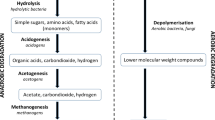
Abstract
High concentrations of ammonium, nitrite, and nitrate always induce inhibition in anaerobic wastewater treatment. Due to the complexity and vulnerability of the microbial community (especially methanogens) in anaerobic sludge, little is understood about its underlying microbial mechanism under such inhibition. In this study, the shifts of microbial communities in anaerobic sludge under increasing levels of nitrite, nitrate, and ammonium ions were compared. Results show that although half maximal inhibitory concentrations (methanogenesis) were different for nitrite, nitrate, and ammonium ions with EC50 values of 12, 30, and 3000 mg N/L, respectively, bacteria genera Kosmotoga and Brooklawnia dominated in all of the three high-stress inhibitory systems. Network analysis and redundancy analysis (RDA) of the microbial community showed the treatments with nitrate and nitrite ions decreased the modularity of anaerobic microorganisms. RDA showed that specific methanogenic activity was positively related to coenzyme F420 under nitrite inhibition (rp = 0.833, p < 0.05) and closely correlated with viability under nitrate inhibition. Gram-positive and nonmotile Brooklawnia genus showed a negative correlation with physiological characteristics in the ammonia treatments, suggesting its high resistance to ammonia.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information file).
References
Alsouleman K, Linke B, Klang J, Klocke M, Krakat N, Theuerl S (2016) Reorganisation of a mesophilic biogas microbiome as response to a stepwise increase of ammonium nitrogen induced by poultry manure supply. Bioresour Technol 208:200–204
Andalib M, Nakhla G, McIntee E, Zhu J (2011) Simultaneous denitrification and methanogenesis (SDM): review of two decades of research. Desalination 279(1–3):1–14
Ashby KD, Casey TA, Rasmussen MA, Petrich JW (2001) Steady-state and time-resolved spectroscopy of F420 extracted from methanogen cells and its utility as a marker for fecal contamination. Agric Food Chem 49(3):1123–1127
Astals S, Peces M, Batstone DJ, Jensen PD, Tait S (2018) Characterising and modelling free ammonia and ammonium inhibition in anaerobic systems. Water Res 143:127–135
Batstone DJ, Lu Y, Jensen PD (2015) Impact of dewatering technologies on specific methanogenic activity. Water Res 82:78–85
Calli B, Mertoglu B, Inanc B, Yenigun O (2005a) Effects of high free ammonia concentrations on the performances of anaerobic bioreactors. Process Biochem 40(3):1285–1292
Calli B, Mertoglu B, Inanc B, Yenigun O (2005b) Methanogenic diversity in anaerobic bioreactors under extremely high ammonia levels. Enzyme Microb Technol 37(4):448–455
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4044–4064
Chen JL, Ortiz R, Steele TW, Stuckey DC (2014) Toxicants inhibiting anaerobic digestion: a review. Biotechnol Adv 32(8):1523–1534
Chen Y, Lan S, Wang L, Dong S, Zhou H, Tan Z et al (2017) A review: driving factors and regulation strategies of microbial community structure and dynamics in wastewater treatment systems. Chemosphere 174:173–182
Clarens M, Bernet N, Delgenès J, Moletta R (1998) Effects of nitrogen oxides and denitrification by Pseudomonas stutzeri on acetotrophic methanogenesis by Methanosarcina mazei. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 25(3):271–276
Elias DA, Krumholz LR, Tanner RS, Suflita JM (1999) Estimation of methanogen biomass by quantitation of coenzyme M. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(12):5541–5545
EPA of China (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring analysis method, 4th edn. Chinese Environment Science Publisher, Beijing
Etchebehere C, Castelló E, Wenzel J, Del Pilar A-R, Borzacconi L, Buitrón G et al (2016) Microbial communities from 20 different hydrogen-producing reactors studied by 454 pyrosequencing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(7):3371–3384
Fang J, Lyon DY, Wiesner MR, Dong J, Alvarez PJJ (2007) Effect of a fullerene water suspension on bacterial phospholipids and membrane phase behavior. Environ Sci Technol 41(7):2636–2642
Fotidis IA, Karakashev D, Angelidaki I (2014) The dominant acetate degradation pathway/methanogenic composition in full-scale anaerobic digesters operating under different ammonia levels. Int J Environ Sci 11(7):2087–2094
Fu H, Wang J, Ren H, Ding L (2022) Acceleration of start-up of moving bed biofilm reactor at low temperature by adding specialized quorum sensing bacteria. Bioresour Technol 358:127249
Fujishima S, Miyahara T, Noike T (2000) Effect of moisture content on anaerobic digestion of dewatered sludge: ammonia inhibition to carbohydrate removal and methane production. Water Sci Technol 41(3):119–127
Gallert C, Winter J (1997) Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic wastes: effect of ammonia on glucose degradation and methane production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48(3):405–410
Jo SJ, Kwon H, Jeong S, Lee C, Kim TG (2016) Comparison of microbial communities of activated sludge and membrane biofilm in 10 full-scale membrane bioreactors. Water Res 101:214–225
Klüber HD, Conrad R (1998) Inhibitory effects of nitrate, nitrite, NO and N2O on methanogenesis by Methanosarcina barkeri and Methanobacterium bryantii. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 25(4):331–339
Lin Q, De Vrieze J, Li C, Li J, Li J, Yao M et al (2017) Temperature regulates deterministic processes and the succession of microbial interactions in anaerobic digestion process. Water Res 123:134–143
Ma S, Ding L, Huang H, Geng J, Xu K, Zhang Y et al (2016) Effects of DO levels on surface force, cell membrane properties and microbial community dynamics of activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 214:645–652
