Abstract
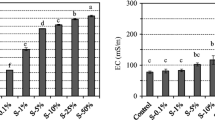
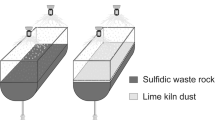
The dissolution of heavy metals from the waste rock is controlled by many factors. Herein, we investigated the release behavior of iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) from sulfide waste rock under the actions of microorganisms and different environmental factors (solution pH value, particle size of waste rock, temperature, Fe3+ concentration). The release quantity of heavy metals was negatively correlated with pH and particle size and positively correlated with ambient temperature and Fe3+ concentration. Under the experimental conditions of pH value of 3.0, temperature of 35°C, and waste stone particle size of less than 0.075 mm,, the release quantity of Fe, Cr, Cu, and Zn reached 3680, 18.32, 132.20, 26.60 mg·kg−1 after 20 days of leaching, respectively. Rising the temperature to 45 °C, Fe, Cr, Cu, and Zn release quantities increased to 89.30, 5.81, 105.08, and 28.00 mg·kg−1. Six hundred milligrams per liter Fe3+ increased the release of heavy metals considerably (2.63–65.48 folds). The presence of microorganisms can significantly facilitate the release of heavy metals. Compared to the control group, the release quantities of Fe, Cr, Cu, and Zn increased 4.29, 3.17, 1.54, and 2.39 times, respectively. In addition, the waste rock under microbial action was more seriously corroded than that under chemical factors. The release behavior of these four heavy metals was consistent with the interfacial chemical reaction control model, indicating that the reactions mainly occurred on the surface of the waste rock. This study provides an essential reference for the study of heavy metal leaching behavior.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Acres RG, Harmer SL, Beattie DA (2010) Synchrotron XPS studies of solution exposed chalcopyrite, bornite, and heterogeneous chalcopyrite with bornite. Int J Miner Process 94:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2009.11.006
Arenas D, Andrade ML, Lago M, Rodríguez A, Vega FA (2014) Sequential extraction of heavy metals in soils from a copper mine. Geoderma 230-231:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.04.011
Ávila PF, Silva EF, Salgueiro AR, Farinha JA (2008) Geochemistry and mineralogy of mill tailings impoundments from the Panasqueira Mine (Portugal): implications for the surrounding environment. Mine Water Environ 27:210–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-008-0046-4
Ávila PF, Silva EF, Candeias C (2017) Health risk assessment through consumption of vegetables rich in heavy metals: the case study of the surrounding villages from Panasqueira mine, Central Portugal. Environ Geochem Health 39:565–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9834-0
Blackmore S, Vriens B, Sorensen M, Power LM, Smith L, Hallan SJ, Mayer KU, Beckie RD (2018) Microbial and geochemical controls on waste rock weathering and drainage quality. Sci Total Environ 640-641:1004–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.374
Byerley J, Scharer J (1992) Natural release of copper and zinc into the aquatic environment. Hydrometallurgy 30:107–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-386X(92)90080-J
Candeias C, Ávila PF, Silva EF, Ferreira A, Salgueiro AR, Teixeira JP (2014a) Acid mine drainage from the Panasqueira mine and its influence on Zêzere river (Central Portugal). J Afr Earth Sci 99:705–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.10.006
Candeias C, Melo R, Ávila PF, Sliva EF, Salgueiro AR, Teixeira JP (2014b) Heavy metal pollution in mine-soil-plant system in S. Francisco de Assis - Panasqueira mine (Portugal). Appl Geochem 44:12–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.07.009
Cánovas ACG, Macías F, López BP, Basallote MD, Olías M, Nieto JM (2019) Mineral reactivity in sulphide mine wastes: influence of mineralogy and grain size on metal release. Eur J Mineral 31:263–273. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/2019/0031-2843
Descostes M, Vitorge P, Beaucaire C (2004) Pyrite dissolution in acidic media. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:4559–4569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.04.012
Dong YB, Liu Y, Lin H (2018) Leaching behavior of V, Pb, Cd, Cr and As from stone coal waste rock with different particle sizes. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25:861–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1635-2
Elberling B (2005) Temperature and oxygen control on pyrite oxidation in frozen mine tailings. Cold Reg Sci Technol 41:121–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2004.09.004
Elghali A, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Bouzahzah H (2019) Determination of the available acid-generating potential of waste rock, part II: Waste management involvement. Appl Geochem 100:316–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.010
Embile JR, Walder I, Madai F, Móricz F, Rzepka P, Walder P (2016) Grain size effects on mine water quality and acid/neutral rock drainage production in kinetic testing using Recsk Porphyry Skarn Cu-Zn deposit rocks. Mine Water Environ 35:421–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-015-0369-x
Ethier MP, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, Garneau P (2012) Effect of temperature on the weathering of various waste rock types from the Raglan Mine. Cold Reg Eng 2012:800–810. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784412473.079
Feng A, Lyu Z, Wu Q, Yang H, Wu B, Cao J (2018) Big data research on mining solid wastes. Conserv Util Min Resourc 214:46–49+57. https://doi.org/10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2018.02.008
Gan XW, Wang J, Zhao HB, Hu MH, Tao L, Qiu GZ (2017) Effect of Fe3+ on stepwise bioleaching of chalcopyrite and marmatite. Min Metall Eng 37:78–80. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.01.021
Huang T, Li DW (2014) Presentation on mechanisms and applications of chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching in biohydrometallurgy: a presentation. Biotechnol Rep 4:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.09.003
Kaasalainen H, Lundberg P, Aiglsperger T, Alakangas L (2019) Impact of declining oxygen conditions on metal(loid) release from partially oxidized waste rock. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20712–20730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05115-z
Khoeurn K, Sakaguchi A, Tomiyama S, Igarashi T (2019) Long-term acid generation and heavy metal leaching from the tailings of Shimokawa mine, Hokkaido, Japan: column study under natural condition. J Geochem Explor 201:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.03.003
