Abstract
Purpose
The synthetic soil based bioremediation approach as reasonable and sustainable practice at the farming level where desired bioremediation could be established at lower cost.
Materials and methods
Metal-tolerant bacteria from different environmental field samples, (a) a municipal dump site, (b) an agricultural field and (c) sludge of electro-plating industries, were screened and characterized. Bioremediation of metal contaminants through isolated bacteria was compared under two different conditions, synthetic soil and basic minimal media containing copper, cobalt and nickel.
Results and discussion
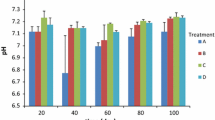
The pollutants arising from industrial effluents are imparting a huge negative impact on agricultural land. Microbes are predominant in heavy metal-contaminated sites, which signifies as a potential opportunity for the researchers towards bioremediation. Three bacterial species showed high metal tolerance; 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) analysis revealed that the organisms were Proteus vulgaris strain, Stenotrophomonas sp. and Bacillus thuringiensis. Percentage removal of metals was also analysed under different concentrations and pH.
Conclusions
The current tested methods are helpful in streamlining the natural compliance of fragile elements and its uptake into the microbial system under in vitro and in situ conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abskharon RNN, Gad El-Rab SMF, Hassan SHA, Shoreit AAM (2009) Reduction of toxic hexavalent chromium by E. coli. J Biotechnol Biochem 4:98–103
Appenroth KJ (2010) Definition of “heavy metals” and their role in biological systems. In: Sherameti I, Varma A (eds) Soil heavy metals, soil biology, vol 19. Springer, Berlin, pp 19–29
Balaji S, Kalaivani T, Rajasekaran C (2014) Biosorption of zinc and nickel and its effect on growth of different Spirulina strains. Clean Soil Air Water 42:507–512
Bharagava RN, Yadav S, Chandra R (2014) Antibiotic and heavy metal resistance properties of bacteria isolated from the aeration lagoons of common effluent treatment plant (CETP) of tannery industries (Unnao, India). Ind J Biotechnol 13:514–519
Buers KLM, Prince EL, Knowles CJ (1997) The ability of selected bacterial isolates to utilise components of synthetic metal-working fluids as sole sources of carbon and nitrogen for growth. Biotechnol Lett 19:791–794
Chatterjee SK, Bhattacharya I, Chandra G (2010) Biosorption of heavy metals from industrial wastewater by Geobacillus thermodenitrificans. J Hazard Mater 175:117–125
Choi J, Yang JS, Tae Park Y, Kim JO, Kim KJ, Shim YS, Kwon HH, Khan HA, Park JW, Um JG, Jeon BH (2012) Comparison of As, Ni, Zn, Cd, and Pb removals using treatment agents. Environ Technol 33:445–454
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Cui H, Zhou J, Zhao Q, Si Y, Mao J, Fang G, Liang J (2013) Fractions of Cu, Cd, and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil as affected by applications of micro- and nanohydroxyapatite. J Soils Sediments 13:742–752
Deshpande LM, Kapadnis BP, Chopade BA (1993) Metal resistance in Acinetobacter and its relation to beta-lactamase production. Biometals 6:55–59
Dixit R, Malaviya D, Pandiyan K, Singh UB, Sahu A, Shukla R, Singh BP, Rai JP, Sharma PK, Lade H, Paul D (2015) Bioremediation of heavy metals from soil and aquatic environment: an overview of principles and criteria of fundamental processes. Sustainability 7:2189–2212
Eze E, Eze U, Eze C, Ugwu K (2009) Association of metal tolerance with multidrug resistance among bacteria isolated from sewage. J Rural Trop Public Health 8:25–29
Fromin N, Porte B, Lensi R, Hamelin J, Domenach AM, Buatois B, Roggy JC (2012) Spatial variability of the functional stability of microbial respiration process: a microcosm study using tropical forest soil. J Soils Sediments 12:1030–1039
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiol 156:609–643
Gales AC, Reis AO, Jones RN (2001) Contemporary assessment of antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods for polymyxin B and colistin: review of available interpretative criteria and quality control guidelines. J Clin Microbiol 39:183–190
Girma G (2015) Microbial bioremediation of some heavy metals in soils: an updated review. Ind J Sci Res 6:147–161
Gonzalez-Guerrero M, Cano C, Azcon-Aguilar C, Ferrol N (2007) GintMT1 encodes a functional metallothionein in Glomus intraradices that responds to oxidative stress. Mycorrhiza 17:327–335
Hedrich S, Schlomann M, Johnson DB (2011) The iron-oxidizing proteobacteria. Microbiology 157:1551–1564
Hossain MA, Piyatida P, Silva JAT, Fujita M (2012) Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. J Bot 2012:1–37
Jones JB Jr (1977) Elemental analysis of soil extracts and plant tissue ash by plasma emission spectroscopy. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 8:349–365
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 413
Karbasizaed V, Badami N, Emtiazi G (2004) Antimicrobial, heavy metal resistance and plasmid profile of coliforms isolated from nosocomial infections in a hospital in Isfahan, Iran. Afr J Biotechnol 2(10):379–383
Kermani JN, Ghasemi MF, Khosravan A, Farahmand A, Shakibaie MR (2009) Cadmium bioremediation by metal-resistant mutated bacteria isolated from active sludge of industrial effluents. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 7:279–286
