Abstract
The growing relevance of sustainability reporting (SR) has dramatically surged advocacy and interest among both academicians and practitioners. However, few studies have attempted to holistically encapsulate global research on sustainability reporting. The present study employed scientometric analysis on sustainability reporting based 1434 articles extracted from the Web of Science database, published between 1992 and 2022, to comprehensively map the intellectual structure of this field. Domain visualizations were constructed using CiteSpace software to identify networks of co-authorship, keywords, subject categories, institutions, and countries engaged in publishing on SR along with co-citation and cluster analysis. The findings revealed that significant contributions in SR research have originated primarily from developed countries, underscoring the necessity for more research in the context of developing and emerging countries. SR field was found characterized by cohesive research sub-communities but lacked global cooperation. Existing studies in the SR research domain focused mainly on subject categories of business, management, environmental studies, green and sustainable science technology, environmental sciences, and business finance. Analysis of most co-cited authors and content analysis of highly co-cited articles were performed, detailing pioneer works in the field. The principal topics in the body of literature were identified via clusters of co-citations between documents and keywords. Future research focus areas include exploring the link between circular economy and SR, the role of social media, blockchain, artificial intelligence, and other digital technologies in SR, attention on the MSME sector, mandatory reporting, assessment of real impact of SR on investor sentiments and financial analysts’ valuations, assurance, standardization, financial-sector inclusive research, materiality issues, and understanding niche themes of SR, inclusive of monothematic reporting. Implications of the study for policymakers, companies, society, and academia were examined.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas YA, Mehmood W, Lazim YY, Aman-Ullah A (2022a) Sustainability reporting and corporate reputation of Malaysian IPO companies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(52):78726–78738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21320-9
Abbas YA, Mehmood W, Manhal Aliessa MH, Aman-Ullah A (2022b) Level of sustainability reporting of Malaysian IPO companies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(46):69527–69539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20727-8
Abbas YA, Mehmood W, Ali A, Aman-Ullah A (2023) Sustainability reporting and corporate financial performance of IPOs: witnessing emerging market. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28446-4
Adams CA (2015) The International Integrated Reporting Council: a call to action. Crit Perspect Account 27:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2014.07.001
Adams CA, Larrinaga C (2019) Progress: engaging with organisations in pursuit of improved sustainability accounting and performance. Account, Audit Account J 32(8):2367–2394. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-03-2018-3399
Adams CA, Larrinaga-González C (2007) Engaging with organisations in pursuit of improved sustainability accounting and performance. Account, Audit Account J 20(3):333–355. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570710748535
Alazzani A, Wan-Hussin WN (2013) Global Reporting Initiative’s environmental reporting: a study of oil and gas companies. Ecol Ind 32:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.02.019
Aldrich HE, Pfeffer J (1976) Environments of organizations. Ann Rev Sociol 2:79–105. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.so.02.080176.000455
Alewine HC (2010) A model for conducting experimental environmental accounting research. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 1(2):256–291. https://doi.org/10.1108/20408021011089275
Ali W, Frynas JG, Mahmood Z (2017) Determinants of corporate social responsibility (CSR) disclosure in developed and developing countries: a literature review: determinants of CSR disclosure. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 24(4):273–294. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1410
Al-Tuwaijri SA, Christensen TE, Hughes KE (2004) The relations among environmental disclosure, environmental performance, and economic performance: a simultaneous equations approach. Acc Organ Soc 29(5–6):447–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(03)00032-1
Anwar R, Malik JA (2020) When does corporate social responsibility disclosure affect investment efficiency? A New answer to an old question. SAGE Open 10(2):215824402093112. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020931121
Aryadoust V, Tan HAH, Ng LY (2019) A scientometric review of Rasch measurement: the rise and progress of a specialty. Front Psychol 10:2197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02197
