Abstract
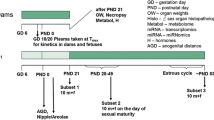
Endocrine disruptors (ED) are compounds dispersed in the environment that modify hormone biosynthesis, affecting hormone-dependent organs such as the prostate. Studies have only focused on evaluating the effects of ED alone or in small groups and short intervals and have not adequately portrayed human exposure. Therefore, we characterized the prostate histoarchitecture of rats exposed to an ED mixture (ED Mix) mimicking human exposure. Pregnant females of the Sprague–Dawley strain were randomly distributed into two experimental groups: Control group (vehicle: corn oil, by gavage) and ED Mix group: received 32.11 mg/kg/day of the ED mixture diluted in corn oil (2 ml/kg), by gavage, from gestational day 7 (DG7) to post-natal day 21 (DPN21). After weaning at DPN22, the male pups continued to receive the complete DE mixture until they were 220 days old when they were euthanized. The ED Mix decreased the epithelial compartment, increased the fractal dimension, and decreased glandular dilation. In addition, low-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia was observed in addition to regions of epithelial atrophy in the group exposed to the ED Mix. Exposure to the mixture decreased both types I and III collagen area in the stroma. We concluded that the ED Mix was able to cause alterations in the prostatic histoarchitecture and induce the appearance of preneoplastic lesions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aponte-López A, Muñoz-Cruz S (2020) Mast cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 1273:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49270-0_9
Aquino AM, Salata GC, Pinho CF, De Freitas ATAG, Périco LL, De Lion Siervo GEM, Mendes LO, Da Cunha De Medeiros P, Justulin LA, Fernandes GSA, Perobelli JE, Scarano WR (2019) Arsenic exposure during prepuberty alters prostate maturation in pubescente rats. Reprod Toxicol 89(136):144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2019.07.010
Axelstad M, Christiansen S, Boberg J, Scholze M, Jacobsen PR, Isling LK, Kortenkamp A, Hass U (2014) Mixtures of endocrine-disrupting contaminants induce adverse developmental effects in preweaning rats. Reproduction 147(4):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-13-0447
Ayala AG, Ro JY (2007) Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: recent advances. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131(8):1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.5858/2007-131-1257-PINRA
Bankl HC, Samorapoompichit P, Pikula B, Latinovic L, Bankl H, Lechner K, Valent P (2001) Characterization of human prostate mast cells and their increase in periprostatic vein thrombosis. Am J Clin Pathol 116(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1309/C0TP-MA3M-K5FX-3Q2F
Boberg J, Johansson HK, Hadrup N, Dreisig K, Berthelsen L, Almstrup K, Vinggaard AM, Hass U (2015) Perinatal exposure to mixtures of anti-androgenic chemicals causes proliferative lesions in rat prostate. Prostate 75(2):126–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22897
Brandt JZ, Silveira LT, Grassi TF, Anselmo-Franci JA, Fávaro WJ, Felisbino SL, Barbisan LF, Scarano WR (2014) Indole-3-carbinol attenuates the deleterious gestational effects of bisphenol A exposure on the prostate gland of male F1 rats. Reprod Toxicol 43:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.11.001
BrehmFlaws EJA (2019) Transgenerational effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on male and female reproduction. Endocrinol 160(6):1421–1435. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2019-00034
Cargnelutti F, Di Nisio A, Palotti F, Sabovic I, Spaziani M, Tarsitano MG, Paoli D, Foresta C (2021) Effects of endocrine disruptors on fetal testis development, male puberty, and transition age. Endocrine 72(2):358–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02436-9
Christiansen S, Kortenkamp A, Axelstad M, Boberg J, Scholze M, Jacobsen PR, Faust M, Lichtensteiger W, Schlumpf M, Burdorf A, Hass U (2012) Mixtures of endocrine disrupting contaminants modelled on human high end exposures: an exploratory study in rats. Int J Androl 35(3):303–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01242.x
Colanzi P, Santinelli A, Mazzucchelli R, Pomante R, Montironi R (1999) Changes in the normal-looking epithelium in prostates with PIN or cancer. Adv Clin Path 3(4):129–134
De Arruda PF, Gatti M, Facio FN Jr, de Arruda JG, Moreira RD, Murta LO Jr, de Arruda LF, de Godoy MF (2013) Quantification of fractal dimension and Shannon’s entropy in histological diagnosis of prostate cancer. BMC Clin Pathol 13:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6890-13-6
