Abstract
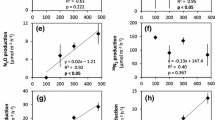
Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure were characterized in subtropical, eutrophic, large (2,338 km2), shallow (1.9 m mean depth), and polymictic Lake Taihu (China) in Sept–Oct 2002 during a cyanobacterial bloom. Population growth and industrialization are factors in trophic status deterioration in Lake Taihu. Sites for investigation were selected along a transect from the Liangxihe River discharge into Meiliang Bay to the main lake. Water column nitrogen and microbial food web measurements were combined with sediment–water interface incubations to characterize and identify important processes related to system nitrogen dynamics. Results indicate a gradient from strong phosphorus limitation at the river discharge to nitrogen limitation or co-limitation in the main lake. Denitrification in Meiliang Bay may drive main lake nitrogen limitation by removing excess nitrogen before physical transport to the main lake. Five times higher nutrient mineralization rates in the water column versus sediments indicate that sediment nutrient transformations were not as important as water column processes for fueling primary production. However, sediments provide a site for denitrification, which, along with nitrogen fixation and other processes, can determine available nutrient ratios. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) was important, relative to denitrification, only at the river discharge site, and nitrogen fixation was observed only in the main lake. Reflecting nitrogen cycling patterns, microbial food web structure shifted from autotrophic (phytoplankton dominated) at the river discharge to heterotrophic (bacteria dominated) in and near the main lake.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, S. & W. S. Gardner, 2002. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) as a nitrogen link, versus denitrification as a sink in a shallow estuary (Laguna Madre/Baffin Bay, Texas). Marine Ecology Progress Series 237: 41–50.
An, S., W. S. Gardner & T. M. Kana, 2001. Simultaneous measurement of denitrification and nitrogen fixation using isotope pairing with membrane inlet mass spectrometry analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67: 1171–1178.
Blackburn, T. H., 1979. Method for measuring rates of NH +4 turnover in anoxic marine sediments, using a 15N–NH +4 dilution technique. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 37: 760–765.
Blomqvist, P., A. Pettersson & P. Hyenstrand, 1994. Ammonium–nitrogen: a key regulatory factor causing dominance of non-nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 132: 141–164.
Bode, A. & Q. Dortch, 1996. Uptake and regeneration of inorganic nitrogen in coastal waters influenced by the Mississippi River: spatial and seasonal variations. Journal of Plankton Research 18: 2251–2268.
Cai, Q., X. Gao, Y. Chen, S. Ma & M. Dokulil, 1997. Dynamic variations of water quality in Lake Taihu and multivariate analysis of its influential factors. Journal of Chinese Geography 7: 72–82.
Caperon, J., D. Schell, J. Hirota & E. Laws, 1979. Ammonium excretion rates in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii, measured by a 15N isotope dilution technique. Marine Biology 54: 33–40.
Chen, Y., B. Qin, K. Teubner & M. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Cochlan, W. P., N. M. Price & P. J. Harrison, 1991. Effects of irradiance on nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton: comparison of frontal and stratified communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 69: 103–116.
Colt, J., 1984. Computation of dissolved gas concentrations in water as functions of temperature, salinity, and pressure. American Fisheries Society Special Publication 14.
Dickman, M., P. Pu & C. Zheng, 1998. Taihu Lake: past, present and future. Journal of Lake Sciences (China) 10(suppl.): 75–83.
Dokulil, M. T. & K. Teubner, 2000. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 438: 1–12.
Downing, J. A., S. B. Watson & E. McCauley, 2001. Predicting cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58: 1905–1908.
Edwards, C. A., T. A. Powell & H. P. Batchelder, 2000. The stability of an NZP model subject to realistic levels of vertical mixing. Journal of Marine Research 58: 37–60.
Elser, J. J., 1999. The pathway to noxious cyanobacteria blooms in lakes: the food web as the final turn. Freshwater Biology 42: 537–543.
Eyre, B. D., S. Rysgaard, T. Dalsgaard & P. B. Christensen, 2002. Comparison of isotope pairing and N2:Ar methods for measuring sediment denitrification—assumptions, modifications, and implications. Estuaries 25: 1077–1087.
Fahnenstiel, G. L., A. E. Krause, M. J. McCormick, H. J. Carrick & C. L. Schelske, 1998. The structure of the planktonic food web in the St. Lawrence Great Lakes. Journal of Great Lakes Research 24: 531–554.
Gardner, W. S., H. A. Bootsma, C. Evans & P. A. St. John, 1995a. Improved chromatographic analysis of 15N:14N ratios in ammonium or nitrate for isotopic addition experiments. Marine Chemistry 48: 271–282.
Gardner, W. S., J. F. Cavaletto, T. H. Johengen, J. R. Johnson, R. T. Heath & J. B. Cotner, 1995b. Effects of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, on community nitrogen dynamics in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Journal of Great Lakes Research 21: 529–544.
Gardner, W. S., P. J. Lavrentyev, H. A. Bootsma, J. F. Cavaletto, F. Troncone & J. B. Cotner, 2000. Effects of natural light on nitrogen dynamics in diverse aquatic environments. Internationale Vereinigung Fur Theoretische Und Angewandte Limnologie 27: 64–73.
