Abstract
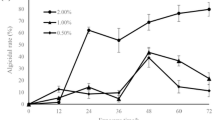
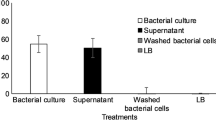
Heterosigma akashiwo (H. akashiwo), a harmful algal species, has been a global environmental problem. Extracellular algicidal compounds (EACs) extracted from Bacillus sp. B1 exhibited algicidal effects against H. akashiwo. However, little is known about the algicidal mechanism and metabolic process. In this study, metabolomics and physiological analyses were combined to investigate the cellular responses of H. akashiwo when treated with EACs. The results indicated that EACs at 10% (vEACs/vsample) showed more than 90% inhibition of H. akashiwo. EAC treatment resulted in excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in algal cells, causing stress responses such as inhibition of photosynthetic pigment synthesis, reduction of sugar synthesis, imbalance of osmotic pressure in the cell membrane, disruption of cell size and morphology, and eventual cell death. The results reveal the underlying mechanism of the algicidal process and provide new insights into algae-bacteria interactions and the application of metabolomics to algal research.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An G, Li J, Lu H, Guo Z (2022) Nitrogen-dependent luteolin effect on Microcystis growth and microcystin-pollution risk — novel mechanism insights unveiled by comparative proteomics and gene expression. Environ Pollut 311:119848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119848
Anand V, Singh PK, Banerjee C, Shukla P (2017) Proteomic approaches in microalgae: perspectives and applications. 3 Biotech 7:197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0831-5
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuar Coast 25:704–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02804901
Bachhawat AK, Yadav S (2018) The glutathione cycle: glutathione metabolism beyond the γ-glutamyl cycle. IUBMB Life 70(7):585–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1756
Baek SH, Jang M-C, Son M, Kim SW, Cho H, Kim YO (2013) Algicidal effects on Heterosigma akashiwo and Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae), and toxic effects on natural plankton assemblages by a thiazolidinedione derivative TD49 in a microcosm. J Appl Phycol 25:1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9905-2
Brussaard CPD (2004) Viral control of phytoplankton populations—a review. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51(2):125–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2004.tb00537.x
Chae Y, Kim D, An Y-J (2016) Effect of fluoride on the cell viability, cell organelle potential, and photosynthetic capacity of freshwater and soil algae. Environ Pollut 219:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.063
Chen S, Zheng T, Ye C, Huannixi W, Yakefu Z, Meng Y, Peng X, Tian Z, Wang J, Ma Y, Yang Y, Ma Z, Zuo Z (2018) Algicidal properties of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fresh leaves and their main compounds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.115
Chen Y, Luo G, Chen S, Zhang D, Xie W, Wang Z, Zheng W, Xu H (2021) The potential of prodigiosin for control of Prorocentrum donghaiense blooms: algicidal properties and acute toxicity to other marine organisms at various trophic levels. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 228:112913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112913
Chia MA, Cordeiro-Araújo MK, Lorenzi AS, Bittencourt-Oliveira M, do C, (2017) Cylindrospermopsin induced changes in growth, toxin production and antioxidant response of Acutodesmus acuminatus and Microcystis aeruginosa under differing light and nitrogen conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.015
Choi I, Son H, Baek J-H (2021) Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates: regulators of immune responses. Life 11(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010069
Dai W, Chen X, Wang X, Xu Z, Gao X, Jiang C, Deng R, Han G (2018) The algicidal fungus Trametes versicolor F21a eliminating blue algae via genes encoding degradation enzymes and metabolic pathways revealed by transcriptomic analysis. Front Microbiol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00826
Eigemann F, Hilt (nee Körner) S, Schmitt-Jansen M (2013) Flow cytometry as a diagnostic tool for the effects of polyphenolic allelochemicals on phytoplankton. Aquat Bot 104:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2012.10.005
Engesmo A, Eikrem W, Seoane S, Smith K, Edvardsen B, Hofgaard A, Tomas CR (2016) New insights into the morphology and phylogeny of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae), with the description of Heterosigma minor sp. nov. Phycologia 55(3):279–294. https://doi.org/10.2216/15-115.1
Gechev TS, Van Breusegem F, Stone JM et al (2006) Reactive oxygen species as signals that modulate plant stress responses and programmed cell death. BioEssays 28(11):1091–1101. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20493
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8714-9_3
