Abstract
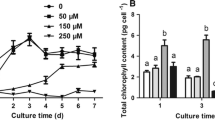
As one of the most threatening challenges to the natural environment and human health, cadmium (Cd) pollution has seriously impacted natural organisms. Green algae, such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (C. reinhardtii), can provide a safer, lower cost, and more effective ecological approach to the treatment of heavy metal ions in wastewater due to their sorption properties. However, heavy metal ions affect C. reinhardtii when adsorbed. Melatonin is able to protect the plant body from damage when the plant is under biotic/abiotic stress. Therefore, we investigated the effects of melatonin on the cell morphology, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, enzymatic activity of the antioxidant system, gene expression, and the ascorbic acid (AsA)-glutathione (GSH) cycle of C. reinhardtii under the stress of Cd (13 mg/L). Our results indicated that Cd significantly induced photoinhibition and overaccumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). By application with the concentration of 1.0 μM melatonin, the algal solute of C. reinhardtii under the Cd stress gradually regained its green color, the cell morphology became intact, and the photosynthetic electron transport function was retained. However, in the melatonin-silenced strain, there was a significant decrease in all of the above indicators. In addition, the use of exogenous melatonin or the expression of endogenous melatonin genes could enhance the intracellular enzyme activities of catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR). It also upregulated the expression of active enzyme genes such as SOD1, CAT1, FSD1, GSH1, GPX5, and GSHR1. These results indicate that the presence of melatonin effectively protects the activity of photosynthetic system II in C. reinhardtii, enhances antioxidant activity, upregulates gene expression in the AsA-GSH cycle, and reduces the level of ROS, thereby alleviating the damage caused by Cd toxicity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Insights into the significance of antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5369–374. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.4.10873
Ahammed GJ, Li X (2022) Melatonin-induced detoxification of organic pollutants and alleviation of phytotoxicity in selected horticultural crops. Horticulturae 8(12):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121142
Ahammed GJ, Yang Y (2022) Anthocyanin-mediated arsenic tolerance in plants. Environm Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 292(Pt B):118475 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118475
Antoniou C, Chatzimichail G, Xenofontos R, Pavlou JJ, Panagiotou E, Christou A, Fotopoulos V (2017) Melatonin systemically ameliorates drought stress-induced damage in Medicago sativa plants by modulating nitro-oxidative homeostasis and proline metabolism. J Pineal Res 62(4):e12401. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12401
Ayenimo JG, Adeeyinwo CE, Amoo IA (2005) Heavy metal pollutants in WARRI RIVER, NIGERIA. Kragujevac J Sciencev 27:43–50
Barrière C, Centeno D, Lebert A, Leroy-Sétrin S, Berdagué JL, Talon R (2001) Roles of superoxide dismutase and catalase of Staphylococcus xylosus in the inhibition of linoleic acid oxidation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 201(2):181–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10754.x
Cao L, Jin XJ, Zhang YX (2019) Melatonin confers drought stress tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.) by modulating photosynthesis, osmolytes, and reactive oxygen metabolism. Photosynthetica 57(3):812–819. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2019.100
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
Chen YY, Tang MY, Wang ST, Wang Q, Zhan WX, Huang G (2016) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil of China based on bibliometrics. Chin J Soil Sci 7(1):219–225
Chen Z, Cao XL, Niu JP (2021) Effects of exogenous ascorbic acid on seed germination and seedling salt-tolerance of alfalfa. PLoS ONE 16(4):e0250926. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250926
Cheng Y, Li X, Fang MY, Ye QJ, Li ZM, Ahammed GJ (2022) Systemic H2O2 signaling mediates epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced cadmium tolerance in tomato. J Hazard Mater 438:129511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129511
Cui G, Zhao X, Liu S, Sun F, Chao Z, Xi Y (2017) Beneficial effects of melatonin in overcoming drought stress in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 118:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.06.014
