Abstract
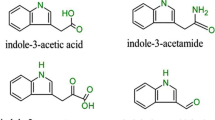
The beneficial effect of compost and compost tea on plant growth and protection is mainly associated with the microbial diversity and the presence of bacteria with plant growth–promoting effect. PGPR are considered as eco-friendly bio-fertilizers that may reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Three composts (AT, A10, and A30) were previously prepared from industrial wastes (olive mill wastewater, olive pomace, coffee ground, and phosphogypsum). In the present study, we isolated three bacterial strains from the compost teas. The phylogenetic identification of these bacterial strains (B.AT, B.A10, and B.A30) showed that they correspond to Serratia liquefaciens (B.AT and B.A10) and Achromobacter spanius (B.A30) species. A further characterization of the PGPR traits of these bacteria showed that they produce siderophore, exopolysaccharides, and IAA. Their effect on potato plant growth, yields, and tuber quality was performed under field culture conditions. Results showed that these strains can be characterized as PGPR, the best effect on potato plant growth was observed with Serratia liquefaciens (B.AT), the best yield and tuber quality was observed with Serratia liquefaciens (B.A10) while bacterial treatment with Achromobacter spanius (B.A30) is a Cd-tolerant PGPR.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaid-Ullah M, Hassan MN, Jamil M, Brader G, Shah MKN, Sessitsch A et al (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: an alternate way to improve yield and quality of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int J Agric Biol 17:51–60
Abdel-Rahman HM, Salem AA, Moustafa MMA, El-Garhy HAS (2017) A novice Achromobacter sp. EMCC1936 strain acts as a plant-growth-promoting agent. Acta Physiol Plant 39:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2360-6
Abo É, Laslo E, Szentes S, Lányi S, Mara G (2019) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: strategies to improve wheat growth and development under sustainable agriculture, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability. Springer, 1–17
Adesemoye AO, Torbert HA, Kloepper JW (2008) Enhanced plant nutrient use efficiency with PGPR and AMF in an integrated nutrient management system. Can J Microbiol 54:876–886
Adesemoye AO, Torbert HA, Kloepper JW (2010) Increased plant uptake of nitrogen from 15N-depleted fertilizer using plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Appl Soil Ecol 46:54–58
AFNOR (1991) Matières fertilisantes et supports de culture, Recueil des normes Françaises. AFNOR, Paris, p 713
Ahmad F, Ahmad I, Khan MS (2008) Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities. Microbiol Res 163:173–181
Aloo BN, Mbega ER, Makumba BA, Hertel R, Danel R (2020) Molecular identification and in vitro plant growth-promoting activities of culturable Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) rhizobacteria in Tanzania. Potato Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-020-09465-x.
Arnon DL (1949) A copper enzyme is isolated chloroplast polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaries. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Aznar A, Dellagi A (2015) New insights into the role of siderophores as triggers of plant immunity: what can we learn from animals? J Exp Bot 66:3001–3010
Backer R, Rokem JS, Ilangumaran G, Lamont J, Praslickova D, Ricci E (2018) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: context, mechanisms of action, and roadmap to commercialization of biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci 9:1473
Baglinière F, Jardin J, Gaucheron F, de Carvalho AF, Vanetti MCD (2017) Proteolysis of casein micelles by heat-stable protease secreted by Serratia liquefaciens leads to the destabilisation of UHT milk during its storage. Int Dairy J 68:38–45
Barra PJ, Inostroza NG, Acuña JJ, Mora ML, Crowley DE, Jorquera MA (2016) Formulation of bacterial consortia from avocado (Persea americana Mill.) and their effect on growth, biomass and superoxide dismutase activity of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Appl Soil Ecol 102:8
Basu A, Prasad P, Das SN, Kalam S, Sayyed RZ, Reddy MS, El Enshasy H (2021) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as green bioinoculants: recent developments, constraints, and prospects. Sustainability 13:1140