Ascui F, Lovell H (2011) As frames collide: making sense of carbon accounting. Account, Audit Account J 24(8):978–999. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513571111184724
Assaf AG, Josiassen A, Cvelbar LK (2012) Does triple bottom line reporting improve hotel performance? Int J Hosp Manag 31(2):596–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2011.08.005
Bakarich KM, Castonguay J“Jack”, O’Brien PE (2020) The use of blockchains to enhance sustainability reporting and assurance*. Account Perspect 19(4):389–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/1911-3838.12241
Baker M, Schaltegger S (2015) Pragmatism and new directions in social and environmental accountability research. Account, Audit Account J 28(2):263–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-08-2012-01079
Bebbington J (1997) Engagement, education and sustainability: a review essay on environmental accounting. Account, Audit Account J 10(3):365–381. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513579710178115
Bebbington J, Brown J, Frame B, Thomson I (2007) Theorizing engagement: the potential of a critical dialogic approach. Account, Audit Account J 20(3):356–381. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570710748544
Bebbington J, Russell S, Thomson I (2017) Accounting and sustainable development: reflections and propositions. Crit Perspect Account 48:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2017.06.002
Bebbington J, Unerman J, O'Dwyer B (eds) (2014) Sustainability accounting and accountability (2nd ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315848419
Benlemlih M, Shaukat A, Qiu Y, Trojanowski G (2018) Environmental and social disclosures and firm risk. J Bus Ethics 152(3):613–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-016-3285-5
Benvenuto M, Aufiero C, Viola C (2023) A systematic literature review on the determinants of sustainability reporting systems. Heliyon 9(4):e14893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14893
Berthelot S, Cormier D, Magnan M (2003) Environmental disclosure research: review and synthesis. J Account Lit 22:1–44
Bewley K, Li Y (2000) Disclosure of environmental information by Canadian manufacturing companies: a voluntary disclosure perspective. In: Advances in Environmental Accounting & Management, vol. 1. Emerald (MCB UP), pp. 201–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1479-3598(00)01011-6
Bosi MK, Lajuni N, Wellfren AC, Lim TS (2022) Sustainability reporting through environmental, social, and governance: a bibliometric review. Sustainability 14(19):12071. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912071
Botosan CA (1997) Disclosure level and the cost of equity capital. Account Rev 72:323–249
Botosan CA, Plumlee MA (2002) A re-examination of disclosure level and the expected cost of equity capital. J Account Res 40(1):21–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-679X.00037
Brammer S, Pavelin S (2008) Factors influencing the quality of corporate environmental disclosure. Bus Strateg Environ 17:120–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.506
Brooks C, Oikonomou I (2018) The effects of environmental, social and governance disclosures and performance on firm value: a review of the literature in accounting and finance. Br Account Rev 50(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2017.11.005
Brown HS, de Jong M, Levy DL (2009) Building institutions based on information disclosure: lessons from GRI’s sustainability reporting. J Clean Prod 17(6):571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.12.009
Burritt RL, Schaltegger S (2010) Sustainability accounting and reporting: fad or trend? Account, Audit Account J 23(7):829–846. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513571011080144
Carvalho MM, Fleury A, Lopes AP (2013) An overview of the literature on technology roadmapping (TRM): contributions and trends. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 80(7):1418–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2012.11.008
Ceulemans K, Molderez I, Van Liedekerke L (2015) Sustainability reporting in higher education: a comprehensive review of the recent literature and paths for further research. J Clean Prod 106:127–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.052
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 57(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen JC, Roberts RW (2010) Toward a more coherent understanding of the organization–society relationship: a theoretical consideration for social and environmental accounting research. J Bus Ethics 97(4):651–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0531-0
Chen C, Song M (2019) Visualizing a field of research: a methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. Plos One 14(10):e0223994. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223994
Chen C, Ibekwe-SanJuan F, Hou J (2010) The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: a multiple perspective cocitation analysis. J Am Soc Inf Sci 61(7):1386–1409. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi
Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC (2014) Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert Opin Biol Ther 14(9):1295–1317. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Chen C (2014) The CiteSpace manual. http://cluster.ischool.drexel.edu/~cchen/citespace/CiteSpaceManual.pdf
Cho CH, Patten DM (2007) The role of environmental disclosures as tools of legitimacy: a research note. Acc Organ Soc 32(7–8):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2006.09.009
Christ KL, Burritt RL (2017) Supply chain-oriented corporate water accounting: a research agenda. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 8(2):216–242. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-05-2016-0029
Churet C, Eccles RG (2014) Integrated reporting, quality of management, and financial performance. J Appl Corp Financ 26(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/jacf.12054
Clarkson MBE (1995) A stakeholder framework for analyzing and evaluation of corporate social performance. Acad Manag Rev 20:92–117. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1995.9503271994
Clarkson PM, Li Y, Richardson GD, Vasvari FP (2008) Revisiting the relation between environmental performance and environmental disclosure: an empirical analysis. Acc Organ Soc 33(4–5):303–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2007.05.003
Clarkson PM, Overell MB, Chapple L (2011) Environmental reporting and its relation to corporate environmental performance. Abacus 47(1):27–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6281.2011.00330.x
Comoli M, Tettamanzi P, Murgolo M (2023) Accounting for ‘ESG’ under disruptions: a systematic literature network analysis. Sustainability 15(8):6633. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086633
Conca L, Manta F, Morrone D, Toma P (2020) The impact of direct environmental, social, and governance reporting: empirical evidence in European-listed companies in the agri-food sector. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1080–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2672
Connelly BL, Hoskisson RE, Tihanyi L, Certo ST (2010) Ownership as a form of corporate governance: ownership as a form of corporate governance. J Manag Stud 47(8):1561–1589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2010.00929.x
Cooper SM, Owen DL (2007) Corporate social reporting and stakeholder accountability: the missing link. Acc Organ Soc 32(7–8):649–667
Daub C-H (2007) Assessing the quality of sustainability reporting: an alternative methodological approach. J Clean Prod 15(1):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.08.013
de Villiers C, Rinaldi L, Unerman J (2014) Integrated reporting: insights, gaps and an agenda for future research. Account, Audit Account J 27(7):1042–1067. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-06-2014-1736
Deegan C (2002) Introduction: The legitimising effect of social and environmental disclosures – a theoretical foundation. Account, Audit Account J 15(3):282–311. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570210435852
Deegan C (2017) Twenty five years of social and environmental accounting research within critical perspectives of accounting: hits, misses and ways forward. Crit Perspect Account 43:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2016.06.005
Deegan C, Gordon B (1996) A study of the environmental disclosure practices of Australian corporations. Account Bus Res 26(3):187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00014788.1996.9729510
Dhaliwal DS, Li OZ, Tsang A, Yang YG (2011) Voluntary nonfinancial disclosure and the cost of equity capital: the initiation of corporate social responsibility reporting. Account Rev 86(1):59–100. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.00000005
Di Vaio A, Palladino R, Hassan R, Alvino F (2020) Human resources disclosure in the EU Directive 2014/95/EU perspective: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 257:120509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120509
Dienes D, Sassen R, Fischer J (2016) What are the drivers of sustainability reporting? A systematic review. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 7(2):154–189. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-08-2014-0050
DiMaggio PJ, Powell WW (1983) The iron cage revisited: institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Am Sociol Rev 48(2):147. https://doi.org/10.2307/2095101
Dumay J, Bernardi C, Guthrie J, Demartini P (2016) Integrated reporting: a structured literature review. Account Forum 40(3):166–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2016.06.001
Dunning T (1993) Accurate methods for the statistics of surprise and coincidence. Comput Linguist 19(1):61–74
Dye R (1985) Disclosure of nonproprietary information. J Account Res 23(1):123–145
Eccles R, Krzus M (2010) One Report: Integrated Reporting for a Sustainable Strategy. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, N.J.
