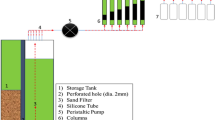
Abstract
In this work, convective–dispersive and pore volume and surface diffusion models have been used to analyze Pb(II) adsorption from an aqueous solution over a nanostructured γ-alumina adsorbent in a packed bed adsorber. The models encompassing partial differential equation and a linear algebraic equation coupled with isotherm have been simulated in gPROMS using the backward finite difference approach. The predicted breakthrough curves of Pb(II) adsorption concerning flow rate, initial metal concentration, and bed height were matched with the experimental data. The accuracy of model predictions was analyzed through statistical measures such as coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error, and chi-squared value. The simulation results also predicted the axial dispersion, distribution coefficient, mass transfer coefficient, pore volume, and surface diffusion coefficient, which are, otherwise, difficult to measure experimentally and, in turn, have been used to assess the mass transfer characteristics of continuous Pb(II) adsorption. Additionally, the values of breakthrough time, exhaustion time, adsorption column capacity, and mass transfer zone were determined as a function of flow rate, bed height, and initial metal concentration. Surface and pore volume diffusions (10−11–10−10 m2/s) apparently controlled the continuous adsorption process, with surface diffusion being dominant. The transport parameters evaluated in the current study could be beneficial for the large-scale Pb(II)/nanostructured γ-alumina adsorption system. As evident from the successful simulation, the developed gPROMS program can also be applied to other adsorbate/adsorbent systems with a slight modification concerning the operating parameters.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Code developed during this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- \(C\) :
-
Heavy metal ion concentration in bulk liquid phase (mg/L)
- \({C}_{0}\) :
-
Initial heavy metal ion concentration in bulk liquid phase (mg/L)
- \({C}_{P}\) :
-
Heavy metal ion concentration within the adsorbent (mg/L)
- \({D}_{AB}\) :
-
Molecular diffusivity of heavy metal in aqueous solution (m2/s)
- \({D}_{L}\) :
-
Axial dispersion coefficient (m2/s)
- \({D}_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Pore volume diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- \({D}_{\mathrm{s}}\) :
-
Surface diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- \({K}_{\mathrm{d}}\) :
-
Distribution coefficient (m3/kg)
- \({k}_{L}\) :
-
Mass transfer coefficient (m/s)
- \({k}_{\mathrm{Th}}\) :
-
Thomas model constant (mL/min/mg)
- \({k}_{\mathrm{YN}}\) :
-
Yoon-Nelson rate constant (min−1)
- \(L\) :
-
Length of packed bed adsorber (m)
- \(m\) :
-
Mass of adsorbent (g)
- \({M}_{B}\) :
-
Molecular weight of water (g/mol)
- \({N}_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Mass transport due to pore volume diffusion (mg/m2/s)
- \({N}_{\mathrm{s}}\) :
-
Mass transport due to surface diffusion (mg/m2/s)
- \(Q\) :
-
Volumetric flow rate (mL/min)
- \(q\) :
-
Adsorption capacity at equilibrium (mg/g)
- \({q}_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Adsorption capacity within the particle (mg/g)
- \({q}_{\mathrm{eq}}\) :
-
Adsorption capacity of the packed bed adsorber (mg/g)
- \({q}_{\mathrm{Th}}\) :
-
Maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g)
- \({q}_{\mathrm{total}}\) :
-
Total Pb(II) adsorbed in the column (g)
- \(R\) :
-
Radius of the adsorbent particle (m)
- \(r\) :
-
Radial distance within the adsorbent particle (m)
- \(Re\) :
-
Reynolds number
- \(S\) :
-
External surface area of adsorbent per unit mass (m2/kg)
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(Sh\) :
-
Sherwood number
- \(t\) :
-
Time (min)
- \({t}_{\mathrm{b}}\) :
-
Breakthrough time (min)
- \({t}_{\mathrm{e}}\) :
-
Exhaustion time (min)
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature (K)
- \(V\) :
-
Volume of heavy metal solution (mL)
- \({V}_{A}\) :
-
Molal volume of heavy metals at normal boiling point (cm3/g/mol)
- \({v}_{z}\) :
-
Interstitial velocity (m/s)
- \(z\) :
-
Axial distance (m)
- \({\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{b}}\) :
-
Bed voidage
- \({\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Porosity of particle
- \({\rho }_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Density of the adsorbent (kg/m3)
- \({\rho }_{\mathrm{water}}\) :
-
Density of the water (kg/m3)
- \(\tau\) :
-
Tortuosity factor
- \({\tau }_{\mathrm{YN}}\) :
-
Time required for 50% adsorbate breakthrough (min)
- \({\mu }_{\mathrm{s}}\) :
-
Viscosity of solution (kg/m/s)
- \({\mu }_{\mathrm{water}}\) :
-
Viscosity of water (kg/m/s)
- \(\phi\) :
-
Association parameter for water
- \({\chi }^{2}\) :
-
Chi-squared value
References
Afkhami A, Saber-Tehrani M, Bagheri H (2010) Simultaneous removal of heavy-metal ions in wastewater samples using nano-alumina modified with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J Hazard Mater 181:836–844
Aftab RA, Zaidi S, Danish M et al (2021) Support vector regression-based model for phenol adsorption in rotating packed bed adsorber. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–12