Nelson MC, Morrison M, Yu Z (2011) A meta-analysis of the microbial diversity observed in anaerobic digesters. Bioresour Technol 102(4):3730–3739
Niu C, Geng J, Ren H, Ding L, Xu K (2012) The cold adaptability of microorganisms with different carbon source in activated sludge treating synthetical wastewater. Bioresour Technol 123:66–71
Niu C, Liang W, Ren H, Geng J, Ding L, Xu K (2014) Enhancement of activated sludge activity by 10–50mT static magnetic field intensity at low temperature. Bioresour Technol 159:48–54
Pan X, Zhao L, Li C, Angelidaki I, Lv N, Ning J, Cai G, Zhu G (2021) Deep insights into the network of acetate metabolism in anaerobic digestion: focusing on syntrophic acetate oxidation and homoacetogenesis. Water Res 190:116774
Qiu Y, Hanada S, Ohashi A, Harada H, Kamagata Y, Sekiguchi Y (2008) Syntrophorhabdus aromaticivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., the first cultured anaerobe capable of degrading phenol to acetate in obligate syntrophic associations with a hydrogenotrophic methanogen. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(7):2051–2058
Rajagopal R, Massé DI, Singh G (2013) A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour Technol 143:632–641
Roy R, Klüber HD, Conrad R (1997) Early initiation of methane production in anoxic rice soil despite the presence of oxidants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 24(4):311–320
Russell JB, Cook GM (1995) Energetics of bacterial growth: balance of anabolic and catabolic reactions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 59(1):48–62
Sarti A, Pozzi E, Chinalia FA, Ono A, Foresti E (2010) Microbial processes and bacterial populations associated to anaerobic treatment of sulfate-rich wastewater. Process Biochem 45(2):164–170
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Sun R, Zhou A, Jia J, Liang Q, Liu Q, Xing D et al (2015) Characterization of methane production and microbial community shifts during waste activated sludge degradation in microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour Technol 175:68–74
Sun C, Cao W, Banks CJ, Heaven S, Liu R (2016) Biogas production from undiluted chicken manure and maize silage: a study of ammonia inhibition in high solids anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 218:1215–1223
Thauer RK, Kaster A, Seedorf H, Buckel W, Hedderich R (2008) Methanogenic archaea: ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation. Nat Rev Microbiol 6(8):579–591
Velten S, Hammes F, Boller M, Egli T (2007) Rapid and direct estimation of active biomass on granular activated carbon through adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) determination. Water Res 41(9):1973–1983
Vigneron V, Ponthieu M, Barina G, Audic J, Duquennoi C, Mazéas L et al (2007) Nitrate and nitrite injection during municipal solid waste anaerobic biodegradation. Waste Manage 27(6):778–791
Westerholm M, Levén L, Schnürer A (2012) Bioaugmentation of syntrophic acetate-oxidizing culture in biogas reactors exposed to increasing levels of ammonia. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(21):7619–7625
Wiegant WM, Zeeman G (1986) The mechanism of ammonia inhibition in the thermophilic digestion of livestock wastes. Agric Wastes 16(4):243–253
Wilson LP, Loetscher LH, Sharvelle SE, Susan K (2013) Microbial community acclimation enhances waste hydrolysis rates under elevated ammonia and salinity conditions. Bioresour Technol 146:15–22
Zhang C, Yuan Q, Lu Y (2014) Inhibitory effects of ammonia on methanogen mcrA transcripts in anaerobic digester sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(2):368–377
Zhou Y, Ganda L, Lim M, Yuan Z, Kjelleberg S, Ng WJ (2010) Free nitrous acid (FNA) inhibition on denitrifying poly-phosphate accumulating organisms (DPAOs). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(1):359–369
Zhou X, Meile L, Kreuzer M, Zeitz JO (2013) The effect of saturated fatty acids on methanogenesis and cell viability of Methanobrevibacter ruminantium. Archaea, Vancouver BC
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Ren H, Geng J, Xu K, Huang H et al (2015) Physicochemical characteristics and microbial community evolution of biofilms during the start-up period in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 180:345–351
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Science and Technology Major Project (no. 2017ZX07202003) and the National Science & Technology Support Program of China (no. 2014BAC08B05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Runhua Su and Lina Zhou contributed to formal analysis, investigation, data curation, and writing—original draft; Bo Fu, Huimin Fu, and Yanan Shuang contributed to methodology and validation; Lin Ye and Haijun Ma contributed to resources, supervision, and visualization; Haidong Hu and Hongqiang Ren contributed to writing—review and editing; Lili Ding contributed to software, conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, visualization, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Runhua Su and Lina Zhou contributed equally to all aspects of conceptualizing planning, sample and data collection, data analysis, and preparation of the manuscript
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, R., Zhou, L., Ding, L. et al. How anaerobic sludge microbiome respond to different concentrations of nitrite, nitrate, and ammonium ions: a comparative analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 49026–49037 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25704-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25704-3