Elkington J (1997) Cannibals with forks: the triple bottom line of 21st century business. Capstone
Epstein M, Flamholtz E, McDonough JJ (1976) Corporate social accounting in the United States of America: state of the art and future prospects. Acc Organ Soc 1(1):23–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(76)90005-2
Farisyi S, Musadieq MA, Utami HN, Damayanti CR (2022) A systematic literature review: determinants of sustainability reporting in developing countries. Sustainability 14(16):10222. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610222
Farooq MB, de Villiers C (2018) The shaping of sustainability assurance through the competition between accounting and non-accounting providers. Account, Audit Account J 32(1):307–336. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-10-2016-2756
Ferrer E, López-Arceiz FJ, Rio C (2020) Sustainability disclosure and financial analysts’ accuracy: the European case. Bus Strateg Environ 29(8):2939–2952. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2549
Fifka MS (2013) Corporate responsibility reporting and its determinants in comparative perspective - a review of the empirical literature and a meta-analysis: corporate responsibility reporting and its determinants. Bus Strateg Environ 22(1):1–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.729
Flower J (2015) The International Integrated Reporting Council: a story of failure. Crit Perspect Account 27:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2014.07.002
Freeman RE (1984) Strategic management: a stakeholder approach. Pitman
Fuoli M (2018) Building a trustworthy corporate identity: a corpus-based analysis of stance in annual and corporate social responsibility reports. Appl Linguis 39(6):846–885. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amw058
Garrido-Miralles P, Zorio-Grima A, García-Benau MA (2016) Sustainable development, stakeholder engagement and analyst forecasts’ accuracy: positive evidence from the Spanish setting: CSR reporting impact on analyst forecasts’ accuracy. Sustain Dev 24(2):77–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1607
Gerged AM, Matthews L, Elheddad M (2020) Mandatory disclosure, greenhouse gas emissions and the cost of equity capital: UK evidence of a U-shaped relationship. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):908–930. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2661
Gilsbach L, Schütte P, Franken G (2022) Water reporting in mining: are corporates losing sight of stakeholder interests? J Clean Prod 345:131016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131016
Gray R (2001) Thirty years of social accounting, reporting and auditing: what (if anything) have we learnt? Bus Ethics: A Eur Rev 10(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8608.00207
Gray R (2002) The social accounting project and accounting organizations and society privileging engagement, imaginings, new accountings and pragmatism over critique? Acc Organ Soc 27(7):687–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(00)00003-9
Gray R (2010) Is accounting for sustainability actually accounting for sustainability…and how would we know? An exploration of narratives of organisations and the planet. Acc Organ Soc 35(1):47–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2009.04.006
Gray R, Kouhy R, Lavers S (1995) Corporate social and environmental reporting: a review of the literature and a longitudinal study of UK disclosure. Account, Audit Account J 8(2):47–77. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513579510146996
Gray R, Owen D, Adams CA (1996) Accounting & Accountability: changes and challenges in corporate social and environmental reporting. Prentice Hall
Greco G, Sciulli N, D’onza G (2012) From Tuscany to Victoria: some determinants of sustainability reporting by local councils. Local Gov Stud 38(5):681–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/03003930.2012.679932
GRI (2016) GRI 101 Foundation. Global Reporting Initiative. https://www.globalreporting.org/media/55yhvety/gri-101-foundation-2016.pdf?page=23
Guidry RP, Patten DM (2012) Voluntary disclosure theory and financial control variables: an assessment of recent environmental disclosure research. Account Forum 36(2):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2012.03.002
Guix M, Font X, Bonilla-Priego MJ (2019) Materiality: stakeholder accountability choices in hotels’ sustainability reports. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 31(6):2321–2338. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-05-2018-0366
Gulluscio C, Puntillo P, Luciani V, Huisingh D (2020) Climate change accounting and reporting: a systematic literature review. Sustainability 12(13):5455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135455
Hąbek P (2014) Evaluation of sustainability reporting practices in Poland. Qual Quant 48(3):1739–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-013-9871-z
