Abstract
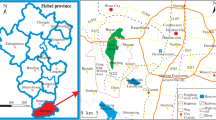
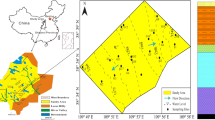
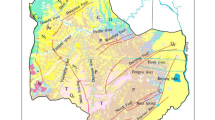
The exploitation of coal resources has disturbed the equilibrium of the original groundwater system, resulting in a perturbation of the deep groundwater dynamic conditions and hydrochemical properties. Exploring the formation of mine water chemistry under the conditions of deep coal seam mining in the Ordos Basin provides a theoretical basis for the identification of sources of mine water intrusion and the development and utilization of water resources. This paper takes Longwanggou Coal Mine as the research area, collects a total of 106 groups of water samples from the main water-filled aquifers, comprehensively uses Piper trilinear diagram, Gibbs diagram, ion correlation, ion ratio coefficient and mineral saturation index analysis, and carries out inverse geochemical modeling with PHREEQC software, so as to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics and causes of the main water-filled aquifers in deep-buried coal seams in the research area. The results show that the main hydrochemical processes in the study area are leaching and cation exchange, and the groundwater is affected by carbonate (calcite, dolomite), silicate (gypsum) and evaporite. Calculations of mineral saturation indices and PHREEQC simulations have led to the conclusion that the dissolution of rock salt and gypsum in groundwater accounts for most of the ionic action. Na+, Cl− and SO42− are mainly derived from the dissolution of rock salt and gypsum minerals, while Ca2+ and Mg2+ are mostly derived from the dissolution of dolomite and calcite. The results of the inverse geochemical modeling are consistent with the theoretical analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Al-Barakah FN, Al-jassas AM, Aly AA (2017) Water quality assessment and hydrochemical characterization of Zamzam groundwater, Saudi Arabia. Appl Water Sci 7(7):3985–3996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0549-x
An TD, Tsujimura M, Le PV, Kawachi A, Ha DT (2014) Chemical Characteristics of Surface Water and Groundwater in Coastal Watershed, Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Procedia Environ Sci 20:712–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2014.03.085
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Bai X, Tian X, Li J, Wang X, Li Y, Zhou Y (2022) Assessment of the Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in A Typical Alluvial-Proluvial Plain in China: An Example from Western Yongqing County. Water 14(15):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152395
Boonkaewwan S, Sonthiphand P, Chotpantarat S (2020) Mechanisms of arsenic contamination associated with hydrochemical characteristics in coastal alluvial aquifers using multivariate statistical technique and hydrogeochemical modeling: a case study in Rayong province, eastern Thailand. Environ Geochem Hlth 43(1):537–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00728-7
Chen Y, Zhu S, Yang C, Xiao S (2021) Analysis of hydrochemical evolution in main discharge aquifers under mining disturbance and water source identification. Environ Sci Pollut R 28(21):26784–26793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12639-w
Chen X, Zhang H, Cai Y (2023b) Hydrochemical characteristics and processes of groundwater in the Cenozoic pore aquifer under coal mining. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:33334–33348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24561-w
Chen L, Xie W, Feng X, Zhang N, Yin X (2017) Formation of hydrochemical composition and spatio-temporal evolution mechanism under mining-induced disturbance in the Linhuan coal-mining district. Arab J Geosci 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2831-5
Chen J, Yan B, Xu T, Xia F (2023a) Hydrochemical evolution characteristics and mechanism of groundwater funnel areas under artificial governance in Hengshui City, North China. Ecol Indic 148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110059
Chung SY, Rajendran R, Senapathi V, Sekar S, Ranganathan PC, Oh YY, Elzain HE (2020) Processes and characteristics of hydrogeochemical variations between unconfined and confined aquifer systems: a case study of the Nakdong River Basin in Busan City. Korea Environ Sci Pollut R 27(9):10087–10102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07451-6
Dong F, Yin H, Cheng W, Li Y, Qiu M, Zhang C, Tang R, Xu G, Zhang L (2022) Study on water inrush pattern of Ordovician limestone in North China Coalfield based on hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes: A case study in Binhu and Wangchao Coal Mine of Shandong Province, China. J Clean Prod 380(P2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134954
Feth J, Gibbs R (1971) Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry: Evaporation-Crystallization Process. Science 172(3985):870–872. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.172.3985.870
Fu T, Li C, Wang Z, Qi C, Chen G, Fu Y, Su Q, Xu X, Liu W, Yu H (2023) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in Guangxi coastal areas, China. Mar pollut bulletin 188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114564
Gao Z, Han C, Xu Y, Zhao Z, Luo Z, Liu J (2021) Assessment of the water quality of groundwater in Bohai Rim and the controlling factors—a case study of northern Shandong Peninsula, north China. Environ Pollut 285:117482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117482
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 170(3962):1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Hakimi Y, Orban P, Deschamps P, Brouyere S (2021) Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer system: Insights from Mzab Ridge and surrounding regions, North of the Algerian Sahara. J Hydrol- Reg Stud 34:100791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100791
He L, Lv G, Hu A, Yang L, Guo Y, Li G (2022) Mine Water Bursting Water Source Discrimination Based on Hydrochemical Features Analysis. Coal Geol China 34(06):34–39. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.06.07
Jiang B, Gao J, Du K, Deng X, Zhang K (2022) Insight into the water–rock interaction process and purification mechanism of mine water in underground reservoir of Daliuta coal mine in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:28538–28551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18161-3
Khan A F, Srinivasamoorthy K, Rabina C (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater along the coastal tracts of Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, India. Appl Water Sci 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-1158-7
