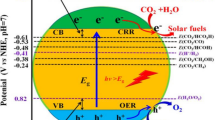
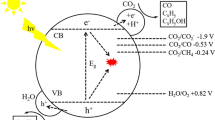
Abstract
In recent years, with global climate change, the utilization of carbon dioxide as a resource has become an important goal of human society to achieve carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. Among them, the catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to generate renewable fuels has received great attention. As one of these methods, photocatalysis has its unique properties and mechanism, which can only rely on sunlight without inputting other energy. It is an emerging discipline with great development prospects. The core of photocatalysis lies in the development of photocatalysts with high activity, high selectivity, low cost, and high durability. This review first introduces the background and mechanism of photocatalysis, then introduces various types of photocatalysts based on different substrates, and analyzes the methods and mechanisms to improve the activity and selectivity of photocatalysts. Finally, combining the plasmon effect with photocatalysis, the review analyzes the promoting effect of the plasmon effect on the photocatalytic carbon dioxide synthesis of renewable fuels, which provides a new idea for it.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This is not applicable.
References
Ahmed N, Shibata Y, Taniguchi T, Izumi Y (2011) Photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into methanol using zinc–copper–M (III)(M = aluminum, gallium) layered double hydroxides. J Catal 279:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2011.01.004
Akhundi A, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Abitorabi M, Rahim Pouran S (2019) Review on photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to value-added compounds and renewable fuels by graphitic carbon nitride-based photocatalysts. Catal Rev 61:595–628. https://doi.org/10.1080/01614940.2019.1654224
Ali S, Razzaq A, In S-I (2019) Development of graphene based photocatalysts for CO2 reduction to C1 chemicals: a brief overview. Catal Today 335:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.12.003
Appel AM, Bercaw JE, Bocarsly AB, Dobbek H, DuBois DL, Dupuis M, Ferry JG, Fujita E, Hille R, Kenis PJ (2013) Frontiers, opportunities, and challenges in biochemical and chemical catalysis of CO2 fixation. Chem Rev 113:6621–6658. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300463y
Chen S, Yang Z, Meng L, Li J, Williams CT, Tian Z (2015) Electromagnetic enhancement in shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman scattering from gold flat surfaces. J Phys Chem C 119:5246–5251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01254
Chen Y, Wang D, Deng X, Li Z (2017) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Catal Sci Technol 7:4893–4904. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY01653K
Cheng H, Huang B, Liu Y, Wang Z, Qin X, Zhang X, Dai Y (2012) An anion exchange approach to Bi2WO6 hollow microspheres with efficient visible light photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to methanol. Chem Commun 48:9729–9731. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc35289c
Cheng X-M, Gu Y, Zhang X-Y, Dao X-Y, Wang S-Q, Ma J, Zhao J, Sun W-Y (2021) Crystallographic facet heterojunction of MIL-125-NH2 (Ti) for carbon dioxide photoreduction. Appl Catal B 298:120524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120524
Corma A, Garcia H (2013) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 for fuel production: possibilities and challenges. J Catal 308:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2013.06.008
Cortés E (2018) Activating plasmonic chemistry. Science 362:28–29. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav1133
Emeline AV, Ryabchuk V, Serpone N (2000) Factors affecting the efficiency of a photocatalyzed process in aqueous metal-oxide dispersions: prospect of distinguishing between two kinetic models. J Photochem Photobiol A 133:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(00)00225-2
Fang Z-B, Liu T-T, Liu J, Jin S, Wu X-P, Gong X-Q, Wang K, Yin Q, Liu T-F, Cao R (2020) Boosting interfacial charge-transfer kinetics for efficient overall CO2 photoreduction via rational design of coordination spheres on metal–organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 142:12515–12523. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c05530
Fresno F, Reñones P, Alfonso E, Guillén C, Trigo J, Herrero J, Collado L, de la Peña OV (2018) Influence of surface density on the CO2 photoreduction activity of a DC magnetron sputtered TiO2 catalyst. Appl Catal B 224:912–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.022