Klauber C (2008) A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution. Int J Miner Process 86:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2007.09.003
Klauber C, Parker A, Bronswijk W, Watling H (2001) Sulphur speciation of leached chalcopyrite surfaces as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Int J Miner Process 62:65–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-7516(00)00045-4
Lawrence K, Ray E, Hein N, Hilary R (2015) Dissolution kinetics of South African coal fly ash and the development of a semi-empirical model to predict dissolution. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 21:32–32. https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ140423032K
Li J, Kawashima N, Kaplun K, Absolon VJ (2010) Chalcopyrite leaching: the rate controlling factors. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:2881–2893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2010.02.029
Liu YG, Zhou M, Zeng GM, Wang X, Lin X, Fan T, Xu WH (2008) Bioleaching of heavy metals from mine tailings by indigenous sulfur-oxidizing bacteria: effects of substrate concentration. Bioresour Technol 99:4124–4129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.064
Lottermoser BG (2010) Mine wastes: characterization, treatment, and environmental impacts. Springer, Berlin
Lu JN, Yuan FQ, Leiviskȁ T (2019) The effect of temperature on the leaching of Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni and Zn from tailings, Ballangen deposit, Norway. Int J Environ Impacts 2:366–381. https://doi.org/10.2495/EI-V2-N4-366-381
Mangold S, Harneit K, Rohwerder T, Claus G (2008) Novel combination of atomic force microscopy and epifluorescence microscopy for visualization of leaching bacteria on pyrite. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:410–414. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01812-0
Modoi OC, Roba C, Toeroek Z, Ozunu A (2014) Environmental risk due to heavy metal pollution of water resulted from mining wastes in NW Romania. Environ Eng Manag J 13:2325–2336. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2014.260
Montes-Botella C, Tenorio MD (2003) Water characterization and seasonal heavy metal distribution in the Odiel River (Huelva, Spain) by means of principal component analysis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-003-0139-9
Perlatti F, Martins E, Oliveirac DP, Ruiz F, Asensio V, Rezende CF, Otero XL, Ferreira TO (2020) Copper release from waste rocks in an abandoned mine (NE, Brazil) and its impacts on ecosystem environmental quality. Chemosphere 262:127843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127843
Qureshi A, Maurice C, Ölander B (2016) Potential of coal mine waste rock for generating acid mine drainage. J Geochem Explor 160:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.10.014
Richard TA, David WB, Brenda LB, David CS, Leslie S, Ritchie AM (2015) Waste-rock hydrogeology and geochemistry. Appl Geochem 57:140–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.06.020
Rohwerder T, Gehrke T, Kinzler K, Sand W (2003) Bioleaching review part A: progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1448-7
Sand W, Gehrke T, Jozsa PG, Schippers A (2001) (Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching: direct vs. indirect bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 59:159–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00180-8
Voegelin A, Barmettler K, Kretzschmar R (2003) Heavy metal release from contaminated soils: comparison of column leaching and batch extraction results. J Environ Qual 32:865–875. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.8650
Vriens B, Plante B, Seigneur N, Jamieson H (2020) Mine waste rock: insights for sustainable hydrogeochemical management. Minerals 10:728. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090728
Wang ZK, Li XJ, Feng S, Chen Y, Chi J, Qu W, Mo YQ, Luo Q, Pu F, Guo XM (2014) Influence of environmental factors on release of heavy metals in ore at the port stockyard. Rock Min Anal 33:256–261. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.02.017
Wang HH, Li GQ, Zhao D, Ma JH, Yang J (2017) Dephosphorization of high phosphorus oolitic hematite by acid leaching and the leaching kinetics. Hydrometallurgy 171:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.04.015
Wang P, Sun ZH, Hu YA, Zhen HF (2019) Leaching of heavy metals from abandoned mine tailings brought by precipitation and the associated environmental impact. Sci Total Environ 695:133893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133893
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances. Springer, Berlin
Yan J, Tan QY, Sun HY, Zhang YP, Gao HS, Renman R (2019) Sulfide mineral dissolution microbes: community structure and function in industrial bioleaching heaps. Green Energy Environ 4:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2018.04.001
Zhang X, Yang HH, Cui ZJ (2017) Migration and speciation of heavy metal in salinized mine tailings affected by iron mining. Water Sci Technol 76:1867–1874. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.369
Zhang SQ, Yang HY, Tong LL, Li JF, Ma PC, Chen GM (2021) Research status of bioleaching of sulfide minerals and bacteria synergy mechanisms. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy) 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2021.04.001
Zhou J, Dang Z, Cai M, Liu C (2007) Soil heavy metal pollution around the Dabaoshan Mine, Guangdong Province, China. Pedosphere 17:588–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60069-1
Zhu W, Xia JL, Yang Y, Nie ZY, Zheng L, Ma CY, Zhang RY, Peng AA, Tang L, Qiu GZ (2011) Sulfur oxidation activities of pure and mixed thermophiles and sulfur speciation in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Bioresour Technol 102:3877–3882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.090
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1805001) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-MP-20-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yingbo Dong: Conceptualization; supervision; validation; resources; writing, review and editing; funding acquisition; project administration.
Danni Chen: Conceptualization; methodology; writing, original draft; investigation; formal analysis; data curation.
Hai Lin: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing — review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Luke Mosley
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Chen, D. & Lin, H. The behavior of heavy metal release from sulfide waste rock under microbial action and different environmental factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 75293–75306 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20555-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20555-w