De Marzo AM, Nelson WG, Bieberich CJ, Yegnasubramanian S (2010) Prostate cancer: new answers prompt new questions regarding cell of origin. Nat Rev Urol 7(12):650–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2010.188
Duarte AH, Colli S, Alves-Pereira JL, Martins MP, Sampaio FJB, Ramos CF (2012) Collagen I and III and metalloproteinase gene and protein expression in prostate cancer in relation to Gleason score. Int Braz J Urol 38(3):341–355
ECHA (2010) Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment Chapter R.8: Characterization of dose [concentration]-response for human health
Epstein JI (1995) Grading of prostate adenocarcinomas. In: Epstein JI. Prostate biopsy interpretation. New York: Lippincott-Raven Publishers 65–85
Epstein JI, Herawi M (2007) Prostate needle biopsies containing prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or atypical foci suspicious for carcinoma: implications for patient care. J Urol 175(3 Pt 1):820–834
Fávaro WJ, Cagnon VHA (2008) Immunolocalization of androgen and oestrogen receptors in the ventral lobe of rat (Rattus norvegicus) prostate after long-term treatment with ethanol and nicotine. Int J Androl 31(6):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00817.x
Fávaro WJ, Hetzl AC, Reis LO, Ferreira U, Billis A, Cagnon VH (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting in nonneoplastic and neoplastic prostatic glands: artifact or molecular involvement. Pathol Oncol Res 18(2):285–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9440-5
Gonçalves BF, Campos SG, Costa CF, Scarano WR, Góes RM, Taboga SR (2015) Key participants of the tumor microenvironment of the prostate: an approach of the structural dynamic of cellular elements and extracellular matrix components during epithelial-stromal transition. Acta Histochem 117(1):4–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2014.10.009
Gonçalves BF, de Campos SGP, Góes RM, Scarano WR, Taboga SR, Vilamaior PSL (2017) Dual action of high estradiol doses on MNU-induced prostate neoplasms in a rodent model with high serum testosterone: protective effect and emergence of unstable epithelial microenvironment. Prostate 77(9):970–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23353
Hass U, Scholze M, Christiansen S, Dalgaard M, Vinggaard AM, Axelstad M, Metzdorff SB, Kortenkamp A (2007) Combined exposure to anti-androgens exacerbates disruption of sexual differentiation in the rat. Environ Health Perspect 174:648–657. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9360
Huang DY, Zheng CC, Pan Q, Wu SS, Su X, Li L, Wu JH, Sun ZY (2018) Oral exposure of low-dose bisphenol A promotes proliferation of dorsolateral prostate and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in aged rats. Sci Rep 8(1):490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18869-8
ImageJ (2004) RGB Measure. RGB_Measure.java ed: Wayne Rasband
Isling LK, Boberg J, Jacobsen PR, Mandrup KR, Axelstad M, Christiansen S, Vinggaard AM, Taxvig C, Kortenkamp A, Hass U (2014) Late-life effects on rat reproductive system after developmental exposure to mixtures of endocrine disrupters. Reproduction 147(4):465–476. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-13-0448
Johansson HK, Jacobsen PR, Hass U, Svingen T, Vinggaard AM, Isling LK, Axelstad M, Christiansen S, Boberg J (2016) Perinatal exposure to mixtures of endocrine disrupting chemicals reduces female rat follicle reserves and accelerates reproductive aging. Reprod Toxicol 61:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.03.045
Junqueira LC, Cossermelli W, Brentani R (1978) Differential staining of collagens type I, II and III by Sirius red and polarization microscopy. Arch Histol Jpn 41(3):267–274. https://doi.org/10.1679/aohc1950.41.267
Kahn LG, Philippat C, Nakayama SF, Slama R, Trasande L (2020) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: implications for human health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 8(8):703–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30129-7
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol 8(6):e1000412. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412
Kristensen DM, Lesné L, Le Fol V, Desdoits-Lethimonier C, Dejucq-Rainsford N, Leffers H, Jégou B (2012) Paracetamol (acetaminophen), aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) and indomethacin are anti-androgenic in the rat foetal testis. Int J Androl 35(3):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2012.01282.x