Ganesh I (2014) Conversion of carbon dioxide into methanol–a potential liquid fuel: fundamental challenges and opportunities (a review). Renew Sust Energ Rev 31:221–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.11.045
Gellé A, Jin T, de la Garza L, Price GD, Besteiro LV, Moores A (2019) Applications of plasmon-enhanced nanocatalysis to organic transformations. Chem Rev 120:986–1041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00187
Guo K, Zhu X, Peng L, Fu Y, Ma R, Lu X, Zhang F, Zhu W, Fan M (2021) Boosting photocatalytic CO2 reduction over a covalent organic framework decorated with ruthenium nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 405:127011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127011
Habisreutinger SN, Schmidt-Mende L, Stolarczyk JK (2013) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7372–7408. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201207199
Hartland GV (2011) Optical studies of dynamics in noble metal nanostructures. Chem Rev 111:3858–3887. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1002547
Heo JN, Kim J, Do JY, Park N-K, Kang M (2020) Self-assembled electron-rich interface in defected ZnO: rGO-Cu: Cu2O, and effective visible light-induced carbon dioxide photoreduction. Appl Catal B 266:118648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118648
Hepburn C, Adlen E, Beddington J, Carter EA, Fuss S, Mac Dowell N, Minx JC, Smith P, Williams CK (2019) The technological and economic prospects for CO2 utilization and removal. Nature 575:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1681-6
Hou J, Cao S, Wu Y, Gao Z, Liang F, Sun Y, Lin Z, Sun L (2017) Inorganic colloidal perovskite quantum dots for robust solar CO2 reduction. Chem-Eur J 23:9481–9485. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201702237
Hou W, Hung WH, Pavaskar P, Goeppert A, Aykol M, Cronin SB (2011) Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbon fuels via plasmon-enhanced absorption and metallic interband Transitions. ACS Catal 1:929–936. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs2001434
Howe RF, Gratzel M (1987) EPR study of hydrated anatase under UV irradiation. J Phys Chem 91:3906–3909. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100298a035
Hu CY, Zhou J, Sun CY, Mm C, Wang XL, Su ZM (2019) HKUST-1 derived hollow C-Cu2 − xS nanotube/g-C3N4 composites for visible-light CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor. Chem-Eur J 25:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201804925
Inoue T, Fujishima A, Konishi S, Honda K (1979) Photoelectrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders. Nature 277:637–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/277637a0
Inoue Y (2009) Photocatalytic water splitting by RuO2-loaded metal oxides and nitrides with d0- and d10 -related electronic configurations. Energy Environ Sci 2:364–386. https://doi.org/10.1039/B816677N
Jiao J, Wei Y, Chi K, Zhao Z, Duan A, Liu J, Jiang G, Wang Y, Wang X, Han C (2017a) Platinum nanoparticles supported on TiO2 photonic crystals as highly active photocatalyst for the reduction of CO2 in the presence of water. Energy Technol 5:877–883. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201600572
Jiao X, Chen Z, Li X, Sun Y, Gao S, Yan W, Wang C, Zhang Q, Lin Y, Luo Y (2017b) Defect-mediated electron–hole separation in one-unit-cell ZnIn2S4 layers for boosted solar-driven CO2 reduction. J Am Chem Soc 139:7586–7594. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b02290
Jiao X, Zheng K, Hu Z, Sun Y, Xie Y (2020) Broad-spectral-response photocatalysts for CO2 reduction. ACS Central Sci 6:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c00325
Kamat PV, Hartland GV (2018) Plasmons for energy conversion. ACS Energy Lett 3:1467–1469. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00721
Kannan N, Vakeesan D (2016) Solar energy for future world:-a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 62:1092–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.05.022
Kar P, Zeng S, Zhang Y, Vahidzadeh E, Manuel A, Kisslinger R, Alam KM, Thakur UK, Mahdi N, Kumar P (2019) High rate CO2 photoreduction using flame annealed TiO2 nanotubes. Appl Catal B 243:522–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.08.002
Karkas MD, Verho O, Johnston EV, Br Å (2014) Artificial photosynthesis: molecular systems for catalytic water oxidation. Chem Rev 114:11863–12001. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400572f
Kohno Y, Tanaka T, Funabiki T, Yoshida S (1998) Identification and reactivity of a surface intermediate in the photoreduction of CO2 with H2 over ZrO2. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 94:1875–1880. https://doi.org/10.1039/A801055B