Kumar M, Kaur N, Kamini G, Pathak R, Khasa YP, Raj L (2013) Reporting heavy metal resistance bacterial strains from industrially polluted sites of northern India using fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) analysis and plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Adv Sci Lett 19:3311–3314
Maegan JO, Ilenys MPD (2009) Influence of microbial growth on the redox potential of fermented cucumbers. J Food Sci 74:M149–M153
Mao DP, Zhou Q, Chen CY, Quan ZX (2012) Coverage evaluation of universal bacterial primers using the metagenomic datasets. BMC Microbiol 12:66
McArthur JV, Tuckfield RC (2000) Spatial patterns in antibiotic resistance among steam bacteria: effects of industrial pollution. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3722–3726
McLaughlin MJ, Zarcinas BA, Stevens DP, Cook N (2000) Soil testing for heavy metals. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1661–1700
Mishra A, Malik A (2013) Recent advances in microbial metal bioaccumulation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:1162–1222
Monachese M, Burton JP, Reid G (2012) Bioremediation and tolerance of humans to heavy metals through microbial processes: a potential role for probiotics? Appl Environ Microbiol 78:6397–6404
Mudhoo A, Garg VK, Wang S (2012) Removal of heavy metals by biosorption. Environ Chem Lett 10:109–117
Nieto JJ, Fernandez-Castillo R, Marquez MC, Ventosa A, Quesada E, Ruiz-Berraquero F (1989) Survey of metal tolerance in moderately halophilic eubacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2385–2390
Noorjahan CM (2014) Physicochemical characteristics, identification of bacteria and biodegradation of industrial effluent. J Bioremed Biodeg 5:219
Ozaki T, Kimura T, Ohnuki T, Yoshida Z, Francis A (2003) Association mechanisms of europium (III) and curium (III) with Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2800–2805
Pantano G, Campanha MB, Moreira AB, Bisinoti MC (2014) Occurrence of Cu and Cr in the sedimentary humic substances and pore water from a typical sugar cane cultivation area in São Paulo, Brazil. J Soils Sediments 14:377–384
Perpetuo EA, Souza CB, Nascimento CAO (2011) Engineering bacteria for bioremediation. In: Carpi A (ed) Progress in molecular and environmental bioengineering: from analysis and modeling to technology applications. InTech, Rijeka, pp 605–632
Ray SA, Ray MK (2009) Bioremediation of heavy metal toxicity-with special reference to chromium. Al Ameen J Med Sci 2:57–63
Roane TM, Kellogg ST (1996) Characterization of bacterial communities in heavy metal contaminated soils. Can J Microbiol 42:593–603
Singh M, Ansari AA, Müller G, Singh IB (1997) Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of the Gomati River (a tributary of the Ganga River): effects of human activities. Environ Geol 29:246–252
Srinath T, Verma T, Ramteke PW, Garg SK (2002) Chromium (VI) biosorption and bioaccumulation by chromate resistant bacteria. Chemosphere 48:427–435
Sriprang R, Murooka Y (2007) Accumulation and detoxification of metals by plants and microbes. In: Singh SN, Tripathi RD (eds) Environmental bioremediation technologies. Springer, Berlin, pp 77–100
Tan YF, O’Toole N, Taylor NL, Millar AH (2010) Divalent metal ions in plant mitochondria and their role in interactions with proteins and oxidative stress-induced damage to respiratory function. Plant Physiol 152:747–761
Taylor JK (1987) Quality assurance of chemical measurements. Lewis Publishers, Inc, Chelsea
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In: Luch A (ed) Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology. Springer, Basel, pp 133–164
Umysova D, Vitova M, Douskova I, Bisova K, Hlavova M, Cizkova M, Machat J, Doucha J, Zachleder V (2009) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of selenium compounds in the green alga Scenedesmus quadricauda. BMC Plant Biol 9:58
Venosa AD (2004) Literature review on the use of commercial bioremediation agents for cleanup of oil-contaminated estuarine environments. National risk management research laboratory, office of research and development, U.S. environmental protection agency, Cincinnati, OH, pp 1–56
Weber KA, Achenbach LA, Coates JD (2006) Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:752–764
Wireman J, Liebert CA, Smith T, Summers AD (1997) Association of mercury resistance with antibiotic resistance in gram-negative fecal bacteria of primates. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4494–4503
Xu ZH, Ward S, Chen CR, Blumfield T, Prasolova NV, Liu JX (2008) Soil carbon and nutrient pools, microbial properties and gross nitrogen transformations in adjacent natural forest and hoop pine plantations of subtropical Australia. J Soils Sediments 8:99–105
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Amity University Uttar Pradesh and Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India. The authors are grateful to the University for the support.
Author contributions
MK and JS both are having joint corresponding authorship based on the equal contribution. MK, JS, VK, AV, AP, AKS and AA were involved in manuscript designing and data interpretation. AP was involved in sample collection and analysis. JS and RP were involved in the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Kirk T. Semple
Manoj Kumar and Vivek Kumar contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Kumar, V., Varma, A. et al. An efficient approach towards the bioremediation of copper, cobalt and nickel contaminated field samples. J Soils Sediments 16, 2118–2127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1398-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1398-1