Cuypers A, Smeets K, Ruytinx J, Opdenakker K, Keunen E, Remans T, Horemans N, Vanhoudt N, Van Sanden S, Van Belleghem F, Guisez Y, Colpaert J, Vangronsveld J (2011) The cellular redox state as a modulator in cadmium and copper responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. J Plant Physiol 168(4):309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.010
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70(2):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90488-7
Gupta GS, Yadav G, Tiwari S (2020) Bioremediation of heavy metals: a new approach to sustainable agriculture. Restoration of wetland ecosystem: a trajectory towards a sustainable environment, pp 195–226
Halliwell B (2006) Reactive species and antioxidants. redox biology is a fundamental theme of aerobic life. Plant Physiol 141(2):312–322 https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.07707
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007) Antioxidant defences: endogenous and diet derived. J Free Radic Biol Med 4:79–186
Hasan MK, Liu C, Wang F, Ahammed GJ, Zhou J, Xu MX, Yu JQ, Xia XJ (2016) Glutathione-mediated regulation of nitric oxide, S-nitrosothiol and redox homeostasis confers cadmium tolerance by inducing transcription factors and stress response genes in tomato. Chemosphere 161:536–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.053
Hasanuzzaman MB, Anee TI, Parvin K, Nahar K, Mahmud JA, Fujita M (2019) Regulation of ascorbate-glutathione pathway in mitigating oxidative damage in plants under abiotic stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(9):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090384
Junglee S, Urban L, Sallanon H, Lopez-Lauri F (2014) Optimized assay for hydrogen peroxide determination in plant tissue using potassium iodide. Am J Anal Chem 5(11):730. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2014.511081
Küpper H, Andresen E (2016) Mechanisms of metal toxicity in plants. Metallomics 8(3):269–285. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mt00244c
Liu W, Guo C, Huang D, Li H, Wang C (2021) The papain-like cysteine protease HpXBCP3 from Haematococcus pluvialis involved in the regulation of growth, salt stress tolerance and chlorophyll synthesis in microalgae. Int J Mol Sci 22(21):11539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111539
Liu CX, Yang T, Zhou H, Ahammed GJ, Qi ZY, Zhou, J (2022) The E3 ubiquitin ligase gene Sl1 is critical for cadmium tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum L. antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 11(3):456 https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030456
Ma X, Zhang J, Burgess P, Rossi S, Huang B (2018) Interactive effects of melatonin and cytokinin on alleviating drought-induced leaf senescence in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera). Environ Exp Bot 145:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.10.010
Mallick N, Mohn FH (2003) Use of chlorophyll fluorescence in metal-stress research: a case study with the green microalga Scenedesmus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 55(1):64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0147-6513(02)00122-7
Meng JF, Xu TF, Wang ZZ, Fang YL, Xi ZM, Zhang ZW (2014) The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water-deficient stress: antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. J Pineal Res 57(2):200–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12159
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9(10):490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants
Mirza H, Kamrun N, Gill SS, Alharby HF, Razafindrabe B, Masayuki F (2017) Hydrogen Peroxide Pretreatment Mitigates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress in Brassica napus L.: An Intrinsic Study on Antioxidant Defense and Glyoxalase Systems. Front Plant 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00115
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
Owen JB, Butterfield DA (2010) Measurement of oxidized/reduced glutathione ratio. Methods Mol Biol 648:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-756-3_18
Qin S, Liu H, Nie Z, Gao W, Li C, Lin Y, Zhao P (2018) AsA–GSH cycle and antioxidant enzymes play important roles in Cd tolerance of wheat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(5):684–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2471-9
Shah AA, Ahmed S, Ali A, Yasin NA (2020) 2-Hydroxymelatonin mitigates cadmium stress in cucumis sativus seedlings: modulation of antioxidant enzymes and polyamines. Chemosphere 243:125308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125308
Shah M, Guo S, Baloch AR, Sun J, Shu S, Wang Y, Ahammed GJ, Kabir K, Roy R (2020) Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110593