Hahn R, Kühnen M (2013) Determinants of sustainability reporting: a review of results, trends, theory, and opportunities in an expanding field of research. J Clean Prod 59:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.07.005
Hamrouni A, Boussaada R, Ben Farhat Toumi N (2019) Corporate social responsibility disclosure and debt financing. J Appl Acc Res 20(4):394–415. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAAR-01-2018-0020
Hogner RH (1982) Corporate social reporting: eight decades of development at U.S. Steel.Research in Corporate Social Performance and Policy 4, Preston LE, ed. JAI Press, Greenwich, CT 243–250
Hongming X, Ahmed B, Hussain A, Rehman A, Ullah I, Khan FU (2020) Sustainability reporting and firm performance: the demonstration of Pakistani firms. SAGE Open, July-September, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020953180
Hooghiemstra R (2000) Corporate communication and impression management—new perspectives why companies engage in corporate social reporting. J Bus Ethics 27:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4311-0_7
Huang C-L, Kung F-H (2010) Drivers of environmental disclosure and stakeholder expectation: evidence from Taiwan. J Bus Ethics 96(3):435–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0476-3
Huizing A, Carel Dekker H (1992) The environmental issue on the Dutch political market. Acc Organ Soc 17(5):427–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(92)90039-U
Jensen MC, Meckling WH (1976) Theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership Structure. J Financ Econ 3(4):305–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-405X(76)90026-X
Jones MJ, Solomon JF (2013) Problematising accounting for biodiversity. Account, Audit Account J 26(5):668–687. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-03-2013-1255
Junior FH (2017) Strategic aspects in sustainability reporting in oil & gas industry: the comparative case-study of Brazilian Petrobras and Spanish Repsol. Ecol Ind 72:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.007
Kareiva PM, McNally BW, McCormick S, Miller T, Ruckelshaus M (2015) Improving global environmental management with standard corporate reporting. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(24):7375–7382. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408120111
Kennedy Nyahunzvi D (2013) CSR reporting among Zimbabwe’s hotel groups: a content analysis. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 25(4):595–613. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596111311322943
Klarin A, Suseno Y (2023) An integrative literature review of social entrepreneurship research: mapping the literature and future research directions. Bus Soc 62(3):565–611. https://doi.org/10.1177/00076503221101611
Kleindorfer PR, Singhal K, Wassenhove LNV (2005) Sustainable operations management. Prod Oper Manag 14(4):482–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1937-5956.2005.tb00235.x
Kordsachia O (2020) A risk management perspective on CSR and the marginal cost of debt: empirical evidence from Europe. RMS. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-020-00392-2
KPMG (2020) The time has come: the KPMG survey of sustainability reporting 2020. https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/xx/pdf/2020/11/the-time-has-come.pdf
Lamberton G (2005) Sustainability accounting—a brief history and conceptual framework. Account Forum 29(1):7–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2004.11.001
Lee TM, Hutchison PD (2005) The decision to disclose environmental information: a research review and agenda. Adv Account 21:83–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0882-6110(05)21004-0
Lehman G, Kuruppu SC (2017) A framework for social and environmental accounting research. Account Forum 41(3):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2017.07.001
Li Y, Rong Y, Ahmad UM, Wang X, Zuo J, Mao G (2021) A comprehensive review on green buildings research: bibliometric analysis during 1998–2018. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(34):46196–46214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12739-7
Lindblom CK (1983) The concept of organizational legitimacy and its implications for corporate social responsibility disclosure. American Accounting Association Public Interest Section, Working paper
Lindblom CK (1994) The implications of organizational legitimacy for corporate social performance and disclosure. In: Critical perspectives on accounting conference, New York
Lodhia S, Hess N (2014) Sustainability accounting and reporting in the mining industry: current literature and directions for future research. J Clean Prod 84:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.094
Lodhia S, Kaur A, Stone G (2020) The use of social media as a legitimation tool for sustainability reporting: a study of the top 50 Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) listed companies. Meditari Account Res 28(4):613–632. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEDAR-09-2019-0566