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018) Geochemistry, Hydraulic Connectivity and Quality Appraisal of Multilayered Groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Liang C, Wang W, Ke X, Ou A, Wang D (2022) Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Strontium-Rich Groundwater in Tianjiazhai, Fugu, China. Water 14:1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121874
Lin Y, Ren H, Wu Y, Cao F, Jia F, Qu P (2019) The evolution of hydrogeochemical characteristics of a typical piedmont karst groundwater system in a coal-mining area, Northern China. Environ Earth Sci 78(18). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8563-y
Liu J, Hao Y, Gao Z, Wang M, Liu M, Wang Z, Wang S (2019) Determining the factors controlling the chemical composition of groundwater using multivariate statistics and geochemical methods in the Xiqu coal mine, North China. Environ Earth Sci 78(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8366-1
Liu J, Wang H, Jin D, Xu F, Zhao C (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan formation in the Pingdingshan coalfield. Environ Earth Sci 79(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8898-4
Long L, Wang S, Xiao L, Peng T, Tang B (2021) Study on hydrogeological conditions of Dafosi mine field based on hydrochemical characteristics analysis. Coal Eng 53(10):131–136. https://doi.org/10.11799/ce202110026
Marandi A, Shand P (2018) Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009
Mayo AL, Loucks MD (1995) Solute and isotopic geochemistry and ground water flow in the central Wasatch Range, Utah. J Hydrol 172(1–4):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-e
Miao Q, Li X, Xu Y, Liu C, Xie R, Lv Z (2021) Chemical characteristics of groundwater and source identification in a coastal city. Plos One 16(8). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256360
Mondal NC, Singh VP, Singh VS, Saxena VK (2010) Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. J Hydrol 388(1–2):100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.04.032
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans-Am Geophys Union 25(6):914. https://doi.org/10.1029/tr025i006p00914
Schoeller H (1967) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development, Water Resource Series No. 33. UNESCO, Paris, pp 44–52
Shang T, Xu Z, Gong X, Li X, Tian S, Guan Y (2021) Application of electrical sounding to determine the spatial distribution of groundwater quality in the coastal area of Jiangsu Province, China. J Hydrol 599:126348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126348
Tang R, Dong S, Zhang M, Zhou Z, Zhang C, Li P, Bai M (2023) Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality of Shallow Groundwater in Desert Area of Kunyu City, Southern Margin of Tarim Basin, China. Water 15(8):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081563
Tiwari AK, Pisciotta A, De MM (2019) Evaluation of groundwater salinization and pollution level on Favignana Island, Italy. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.016
Wang Y, Jiao JJ (2012) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined Quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River Delta, China. J Hydrol 438–439:112–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.008
Wang M, Zhu Y, Mao W, Ye M, Yang J (2023) Chemical characteristics and reactive transport of soil salt ions in frozen soil during the freeze and thaw period. J Hydrol 621:129580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129580
Wisitthammasri W, Chotpantarat S, Thitimakorn T (2020) Multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics of a volcano sedimentary aquifer in Saraburi Province, Thailand. J Hydrol- Reg Stud 32:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2020.100745
Wu C, Fang C, Wu X, Zhu G, Zhang Y (2020) Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater using self-organizing maps in the Hangjinqi gasfield area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Geosci Front. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.09.012
Xiao Y, Zhang J, Long A, Xu S, Guo T, Gu X, Deng X (2023) Zhang Pei (2023) Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Quaternary Groundwater in Baoshan Basin, Western Yunnan, China. Water 15(15):2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152736
Yang Q, Li Z, Ma H, Wang L, Martín JD (2016) Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the Southeastern part of Ordos basin, China. Environ Pollut 218:879–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.017
Yang P, Luo D, Hong A, Ham B, Xie S, Ming X, Wang Z, Pang Z (2019) Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of the carbonate-evaporite aquifers controlled by deep-seated faults using major ions and environmental isotopes. J Hydrol 579:124116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124116
Zhang Z, Lv D, Hower JC, Wang L, Shen Y, Zhang A, Xu J, Gao J (2023) Geochronology, mineralogy, and geochemistry of tonsteins from the Pennsylvanian Taiyuan Formation of the Jungar Coalfield, Ordos Basin, North China. Int J Coal Geol 267:0166–5162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2023.104183
Zhu Y, Yang Q, Wang H, Yang J, Zhang X, Li Z, Martín J D (2023) A hydrochemical and isotopic approach for source identification and health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic pollution in the central Yinchuan basin. Environ Res 231(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116153
Funding
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MD013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Chang Lu: Conceptualization, Writing—Original Draft, Formal analysis. Wenju Cheng: Methodology, Writing—Review & Editing. Huiyong Yin: Methodology, Material preparation. Shuo Li: Data Curation, Validation. Yian Zhang: Software. Fangying Dong: Writing—Review & Editing. Yuxiao Cheng: Visualization, Software. Xiaorong Zhang: Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chang Lu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Cheng, W., Yin, H. et al. Study on inverse geochemical modeling of hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater system in coal mine area – a case study of Longwanggou Coal Mine in Ordos Basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 16583–16600 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32153-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32153-z