instruction, 65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2019.101245.
Hasselhorn, M. (1995). Beyond production deficiency and utilization inefficiency: Mechanisms of the emergence of strategic categorization in episodic memory tasks. In F. E. Weinert & W. Schneider (Eds.), Memory performance and competencies. Issues in growth and development (pp. 141–159). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Heller, K., & Perleth, C. (2000). Kognitiver Fähigkeitstest für 4. und 12. Klassen. [Cognitive ability test for 4th and 12th grades] (3rd ed.). Weinheim: Beltz-Test.
Hulleman, C. S., & Cordray, D. S. (2009). Moving from the lab to the field: The role of fidelity and achieved relative intervention strength. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 2, 88–110.
Jacobs, J. E., & Paris, S. G. (1987). Children’s metacognition about reading: Issues in definition, measurement, and instruction. Educational Psychologist, 22, 255–278.
Kim, H. J., & Pedersen, S. (2011). Advancing young adolescents’ hypothesis-development performance in a computer-supported and problem-based learning environment. Computers and Education, 57, 1780–1789.
King, A. (1991). Improving lecture comprehension: Effects of a metacognitive strategy. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 5, 331–346.
Kirschner, P. A., & Stoyanov, S. (2018). Educating youth for nonexistent/not yet existing professions. Educational Policy, 34, 477–517. https://doi.org/10.1177/0895904818802086.
Klahr, D., & Dunbar, K. (1988). Dual space search during scientific reasoning. Cognitive Science, 12, 1–48.
Kramarski, B., Mevarech, Z. R., & Arami, M. (2002). The effects of metacognitive instruction on solving mathematical authentic tasks. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 49, 225–250.
Latham, G. P., & Seijts, G. H. (1999). The effects of proximal and distal goals on performance on a moderately complex task. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 20, 421–429.
Lee, Y., Capraro, M. M., Capraro, R. M., & Bicer, A. (2018). A meta-analysis: Improvement of students’ algebraic reasoning through metacognitive training. International Education Studies, 11, 42–49.
Leopold, C., & Leutner, D. (2015). Improving students’ science text comprehension through metacognitive self-regulation when applying learning strategies. Metacognition and Learning, 10, 313–346.
Lotz, C. (2018). Predicting educational success: What’s beyond intelligence. Doctoral dissertation. University of Saarland.
Maag Merki, K. M., Ramseier, E., & Karlen, Y. (2013). Reliability and validity analyses of a newly developed test to assess learning strategy knowledge. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 12, 391–408.
Mayer, R. E. (1996). Learning strategies for making sense out of expository text: The SOI model for guiding three cognitive processes in knowledge construction. Educational Psychology Review, 8, 357–371.
Mayer, R. E. (1998). Cognitive, metacognitive, and motivational aspects of problem solving. Instructional Science, 26, 49–63.
Mihalca, L., Mengelkmap, C., & Schnotz, W. (2017). Accuracy of metacognitive judgements as a moderator of learner control effectiveness in problem-solving tasks. Metacognition and Learning, 12, 1556–1623.
Miller, T. M., & Geraci, L. (2011). Unskilled but aware: Reinterpreting overconfidence in low-performing students. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 37, 502.
Neuenhaus, N., Artelt, C., Lingel, K., & Schneider, W. (2011). Fifth graders metacognitive knowledge: General or domain-specific. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 26, 163–178.
Nietfeld, J. L., Cao, L., & Osborne, J. W. (2005). Metacognitive monitoring accuracy and student performance in the postsecondary classroom. The Journal of Experimental Education, 74, 7–28.
O’Sullivan, T. J., & Pressley, M. (1984). Completeness of instruction and strategy transfer. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 38, 275–288.
Ohtani, K., & Hisasaka, T. (2018). Beyond intelligence: A meta-analytic review of the relationship among metacognition, intelligence, and academic performance. Metacognition and Learning, 13, 179–212.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. (2016). OECD-Wirtschaftsberichte: Deutschland 2016. OECD Publishing.
Palinscar, A. S., & Brown, A. L. (1984). Reciprocal teaching of comprehension-fostering and comprehension-monitoring activities. Cognition and Instruction, 1, 117–175.
Paris, S., & Paris, A. H. (2001). Classroom applications of research on self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 36(2), 89–101.