Kohno Y, Tanaka T, Funabiki T, Yoshida S (2000) Photoreduction of CO2 with H2 over ZrO2. A study on interaction of hydrogen with photoexcited CO2. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:2635–2639. https://doi.org/10.1039/B001642J
Kudo A, Miseki Y (2009) Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem Soc Rev 38:253–278. https://doi.org/10.1039/B800489G
Kumar A, Raizada P, Kumar Thakur V, Saini V, Aslam Parwaz Khan A, Singh N, Singh P (2021) An overview on polymeric carbon nitride assisted photocatalytic CO2 reduction: strategically manoeuvring solar to fuel conversion efficiency. Chem Eng Sci 230:116219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.116219
Li X, Chen J, Li H, Li J, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhou J (2011) Photoreduction of CO2 to methanol over Bi2S3/CdS photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. J Nat Gas Chem 20:413–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-9953(10)60212-5
Li K, Peng B, Peng T (2016a) Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 conversion to solar fuels. ACS Catal 6:7485–7527. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b02089
Li M, Zhang L, Wu M, Du Y, Fan X, Wang M, Zhang L, Kong Q, Shi J (2016b) Mesostructured CeO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposites: remarkably enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction by mutual component activations. Nano Energy 19:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.11.010
Li X, Wu Y, Zhang S, Cai B, Gu Y, Song J, Zeng H (2016c) CsPbX3 Quantum dots for lighting and displays: room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 26:2435–2445. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201600109
Li S, Miao P, Zhang Y, Wu J, Zhang B, Du Y, Han X, Sun J, Xu P (2021a) Recent advances in plasmonic nanostructures for enhanced photocatalysis and electrocatalysis. Adv Mater 33:2000086. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000086
Li X, Kawai K, Fujitsuka M, Osakada Y (2021b) COF-based photocatalyst for energy and environment applications. Surf Interf 25:101249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101249
Li X, Zhang J, Dai K, Fan K, Liang C (2021c) Cd3(C3N3S3)2 Polymer/Sn Schottky heterojunction for broadband-solar highly selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Sol RRL 5:2100788. https://doi.org/10.1002/solr.202100788
Li Z, Raziq F, Liu C, Bai L, Jing L (2017) Surface-engineering strategies for g-C3N4 as efficient visible-light photocatalyst. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 6:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2017.05.006
Liang L, Lei F, Gao S, Sun Y, Jiao X, Wu J, Qamar S, Xie Y (2015) Single unit cell bismuth tungstate layers realizing robust solar CO2 reduction to methanol. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:13971–13974. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201506966
Liao Y, Hu Z, Gu Q, Xue C (2015) Amine-functionalized ZnO nanosheets for efficient CO2 capture and photoreduction. Molecules 20:18847–18855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201018847
Lin L-Y, Nie Y, Kavadiya S, Soundappan T, Biswas P (2017) N-doped reduced graphene oxide promoted nano TiO2 as a bifunctional adsorbent/photocatalyst for CO2 photoreduction: Effect of N species. Chem Eng J 316:449–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.125
Liu H, Wang M, Wang Y, Liang Y, Cao W, Su Y (2011) Ionic liquid-templated synthesis of mesoporous CeO2–TiO2 nanoparticles and their enhanced photocatalytic activities under UV or visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A 223:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.06.014
Liu L, Zhao C, Zhao H, Pitts D, Li Y (2013) Porous microspheres of MgO-patched TiO2 for CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor: temperature-dependent activity and stability. Chem Commun 49:3664–3666. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC39054C
Liu B, Zhao X, Terashima C, Fujishima A, Nakata K (2014) Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of heterogeneous photocatalysis for semiconductor systems. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8751–8760. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55317E
Liu L, Zhao C, Miller JT, Li Y (2017) Mechanistic study of CO2 photoreduction with H2O on Cu/TiO2 nanocomposites by in situ X-ray absorption and infrared spectroscopies. J Phys Chem C 121:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10835
Liu X, Ye M, Zhang S, Huang G, Li C, Yu J, Wong PK, Liu S (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic CO2 valorization over TiO2 hollow microspheres by synergetic surface tailoring and Au decoration. J Mater Chem A 6:24245–24255. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA09661A
