Abstract
Purpose
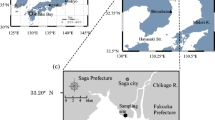
Sediment denitrification is a dominant mechanism for nitrogen removal and can help to minimize lake eutrophication. However, the spatio-temporal variability of denitrification rates and its controlling factors in sediments of large shallow lakes are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the controlling factors on the temporal and spatial variability of denitrification rates in Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China, to determine the contribution of denitrification on the total lacustrine nitrogen budget.
Materials and methods
We collected 18 intact monthly sediment cores and an additional 36 seasonal sediment cores from January 2013 to January 2014. Cores were collected from the inner and outer sections of Meiliang Bay for analysis of denitrification rates and sediment properties. We also collected in situ surface water samples for water quality analysis. Denitrification rates at the sediment-water interface (SWI) were measured using acetylene inhibition techniques and intact sediment core incubation. We used a t test to determine the differences in water quality and sediment properties between the two sites and a one-way ANOVA to identify seasonal differences in denitrification rates, water quality, and sediment properties. We also applied Pearson’s correlation, distance-based redundancy analysis (db-RDA) and random forest model to identify the relationships between denitrification rates and environmental factors.
Results and discussion
Denitrification rates ranged from 0.76 to 40.94 μmol N m−2 h−1 and 0.13 to 52.55 μmol N m−2 h−1, with annual mean values of 19.97 and 17.15 μmol N m−2 h−1 for the Inner and Outer Bay, respectively. Sediment denitrification rates in the Inner and Outer Bay showed similar seasonal variability, with the highest values in spring and summer and the lowest values in autumn. Nitrate addition was shown to significantly increase denitrification rates in summer and autumn (P < 0.05); however, carbon addition showed no significant influence on denitrification rates in the four seasons. Our results imply that denitrification rates were nitrate-limited in summer and autumn. Distance-based redundancy analysis (db-RDA) and random forest model showed that denitrification rates were mainly determined by nitrate, temperature, and chlorophyll a (Chla), and that nitrate in the water column was the most important predictor of denitrification rates.
Conclusions
In general, denitrification rates showed significant seasonal variability in Meiliang Bay due to the co-regulation of both water temperature and nitrate concentrations. The dominance of each controlling factor on denitrification rates varied in different seasons. Based on our calculations, nitrogen removal by denitrification accounted for approximately 10.7% of the total nitrogen input to Taihu Lake. Therefore, we suggest the need for effective measures to reduce external nitrogen inputs of to Lake Taihu to prevent on-going eutrophication.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam G, Duncan H (2001) Development of a sensitive and rapid method for the measurement of total microbial activity using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) in a range of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:943–951
Álvarez-Cobelas M, Piña-Ochoa E, Sánchez-Carrillo S, Delgado-Huertas A (2019) Spatial variability of denitrification along a nitrate-rich seepage chain of lakes (Ruidera Natural Park, Central Spain). Limnetica 38(2):607–621
Baeseman JL, Smith RL, Silverstein J (2006) Denitrification potential in stream sediments impacted by acid mine drainage: effects of pH, various electron donors, and iron. Microb Ecol 51:232–241
Brezonik PL, Lee GF (1968) Dentrification as a nitrogen sink in Lake Mendota, Wisconsin. Environ Sci Technol 2(2):120–125
Bruesewitz DA, Tank JL, Hamilton SK (2012) Incorporating spatial variation of nitrification and denitrification rates into whole-lake nitrogen dynamics. J Geophys Res-Biogeo 117:G3
Chen MS, Cui JZ, Lin J, Ding SM, Gong MD (2018) Successful control of internal phosphorus loading after sediment dredging for 6 years: a field assessment using high-resolution sampling techniques. Sci Total Environ 616-617:927–936
Christensen PB, Srensen J (1986) Temporal variation of denitrification activity in plant-covered littoral sediment from Lake Hampen, Denmark. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1174–1179