Perels, F., Gürtler, T., & Schmitz, B. (2005). Training of self-regulatory and problem-solving competence. Learning and Instruction, 15, 123–139.
Perkins, D. N., & Salomon, G. (1988). Teaching for transfer. Educational Leadership, 46, 22–32.
Perkins, D. N., & Salomon, G. (1989). Are cognitive skills context-bound? Educational Researcher, 18, 16–25.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic Press.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D., Garcia, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1993). Reliability and predictive validity of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ). Educational and Psychological Measurement, 53, 801–813.
Robertson, S. I. (2000). Imitative problem solving: why transfer of learning often fails to occur, Instructional Science, 28, 263–289
Roelle, J., Nowitzki, C., & Berthold, K. (2017). Do cognitive and metacognitive processes set the stage for each other? Learning and Instruction, 50, 54–64.
Scharff, L., Draeger, J., Verpoorten, D., Devlin, M., Dvorakova, L. S., Lodge, J. M., & Smith, S. (2017). Exploring metacognition as support for learning transfer. Teaching & Learning Inquiry, 5, 1–8.
Schraw, G. (2001). Promoting general metacognitive awareness. In H. J. Hartman (Ed.), Metacognition in learning and instruction. Theory, research and practice (pp. 3–16). Netherlands: Springer.
Schraw, G., & Dennison, R. S. (1994). Assessing metacognitive awareness. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 19, 460–475.
Schraw, G., & Nietfeld, J. (1998). A further test of the general monitoring skill hypothesis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 236–248.
Schraw, G., Dunkle, M. E., Bendixen, L. D., & Roedel, T. D. (1995). Does a general monitoring skill exist? Journal of Educational Psychology, 87, 433–444.
Schraw, G., Crippen, K. J., & Hartley, K. (2006). Promoting self-regulation in science education: Metacognition as a part of a broader perspective on learning. Research in Science Education, 36, 111–139.
Schuster, C., Stebner, F., Leutner, D., & Wirth, J. (2018). Förderung des transfers metakognitiver Lernstrategien durch direktes und indirektes training [Promote transfer of metacognitive learning strategies through direct and indirect training]. Unterrichtswissenschaft, 46, 409–435.
Schwinger, M., Steinmayr, R., & Spinath, B. (2009). How do motivational regulation strategies affect achievement: Mediated by effort management and moderated by intelligence. Learning and Individual Differences, 19, 621–627.
Souvignier, E., & Mokhlesgerami, J. (2006). Using self-regulation as a framework for implementing strategy-instruction to foster reading comprehension. Learning and Instruction, 16, 57–71.
Spörer, N., & Glaser, C. (2010). Förderung selbstregulierten Lernens im schulischen Kontext [Promoting self-regulated learning in the school context]. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie, 24, 171–175.
Stalbovs, K., Scheiter, K., & Gerjets, P. (2015). Implementation intentions during multimedia learning: Using if-then plans to facilitate cognitive processing. Learning and Instruction, 35, 1–15.
Stebner, F., Schmeck, A., Marschner, J., Leutner, D., & Wirth. J. (2015). Ein Training zur Förderung des selbstregulierten Lernens durch Experimentieren [Training to promote self-regulated learning through experimentation]. In H. Wendt & W. Bos (Eds.), Auf dem Weg zum Ganztagsgymnasium. Erste Ergebnisse der wissenschaftlichen Begleitforschung zum Projekt Ganz In (pp. 396–413). Münster Waxmann Verlag.
Stebner, F., Pfänder, H., Schuster, C., Schurig, M., van den Bogaert, V., & Strähle, P. (2019). Implementing self-regulated learning at all-day schools using the analytic framework of developmental processes. In M. Schüpbach & N. Lilla (Eds.), Extended education from an international comparative point of view (pp. 23–35). Berlin Springer.
Stoeger, H., & Ziegler, A. (2008). Evaluation of a classroom-based training to improve self-regulation in time management tasks during homework activities with fourth graders. Metacognition Learning, 3, 207–230.
Su, D., & Steiner, P. M. (2018). An evaluation of experimental designs for constructing vignette sets in factorial surveys. Sociological Methods & Research, 6, 128–138.
Swanson, H. L. (1990). Influence of metacognitive knowledge and aptitude on problem solving. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 306–314.
Sweller, J., & Paas, F. (2017). Should self-regulated learning be integrated with cognitive load theory? A commentary. Learning and Instruction, 51, 85–89.