Shahid M, Pourrut B, Dumat C, Nadeem M, Aslam M, Pinelli E (2014) Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 232:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-06746-9_1
Sharma A, Wang J, Xu D, Tao S, Chong S, Yan D, Li Z, Yuan H, Zheng B (2020) Melatonin regulates the functional components of photosynthesis, antioxidant system, gene expression, and metabolic pathways to induce drought resistance in grafted Carya cathayensis plants. Sci Total Environ 713:136675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136675
Shu S, Yuan LY, Guo SR, Sun J, Yuan YH (2013) Effects of exogenous spermine on chlorophyll fluorescence, antioxidant system and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in Cucumis sativus L. under salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 63:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.11.028
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.01.006
Tiwari RK, Lal MK, Naga KC, Kumar R, Sharma S (2020) Emerging roles of melatonin in mitigating abiotic and biotic stresses of horticultural crops. Scientia Horticulturae 272:109592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109592
Tscheikner-Gratl F, Bellos V, Schellart A, Moreno-Rodenas A, Muthusamy M, Langeveld J, Clemens F, Benedetti L, Rico-Ramirez MA, Carvalho RD (2019) Recent insights on uncertainties present in integrated catchment water quality modelling. Water Res 150:368–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.079
Wang K, Xing Q, Ahammed GJ, Zhou J (2022) Functions and prospects of melatonin in plant growth, yield, and quality. J Exp Bot 73(17):5928–5946. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erac233
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils From China. Microchem J 94(2):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2009.09.014
Xia H, Ni Z, Hu R, Lin L, Deng H, Wang J, Tang Y, Sun G, Wang X, Li H (2020) Melatonin alleviates drought stress by a non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidative system in kiwifruit seedlings. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030852
Yao M, Ge W, Zhou Q, Zhou X, Luo M, Zhao Y, Wei B, Ji S (2021) Exogenous glutathione alleviates chilling injury in postharvest bell pepper by modulating the ascorbate-glutathione (AsA-GSH) cycle. Food chem 352:129458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129458
Yu Y, Teng Z, Mou Z, Lv Y, Li T, Chen S, Zhao D, Zhao Z (2020) Melatonin confers heavy metal-induced tolerance by alleviating oxidative stress and reducing the heavy metal accumulation in Exophiala pisciphila, a dark septate endophyte (DSE). BMC Microbiol 21(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-021-02098-1
Zhang H, Reynolds M (2019) Cadmium exposure in living organisms: a short review. Sci the Total Environ 678:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.395
Zhang Z, Hu Q, Liu Y, Cheng P, Cheng H, Liu W, Xing X, Guan Z, Fang W, Chen S, Jiang J, Chen F (2019) Strigolactone represses the synthesis of melatonin, thereby inducing floral transition in Arabidopsis thaliana in an FLC-dependent manner. J Pineal Res 67(2):e12582. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12582
Zhang Z, Wu J, Xi Y, Zhang L, Wang-Pruski G (2021) Effects of autotoxicity on seed germination, gas exchange attributes and chlorophyll fluorescence in melon seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 41(3):993–1003
Zhou L, Zhao Y, Wang S (2015) Cadmium transfer and detoxification mechanisms in a soil–mulberry–silkworm system: phytoremediation potential. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(22):18031–18039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5011-8
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572665) and the Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Basic Research Program (2022JZ-15), Shannxi Provincial Department of Education Research Project (Key Laboratory Project) (18JS112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fangbing Qi and Yingjuan Wang: methodology, validation, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Yu Gao and Jiaqi Liu: formal analysis and wring—review and editing. Yingjuan Wang: funding acquisition. Xiangyu Yao and Ziyi Wu: methodology, conceptualization, and wring—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Fangbing Qi and Yu Gao are co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, F., Gao, Y., Liu, J. et al. Alleviation of cadmium-induced photoinhibition and oxidative stress by melatonin in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 78423–78437 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27561-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27561-6