Liu X, Chen Y, Wang Q, Li L, Du L, Tian G (2021) Improved charge separation and carbon dioxide photoreduction performance of surface oxygen vacancy-enriched zinc ferrite@ titanium dioxide hollow nanospheres with spatially separated cocatalysts. J Colloid Interf Sci 599:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.104
Low J, Yu J, Ho W (2015) Graphene-based photocatalysts for CO2 reduction to solar fuel. J Phys Chem Lett 6:4244–4251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01610
Low J, Yu J, Jaroniec M, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdi AA (2017) Heterojunction photocatalysts. Adv Mater 29:1601694. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201601694
Mai H, Le TC, Chen D, Winkler DA, Caruso RA (2022) Machine learning for electrocatalyst and photocatalyst design and discovery. Chem Rev 122:13478–13515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00061
Masih D, Ma Y, Rohani S (2017) Graphitic C3N4 based noble-metal-free photocatalyst systems: a review. Appl Catal B 206:556–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.061
Mateo D, Cerrillo JL, Durini S, Gascon J (2021) Fundamentals and applications of photo-thermal catalysis. Chem Soc Rev 50:2173–2210. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS00357C
Mehregan S, Hayati F, Mehregan M, Isari AA, Jonidi Jafari A, Giannakis S, Kakavandi B (2022) Exploring the visible light–assisted conversion of CO2 into methane and methanol, using direct Z-scheme TiO2@g-C3N4 nanosheets: synthesis and photocatalytic performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:74951–74966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21048-6
Meng X, Ouyang S, Kako T, Li P, Yu Q, Wang T, Ye J (2014) Photocatalytic CO2 conversion over alkali modified TiO2 without loading noble metal cocatalyst. Chem Commun 50:11517–11519. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC04848B
Mkhalid IA, Mohamed RM, Ismail AA, Alhaddad M (2021) Z-scheme g-C3N4 nanosheet photocatalyst decorated with mesoporous CdS for the photoreduction of carbon dioxide. Ceram Int 47:17210–17219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.032
Mousavi M, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pouran SR (2018) Review on magnetically separable graphitic carbon nitride-based nanocomposites as promising visible-light-driven photocatalysts. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29:1719–1747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8166-x
Muñoz-Batista MJ, Kubacka A, Gómez-Cerezo MN, Tudela D, Fernández-García M (2013) Sunlight-driven toluene photo-elimination using CeO2-TiO2 composite systems: a kinetic study. Appl Catal B 140:626–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.071
Nguyen TDC, Nguyen TPLC, Mai HTT, Dao V-D, Nguyen MP (2017) Novel photocatalytic conversion of CO2 by vanadium-doped tantalum nitride for valuable solar fuel production. J Catal 352:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.04.020
Ochedi FO, Liu D, Yu J, Hussain A, Liu Y (2021) Photocatalytic, electrocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:941–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01131-5
Ola O, Maroto-Valer MM (2015) Review of material design and reactor engineering on TiO2 photocatalysis for CO2 reduction. J Photochem Photobiol C 24:16–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.06.001
Ou M, Tu W, Yin S, Xing W, Wu S, Wang H, Wan S, Zhong Q, Xu R (2018) Amino-assisted anchoring of CsPbBr 3 perovskite quantum dots on porous g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:13570–13574. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201808930
Ozin GA (2015) Throwing new light on the reduction of CO2. Adv Mater 27:1957–1963. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500116
Pan Y-X, Sun Z-Q, Cong H-P, Men Y-L, Xin S, Song J, Yu S-H (2016) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction highly enhanced by oxygen vacancies on Pt-nanoparticle-dispersed gallium oxide. Nano Res 9:1689–1700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1063-4
Pan Y-X, You Y, Xin S, Li Y, Fu G, Cui Z, Men Y-L, Cao F-F, Yu S-H, Goodenough JB (2017) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction by carbon-coated indium-oxide nanobelts. J Am Chem Soc 139:4123–4129. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b00266
Park H-a, Choi JH, Choi KM, Lee DK, Kang JK (2012) Highly porous gallium oxide with a high CO2 affinity for the photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into methane. J Mater Chem 22:5304–5307. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30337J