Guo X, Liu X, Wu L, Pan J, Yang H (2016) The algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp. strain GLY-2107 against bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa is regulated by N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. Environ Microbiol 18(11):3867–3883. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13346
Helliwell KE, Pandhal J, Cooper MB, Longworth J, Kudahl UJ, Russo DA, Tomsett EV, Bunbury F, Salmon DL, Smirnoff N, Wright PC, Smith AG (2018) Quantitative proteomics of a B12-dependent alga grown in coculture with bacteria reveals metabolic tradeoffs required for mutualism. New Phytol 217(2):599–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14832
Hou S, Shu W, Tan S, Zhao L, Yin P (2016) Exploration of the antioxidant system and photosynthetic system of a marine algicidal Bacillus and its effect on four harmful algal bloom species. Can J Microbiol 62(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2015-0425
Huang L, Lu D, Zhang P, Diao J, Zhou Z (2012) Enantioselective toxic effects of hexaconazole enantiomers against Scenedesmus obliquus. Chirality 24(8):610–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22018
Hyka P, Lickova S, Přibyl P, Melzoch K, Kovar K (2013) Flow cytometry for the development of biotechnological processes with microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 31(1):2–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.04.007
Jahnke A, Mayer P, Schäfer S, Witt G, Haase N, Escher BI (2016) Strategies for transferring mixtures of organic contaminants from aquatic environments into bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5424–5431. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04687
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol Pflanzen 167(2):191–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-3796(17)30778-3
Kastaniotis AJ, Autio KJ, Kerätär JM, Monteuuis G, Mäkelä AM, Nair RR, Pietikäinen LP, Shvetsova A, Chen Z, Hiltunen JK (2017) Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis, fatty acids and mitochondrial physiology. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.08.011
Kempton J, Keppler CJ, Lewitus A, Shuler A, Wilde S (2008) A novel Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) bloom extending from a South Carolina bay to offshore waters. Harmful Algae 7(2):235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2007.08.003
Khan S, Arakawa O, Onoue Y (1997) Neurotoxins in a toxic red tide of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae) in Kagoshima Bay, Japan. Aquac Res 28(1):9–14. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.1997.t01-1-00823.x
Kim S-C, Lee D-K (2005) Preparation of TiO2-coated hollow glass beads and their application to the control of algal growth in eutrophic water. Microchem J 80(2):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2004.07.008
Lee E-H, Lee S-W, Saraf RF (2014) Noninvasive measurement of membrane potential modulation in microorganisms: photosynthesis in green algae. ACS Nano 8(1):780–786. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn405437z
Li Y, Zhu H, Guan C, Zhang H, Guo J, Chen Z, Cai G, Lei X, Zheng W, Tian Y, Xiong X, Zheng T (2014) Towards molecular, physiological, and biochemical understanding of photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in the toxic Alexandrium tamarense induced by a marine bacterium. Appl Microbiol Biot 98:4637–4652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5578-x
Li Y, Lei X, Zhu H, Zhang H, Guan C, Chen Z, Zheng W, Fu L, Zheng T (2016) Chitinase producing bacteria with direct algicidal activity on marine diatoms. Sci Rep 6:21984. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21984
Li D, Kang X, Chu L, Wang Y, Song X, Zhao X, Cao X (2021) Algicidal mechanism of Raoultella ornithinolytica against Microcystis aeruginosa: antioxidant response, photosynthetic system damage and microcystin degradation. Environ Pollut 287:117644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117644
Lin Z, Chen B, Zhao L (2020) Fluorescence-based bioassays with dose–response curve and relative potency in measuring algicidal virulence of Bacillus sp. B1 exudates against Heterosigma akashiwo. Sci Total Environ 724(1):137691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137691
Long M, Tallec K, Soudant P, Grand FL, Donval A, Lambert C, Sarthou G, Jolley DF, Hégaret H (2018) Allelochemicals from Alexandrium minutum induce rapid inhibition of metabolism and modify the membranes from Chaetoceros muelleri. Algal Res 35:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.09.023
Lu L, Niu X, Zhang D, Ma J, Zheng X, Xiao H, Huang X, Lin Z, Hu H (2021) The algicidal efficacy and the mechanism of Enterobacter sp EA-1 on Oscillatoria dominating in aquaculture system. Environ Res 197:111105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111105
Lyu P, Li H, Zheng X, Zhang H, Wang C, Qin Y, Xia B, Wang D, Xu S, Zhuang X (2022) Oxidative stress of Microcystis aeruginosa induced by algicidal bacterium Stenotrophomonas sp. KT48. Appl Microbiol Biot 106:4329–4340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11959-2