Allan M, Fagel N, Van Rampelbergh M et al (2015) Lead concentrations and isotope ratios in speleothems as proxies for atmospheric metal pollution since the industrial revolution. Chem Geol 401:140–150
Banerjee S, Dubey S, Gautam RK et al (2019) Adsorption characteristics of alumina nanoparticles for the removal of hazardous dye, Orange G from aqueous solutions. Arab J Chem 12:5339–5354
Basu M, Guha AK, Ray L (2019) Adsorption of lead on lentil husk in fixed bed column bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 283:86–95
Behera PS, Sarkar R, Bhattacharyya S (2016) Nano alumina: a review of the powder synthesis method. Interceram - Int Ceram Rev 65:10–16
Bhat A, Megeri GB, Thomas C et al (2015) Adsorption and optimization studies of lead from aqueous solution using γ-alumina. J Environ Chem Eng 3:30–39
Černá M (1995) Use of solvent extraction for the removal of heavy metals from liquid wastes. Environ Monit Assess 34:151–162
Chaoua S, Boussaa S, El Gharmali A, Boumezzough A (2019) Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 18:429–436
Chatterjee S, Mondal S, De S (2018) Design and scaling up of fixed bed adsorption columns for lead removal by treated laterite. J Clean Prod 177:760–774
Cruz-Olivares J, Pérez-Alonso C, Barrera-Díaz C et al (2013) Modeling of lead (II) biosorption by residue of allspice in a fixed-bed column. Chem Eng J 228:21–27
Danish M, Ansari KB, Aftab RA et al (2021) gPROMS-driven modeling and simulation of fixed bed adsorption of heavy metals on a biosorbent: benchmarking and case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–16
Danish M, Ansari KB, Danish M et al (2022) Developing convective–dispersive transport model to characterize fixed-bed adsorption of lead (II) over activated tea waste biosorbent. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 1–15
Díaz-Blancas V, Aguilar-Madera CG, Flores-Cano JV et al (2020) Evaluation of mass transfer mechanisms involved during the adsorption of metronidazole on granular activated carbon in fixed bed column. J Water Process Eng 36:101303
Dotto GL, Mckay G (2020) Current scenario and challenges in adsorption for water treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103988
Faust SD, Aly OM (1986) Adsorption process for water treatment. Butterworth-Heinemann, Stoneham
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Ahmadi A et al (2021) Adsorption mercury, cobalt, and nickel with a reclaimable and magnetic composite of hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4/polydopamine. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105709
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Hemmati S et al (2021b) Zn2+ removal from the aqueous environment using a polydopamine/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 magnetic composite under ultrasonic waves. RSC Adv 11:27309–27321
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Hosseini SS et al (2021) Hydroxyapatite biomaterial production from chicken (femur and beak) and fishbone waste through a chemical less method for Cd2+ removal from shipbuilding wastewater. J Hazard Mater 413:125428
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Mohammadi R et al (2022) Development of new magnetic adsorbent of walnut shell ash/starch/Fe3O4 for effective copper ions removal: treatment of groundwater samples. Chemosphere 296:133978
Franco DSP, Fagundes JLS, Georgin J et al (2020) A mass transfer study considering intraparticle diffusion and axial dispersion for fixed-bed adsorption of crystal violet on pecan pericarp (Carya illinoensis). Chem Eng J 397:125423
Gharabaghi M, Irannajad M, Azadmehr AR (2012) Selective sulphide precipitation of heavy metals from acidic polymetallic aqueous solution by thioacetamide. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:954–963
Jain R, Mathur M, Sikarwar S, Mittal A (2007) Removal of the hazardous dye rhodamine B through photocatalytic and adsorption treatments. J Environ Manage 85:956–964
Khatoon A, Uddin MK, Rao RAK (2018) Adsorptive remediation of Pb(II) from aqueous media using Schleichera oleosa bark. Environ Technol Innov 11:1–14
Kumar S, Zafar M, Prajapati JK et al (2011) Modeling studies on simultaneous adsorption of phenol and resorcinol onto granular activated carbon from simulated aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 185:287–294
Kushwaha AK, Gupta N, Chattopadhyaya MC (2017) Adsorption behavior of lead onto a new class of functionalized silica gel. Arab J Chem 10:S81–S89
Lanphear BP (2015) The impact of toxins on the developing brain. Annu Rev Public Health 36:211–230
Leyva-Ramos R, Geankoplis CJ (1985) Model simulation and analysis of surface diffusion of liquids in porous solids. Chem Eng Sci 40:799–807
Liu SL, Wang YN, Lu KT (2014) Preparation and pore characterization of activated carbon from Ma bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus) by H3PO4 chemical activation. J Porous Mater 21:459–466
Meitei MD, Prasad MNV (2013) Lead (II) and cadmium (II) biosorption on Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleiden biomass. J Environ Chem Eng 1:200–207
Needleman H (2004) Lead poisoning. Annu Rev Med 55:209–222