Paul K, Giri P (2018) Plasmonic metal and semiconductor nanoparticle decorated TiO2-based photocatalysts for solar light driven photocatalysis. In: Wandelt K (ed) Encyclopedia of interfacial chemistry. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 786–794
Peng L, Chang S, Liu Z, Fu Y, Ma R, Lu X, Zhang F, Zhu W, Kong L, Fan M (2021) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic CO2 reduction over ketoenamine-based covalent organic frameworks: role of the host functional groups. Catal Sci Technol 11:1717–1724. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CY02061C
Pera-Titus M (2014) Porous inorganic membranes for CO2 capture: present and prospects. Chem Rev 114:1413–1492. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400237k
Pham T-D, Lee B-K (2017) Novel capture and photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into solar fuels by metals co-doped TiO2 deposited on PU under visible light. Appl Catal A 529:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2016.10.019
Qiao J, Liu Y, Hong F, Zhang J (2014) A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem Soc Rev 43:631–675. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60323G
Qin Z, Tian H, Su T, Ji H, Guo Z (2016) Soft template inducted hydrothermal BiYO3 catalysts for enhanced formic acid formation from the photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. RSC Adv 6:52665–52673. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA03340G
Ran J, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2018) Cocatalysts in semiconductor-based photocatalytic CO2 reduction: achievements, challenges, and opportunities. Adv Mater 30:1704649. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704649
Razali NAM, Lee KT, Bhatia S, Mohamed AR (2012) Heterogeneous catalysts for production of chemicals using carbon dioxide as raw material: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:4951–4964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.012
Ren X, Gao M, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Cao X, Wang B, Wang X (2020) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on BiOX: Effect of halogen element type and surface oxygen vacancy mediated mechanism. Appl Catal B 274:119063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119063
Ribeiro CS, Lansarin MA (2021) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Bi2WO6 with PVP addition for CO2 reduction into ethanol under visible light. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:23667–23674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10765-5
Sakakura T, Choi J-C, Yasuda H (2007) Transformation of carbon dioxide. Chem Rev 107:2365–2387. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068357u
Schenk PM, Thomas-Hall SR, Stephens E, Marx UC, Mussgnug JH, Posten C, Kruse O, Hankamer B (2008) Second generation biofuels: high-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production. BioEnergy Res 1:20–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-008-9008-8
Serpone N, Lawless D, Khairutdinov R (1995) Size effects on the photophysical properties of colloidal anatase TiO2 particles: size quantization versus direct transitions in this indirect semiconductor? J Phys Chem 99:16646–16654. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100045a026
Shih CF, Zhang T, Li J, Bai C (2018) Powering the future with liquid sunshine. Joule 2:1925–1949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.08.016
Silva LC, Anand M (2013) Probing for the influence of atmospheric CO2 and climate change on forest ecosystems across biomes. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 22:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2012.00783.x
Song J, Li J, Li X, Xu L, Dong Y, Zeng H (2015) Quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on inorganic perovskite cesium lead halides (CsPbX3). Adv Mater 27:7162–7167. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502567
Song Q, Zhou Y, Hu J, Zhou C, Shi X, Li D, Jiang D (2021) Synergistic effects of surface Lewis base/acid and nitrogen defect in MgAl layered double oxides/carbon nitride heterojunction for efficient photoreduction of carbon dioxide. Appl Surf Sci 563:150369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150369
Su T, Tian H, Qin Z, Ji H (2017) Preparation and characterization of Cu modified BiYO3 for carbon dioxide reduction to formic acid. Appl Catal B 202:364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.035
Sun Z, Yang Z, Liu H, Wang H, Wu Z (2014) Visible-light CO2 photocatalytic reduction performance of ball-flower-like Bi2WO6 synthesized without organic precursor: effect of post-calcination and water vapor. Appl Surf Sci 315:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.07.153