Clough TJ, Buckthought LE, Kelliher FM, Sherlock RR (2007) Diurnal fluctuations of dissolved nitrous oxide (N2O) concentrations and estimates of N2O emissions from a spring-fed river: implications for IPCC methodology. Glob Chang Biol 13:1016–1027
DeSimone LA, Howes BL (1998) Nitrogen transport and transformations in a shallow aquifer receiving wastewater discharge: a mass balance approach. Water Resour Res 34(2):271–285
Elith J, Leathwick JR, Hastie T (2008) A working guide to boosted regression trees. J Anim Ecol 77:802–813
Feld CK, Segurado P, Gutierrez-Canovas C (2016) Analysing the impact of multiple stressors in aquatic biomonitoring data: A ‘cookbook’ with applications in R. SciTotal Environ 573:1320–1339
García-Ruiz R, Pattinson SN, Whitton BA (1998a) Denitrification in sediments of the freshwater tidal Yorkshire Ouse. Sci Total Environ 210-211:321–327
García-Ruiz R, Pattinson SN, Whitton BA (1998b) Denitrification and nitrous oxide production in sediments of the Wiske, a lowland eutrophic river. Sci Total Environ 210-211:307–320
Gardner WS, Nalepa TF, Malczyk JM (1987) Nitrogen mineralization and denitrification in Lake Michigan sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 32:1226–1238
Graca B, Burska D, Matuszewska K (2004) The impact of dredging deep pits on organic matter decomposition in sediments. Water Air Soil Poll 158:237–259
Grantz EM, Kogo A, Scott JT (2012) Partitioning whole-lake denitrification using in situ dinitrogen gas accumulation and intact sediment core experiments. Limnol Oceanogr 57(4):925–935
Groffman PM, Altabet MA, Böhlke JK, Butterbach-Bahl K, David MB, Firestone MK, Giblin AE, Kana TM, Nielsen LP, Voytek MA (2006) Methods for measuring denitrification: diverse approaches to a difficult problem. Ecol Appl 16(6):2091–2122
Harrison JA, Maranger RJ, Alexander RB, Giblin AE, Jacinthe PA, Mayorga E, Seitzinger SP, Sobota DJ, Wollheim WM (2009) The regional and global significance of nitrogen removal in lakes and reservoirs. Biogeochemistry 93:143–157
Hasegawa T, Okino T (2004) Seasonal variation of denitrification rate in Lake Suwa sediment. Limnology 5:33–39
Hedin LO, von Fischer JC, Ostrom NE, Kennedy BP, Brown MG, Robertson GP (1998) Thermodynamic constraints on nitrogen transformations and other biogeochemical processes at soil-stream interfaces. Ecology 79:684–703
Helmer C, Labroue L (1993) Denitrification in gravel-pit lakes. Hydrobiologia 252:35–44
Hu WP, Zhai SJ, Zhe ZC, Han HJ (2008) Impacts of the Yangtze River water transfer on the restoration of Lake Taihu. Ecol Eng 34:30–49
Ishwaran H, Kogalur U (2014) Random forests for survival, regression and classification (RF-SRC), R package version 1.6. URL. https://CRANR-projectorg/package=randomForestSRC
Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Kristensen P, Christensen PB, Søndergaard M (1992) Nitrogen loss and denitrification as studied in relation to reductions in nitrogen loading in a shallow, hypertrophic lake (Lake Søbygård, Denmark). Int Rev Gesam Hydrobiol 77:29–42
Johnson KM, Hughes JE, Donaghay PL, Sieburth JM (1990) Bottle-calibration static head space method for the determination of methane dissolved in seawater. Anal Chem 62:2408–2412
Kaspar HF (1985) The denitrification capacity of sediment from a hypereutrophic lake. Freshw Biol 15:449–453
Keeney DR, Chen RL, Graetz DA (1971) Importance of denitrification and nitrate reduction in sediments to the nitrogen budgets of lakes. Nature 233(3):66–67
Kreiling RM, Richardson WB, Cavanaugh JC, Bartsch LA (2011) Summer nitrate uptake and denitrification in an upper Mississippi River backwater lake: the role of rooted aquatic vegetation. Biogeochemistry 104:309–324
Liu WZ, Yao L, Jiang XL, Guo LD, Cheng XL, Liu GH (2018a) Sediment denitrification in Yangtze lakes is mainly influenced by environmental conditions but not biological communities. Sci Total Environ 616-617:978–987
Liu SQ, Wang C, Hou J, Wang PF, Miao LZ, Fan XL, You GX, Xu Y (2018b) Effects of Ag and Ag2S nanoparticles on denitrification in sediments. Water Res 137:28–36
Liu D, Zhong J, Zheng X, Fan C, Yu J, Zhong W (2018c) N2O fluxes and rates of nitrification and denitrification at the sediment–water interface in Taihu Lake, China. Water 10:911
Lu GH, Ma Q, Zhang JH (2011) Analysis of black water aggregation in Taihu Lake. Water Sci Eng 4:374–385