Nriagu JO (1979) Global inventory of natural and anthropogenic emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere. Nature 279:409–411
Nzediegwu C, Naeth MA, Chang SX (2021) Lead(II) adsorption on microwave-pyrolyzed biochars and hydrochars depends on feedstock type and production temperature. J Hazard Mater 412:125255
Ocampo-Pérez R, Leyva-Ramos R, Sanchez-Polo M, Rivera-Utrilla J (2013) Role of pore volume and surface diffusion in the adsorption of aromatic compounds on activated carbon. Adsorption 19:945–957
Patel H (2020) Batch and continuous fixed bed adsorption of heavy metals removal using activated charcoal from neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf powder. Sci Rep 1–12
Peighambardoust SJ, Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SH, et al (2021) Decoration of Citrus limon wood carbon with Fe3O4 to enhanced Cd2+ removal: a reclaimable and magnetic nanocomposite. Chemosphere 282:131088
Qian W, Song Q, Ding H, Xie W (2018) Computational simulations of the mass transfer zone in GS adsorption column packed with Fe3+ type ion exchanger. Chemosphere 215:507–514
Rahmani A, Mousavi HZ, Fazli M (2010) Effect of nanostructure alumina on adsorption of heavy metals. Desalination 253:94–100
Rastegar SO, Gu T (2017) Empirical correlations for axial dispersion coefficient and Peclet number in fixed-bed columns. J Chromatogr A 1490:133–137
Riazi M, Keshtkar AR, Moosavian MA (2016) Biosorption of Th(IV) in a fixed-bed column by Ca-pretreated Cystoseira indica. J Environ Chem Eng 4:1890–1898
Romero-Gonzalez J, Walton JC, Peralta-videa JR et al (2009) Modeling the adsorption of Cr(III) from aqueous solution onto Agave lechuguilla biomass: study of the advective and dispersive transport. J Hazard Mater 161:360–365
Saadi Z, Saadi R, Fazaeli R (2013) Fixed-bed adsorption dynamics of Pb (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using nanostructured γ-alumina. J Nanostructure Chem 3:2–9
Saadi Z, Saadi R, Fazaeli R (2015) Dynamics of Pb(II) adsorption on nanostructured γ-alumina: calculations of axial dispersion and overall mass transfer coefficients in the fixed-bed column. J Water Health 13:790–800
Sanchez-Valente J, Bokhimi X, Toledo JA (2004) Synthesis and catalytic properties of nanostructured aluminas obtained by sol-gel method. Appl Catal A Gen 264:175–181
Shaidan NH, Eldemerdash U, Awad S (2012) Removal of Ni(II) ions from aqueous solutions using fixed-bed ion exchange column technique. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43:40–45
Shek CH, Lai JKL (1997) Transformation evolution and infrared absorption spectra of amorphous and crystalline nano-Al2O3 powders. Nanostructured Mater 8:605–610
Souza PR, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2017) Detailed numerical solution of pore volume and surface diffusion model in adsorption systems. Chem Eng Res Des 122:298–307
Sultana M, Rownok MH, Sabrin M et al (2022) A review on experimental chemically modified activated carbon to enhance dye and heavy metals adsorption. Clean Eng Technol 6:100382
Tehrani-Bagha AR, Mahmoodi NM, Menger FM (2010) Degradation of a persistent organic dye from colored textile wastewater by ozonation. Desalination 260:34–38
Thomas HC (1944) Heterogeneous ion exchange in a flowing system. J Am Chem Soc 66:1664–1666
Triantafyllidou S, Edwards M (2012) Lead (Pb) in tap water and in blood: implications for lead exposure in the United States. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:1297–1352
Usman MA, Aftab RA, Zaidi S et al (2021) Adsorption of aniline blue dye on activated pomegranate peel: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics and support vector regression modelling. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1–18
Varatharajan K, Dash S, Arunkumar A et al (2003) Synthesis of nanocrystalline α-Al2O3 by ultrasonic flame pyrolysis. Mater Res Bull 38:577–583
Verma A, Kumar S, Kumar S (2016) Biosorption of lead ions from the aqueous solution by Sargassum filipendula: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 4:4587–4599
Verma A, Kumar S, Kumar S (2017) Statistical modeling, equilibrium and kinetic studies of cadmium ions biosorption from aqueous solution using S. filipendula. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2290–2304
Wilke CR, Chang P (1955) Correlation of diffusion coefficients in dilute solutions. AIChE J 1:264–270
Yoon YH, Nelson J (1992) Breakthrough time and adsorption capacity of respirator cartridges. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 53:303–316
Acknowledgements
The first author acknowledges the University Grant Commission (UGC) for the non-NET financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohd Danish: gPROMS-driven modeling of Pb(II) adsorption and initial draft preparation; Khursheed B. Ansari: conceptualization, draft editing, and revision; Mohammad Danish: initial concept of the work, visualization, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danish, M., Ansari, K.B. & Danish, M. Adsorptive removal of Pb(II) using nanostructured γ-alumina in a packed bed adsorber: Simulation using gPROMS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 42629–42642 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20175-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20175-4