Szulejko JE, Kumar P, Deep A, Kim K-H (2017) Global warming projections to 2100 using simple CO2 greenhouse gas modeling and comments on CO2 climate sensitivity factor. Atmos Pollut Res 8:136–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.08.002
Tahir M, Tahir B, Amin NAS, Alias H (2016) Selective photocatalytic reduction of CO2 by H2O/H2 to CH4 and CH3OH over Cu-promoted In2O3/TiO2 nanocatalyst. Appl Surf Sci 389:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.155
Tan L-L, Ong W-J, Chai S-P, Mohamed AR (2017) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O over graphene oxide-supported oxygen-rich TiO2 hybrid photocatalyst under visible light irradiation: process and kinetic studies. Chem Eng J 308:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.050
Teramura K, Iguchi S, Mizuno Y, Shishido T, Tanaka T (2012) Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 in water over layered double hydroxides. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:8008–8011. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201201847
Thang NQ, Sabbah A, Chen L-C, Chen K-H, Hai LV, Thi CM, Viet PV (2021) Localized surface plasmonic resonance role of silver nanoparticles in the enhancement of long-chain hydrocarbons of the CO2 reduction over Ag-gC3N4/ZnO nanorods photocatalysts. Chem Eng Sci 229:116049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.116049
Tian J, Sang Y, Zhao Z, Zhou W, Wang D, Kang X, Liu H, Wang J, Chen S, Cai H (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic performances of CeO2/TiO2 nanobelt heterostructures. Small 9:3864–3872. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201202346
Toe CY, Tsounis C, Zhang J, Masood H, Gunawan D, Scott J, Amal R (2021) Advancing photoreforming of organics: highlights on photocatalyst and system designs for selective oxidation reactions. Energy Environ Sci 14:1140–1175. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EE03116J
Torelli DA, Francis SA, Crompton JC, Javier A, Thompson JR, Brunschwig BS, Soriaga MP, Lewis NS (2016) Nickel–gallium-catalyzed electrochemical reduction of CO2 to highly reduced products at low overpotentials. ACS Catal 6:2100–2104. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b02888
Truc NTT, Bach LG, Hanh NT, Pham T-D, Le Chi NTP, Tran DT, Nguyen MV (2019) The superior photocatalytic activity of Nb doped TiO2/g-C3N4 direct Z-scheme system for efficient conversion of CO2 into valuable fuels. J Colloid Interface Sci 540:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.005
Villarreal TL, Gómez R, Neumann-Spallart M, Alonso-Vante N, Salvador P (2004) Semiconductor photooxidation of pollutants dissolved in water: a kinetic model for distinguishing between direct and indirect interfacial hole transfer. I. Photoelectrochemical experiments with polycrystalline anatase electrodes under current doubling and absence of recombination. J Phys Chem B 108:15172–15181. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp049447a
Vu NN, Kaliaguine S, Do TO (2019) Critical aspects and recent advances in structural engineering of photocatalysts for sunlight-driven photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into fuels. Adv Funct Mater 29:1901825. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201901825
Wang Y, Li B, Zhang C, Cui L, Kang S, Li X, Zhou L (2013) Ordered mesoporous CeO2-TiO2 composites: highly efficient photocatalysts for the reduction of CO2 with H2O under simulated solar irradiation. Appl Catal B 130:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.019
Wang W-N, Soulis J, Yang YJ, Biswas P (2014) Comparison of CO2 photoreduction systems: a review. Aerosol Air Qual Res 14:533–549. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.09.0283
Wang C, Yang S, Chen X, Wen T, Yang HG (2017a) Surface-functionalized perovskite films for stable photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Mater Chem A 5:910–913. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA08812K
Wang W, Xu D, Cheng B, Yu J, Jiang C (2017b) Hybrid carbon@TiO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity. J Mater Chem A 5:5020–5029. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA11121A
Wang Y, Xia Q, Bai X, Ge Z, Yang Q, Yin C, Kang S, Dong M, Li X (2018) Carbothermal activation synthesis of 3D porous g-C3N4/carbon nanosheets composite with superior performance for CO2 photoreduction. Appl Catal B 239:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.08.018