Mahadeo JD, Oogarah-Hanuman V, Soobaroyen T (2011) A longitudinal study of corporate social disclosures in a developing economy. J Bus Ethics 104(4):545–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0929-3
Mahoney JT, Qian L (2013) Market frictions as building blocks of an organizational economics approach to strategic management: market frictions as building blocks. Strateg Manag J 34(9):1019–1041. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.2056
Marquis C, Qian C (2014) Corporate social responsibility reporting in China: symbol or substance? Organ Sci 25(1):127–148. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2013.0837
Martin-Ortega O, Hoekstra J (2019) Reporting as a means to protect and promote human rights? The EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive. Eur Law Rev 44(5):622–645. http://repository.essex.ac.uk/id/eprint/25494
Mata C, Fialho A, Eugénio T (2018) A decade of environmental accounting reporting: what we know? J Clean Prod 198:1198–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.087
Mathews MR (1984) A suggested classification for social accounting research. J Account Public Policy 3(3):199–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4254(84)90017-6
Mathews MR (1997) Twenty-five years of social and environmental accounting research is there a silver jubilee to celebrate? Account, Audit Account J 10(4):481–531
Mehmood W, Ahmad A, Aman-Ullah A, Mohd-Rashid R (2023a) Modern slavery: a literature review using bibliometric analysis and the nexus of governance. J Public Affairs 23(1):e2832. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2832
Mehmood W, Mohd-Rashid R, Abdullah Y, Patwary AK, Aman-Ullah A (2023b) Inclusive mapping of initial public offerings: a bibliometric and literature review study. Qual Quant 57(1):655–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-022-01387-9
Meyer JW, Rowan B (1977) Institutional organizations: formal structure as myth and ceremony. Am J Sociol 83(2):340–363
Michelon G, Pilonato S, Ricceri F (2015) CSR reporting practices and the quality of disclosure: an empirical analysis. Crit Perspect Account 33:59–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2014.10.003
Michelon G, Pilonato S, Ricceri F, Roberts RW (2016) Behind camouflaging: traditional and innovative theoretical perspectives in social and environmental accounting research. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 7(1):2–25. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-12-2015-0121
Milne MJ (2002) Positive accounting theory, political costs and social disclosure analyses: a critical look. Crit Perspect Account 13(3):369–395. https://doi.org/10.1006/cpac.2001.0509
Milne MJ, Gray R (2013) W(h)ither ecology? The triple bottom line, the Global Reporting Initiative, and corporate sustainability reporting. J Bus Ethics 118(1):13–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-012-1543-8
Minutiello V, Tettamanzi P (2022) The quality of nonfinancial voluntary disclosure: a systematic literature network analysis on sustainability reporting and integrated reporting. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 29(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2195
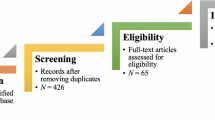
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, for the PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339(jul 21 1):b2535–b2535. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Niazi M, Hussain A (2011) Agent-based computing from multi-agent systems to agent-based models: a visual survey. Scientometrics 89(2):479–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-011-0468-9
Olawumi TO, Chan DWM (2018) A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development. J Clean Prod 183:231–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.162
Opferkuch K, Caeiro S, Salomone R, Ramos TB (2021) Circular economy in corporate sustainability reporting: a review of organisational approaches. Bus Strateg Environ 30(8):4015–4036. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2854
Owen D (2008) Chronicles of wasted time?: a personal reflection on the current state of, and future prospects for, social and environmental accounting research. Account, Audit Account J 21(2):240–267. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570810854428
Parker LD (2005) Social and environmental accountability research: a view from the commentary box. Account, Audit Account J 18(6):842–860. https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570510627739
Parker LD (2011) Twenty-one years of social and environmental accountability research: a coming of age. Account Forum 35(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accfor.2010.11.001
Pasko O, Chen F, Oriekhova A, Brychko A, Shalyhina I (2021) Mapping the literature on sustainability reporting: a bibliometric analysis grounded in Scopus and Web of Science core collection. Eur J Sustain Dev 10(1):303. https://doi.org/10.14207/ejsd.2021.v10n1p303