Martín-González A, Díaz S, Borniquel S, Gallego A, Gutiérrez JC (2006) Cytotoxicity and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by ciliated protozoa isolated from urban wastewater treatment plants. Res Microbiol 157(2):108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2005.06.005
Mayali X, Azam F (2004) Algicidal bacteria in the sea and their impact on algal blooms. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2004.tb00538.x
Nam S-H, An Y-J (2015) Cell size and the blockage of electron transfer in photosynthesis: proposed endpoints for algal assays and its application to soil alga Chlorococcum infusionum. Chemosphere 128:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.005
Nam K-H, Kim Y-J, Moon YS, Pack I-S, Kim C-G (2017) Salinity affects metabolomic profiles of different trophic levels in a food chain. Sci Total Environ 599–600(1):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.003
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60(3):324–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.06.010
Quan H, Zhang Y, Yin P, Zhao L (2021) Effects of two algicidal substances, ortho-tyrosine and urocanic acid, on the growth and physiology of Heterosoigma akashiwo. Environ Pollut 284:117004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117004
Shetty P, Gitau MM, Maróti G (2019) Salinity stress responses and adaptation mechanisms in eukaryotic green microalgae. Cells 8(12):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121657
Sun R, Sun P, Zhang J, Esquivel-Elizondo S, Wu Y (2018) Microorganisms-based methods for harmful algal blooms control: a review. Bioresour Technol 248:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.175
van Tol HM, Amin SA, Armbrust EV (2017) Ubiquitous marine bacterium inhibits diatom cell division. ISME J 11:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.112
Wang R, Liu Q (2022) Responses of bloom-forming Heterosigma akashiwo to allelochemical linoleic acid: growth inhibition, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.793567
Wang R, Hua M, Yu Y, Zhang M, Xian Q-M, Yin D-Q (2016) Evaluating the effects of allelochemical ferulic acid on Microcystis aeruginosa by pulse-amplitude-modulated (PAM) fluorometry and flow cytometry. Chemosphere 147:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.109
Wang R, Xue Q, Wang J, Tan L, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Anderson DM (2017) Effects of an allelochemical in Phaeodactylum tricornutum filtrate on Heterosigma akashiwo: morphological, physiological and growth effects. Chemosphere 186:527–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.024
Wei P, Ma H, Fu H, Xu Z, Qu X (2022) Efficient inhibition of cyanobacteria M aeruginosa growth using commercial food-grade fumaric acid. Chemosphere 301:134659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134659
Yang K, Chen Q, Zhang D, Zhang H, Lei X, Chen Z, Li Y, Hong Y, Ma X, Zheng W, Tian Y, Zheng T, Xu H (2017) The algicidal mechanism of prodigiosin from Hahella sp KA22 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Rep 7:7750. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08132-5
Young T, Alfaro AC (2018) Metabolomic strategies for aquaculture research: a primer. Rev Aquacult 10(1):26–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12146
Yu X, Cai G, Wang H, Hu Z, Zheng W, Lei X, Zhu X, Chen Y, Chen Q, Din H, Xu H, Tian Y, Fu L, Zheng T (2018) Fast-growing algicidal Streptomyces sp. U3 and its potential in harmful algal bloom controls. J Hazard Mater 341:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.046
Yuan W, Lin X, Zhong S, Chen J, Wang Z, Sun J (2020) Enhanced pyruvic acid yield in an osmotic stress-resistant mutant of Yarrowia lipolytica. Electron J Biotechnol 44:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2020.01.002
Zhang H, Meng G, Mao F, Li W, He Y, Gin KY-H, NamOng C (2019) Use of an integrated metabolomics platform for mechanistic investigations of three commonly used algaecides on cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. J Hazard Mater 367:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.069
Zhang S, Zheng W, Wang H (2020) Physiological response and morphological changes of Heterosigma akashiwo to an algicidal compound prodigiosin. J Hazard Mater 385(5):121530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121530
Zhu X, Dao G, Tao Y, Zhan X, Hu H (2021) A review on control of harmful algal blooms by plant-derived allelochemicals. J Hazard Mater 401:123403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123403
Funding
The research is financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (grant number 21316072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuanyue Li and Zehong Lin designed the study. Xuanyue Li and Zehong Lin performed the experimental analysis. Xuanyue Li and Ling Zhao coordinated and wrote the manuscript. Ling Zhao obtained the funding. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lin, Z., Yuan, M. et al. The effects of extracellular algicidal compounds of Bacillus sp. B1 on Heterosigma akashiwo: a metabolomics approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 35635–35645 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24255-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24255-3