Gu, B., K. E. Havens, C. L. Schelske & B. H. Rosen, 1997. Uptake of dissolved nitrogen by phytoplankton in a eutrophic subtropical lake. Journal of Plankton Research 19: 759–770.
Havens, K. E., T. Fukushima, P. Xie, T. Iwakuma, R. T. James, N. Takamura, T. Hanazato & T. Yamamoto, 2001. Nutrient dynamics and the eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA). Environmental Pollution 111: 263–272.
Hewson, I., J. M. O’Neil, C. A. Heil, G. Bratbak & W. C. Dennison, 2001. Effects of concentrated viral communities on photosynthesis and community composition of co-occurring benthic microalgae and phytoplankton. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 25: 1–10.
Huang, Y., 2000. The water quality of Lake Taihu and its protection, pp. 239–246. In Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology (ed), Research on Lake Sciences. Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Hyenstrand, P., P. Blomqvist & A. Pettersson, 1998. Factors determining cyanobacterial success in aquatic systems: a literature review. Ergebnisse der Limnologie 51: 41–62.
Jacoby, J. M., D. C. Collier, E. B. Welch, F. J. Hardy & M. Crayton, 2000. Environmental factors associated with a toxic bloom of Microcystis aeruginosa. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 57: 231–240.
Jin, X. & Q. Tu (eds), 1990. Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis of Lake Eutrophication (2nd edn.). Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing, 240 pp (in Chinese).
Kana, T. M., C. Darkangelo, M. D. Hunt, J. B. Oldham, G. E. Bennett & J. C. Cornwell, 1994. Membrane inlet mass spectrometer for rapid high-precision determination of N2, O2, and Ar in environmental water samples. Analytical Chemistry 66: 4166–4170.
Lavrentyev, P. J., H. A. Bootsma, T. H. Johengen, J. F. Cavaletto & W. S. Gardner, 1998. Microbial plankton response to resource limitation: insights from the community structure and seston stoichiometry in Florida Bay, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series 165: 45–57.
Lavrentyev, P. J., W. S. Gardner & L. Yang, 2000. Effects of the zebra mussel on nitrogen dynamics and the microbial community at the sediment–water interface. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21: 187–194.
Loferer-Krossbacher, M., J. Klima & R. Psenner, 1998. Determination of bacterial cell dry mass by transmission electron microscopy and densitometric image analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64: 688–694.
McCarthy, M. J. & W. S. Gardner, 2003. An application of membrane inlet mass spectrometry to measure denitrification in a recirculating mariculture system. Aquaculture 218: 341–355.
Menden-Deuer, S. & E. J. Lessard, 2000. Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 569–579.
Nedwell, D. B. & L. F. Dong, 2002. Authors’ reply to letters to the editor: nitrous oxide formation in the Colne estuary in England: the central role of nitrite. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68: 5202–5204.
Nielsen, L. P., 1992. Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 86: 357–362.
Porter, K. G. & Y. C. Feig, 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnology and Oceanography 25: 943–948.
Pu, P. & J. Yan, 1998. Taihu Lake—a large shallow lake in the East China Plain. Journal of Lake Sciences (China) 10(suppl.): 1–12.
Putt, M. & D. K. Stoecker, 1989. An experimentally determined carbon: volume ratio for marine oligotrichous ciliates from estuarine and coastal waters. Limnology and Oceanography 34: 177–183.
Qin, B., P. Xu, Q. Wu, L. Luo & Y. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Seitzinger, S. P., 1988. Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 702–724.
Shapiro, J., 1990. Current beliefs regarding dominance by blue-greens: the case for the importance of CO2 and pH. Internationale Vereinigung Fur Theoretische Und Angewandte Limnologie 24: 38–54.
Sherr, E. B., D. A. Caron & B. F. Sherr, 1993. Staining of heterotrophic protists for visualization via epifluorescence microscopy. In Kemp, P. F., B. F. Sherr, E. B. Sherr & J. J. Cole (eds), Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology. Lewis, London: 213–228.
Tiedje, J. M., 1988. Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to Ammonium. In Zehnder, A. J. B. (ed.), Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms. Wiley, New York, 179–244.
Tobias, C. R., I. C. Anderson, E. A. Canuel & S. A. Macko, 2001. Nitrogen cycling through a fringing marsh-aquifer ecotone. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 25–39.
Velji, M. I. & L. J. Albright, 1993. Improved sample preparation for enumeration of aggregated aquatic substrate bacteria. In Kemp, P. F., B. F. Sherr, E. B. Sherr & J. J. Cole (eds), Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology. Lewis, London, 139–142.
Zumft, W. G., 1997. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 61: 533–616.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (contract No. KZCX1-SW-12), the National Science Foundation of China (Grant #40371104), and the Nancy Lee and Perry R. Bass Regents Chair in Marine Science held by Gardner. Several members of the faculty, staff, and graduate students at the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research contributed field assistance and discussion during this project. Special assistance was provided by Dr. Zhu Guangwei. The authors thank Dr. Dmitri Sobolev for comments on the manuscript and Dr. Hilairy Hartnett for discussion on dissolved gas sample preservation techniques.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, M.J., Lavrentyev, P.J., Yang, L. et al. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 581, 195–207 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0496-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0496-2