Beijerinck MW (1901) Ueber Oligonitophile Mikroben, Zentralblattfiir Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde, Infektionskrankheiten and Hygiene. Abteilung II 7:561–582
Belimov AA, Dodd IC, Hontzeas N, Theobald JC, Safronova VI, Davies WJ (2009) Rhizosphere bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase increase yield of plants grown in drying soil via both local and systemic hormone signalling. New Phytol 181:413–423
Bhardwaj D, Ansari MW, Sahoo RK, Tuteja N (2014) Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microb Cell Fact 13:1–10
Biswas JK, Banerjee A, Rai M, Naidu R, Biswas B, Vilthanaje M, Dash MC, Sarkar SK, Meers E (2018) Potential application of selected metal resistant phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from the gut of earthworm (Metaphire posthuma) in plant growth promotion. Geoderma 330:117–124
Bric JM, Bostock RM, Silverstone SE (1991) Rapid in situ assay for indoleacetic acid production by bacteria immobilized on nitrocellulose membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:535–538
Brown ME (1974) Seed and root bacterization. Annu Rev Phytopatol 12:181–197
Bruins MR, Kapil S, Oehme FW (2000) Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:198–207
Cakmakc R, Donmez MF, Erdogan U (2007) The effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on barley seedling growth, nutrient uptake, some soil properties, and bacterial counts. Turk J Agric for 31(Suppl 3):189–199
Cardinale M, Ratering S, Suarez C, Zapata Montoya AM, Geissler-Plaum R, Schnell S (2015) Paradox of plant growth promotion potential of rhizobacteria and their actual promotion effect on growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under salt stress. Microbiol Res 181:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.08.002
Castano R, Borrero C, Aviles M (2011) Organic matter fractions by SP-MAS 13C NMR and microbial communities involved in the suppression of Fusarium wilt in organic growth media. Biol Control 58:286–293
Chen M, Xu P, Zeng G, Yang C, Huang D, Zhang J (2015) Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol Adv 33:745–755
De Corato U (2020) Agricultural waste recycling in horticultural intensive farming systems by on-farm composting and compost based tea application improves soil quality and plant health: a review under the perspective of a circular economy. Sci Total Environ 738:139840
De Vleesschauwer D, Höfte M (2009) Rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance. Adv Bot Res 51:223–281
Devi KA, Pandey P, Sharma GD (2016) Plant growth-promoting endophyte serratia marcescens AL2-16 enhances the growth of achyranthes aspera L., a medicinal plant. HAYATI J Biosci 23:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjb.2016.12.006
Dey R, Pal K, Bhatt D, Chauhan S (2004) Growth promotion and yield enhancement of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol Res 159:371–394
Diánez F, Santos M, Tello JC (2005) Suppresion of soilborne pathogens by compost, suppresive effects of grape marc compost on phytopathogenics oomycetes. Acta Hort 697:441–460
Dimkpa CO, Merten D, Svatoš A, Büchel G, Kothe E (2009) Siderophores mediate reduced and increased uptake of cadmium by Streptomyces tendae F4 and sunflower (Helianthus annuus), respectively. J Appl Microbiol 107:1687–1696
Ding Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen S (2005) Isolation and identification of nitrogen fixing bacilli from plant rhizospheres in Beijing region. J Appl Microbiol 99:1271–2128
Dutta S, Podile AR (2010) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): the bugs to debug the root zone. Crit Rev Microbiol 36:232–244. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408411003766806
El-Esawi MA, Alaraidh IA, Alsahli AA, Alzahrani SM, Ali HM, Alayafi AA, Ahmad M (2018) Serratia liquefaciens KM4 improves salt stress tolerance in maize by regulating redox potential, ion homeostasis, leaf gas exchange and stress-related gene expression. Int J Mol Sci 19:3310
Elkoca E, Kantar F, Sahin F (2008) Influence of nitrogen fixing and phosphorus solubilising bacteria on the nodulation, plant growth and yield of chickpea. J Plant Nutr 31:157–171
Etesami H, Alikhani HA, Hosseini HM (2015) Indole-3-acetic acid and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: bacterial traits required in rhizosphere, rhizoplane and/or endophytic competence by beneficial bacteria. Bacterial metabolites in sustainable agroecosystem. Springer 183–258.
