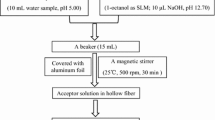
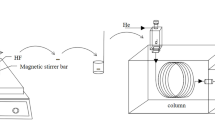
Abstract
To explore the mechanism of extraction and enrichment of three nitrophenol isomers by charge-transfer supramolecular synergistic three-phase microextraction system, a charge transfer supramolecular-mediated hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction (CTSM-HF-LPME) combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detector (HPLC–UV) method was established for the determination of real environmental water samples. In this study, the three nitrophenols (NPs) formed charge-transfer supramolecules with electron-rich hollow fibers, which promoted the transport of NPs in the three-phase extraction system and greatly increased the EFs of NPs. The relationships between the EFs of NPs and their solubility, pKa, apparent partition coefficient, equilibrium constant, and structural property parameters were investigated and discussed. At the same time, most of factors affecting the EFs of NPs were investigated and optimized, such as the type of extraction solvent, pH value of sample phase and acceptor phase, extraction time, and stirring speed. Under optimal conditions, the EFs of o-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, and p-nitrophenol were 163, 145, and 87, respectively. With good linearity in the range of 5 × 10−7 ~ 1 µg/mL, and the limit of detection of 0.1 pg/mL, the relative standard deviations of the method precision were lower than 7.4%, and the average recoveries were between 98.6 and 106.4%. This method had good selectivity and sensitivity, satisfactory precision, and accuracy and had been successfully applied to the trace detection of real water samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials will be provided under formal request.
References
Alcudia-León MC, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2011) Determination of phenols in waters by stir membrane liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr A 1218:2176–2181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.02.033
Ali N, Yadollah Y, Hasan B, Mohammad T (2018) Extraction and determination of trace amounts of three anticancer pharmaceuticals in urine by three-phase hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction based on two immiscible organic solvents followed by HPLC. J Sep Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201800183
Bishop EJ, Mitra S (2007) Measurement of nitrophenols in air samples by impinger sampling and supported liquid membrane micro-extraction. Anal Chim Acta 583:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.10.008
Boddu V, Kim S, Adkins J, Weimer E, Paul T, Damavarapu R (2017) Sensitive determination of nitrophenol isomers by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography in conjunction with liquid–liquid extraction. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2017.1381235
Chen C, Zhang Y, Shen J (2019) Study on relationship between nitrophenol degradation and its structure in bioelectrochemical system. Technol Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2019.02.010
Diuzheva A, Locatelli M, Tartaglia A, Goga M, Andruch V (2020) Application of liquid-phase microextraction to the analysis of plant and herbal samples. Phytochem Anal. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2939
Epa US (2014) Priority pollutant list. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/priority-pollutant-list-epa.pdf
Fang H, Ting D, Xinyu J (2013) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of phenolic compounds using solidified floating organic droplets, and their determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0937-8
Faraji M, Noormohammadi F, Adeli M (2020) Preparation of a ternary deep eutectic solvent as extraction solvent for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of nitrophenols in water samples. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103948
Feng S, Mu Z, Liu H, Huang J, Li X, Yang Y (2019) A novel application of fluorine doped carbon dots combining vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of 4-nitrophenol with spectrofluorimetric method. J Fluoresc 29:1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02427-8
Fikarova K, Horstkotte B, Sklenarova H, Svec F, Solich P (2019) Automated continuous-flow in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of mono-nitrophenols from large sample volumes using a novel approach to multivariate spectral analysis. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.044
Geng LA, Lin LA, Pjw B, Wx A, Xin LA, Le CA, Wl C, Xz C, Cx C (2021) A simple and rapid head space-single drop microextraction-‘spectro-pipette’ (HS-SDME-SP) method for the on-site measurement of arsenic species in natural waters. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106441
Han SY, Qiao JQ, Zhang YY, Lian HZ, Xin G (2012) Determination of n-octanol/water partition coefficients of weak ionizable solutes by RP-HPLC with neutral model compounds. Talanta 97:355–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.04.045
Harrison M, Barra S, Borghesi D, Vione D, Arsene C, Olariu RI (2005) Nitrated phenols in the atmosphere: a review. Atmos Environ 39:231–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.09.044
Hashemi B, Zohrabi P, Kim KH, Shamsipur M, Deep A, Hong J (2017) Recent advances in liquid-phase microextraction techniques for the analysis of environmental pollutants. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.08.014
Javadi T, Farajmand B, Yaftian MR, Zamani A (2019) Homogenizer assisted dispersive liquid-phase microextraction for the extraction-enrichment of phenols from aqueous samples and determination by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1614:460733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460733
Liang Z, Lee HK (2001) Liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction of nitrophenols with a hollow fiber membrane prior to capillary liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 924:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)00906-2
Liang G, Lee HK (2011) Ionic liquid based three-phase liquid–liquid–liquid solvent bar microextraction for the determination of phenols in seawater samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:4299–4306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.05.031
Lin CY, Huang SD (2008) Determination of nitrophenols in water using dynamic liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction under non-equilibrium consideration. J Chin Chem Soc 55:740–749. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.200800111
Ma WY, Xing RR, Hu S, Chen X, Bai XH (2014) A novel hollow fiber/graphene oxide/solvent bar microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for preconcentration and determination of tanshinones and salvianolic acids in Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza. Anal Methods 6:7285–7293. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY00990H
Mei M, Huang X, Yu J, Yuan D (2015) Sensitive monitoring of trace nitrophenols in water samples using multiple monolithic fiber solid phase microextraction and liquid chromatographic analysis. Talanta 134:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.059