Wang M, Shen M, Jin X, Tian J, Li M, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Li Y, Shi J (2019) Oxygen vacancy generation and stabilization in CeO2–x by Cu introduction with improved CO2 photocatalytic reduction activity. ACS Catal 9:4573–4581. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03975
Wang J, Wang J, Li N, Du X, Ma J, He C, Li Z (2020) Direct Z-Scheme 0D/2D heterojunction of CsPbBr 3 quantum dots/Bi2WO6 nanosheets for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interf 12:31477–31485. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c08152
Wang H-N, Zou Y-H, Sun H-X, Chen Y, Li S-L, Lan Y-Q (2021a) Recent progress and perspectives in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 reduction through a solid–gas mode. Coord Chem Rev 438:213906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213906
Wang J, Wang Y, Li G, Xiong Y, Zhang M, Zhang S, Zhong Q (2021b) Sodium doped flaky carbon nitride with nitrogen defects for enhanced photoreduction carbon dioxide activity. J Colloid Interf S 603:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.06.113
Wang Y, Xu Y, Wang Y, Qin H, Li X, Zuo Y, Kang S, Cui L (2016a) Synthesis of Mo-doped graphitic carbon nitride catalysts and their photocatalytic activity in the reduction of CO2 with H2O. Catal Commun 74:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2015.10.029
Wang Y, Zhao J, Wang T, Li Y, Li X, Yin J, Wang C (2016b) CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor on highly dispersed CeO2/TiO2 catalysts: surface species and their reactivity. J Catal 337:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.12.030
Wu B, Liu D, Mubeen S, Chuong TT, Moskovits M, Stucky GD (2016) Anisotropic growth of TiO2 onto gold nanorods for plasmon-enhanced hydrogen production from water reduction. J Am Chem Soc 138:1114–1117. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b11341
Wu L-Y, Mu Y-F, Guo X-X, Zhang W, Zhang Z-M, Zhang M, Lu T-B (2019) Encapsulating perovskite quantum dots in iron-based metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:9491–9495. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201904537
Xiang X, Pan F, Li Y (2018) A review on adsorption-enhanced photoreduction of carbon dioxide by nanocomposite materials. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 1:6–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-017-0001-6
Xie S, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Deng W, Wang Y (2014) MgO-and Pt-promoted TiO2 as an efficient photocatalyst for the preferential reduction of carbon dioxide in the presence of water. ACS Catal 4:3644–3653. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs500648p
Xu Y-F, Yang M-Z, Chen B-X, Wang X-D, Chen H-Y, Kuang D-B, Su C-Y (2017) A CsPbBr 3 perovskite quantum dot/graphene oxide composite for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J Am Chem Soc 139:5660–5663. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b00489
Yan SC, Ouyang SX, Gao J, Yang M, Feng JY, Fan XX, Wan LJ, Li ZS, Ye JH, Zhou Y (2010) A room-temperature reactive-template route to mesoporous ZnGa2O4 with improved photocatalytic activity in reduction of CO2. Angew Chem 122:6544–6548. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201003270
Yan L, Xu J, Wang F, Meng S (2018) Plasmon-induced ultrafast hydrogen production in liquid water. J Phys Chem Lett 9:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b02957
Yang P, Wang R, Zhuzhang H, Titirici M-M, Wang X (2020) Photochemical construction of nitrogen-containing nanocarbons for carbon dioxide photoreduction. ACS Catal 10:12706–12715. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c03607
Yang S, Sa R, Zhong H, Lv H, Yuan D, Wang R (2022) Microenvironments enabled by covalent organic framework linkages for modulating active metal species in photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Adv Funct Mater 32:2110694. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202110694
Yoshida S, Kohno Y (2001) A new type of photocatalysis initiated by photoexcitation of adsorbed carbon dioxide on ZrO2. Catal Surv Jpn 4:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011403320301
Yu J, Jin J, Cheng B, Jaroniec M (2014) A noble metal-free reduced graphene oxide–CdS nanorod composite for the enhanced visible-light photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to solar fuel. J Mater Chem A 2:3407–3416. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14493C
Yu B, Zhou Y, Li P, Tu W, Li P, Tang L, Ye J, Zou Z (2016) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over Ag/TiO2 nanocomposites prepared with a simple and rapid silver mirror method. Nanoscale 8:11870–11874. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR02547A