Luo L, Qin BQ, Yang LY, Song YZ (2007) Total inputs of phosphorus and nitrogen by wet deposition into Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiology 581:63–70
Luque-Almagro VM, Gates AJ, Moreno-Vivian C, Ferguson SJ, Richardson DJ, Dolores Roldan M (2011) Bacterial nitrate assimilation: gene distribution and regulation. Biochem Soc T 39:1838–1843
McCarthy MJ, Lavrentyev PJ, Yang L, Zhang L, Chen Y, Qin B, Gardner WS (2007) Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 581(1):195–207
McCarthy MJ, Gardner WS, Lehmann MF, Guindon A, Bird DF (2016) Benthic nitrogen regeneration, fixation, and denitrification in a temperate, eutrophic lake: effects on the nitrogen budget and cyanobacteria blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 61:1406–1423
McCrackin ML, Elser JJ (2010) Atmospheric nitrogen deposition influences denitrification and nitrous oxide production in lakes. Ecology 91(2):528–539
Mengis M, Gachter R, Wehrli B (1997a) Sources and sinks of nitrous oxide (N2O) in deep lakes. Biogeochemistry 38:281–301
Mengis M, Gächter R, Wehrli B, Bernasconi S (1997b) Nitrogen elimination in two deep eutrophic lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1530–1543
Messer J, Brezonik PL (1983) Comparison of denitrification rate estimation techniques in a large, shallow lake. Water Res 17:631–640
Molot L, Dillon P (1993) Nitrogen mass balances and denitrification rates in central Ontario Lakes. Biogeochemistry 20:195–212
Nizzoli D, Bartoli M, Azzoni R, Longhi D, Castaldelli G, Viaroli P (2018) Denitrification in a meromictic lake and its relevance to nitrogen flows within a moderately impacted forested catchment. Biogeochemistry 137:143–161
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O'hara R (2013) Package ‘vegan’. (Community ecology package, version 2)
Otten TG, Xu H, Qin B, Zhu GW (2012) Paerl HW (2012) spatiotemporal patterns and ecophysiology of toxigenic microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: implications for water quality management. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3480–3488
Ottosen LDM, Risgaard-Petersen N, Neilsen LP (1999) Direct and indirect measurements of nitrification and denitrification in the rhizosphere of aquatic macrophytes. Aquat Microb Ecol 19:81–91
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Li YP, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45:1973–1983
Paerl HW, Xu H, Hall NS, Rossignol KL, Joyner AR, Zhu GW, Qin BQ (2015) Nutrient limitation dynamics examined on a multi-annual scale in Lake Taihu, China: implications for controlling eutrophication and harmful algal blooms. J Freshwater Ecol 30:5–24
Palacin-Lizarbe C, Camarero L, Catalan J (2018) Denitrification temperature dependence in remote, cold, and N-poor lake sediments. Water Resour Res 54:1161–1173
Pattinson SN, García-Ruiz R, Whitton BA (1998) Spatial and seasonal variation in denitrification in the Swale-Ouse system, a river continuum. Sci Total Environ 210-211:289–305
Pfenning KS, McMahon PB (1996) Effect of nitrate, organic carbon, and temperature on potential denitrification rates in nitrate-rich riverbed sediments. J Hydrol 187:283–295
Piña-Ochoa E, Álvarez-Cobelas M (2006) Denitrification in aquatic environments: a cross-system analysis. Biogeochemistry 81:111–130
Rissanen AJ, Tiirola M, Ojala A (2011) Spatial and temporal variation in denitrification and in the denitrifier community in a boreal lake. Aquat Microb Ecol 64:27–40
Rivett M, Buss SR, Morgan P, Smith JWN, Bemment CD (2008) Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res 42:4215–4232
Ruban V, López-Sánchez JF, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller PH (1999) Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J Environ Monitor 1:51–56
Saunders DL, Kalff J (2001) Denitrificaiton rates in the sediments of Lake Memphremagog, Canada-USA. Water Res 35(8):1897–1904
Seitzinger SP (1988) Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnol Oceanogr 33:702–724
Seitzinger SP (1990) Denitrifieation in aquatic sediments. In: Revsbech NP, Sørensen J (eds) Denitrification in soil and sediment. FEMS Symposium No. 56. Plenum Press, New York, pp 301–322
Seitzinger SP (1994) Linkages between organic matter mineralization and denitrification in eight riparian wetlands. Biogeochemistry 25:19–39
Seitzinger SP, Nielsen LP, Caffrey J, Christensen PB (1993) Denitrification measurements in aquatic sediments: a comparison of three methods. Biogeochemistry 23(3):147–167