Patten DM (1992) Intra-industry environmental disclosures in response to the Alaskan oil spill: a note on legitimacy theory. Acc Organ Soc 17(5):471–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(92)90042-Q
Patten DM (2019) Seeking legitimacy. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 11(6):1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-12-2018-0332
Patten DM, Shin H (2019) Sustainability accounting, management and policy journal’s contributions to corporate social responsibility disclosure research: a review and assessment. Sustain Account, Manag Policy J 10(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-01-2018-0017
Pedroso TMA, Benvindo-Souza M, de Araújo Nascimento F, Woch J, dos Reis FG, de Melo e Silva D (2022) Cancer and occupational exposure to pesticides: a bibliometric study of the past 10 years. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(12):17464–17475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17031-2
Perego P, Kennedy S, Whiteman G (2016) A lot of icing but little cake? Taking integrated reporting forward. J Clean Prod 136:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.106
Permatasari P, Gunawan J (2023) Sustainability policies for small medium enterprises: who are the actors? Clean Responsib Consum 9:100122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clrc.2023.100122
Pfeffer J, Salancik GR (1978) The external control of organizations: a resource dependence perspective. Harper and Row, New York, NY
Pfeffer J, Salancik GR (2003) The external control of organizations: a resource dependence perspective. Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA
Prado-Lorenzo J-M, Gallego-Alvarez I, Garcia-Sanchez IM (2009) Stakeholder engagement and corporate social responsibility reporting: the ownership structure effect. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 16(2):94–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.189
Prencipe A (2004) Proprietary costs and determinants of voluntary segment disclosure: evidence from Italian listed companies. Eur Account Rev 13(2):319–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/0963818042000204742
Preston LE, Post JE (1975) Private management and public policy. Prentice-Hall, USA
Pucheta-Martínez MC, Bel-Oms I, Olcina-Sempere G (2018) The association between board gender diversity and financial reporting quality, corporate performance and corporate social responsibility disclosure: a literature review. Academia Revista Latinoamericana De Administración 31(1):177–194. https://doi.org/10.1108/ARLA-04-2017-0110
Radhouane I, Nekhili M, Nagati H, Paché G (2018) The impact of corporate environmental reporting on customer-related performance and market value. Manag Decis 56(7):1630–1659. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-03-2017-0272
Rahman S, Khan T, Siriwardhane P (2019) Sustainable development carbon pricing initiative and voluntary environmental disclosures quality. Bus Strateg Environ 28(6):1072–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2302
Reverte C (2009) Determinants of corporate social responsibility disclosure ratings by Spanish listed firms. J Bus Ethics 88(2):351–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-008-9968-9
Rinaldi L, Unerman J, de Villiers C (2018) Evaluating the integrated reporting journey: insights, gaps and agendas for future research. Account, Audit Account J 31(5):1294–1318. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-04-2018-3446
Roberts RW (1992) Determinants of corporate social responsibility disclosure: an application of stakeholder theory. Acc Organ Soc 17(6):595–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(92)90015-K
Salton G, Wong A, Yang CS (1975) A vector space model for automatic indexing. Commun ACM 18(11):613–620. https://doi.org/10.1145/361219.361220
Savić M, Ivanović M, Jain LC (2019) Co-authorship networks: an introduction. In: Savić M, Ivanović M, Jain LC, Complex networks in software, knowledge, and social systems, vol. 148. Springer International Publishing. pp. 179–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91196-0_5
Sengupta P (1998) Corporate disclosure quality and the cost of debt. Account Rev 73(4):459–474. https://doi.org/10.2307/248186
Siew RYJ (2015) A review of corporate sustainability reporting tools (SRTs). J Environ Manag 164:180–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.010
Simnett R, Vanstraelen A, Chua WF (2009) Assurance on sustainability reports: an international comparison. Account Rev 84(3):937–967. https://doi.org/10.2308/accr.2009.84.3.937
Singhania M, Chadha G, Prasad R (2023a) Sustainable finance research: review and agenda. Int J Finance Econ, Early View. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijfe.2854