Mohammad M, Khataei Y, Yamini A, Nazaripour M, Karimi, (2018) Novel generation of deep eutectic solvent as an acceptor phase in three-phase hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for extraction and preconcentration of steroidal hormones from biological fluids. Talanta Int J Pure Appl Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.068
Núñez M, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Fontanals N (2017) Sample treatment for the determination of emerging organic contaminants in aquatic organisms. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.09.007
Ou J, Hu L, Hu L, Li X, Zou H (2006) Determination of phenolic compounds in river water with on-line coupling bisphenol A imprinted monolithic precolumn with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 69:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.12.003
Patsias J, Papadakis EN, Papadopoulou-Mourkidou E (2002) Analysis of phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides and their phenolic conversion products in soil by microwave assisted solvent extraction and subsequent analysis of extracts by on-line solid-phase extraction–liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 959:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00460-0
Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE (2005) Bioanalysis of drugs by liquid-phase microextraction coupled to separation techniques. J Chromatogr, b: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 817:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.08.034
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini M, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1116:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.007
Rutkowska M, Owczarek K, Guardia M, Potka-Wasylka J, Namie-Nik J (2017) Application of additional factors supporting the microextraction process. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.09.005
Salcedo GM, Kupski L, Degang L, Marube LC, Caldas SS, Primel EG (2019) Determination of fifteen phenols in wastewater from petroleum refinery samples using a dispersive liquid—liquid microextraction and liquid chromatography with a photodiode array detector. Microchem J 146:722–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.075
Salvatierra-Stamp VD, Muiz-Valencia R, Jurado JM, Ceballos-Magaa SG (2018) Hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of emerging contaminants in water samples. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.04.012
Sanagi MM, Miskam M, Wan A, Hermawan D, Aboul-Enein HY (2015) Determination of partition coefficient and analysis of nitrophenols by three-phase liquid-phase microextraction coupled with capillary electrophoresis. J Sep Sci 33:2131–2139. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201000172
Seebunrueng K, Dejchaiwatana C, Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2017) Development of supramolecular solvent based microextraction prior to high performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous determination of phenols in environmental water. RSC Adv 7:50143–50149. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07780G
Shuang Hu, Chen X, Wang R-Q, Yang Li, Bai X-H (2019) Natural product applications of liquid-phase microextraction. Trends Anal Chem 113:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.006
Silveira G, Loureno FR, Bruno V, Yonamine M (2020) Fast hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction as a greener alternative for the determination of N, N-dimethyltryptamine and harmala alkaloids in human urine. Front Chem 8.https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.558501
Song RJ, Pu FP, Zhou J, Sun JB, Zeng P, Zhang Q (2014) Three-phase hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction based on a magnetofluid for the analysis of aristolochic acids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400042
Sun JN, Chen J, Shi YP (2014) Multiple functional ionic liquids based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance chromatography for the determination of phenolic compounds in water samples. Talanta 125:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.03.013
Villar-Navarro M, Ramos-Payán M, Pérez-Bernal JL, Fernández-Torres R, Callejón-Mochón M, Má B-L (2012) Application of three phase hollow fiber based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the simultaneous HPLC determination of phenol substituting compounds (alkyl-, chloro- and nitrophenols). Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.020
Wang XY, Chen X, Bai XH (2009) Application of liquid phase microextraction with back extraction in the analysis of phenylpropionic acids. Chin J Anal Chem 37:35–40 (http://www.analchem.cn/article/id/7102)
Wang WT, Chen PS, Huang SD (2018) Characterization of nitrophenols in river, lake, and field water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Int J Environ Ence Technol :1–10https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1806-8
Xing R, Hu S, Chen X, Bai X, Feng M (2015) On-site sampling and sample-preparation approach with a portable sampler based on hollow-fiber/graphene bars for the microextraction of nitrobenzene compounds in lake water. J Sep Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201401129
Yu T, Chong M, Mohd A, Norhayati M, Tahir S (2018) A green solvent holder in electro-mediated microextraction for the extraction of phenols in water. Talanta Int J Pure Appl Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.068
Zhou F, Li X, Zeng Z (2005) Determination of phenolic compounds in wastewater samples using a novel fiber by solid-phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 538:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.009
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the College of Pharmacy, Shanxi Medical University, for providing scientific resources and equipment facilities in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Nature Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (Grant No. 201901D111207) and the National Natural science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81973287).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Zhaohui Wang, Dou-dou Xu, Xiaohong Bai, Shuang Hu, Rong-rong Xing, and Xuan Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zhaohui Wang, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All the participants in this study consented to participate in the cohort.
Consent to publish
Authors agree to publish the article in the Environmental Science and Pollution Research journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ester Heath
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zh., Xu, Dd., Bai, Xh. et al. A study on the enrichment mechanism of three nitrophenol isomers in environmental water samples by charge transfer supramolecular-mediated hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 18973–18984 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23409-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23409-7