Abstract
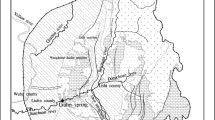
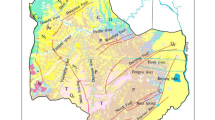
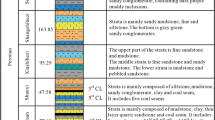
The study of groundwater hydrogeochemistry is of great significance to the development, utilization and protection of regional groundwater resources. In this paper, a complete and comprehensive analysis of three runoff zones is carried out in the Fengfeng mining area of Handan City, Hebei Province, China. The Piper trilinear diagram is used to analyze the types of karst groundwater hydrochemistry, the ionic proportionality coefficient method is used to analyze the sources of groundwater chemistry and the formation process, the chlorine-alkali index is used to react to the exchange reactions between cations, and PHREEQC software is also used to invert the groundwater simulation. The results are: the type of karst water hydrochemical in the study area is mainly HCO3·SO4–Ca·Mg; the ions are mainly influenced by rock halite, carbonate, sulphate, silicate and cation exchange; in the groundwater runoff zone, aragonite, calcite and dolomite are in saturated state, while gypsum and rock halite are in unsaturated state. The study of karst groundwater hydrochemical types, analysis of water-rock interaction and exploration of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms are intended to provide reference for karst water supply security and water resources utilization.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cao, Z., Wei, R., Duan, Q., and Tan, T., Inverse geochemical simulation of water-rock interaction of Xiniudong Underground River of Xinniu Cave, Yellow River, 2012, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 74–76.
Christofi, C., Bruggeman, A., Kuells, C., and Constantinou, C., Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in gabbro of the Troodos Fractured Aquifer, A comprehensive approach, Appl. Geochem., 2020, vol. 114, 104524.
Guo, Y.Y., The Geochemical Evolution of groundwater and the Influence on Regional Groundwater in Abandoned Mines in the Fengfeng Mining Area, China University of Geosciences, 2016.
Hao, C., He, P., Wang, Y., Hou, S., and Dong, J., Study on the evolutionary process of sulfate concentration in Ordovician karst water after coal mining in Fengfeng mine, Carsologica Sinica, 2014, vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 425–431.
Huang, J., Xian, Z., Li, W., Zhang, D., and Zhuang, X., Hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater flow system in the typical coastal plain: a case study of Hangjiahu Plain, Earth Sci., 2021, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 2565–2582.
Liu, J., Deep-buried aquifer in Hujierte mining area hydrogeochemical characteristics and its indication, J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, no. 35, pp. 154–59.
Lu, S., Hydrogeochemical Evolution Characteristics and Simulation of Karst Groundwater in the Jinci Spring Area, Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021.
Luan, F., Zhou, R., Jia, R., Lu, C., Bai, M., and Lian, H., Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in plain areas of Barkol-Yiwu Basin Xinjiang, Environ. Chem., 2017, no. 36.
Lv, X., Liu, J., Zhu, L., Chen, X., and Li, H., Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution Law of Shallow Groundwater in Dingxin Valley of Lower Reaches of Heihe River, J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2020, no. 34, pp. 194–201.
Meng, Q., Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of shallow groundwater in the middle and lower reaches of Shiyang River Basin, J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, no. 35, pp. 80–87.
Nair, I.S., Brindha, K., and Elango L., Assessing the origin and processes controlling groundwater salinization in coastal aquifers through integrated hydrochemical, isotopic and hydrogeochemical modelling techniques, Hydrol. Sci. J., 2021, vol. 66, 1, pp. 152–164.
Su, C., Nie, F.Y., Zhao, G.S., Luo, F., Huang, Q., Ba, J., Li, X., Liang, J., and Yang, Y., Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of strontium-rich groundwater in Xintian County,Hunan Province, Geosci., vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 554–564.
Tong, H., Gao, Z., Liu, J., Peng Y., and Li, C., Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of groundwater in the west of Yi River Basin, Environ. Chem., 2021, vol. 40, pp. 1–12.
Wang, K., Wu, X., Fu, S., Qiu, Y., and Chen H., Hydrochemical evolution and genesis analysis of karst water system in Jinan Spring Basin, Geochimica, 2022, pp. 1–12.
Wei, Y., Li, P., Qian H., and Wu J., Research and application of hydrogeochemical simulation, J. Water Resour. Water Engin., 2010, vol. 21, pp. 58–61.
Wu, X., An, Y., Wei, S., Yin, D., Cui, H., Wang, X, and Wang, Q. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution law of shallow groundwater in Dingxin Valley of lower reaches of Heihe River, J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2021, vol. 35, pp. 103–09.
Yan, Y., Qin, P., Wu, Z., Bai, X., and Shen, Z. Influence on the karst groundwater environment by coal mining in the Fengfeng coal mine area, China Mining Magazine, 2010, vol. 19, pp. 120–25.
Yang, M., Lu, Y., Zhang, F., Zhang, S., Yin, M., and Wu, G., Hydrochemical evolution and geochemical simulation of karst groundwater in Liulin springs, South to North Water Transfers Water Sci. Technol., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 127–134.
Yang, R., Zhou, J., Chen, Y., Lei, M. ans Chen. J., Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the eastern plain of Hotian Prefecture, Xinjiang, Environ. Chem., 2022, vol. 41, pp. 1367–1379.
Zhao, B., and Lv, Y., Hydrogeochemical characteristics and controlling factors of New Shanghai No. 1 Minefield, J. Arid Land Resour. Environ., 2022, p. 36.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41 902 254), the Ecological Wisdom Mine Joint Fund of the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei province (D2020402013) and the key R & D project of Hebei Province (21373901D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kai, B., Hui, S., Guilei, H. et al. Hydrogeochemical Modeling of Karst Groundwater in the Fengfeng Mining Area. Water Resour 50, 948–959 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807822602187
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807822602187