Singhania M, Gupta S, Chadha G, Braune E, Dana LP, Idowu SO (2023b) Mapping 26 years of climate change research in finance and accounting: a systematic scientometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(35):83153–83179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27828-y
Skouloudis A, Evangelinos K, Kourmousis F (2010) Assessing non-financial reports according to the Global Reporting Initiative guidelines: evidence from Greece. J Clean Prod 18(5):426–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.11.015
Sotorrío LL, Sánchez JLF (2010) Corporate social reporting for different audiences: the case of multinational corporations in Spain. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 17(5):272–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.215
Spence M (1973) Job market signaling. Q J Econ 87(3):355. https://doi.org/10.2307/1882010
Spence C, Husillos J, Correa-Ruiz C (2010) Cargo cult science and the death of politics: a critical review of social and environmental accounting research. Crit Perspect Account 21:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2008.09.008
Stechemesser K, Guenther E (2012) Carbon accounting: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 36:17–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.02.021
Suchman MC (1995) Managing legitimacy: strategic and institutional approaches. Acad Manag Rev 20(3):571–610. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1995.9508080331
Tague-Sutcliffe J (1992) An introduction to informetrics. Inform Process Manag 28(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4573(92)90087-G
Thun TW, Zülch H (2023) The effect of chief sustainability officers on sustainability reporting—a management perspective. Bus Strateg Environ 32(4):2093–2110. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3238
Traxler AA, Schrack D, Greiling D (2020) Sustainability reporting and management control – a systematic exploratory literature review. J Clean Prod 276:122725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122725
Tschopp D, Huefner RJ (2015) Comparing the evolution of CSR reporting to that of financial reporting. J Bus Ethics 127(3):565–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2054-6
Ullmann AA (1985) Data in search of a theory: a critical examination of the relationships among social performance, social disclosure, and economic performance of U.S. firms. Acad Manag Rev 10(3):540–557. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1985.4278989
Velte P (2023) Automated text analyses of sustainability & integrated reporting. A literature review of empirical-quantitative research. J Glob Responsib. https://doi.org/10.1108/JGR-09-2022-0090
Velte P, Stawinoga M, Lueg R (2020) Carbon performance and disclosure: a systematic review of governance-related determinants and financial consequences. J Clean Prod 254:120063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120063
Veltri S, Silvestri A (2020) The value relevance of corporate financial and nonfinancial information provided by the integrated report: a systematic review. Bus Strateg Environ, bse.2556. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2556
Verrecchia R (1983) Discretionary disclosure. J Account Econ 5:179–194
Verrecchia R (1990) Information quality and discretionary disclosure. J Account Econ 12(4):365–380
Vitolla F, Raimo N, Rubino M (2019) Appreciations, criticisms, determinants, and effects of integrated reporting: a systematic literature review. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26(2):518–528. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1734
Woodward DG, Edwards P, Birkin F (1996) Organizational legitimacy and stakeholder information provision1. Br J Manag 7(4):329–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.1996.tb00123.x
Yakar Pritchard G, Çalıyurt KT (2021) Sustain Rep Coop Risks 9(6):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks9060117
Yang HH, Craig R, Farley A (2015) A review of Chinese and English language studies on corporate environmental reporting in China. Crit Perspect Account 28:30–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpa.2014.10.001
Zhao X (2017) A scientometric review of global BIM research: analysis and visualization. Autom Constr 80:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2017.04.002
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the University Grants Commission (UGC) of India (under the NET-JRF scheme) for sponsoring/supporting this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing were performed by Gurmani Chadha. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Both authors confirm compliance with ethical standards during the conduct of research.
Consent to participate
N/A.
Consent for publication
N/A.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singhania, M., Chadha, G. Thirty years of sustainability reporting research: a scientometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 102047–102082 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29452-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29452-2