Gaskins MH, Albrecht SL, Hubbell DH (1985) Rhizosphere bacteria and their use to increase plant productivity: a review. Agric Ecosyst Environ 12:99–116
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374
Goswami D, Thakker JN, Dhandhukia PC (2016) Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): a review. Cogent food Agric. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2015.1127500
Günes A, Atatoglu N, Turan M, Esitken A, Ketterings QM (2009) Effects of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms on strawberry yield and nutrient concentrations. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:385–392. Yildirim et al. 2011
Guo LJ, Zhao B, An Q, Tian M (2016) Characteristics of a novel aerobic denitrifying bacterium, Enterobacter cloacae strain HNR. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178:947–959
Hamid S, Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Iqbal MN, Shakir M, Tahir M, Rasool A et al (2021) Bacillus subtilis Y16 and biogas slurry enhanced potassium to sodium ratio and physiology of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) to mitigate salt stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14344-0
Höflich G, Tappe E, Kuhn G, Wiehe W (1997) EinfluX associativer Rhizosph.arenbakterien auf die N.ahrstoffaufnahme und den Ertrag von Mais. Archiv Fuer Acker- Und Pflanzenbau Und Bodenkunde 41:323–333
Hoitink HAJ, Changa CM (2004) Managing soil-borne pathogens. Acta Hortic 635:87–92
Husen E (2003) Screening of soil bacteria for plant growth promotion activities in vitro. Indones J Agric Sci 4:27–31
Ilangumaran G, Smith DL (2017) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in amelioration of salinity stress: a systems biology perspective. Front Plant Sci 8:1768
Ingham ER (1999) What is compost tea? Part 1. Biocycle 40:74–75
Jacobson CB, Pasternak JJ, Glick BR (1994) Partial purification and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2. Can J Microbiol 40:1019–1025
Jha P, Kumar A (2009) Characterization of novel plant growth promoting endophytic bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans from wheat plant. Microb Ecol 58:179–188
Kammoun M, Ghorbel I, Charfeddine S, Kamoun L, Gargouri-Bouzid R, Nouri-Ellouz O (2017) The positive effect of phosphogypsumsupplemented composts on potato plant growth in the field and tuber yield. J Environ Manag 20:475–483
Khabou W, Trigui A, Ghorbel R, Bejar S (1996) L’amidon dans les rameaux d’olivier (Oleaeuropaea) Cv.“Chemlali de sfax” Etude comparative de deux methodes d ’hydrolyse. Olivea 61:57e61.
Khan H, Parmar N, Kahlon RS (2016) Pseudomonas-plant interactions I: plant growth promotion and defense-mediated mechanisms. In: Kahlon RS (ed) Pseudomonas: molecular and applied biology. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland
Kristin A, Miranda H (2013) The root microbiota—a fingerprint in the soil? Plant Soil 370:671–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1647-7
Kumar A, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R (2014) Isolation and characterization of PGPR and their effect on growth, yield and nutrient content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:121–128
Kumar V, Menon S, Agarwal H, Gopalakrishnan D (2017) Characterization and optimization of bacterium isolated from soil samples for the production of siderophores. Resource-Efficient Technologies 3(4):434–439
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp 115–175
Lifshitz R, Kloepper JM, Kozlowski M, Simonson C, Carlso J, Tipping EM, Zaleska I (1987) Growth promotion of canola (rapeseed) seedlings by a strain of Pseudomonas putida under gnotobiotic conditions. Can J Microbiol 33(5):390–395
Lugtenberg B, Kamilova F (2009) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 63:541–556
Ma Y, Prasad MNV, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2011) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnol Adv 29:248–258
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Zhang C, Freitas H (2016) Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growthpromoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. J Hazard Mater 320:36–44
Martínez-Viveros O, Jorquera MA, Crowley DE, Gajardo G, Mora ML (2010) Mechanisms and practical considerations involved in plant growth promotion by Rhizobacteria. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10(3):293–319
Meena VS, Mishra PK, Bisht JK, Pattanayak A (2017) Agriculturally important microbes for sustainable agriculture, Volume 2: Applications in crop production and protection. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978- 981-10-5343-6
Mefteh FB, Daoud A, Chenari BA, Alenezi FN, Luptakova L, Rateb ME, Kadri A, Gharsallah N, Belbahri L (2017) Fungal root microbiome from healthy and brittle leaf diseased date palm trees (Phoenix dactylifera L.) reveals a hidden untapped arsenal of antibacterial and broad spectrum antifungal secondary metabolites. Front Microbiol 8:307