Tschirgi, J. E. (1980). Sensible reasoning: A hypothesis about hypotheses. Child Development, 51, 1–10.
Van Meeuwen, L. W., Brand-Gruwel, S., Kirschner, P. A., de Bock, J. J. P. R., & van Merriënboer, J. G. (2018). Fostering self-regulation in training complex cognitive tasks. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66, 53–73.
Veenman, M. V., & Verheij, J. (2003). Technical students’ metacognitive skills: Relating general vs. specific metacognitive skills to study success. Learning and Individual Differences, 13, 259–272.
Veenman, M. V., Elshout, J. J., & Meijer, J. (1997). The generality versus domain-specificity of metacognitive skills in novice learning across domains. Learning and Instruction, 7, 187–209.
Veenman, M. V., Kok, R., & Blöte, A. W. (2005). The relation between intellectual and metacognitive skills in early adolescence. Instructional Science, 33, 193–211.
Veenman, M., van Hout-Wolters, B., & Afflerbach, P. (2006). Metacognition and learning: Conceptual and methodological considerations. Metacognition Learning, 1, 3–14.
Weinstein, C. E., & Mayer, R. E. (1986). The teaching of learning strategies. In M. C. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research in teaching (pp. 315–327). New York: Macmillan.
Weinstein, C. E., Husman, J., & Dierking, D. R. (2000). Self-regulation interventions with a focus on learning strategies. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 727–747). San Diego: Academic Press.
Wilkinson, L., & Task Force on Statistical Inference. (1999). Statistical methods in psychology journals. American Psychologist, 54, 594–604.
Winne, P. H. (2017). Cognition and metacognition with self-regulated learning. In P. A. Alexander, D. H. Schunk, & J. A. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 36–48). New York: Routledge.
Winne, P. H., & Hadwin, A. F. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. In D. J. Hacker, J. Dunlosky, & A. C. Graesser (Eds.), Metacognition in educational theory and practice (pp. 277–304). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Wirth, J., & Leutner, D. (2008). Self-regulated learning as a competence: Implications of theoretical models for assessment methods. Zeitschrift für Psychologie/Journal of Psychology, 216, 102–110.
Wolters, C. A. (1998). Self-regulated learning and college students’ regulation of motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 224–235.
Wolters, C. A. (2010). Regulation of motivation. Evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 4, 189–205.
Wolters, C. A., & Rosenthal, H. (2000). The relation between students’ motivational beliefs and their use of motivational regulation strategies. International Journal of Educational Research, 33, 801–820.
Zepeda, C. D., Richey, J. E., Ronevich, P., & Nokes-Malach, T. J. (2015). Direct instruction of metacognition benefits adolescent science learning, transfer, and motivation: An in vivo study. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107, 954–970.
Zepeda, C. D., Hlutkowsky, C. O., Partika, A. C., & Nokes-Malach, T. J. (2019). Identifying teachers’ supports of metacognition through classroom talk and its relation to growth in conceptual learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 111, 522–541.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Moylan, A. R. (2009). Self-regulation: Where metacognition and motivation intersect. In D. J. Hacker, J. Dunlosky, & A. C. Graesser (Eds.), Handbook of metacognition in education (pp. 299–315). New York: Routledge.
Zimmerman, B. J., Bonner, S., & Kovach, R. (2002). Developing self-regulated learners: Beyond achievement to self-efficacy. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Acknowledgments
The project “Ganz In. Mit Ganztag mehr Zukunft. Das neue Ganztagsgymnasium NRW” was a joint project of the Mercator Foundation, the Institute for School Development Research Dortmund, the Ministry of School and Education of the State North Rhine-Westphalia and the University Alliance Ruhr. The authors thank these institutions for supporting the project. Further acknowledgments are well deserved by the scientific staff and assistants Benjamin Klein, Friederike Gilsbach, Fabiana Karstens, Soofie Kroß, Carina Maaßen, and Sören-Kristian Berger for carrying out the study together with the authors.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Projekt DEAL. This study was funded by the Stiftung Mercator, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Schuster, C., Stebner, F., Leutner, D. et al. Transfer of metacognitive skills in self-regulated learning: an experimental training study. Metacognition Learning 15, 455–477 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-020-09237-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-020-09237-5