Seitzinger SP, Harrison JA, Böhlke JK, Bouwman AF, Lowrance R, Peterson B, Tobias C, Drecht GV (2006) Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes: a synthesis. Ecol Appl 16:2064–2090
Shang J, Zhang L, Shi C, Fan C (2013) Influence of Chironomid larvae on oxygen and nitrogen fluxes across the sediment water interface (Lake Taihu, China). J Environ Sci 25(5):978–985
Song LR, Chen W, Peng L (2007) Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: a systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res 41:2853–2864
Sørensen J (1978) Denitrification rates in marine sediment as measured by the acetylene inhibition technique. Appl Environ Microb 36:139–143
Van Luijn F, Boers PCM, Lijklema L (1996) Comparison of denitrification rates in lake sediments obtained by the N2 flux method, the 15N isotope pairing technique and the mass balance approach. Water Res 30(4):893–900
Wall LG, Tank JL, Royer TV, Bernot MJ (2005) Spatial and temporal variability in sediment denitrification within an agriculturally influenced reservoir. Biogeochemistry 76:85–111
Wang MR, Zhang HQ, Zhu X (2012) Innovation and practice of cyanobacteria control in Taihu Lake. China water resources and hydropower publishing press. Beijing, China
Wang YC, Li ZK, Li Z, Feng LL, Fan NW, Shen J (2013) Effects of macrophyte-associated nitrogen cycling bacteria on denitrification in the sediments of the eutrophic Gonghu Bay, Taihu Lake. Hydrobiologia 700:329–341
Wang MR, Strokal M, Burek P, Kroeze C, Ma L, Janssen ABG (2019) Excess nutrient loads to Lake Taihu: opportunities for nutrient reduction. Sci Total Environ 664:865–873
Weiss RF, Price BA (1980) Nitrous oxide solubility in water and seawater. Mar Chem 8:347–359
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55(1):420–432
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Hall NS, Wu Y (2015) Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Technol 49:1051–1059
Xu H, Paerl HW, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Hall NS, Zhu MY (2017) Long-term nutrient trends and harmful cyanobacterial bloom potential in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 787(1):229–242
Yang M, Yu JW, Li ZL, Guo ZH, Burch M, Lin TF (2008) Taihu Lake not to blame for Wuxi’s woes. Science 319:158
Yao XL, Zhang L, Zhang YL, Zhang B, Zhao ZH, Zhang YB, Li M, Jiang XY (2018) Nitrogen fixation occurring in sediments: contribution to the nitrogen budget of Lake Taihu, China. J Geophys Res Biogeo 123(9):2661–2674
Zhang YL, Qin BQ, Liu ML (2007) Tempral-spatial variations of chlorophyll a and primary production in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China from 1995–2003. J Plankton Res 39:707–719
Zhang L, Yao XL, Tang CJ, Xu HX, Jiang XY, Zhang YL (2016) Influence of long-term inundation and nutrient addition on denitrification in sandy wetland sediments from Poyang Lake, a large shallow subtropical lake in China. Environ Pollut 219:440–449
Zhao YQ, Xia YQ, Ti CP, Shan J, Li BL, Xia LL, Yan XY (2015) Nitrogen removal capacity of the river network in a high nitrogen loading region. Environ Sci Technol 49:1427–1435
Zhong JC, Fan CX, Liu GF, Zhang L, Shang JG, Gu XZ (2010) Seasonal variation of potential denitrification rates of surface sediment from Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Sci 22(7):961–967
Zhong JC, Yu JH, Zheng XL, Wen SL, Liu DH, Fan CX (2018) Effects of dredging season on sediment properties and nutrient fluxes across the sediment–water interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Water 10:1606
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41371457 and 41771516). We would like to thank the Taihu Lake Laboratory of Ecosystem Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (TLLER) for its logistic support. We would also like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on improving the quality of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Shiming Ding
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 261 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, J., Yu, J., Wang, J. et al. The co-regulation of nitrate and temperature on denitrification at the sediment-water interface in the algae-dominated ecosystem of Lake Taihu, China. J Soils Sediments 20, 2277–2288 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02558-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02558-2