Mehta S, Nautiyal CS (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 43:51–56
Meneses CHSG, Rouws LFM, Simões-Araújo JL, Vidal MS, Baldani JI (2011) Exopolysaccharide production is required for biofilm formation and plant colonization by the nitrogen-fixing endophyte Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 24:1448–1458. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-11-0127
Mengesha WK, Powel SM, Evans KJ, Barry KM (2017) Diverse microbial communities in non-aerated compost teas suppress bacterial wilt. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:49
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination ofreducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–8
Mody B, Bindra M, Modi V (1989). Arch Microbial 153:3842
Morales-Corts MR, Pérez-Sánchez R, Gómez-Sánchez MA (2018) Efficiency of garden waste compost teas on tomato growth and its suppressiveness against soilborne pathogens. Sci Agric 75:400–409
Morris WL, Ducreux L, Griffiths DW, Stewart D, Davies HV, Taylor MA (2004) Carotenogenesis during tuber development and storage in potato. J Exp Bot 55:975–982
Mukherjee A, Bhattacharjee P, Das R, Pal A, Paul AK (2017) Endophytic bacteria with plant growth promotingabilities from Ophioglossum reticulatum L. AIMS Microbiol 3(3):596
Naik PR, Sakthivel N (2006) Functional characterization of a novel hydrocarbonoclastic Pseudomonas sp. strain PUP6 with plant-growth-promoting traits and antifungal potential. Res Microbiol 157:538–546
Nassal D, Spohn M, Eltbany N, Jacquiod S, Smalla K, Marhan S, Kandeler E (2018) Effects of phosphorus-mobilizing bacteria on tomato growth and soil microbial activity. Plant Soil 427:17–37
Ndakidemi PA, Bambara S, Makoi JHJR (2011) Micronutrient uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by rhizobium inoculation, and the supply of molybdenum and lime. Plant Omics J 4(1):40–52
Notununu I, Moleleki L, Roopnarain A, Adeleke R (2022) Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the molecular responses of maize under drought and heat stresses: a review. Pedosphere 32(1):90–106
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, van Wees SCM, Bakker PA (2014) Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:347–375
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Soren T, Maiti TK (2017) Characterization of cadmium resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae MCC 3091 promoted rice seedling growth by alleviating phytotoxicity of cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24419–24437
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Maiti TK (2018) Alleviation of phytotoxic effects of cadmium on rice seedlings by cadmium resistant PGPR strain Enterobacter aerogenes MCC 3092. J Hazard Mater 351:317–329
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28:142–149
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574
Rodrìguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339
Rudrappa T, Biedrzycki ML, Bais HP (2008) Causes and consequences of plant-associated biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:153–66
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saleem A, Ebrahim MKH (2014) Production of amylase by fungi isolated from legume seeds collected in Almadinah Almunawwarah, Saudi Arabia. J Taibah Univ Sci 8:90–97
Samet M, Charfeddine M, Kamoun L, Nouri-Ellouze O, Gargouri-Bouzid R (2018) Effect of compost tea containing phosphogypsum on potato plant growth and protection against Fusarium solani infection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(19):18921–18937
Samet M, Karray F, Mhiri N, Kamoun L, Sayadi S, Gargouri-Bouzid R (2019) Effect of phosphogypsum addition in the composting process on the physico-chemical proprieties and the microbial diversity of the resulting compost tea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(21):21404–21415
Santos RMD, Rigobelo EC (2021) Growth-promoting potential of rhizobacteria isolated from sugarcane. Front Sustain Food Syst 5:105
Sarathambal C, Khankhane PJ, Gharde Y, Kumar B, Varun M, Arun S (2017) The effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on the growth, physiology, and Cd uptake of Arundo donax L. Int J Phytoremed 19:360–370
Sati D, Pande V, Pandey SC et al (2022) Recent advances in PGPR and molecular mechanisms involved in drought stress resistance. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00724-5
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Sessitsch A, Mitter B (2015) 21st century agriculture: integration of plant microbiomes for improved crop production and food security. Microb Biotechnol 8:32–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12180