Yu S, Wilson AJ, Heo J, Jain PK (2018) Plasmonic control of multi-electron transfer and C-C coupling in visible-light-driven CO2 reduction on Au nanoparticles. Nano Lett 18:2189–2194. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b05410
Zeng S, Kar P, Thakur UK, Shankar K (2018) A review on photocatalytic CO2 reduction using perovskite oxide nanomaterials. Nanotechnology 29:052001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa9fb1
Zhang L, Li N, Jiu H, Qi G, Huang Y (2015) ZnO-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as efficient photocatalysts for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Ceram Int 41:6256–6262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.044
Zhang H, Wei J, Dong J, Liu G, Shi L, An P, Zhao G, Kong J, Wang X, Meng X (2016) Efficient visible-light-driven carbon dioxide reduction by a single-atom implanted metal–organic framework. Angew Chem 128:14522–14526. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201608597
Zhang T, Low J, Koh K, Yu J, Asefa T (2018) Mesoporous TiO2 comprising small, highly crystalline nanoparticles for efficient CO2 reduction by H2O. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:531–540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02827
Zhang M, Lu M, Lang ZL, Liu J, Liu M, Chang JN, Li LY, Shang LJ, Wang M, Li SL (2020) Semiconductor/covalent-organic-framework Z-scheme heterojunctions for artificial photosynthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:6500–6506. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202000929
Zhang Z-W, Guo R-T, Tang J-Y, Miao Y-F, Gu J-W, Pan W-G (2021) Fabrication of Bi-BiOCl/MgIn2S4 heterostructure with step-scheme mechanism for carbon dioxide photoreduction into methane. J CO2 Util 45:101453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2021.101453
Zhang W, Huang W, Tan J, Guo Q, Wu B (2022) Heterogeneous catalysis mediated by light, electricity and enzyme via machine learning: paradigms, applications and prospects. Chemosphere 308:136447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136447
Zheng Y, Zhang W, Li Y, Chen J, Yu B, Wang J, Zhang L, Zhang J (2017) Energy related CO2 conversion and utilization: advanced materials/nanomaterials, reaction mechanisms and technologies. Nano Energy 40:512–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.08.049
Zhu X-G, Long SP, Ort DR (2010) Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:235–261. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112206
Zhu X, Ji H, Yi J, Yang J, She X, Ding P, Li L, Deng J, Qian J, Xu H (2018a) A specifically exposed cobalt oxide/carbon nitride 2D heterostructure for carbon dioxide photoreduction. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:17394–17400. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b04123
Zhu Z, Huang W-R, Chen C-Y, Wu R-J (2018b) Preparation of Pd–Au/TiO2–WO3 to enhance photoreduction of CO2 to CH4 and CO. J CO2 Util 28:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2018.10.006
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52076134, 51676127, 51436005, and 51176118), the National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFC0205200, 2016YFC0208000, and 2017YFB0103501), the National Engineering Laboratory for Mobile Source Emission Control Technology (NELMS2017A07), the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Young Scientists (51306115), the Low Speed Marine Engine Project (CDGC01-KT1203), and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars of State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yujun Chen carried out writing—original draft preparation, editing and polishing, and validation. Bin Guan carried out conceptualization, methodology, writing—reviewing, and supervision. Xingze Wu wrote and prepared the original draft. Jiangfeng Guo wrote and prepared the original draft. Zeren Ma wrote and prepared the original draft. Jinhe Zhang wrote and prepared the original draft. Xing Jiang wrote and prepared the original draft. Shibo Bao wrote and prepared the original draft. Yiyan Cao wrote and prepared the original draft. Chengdong Yin wrote and prepared the original draft. Di Ai wrote and prepared the original draft. Yuxuan Chen wrote and prepared the original draft. He Lin was supervised. Zhen Huang was supervised.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This is not applicable.
Consent for publication
This is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Guan, B., Wu, X. et al. Research status, challenges and future prospects of renewable synthetic fuel catalysts for CO2 photocatalytic reduction conversion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 11246–11271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24686-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24686-y