Lacouture A, Lafront C, Peillex C, Pelletier M, Audet-Walsh É (2021) Impacts of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on prostate function and cancer. Environ Res 204:112085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112085
Mandrup KR, Johansson HK, Boberg J, Pedersen AS, Mortensen MS, Jørgensen JS, Vinggaard AM, Hass U (2015) Mixtures of environmentally relevant endocrine disrupting chemicals affect mammary gland development in female and male rats. Reprod Toxicol 54:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.09.016
Mendes LO, Amorim JP, Teixeira GR, Chuffa LG, Fioruci BA, Pimentel TA, de Mello W Jr, Padovani CR, Pereira S, Martinez M, Pinheiro PF, Oliani SM, Martinez FE (2011) Masts cells and etanol consumption: interactions in the prostate, epididymis and testis of UChB rats. Am J Reprod Immunol 66(3):170–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00958.x
Mendes LO, Scarano WR, Rochel-Maia SS, Fioruci-Fontaneli BA, Chuffa LGA, Anselmo-Franci JA, Martinez FE et al (2015) Androgen therapy reverses injuries caused by ethanol consumption in the prostate: testosterone as a possible target to ethanol-related disorders. Life Sci 120:22–30
Montes GS, Krisztán RM, Shigihara KM, Tokoro R, Mourão PA, Junqueira LC (1980) Histochemical and morphological characterization of reticular fibers. Histochemistry 65(2):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00493161
Montironi R, Santinelli A, Mazzucchelli R (2002) Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer. Panminerva Med 44(3):213–220
Montironi R, Mazzucchelli R, Santinelli A, Scarpelli M, Beltran AL, Bostwick DG (2005) Incidentally detected prostate cancer in cystoprostatectomies: pathological and morphometric comparison with clinically detected cancer in totally embedded specimens. Hum Pathol 36(6):646–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2005.03.018
Motrich RD, Salazar FC, Breser ML, Mackern-Oberti JP, Godoy GJ, Olivera C, Paira DA, Rivero VE (2018) Implications of prostate inflammation on male fertility. Andrologia 50(11):e13093. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13093
Peixoto AR, Santos TM, Brandt JZ, Delella FK, Gonçalves BF, Campos SG, Taboga SR, Favaro WJ, Domeniconi RF, Scarano WR (2016) Gestational and lactational exposition to Di-N-butyl-phthalate (DBP) increases inflammation and preneoplastic lesions in prostate of wistar rats after carcinogenic N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU) plus testosterone protocol. Environ Toxicol 31(10):1185–1195. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22126
Prins GS (1992) Neonatal estrogen exposure induces lobe-specific alterations in adult rat prostate androgen receptor expression. Endocrinol 130(6):3703–3714. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.130.6.1597166
Prins GS, Birch L, Tang WY, Ho SM (2007) Developmental estrogen exposures predispose to prostate carcinogenesis with aging. Reprod Toxicol 23(3):374–382
Pu Y, Wang W, Al-Rubaiee M, Gayen SK, Xu M (2012) Determination of optical coefficients and fractal dimensional parameters of cancerous and normal prostate tissues. Appl Spectrosc 66(7):828–834. https://doi.org/10.1366/11-06471
Pylkkänen L, Mäkelä S, Valve E, Härkönen P, Toikkanen S, Santti R (1993) Prostatic dysplasia associated with increased expression of c-myc in neonatally estrogenized mice. J Urol 149(6):1593–1601. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36458-3
Sáttolo S, Carvalho CAF, Cagnon VHA (2004) Influence of hormonal replacement on the ventral lobe of the prostate of rats (Rattus norvegicus albinus) submitted to chronic ethanol treatment. Tissue Cell 36(6):417–430
Scarano WR, Toledo FC, Guerra MT, de Campos SG, Júnior LA, Felisbino SL, Anselmo-Franci JA, Taboga SR, Kempinas Wde G (2009) Long-term effects of developmental exposure to di-n-butyl-phthalate (DBP) on rat prostate: proliferative and inflammatory disorders and a possible role of androgens. Toxicology 262(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.06.011
Scarano WR, Pinho CF, Pissinatti L, Gonçalves BF, Mendes LO, Campos SGP (2018) Cell junctions in the prostate: an overview about the effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCS) in different experimental models. Reprod Toxicol 81:147–154
Scarano WR, Bedrat A, Alonso-Costa LG, Aquino AM, Fantinatti B, Justulin LA, Barbisan LF, Freire PP, Flaws JA, Bernardo L (2019) Exposure to an environmentally relevant phthalate mixture during prostate development induces microRNA upregulation and transcriptome modulation in rats. Toxicol Sci 171(1):84–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz141