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel WW, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194
Setiawati T, Mutmainnah L (2016) Solubilization of potassium containing mineral by microorganisms from sugar cane rhizosphere. Agric Sci Procedia 9:108–117
Sinha S, Mukherjee SK (2008) Cadmium-induced siderophore production by a high Cd-resistant bacterial strain relieved Cd toxicity in plants through root colonization. Curr Microbiol 56:55–60
Sirichaiwetchakul S, Sirithorn P, Manakasem Y (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, fruit yield and quality of cherry tomato under glasshouse conditions. Suranaree J Sci Tech 18:273–280
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tarnawski S, Hamelin J, Jossi M, Aragno M, Fromin N (2006) Phenotypic structure of Pseudomonas populations is altered under elevated pCO2 in the rhizosphere of perennial grasses. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1193–1201
Ullah A, Heng S, Munis MFH, Fahad S, Yang X (2015) Phytoremediation of heavy metal assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: a review. Environ Exp Bot 117:28–40
Ulloa-Ogaz AL, Muñoz-Castellanos LN, Nevárez-Moorillón GV (2015) Biocontrol of phytopathogens: antibiotic production as mechanism of control. In: Mendez-Vilas A (ed) The battle against microbial pathogens: basic science, technological advances and educational programs. Formatex Research Center, Spain, pp 305–309
Valetti L, Iriarte L, Farba A (2018) Growth promotion of rapeseed (Brassica napus) associated with the inoculation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Appl Soil Ecol 132:1–10
van Hullebush ED, Zandvoort MH, Lens PNL (2003) Metal immobilization by biofilms: mechanisms and analytical tools. Environ Sci Technol 2:9–33
Vejan P, Abdullah R, Khadiran T, Ismail S, Nasrulhaq Boyce A (2016) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability—a review. Molecules: 21–573.
Verma M, Satinder K, Brar RD, Tyagi RY, Surampalli J, Valero R (2007) Antagonistic fungi, Trichoderma spp. panoply of biological control. Biochem Eng J 37:1–20
Voisard C, Keel C, Haas D, Defago H (1989) Cyanide production by Pseudomonas fluorescens helps suppress black root of tobacco under gnotobiotic conditions. EMBO J 8:351–358
Walworth JL, Muniz JE (1993) A compendium of tissue nutrient concentration for field-grown potatoes. Am Potato J 70:570–597
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Welsch TT, Gillock ET (2011) Triclosan-resistant bacteria isolated from feedlot and residential soils. J Environ Sci Health Part A 46(4):436–440
Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu CM (2009) Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci 14:1–4
Yildirim E, Karlidag H, Turan M, Dursun A, Goktepe F (2011) Growth, nutrient uptake, and yield promotion of broccoli by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria with manure. Hort Sci 46:932–936
Zahir ZA, Zafar-ul-Hye M, Sajjad S, Naveed M (2011) Comparative effectiveness of Pseudomonas and Serratia sp. containing ACC-deaminase for coinoculation with Rhizobium leguminosarum to improve growth, nodulation, and yield of lentil. Biol Fertil Soils 47:457–465
Zdor RE (2015) Bacterial cyanogenesis: impact on biotic interactions. J Appl Microbiol 118:267–274
Zelaya-Molina LX, Hernández-Soto LM, Guerra-Camacho JE, Monterrubio-López R, Patiño-Siciliano A, Villa-Tanaca L, Hernández-Rodríguez C (2016) Ammonia-oligotrophic and diazotrophic heavy metal-resistant Serratia liquefaciens strains from pioneer plants and mine tailings. Microb Ecol 72:324–346
Zhang S, Reddy M, Kloepper JW (2002) Development of assays for assessing induced 12 systemic resistance by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria against blue mold of 13 tobacco.
Zhao B, Cheng D, Tan P, An Q, Guo JS (2018) Characterization of an aerobic denitrifier Pseudomonas stutzeri strain XL-2 to achieve efficient nitrate removal. Bioresour Techno 250:564–573
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mariem Samet and Imen Ghazala. Dr. Fatma Karray carried out the phylogenetic analysis, Cyrine Abid contributed to the in vitro analysis of the PGPR proprieties, Nour Chiab and Oumèma Nouri-Ellouz contributed to the field trials, Sami Sayadi helped to draft the manuscript and Radhia Gargouri-Bouzid participated in the design of the study and its revision. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mariem Samet and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Publish
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samet, M., Ghazala, I., Karray, F. et al. Isolation of bacterial strains from compost teas and screening of their PGPR properties on potato plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 75365–75379 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21046-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21046-8