Schneider S, Kaufmann W, Strauss V, van Ravenzwaay B (2011) Vinclozolin: a feasibility and sensitivity study of the ILSI-HESI F1-extended one-generation rat reproduction protocol. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 59(1):91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2010.09.010
Seandel M, Noack-Kunnmann K, Zhu D, Aimes RT, Quigley JP (2001) Growth factor induced angiogenesis in vivo requires specific cleavage of fibrillar type I collagen. Blood 97(8):2323–2332. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v97.8.2323
Sfanos KS, Yegnasubramanian S, Nelson WG, De Marzo AM (2018) The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome in prostate cancer development. Nat Ver Urol 15(1):11–24
Shoulders MD, Raines RT (2009) Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem 78:929–958
Stukenborg JB, Mitchell RT, Söder O (2021) Endocrine disruptors and the male reproductive system. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 35(5):101567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2021.101567
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Lavarsanne M, Soerjomataramet I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Taboga SR, Santos AB, Rocha A, Vidal BC, Mello MLS (2003) Nuclear phenotypes and morphometry of human secretoty prostatic cells: acomparative study of benign and malignant lesions in Brazilian patients. Caryologia 56:313–320
Tambasco M, Costello BM, Kouznetsov A (2009) Quantifying the architectural complexity of microscopic images of histology specimens. Micron 40(4):486–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2008.12.004
Waliszewski P, Wagenlehner F, Gattenlöhner S, Weidner W (2015) On the relationship between tumor structure and complexity of the spatial distribution of cancer cell nuclei: a fractal geometrical model of prostate carcinoma. Prostate 75(4):399–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22926
Wang X, Wang Y, Song Q, Wu J, Zhao Y, Yao S, Sun Z, Zhang Y (2017) In utero and lactational exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate increased the susceptibility of prostate carcinogenesis in male offspring. Reprod Toxicol 69:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2017.01.008
Wasiuk A, De Vries VC, Hartmann K, Roers A, Noelle RJ (2009) Mast cells as regulators of adaptive immunity to tumours. Clin Exp Immunol 155(2):140–146
Weibel ER, Paumgartner D (1978) Integrated stereological and biochemical studies on hepatocytic membranes. II. Correction of section thickness effect on volume and surface density estimates. J Cell Biol 77(2):584–597
Welsh M, Saunders PT, Fisken M, Scott HM, Hutchison GR, Smith LB, Sharpe RM (2008) Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization, disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism. J Clin Invest 118(4):1479–1490
Xia B, Wang Y, Wang X, Wu J, Song Q, Sun Z, Zhang Y (2018) In utero and lactational exposure of DEHP increases the susceptibility of prostate carcinogenesis in male offspring through PSCA hypomethylation. Toxicol Lett 292:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.04.022
Acknowledgements
We must thank Laboratory of Pathology from University of Western São Paulo (UNOESTE).
Funding
This work has been supported by the following Brazilian research agencies: São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP, grant 2018/24044–0), Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparations, data collection, and analysis were performed by Thainá Cavalleri Sousa, Letícia Pereira de Souza, Maria Luiza Silva Ricardo, Andreia Yuri Yoshigae, Karianne Delalibera Hinokuma, Ana Beatriz Ratto Gorzoni, and Leonardo de Oliveira Mendes. The data analysis were performed by Thainá Cavalleri Sousa, Ariana Musa de Aquino, Wellerson Rodrigo Scarano, Anthony César de Sousa Castilho, Maria Eduarda Almeida Tavares, Alice Santos Cruz Veras, Giovanna Rampazzo Teixeira, Giselle Alborghetti Nai, and Leonardo de Oliveira Mendes, and all the authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All the experiments were conducted according to the guidelines established by the Brazilian Association for Animal Experimentation (COBEA) and were approved by the Ethics Committee in Animal Use of the University of Western São Paulo (protocol number 6034).
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ludek Blaha
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sousa, T.C., de Souza, L.P., Ricardo, M.L.S. et al. Long exposure to a mixture of endocrine disruptors prediposes the ventral prostate of rats to preneoplastic lesions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 104015–104028 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29768-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29768-z