Abstract
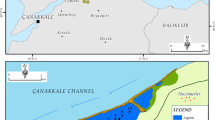
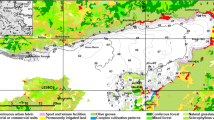
This study aims to investigate the ecological risk level of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in İzmir Inner Gulf. Samples were taken from 16 stations selected in the southern littoral zone of the gulf for four seasons (winter, spring, summer, and autumn). Multi-element, total organic carbon, chlorophyll-a, biogenic silica and carbonate analyses were carried out. To determine contamination level and ecological risks, some indices (enrichment factor, modified hazard quotient and potential risk analysis, toxic risk index, etc.) were calculated. Mo and Pb show significant anthropogenic enrichment in the inner gulf. These are followed by Cu, Cd, and Zn with moderate accumulation. Risk assessment indices point out that Ni, Cr, and Cd have a serious potential to create risk for ecosystem, and these are followed by As, Hg, Pb, Zn, and Cu. According to the spatial distribution, land use maps, and factor analysis, the Cd, Zn, and Cr increases are localized at the mouth of the Poligon Stream. Pb and Cu accumulate at the mouth of four large streams feeding the eastern part of the gulf. Pb and Cu enrichment is associated with traffic and industrial discharges. While one of the sources of Hg is anthropogenic, another source is eutrophication resulting from benthic and planktonic diatom blooms. While Fe and Mn are added to the gulf via rivers as a result of rock and soil erosion, another source is sediment. Cr, As, and Ni come from anthropogenic and lithogenic sources and immobilized in sediment. CO3−2 source is marine (biogenic) and dilutes other immobilized PTEs. It is understood that the peripheral stations rich in allochthonous organic carbon and the stations close to the central area rich in autochthonous organic carbon contribute to the carbon source in question.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request via e-mail.
References
Acevedo-Figueroa D, Jiménez BD, Rodríguez-Sierra CJ (2006) Trace metals in sediments of two estuarine lagoons from Puerto Rico. Environ Pollut 141:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.037
Ahamad MI, Song J, Sun H, Wang X, Mehmood MS, Sajid M, Khan AJ (2020) Contamination level, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metals in the hyporheic zone of the Weihe River, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031070
Altın A, Filiz Z, Iscen CF (2009) Assessment of seasonal variations of surface water quality characteristics for Porsuk Stream. Environ Monit Assess 158:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0564-3
Amin B, Ismail A, Arshad A, Yap CK, Kamarudin MS (2009) Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environ Monit Assess 148:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0159-z
Atalar M, Küçüksezgin F, Duman M, Gönül T (2013) Heavy metal concentrations in surficial and core sediments from İzmir Bay: an assessment of contamination and comparison against sediment quality benchmarks. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1008-5
Bastami KD, Bagheri H, Kheirabadi V, Zaferani GG, Teymori MB, Hamzehpoor A, Soltani F, Haghparast S, Harami SRM, Ghorghani NF, Ganji S (2014) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along southeast coast of the Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bull 81:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.029
Bazrafshan E, Mostafapour FK, Esmaelnejad M, Ebrahimzadeh G, Mohvi A (2016) Concentration of heavy metals in surface water and sediments of Chah Nimeh water reservoir in Sistan and Baluchestan province. Iran. Desalination and Water Treatment 57:9332–9342. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1027958
Bat L, Öztekin A, Şahin F, Arıcı E, Özsandıkçı U (2018) An overview of the Black Sea pollution in Turkey. MedFAR 1:67–86 https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/480276
Bat L, Özkan E. Y (2019). Heavy metal levels in sediment of the Turkish Black Sea Coast. In I. Management Association (Ed.), Oceanography and Coastal Informatics: Breakthroughs in Research and Practice (pp. 86–107). Hershey, PA: IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-7308-1.ch004
Beneditto AM, Semensato GE, Carvalho C, Rezende C (2019) Trace metals in two commercial shrimps from southeast Brazil: Baseline records before large port activities in coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 146:667–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.028
Benson NU, Adedapo AE, Fred-Ahmadu OH, Williams AB, Udosen ED, Ayejuyo OO, Olajire AA (2018) New ecological risk indices for evaluating heavy metals contamination in aquatic sediment: a case study of the Gulf of Guinea. Reg Stud Mar Sci 18:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2018.01.004
Brady JP, Ayoko GA, Martens WN, Goonetilleke A (2015) Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Monit Assess 187:306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4563-x
Chen Y, Liu Q, Xu M, Wang Z (2020) Inter-annual variability of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments of Jiangsu coastal region, China: case study of the Dafeng Port. Mar Pollut Bull. 110720https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110720
Dang P, Gu X, Lin C, Xin M, Zhang H, Ouyang W, Liu X, He M, Wang B (2021) Distribution, sources, and ecological risks of potentially toxic elements in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: under the long-term impact of the Yellow River input. J Hazard Mater 413:125429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125429
De Master DJ (1981) The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1715–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(81)90006-5
Denkhaus E, Salnikow K (2002) Nickel essentiality, toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 42:35–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1040-8428(01)00214-1
ESRI (2021) https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/tools/3d-analyst-toolbox/how-kriging-works.htm. Accessed 11 Apr 2021
Fural Ş, Kükrer S, Cürebal İ, Aykır D (2021) Spatial distribution, environmental risk assessment, and source identification of potentially toxic metals in Atikhisar dam, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess. 16: 193(5) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09062-6
Gao L, Wang Z, Shan J, Chen J, Tang C, Yi M, Zhao X (2016) Distribution characteristics and sources of trace metals in sediment cores from a trans-boundary watercourse: an example from the Shima River, Pearl River Delta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 134:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.08.020
Gaudette HE, Flight WR, Toner L, Folger DW (1974) An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J Sediment Res 44:249–253. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D729D7-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
General Directorate of Meteorology (MGM) (2021) https://izmir.mgm.gov.tr/. Accessed 17 Feb 2021
General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA) (2021) http://earthsciences.mta.gov.tr/mainpage.aspx. Accessed 01 Apr 2021
Gu X, Xu L, Wang Z, Ming X, Dang P, Ouyang W, Lin C, Liu X, He M, Wang B (2021) Assessment of cadmium pollution and subsequent ecological and health risks in Jiaozhou Bay of the Yellow Sea. Sci Total Environ 774:145016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145016
Gülsever G, Arslan ÖÇ (2019) Current status of heavy metal pollution in İzmir inner bay sediments. 2nd International Agriculture. Environment and Health Congress Full Text Abstract Book. 1769–1776
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 8:975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hasan AB, Kabir S, Reza AHM, Zaman MN, Ahsan A, Rashid M (2013) Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index of trace metals in sediments of the ship breaking area of Sitakund Upazilla (Bhatiary–Kumira), Chittagong, Bangladesh. J Geochem Explor 125:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.12.002
Islam MS, Han S, Ahmed MK, Masunaga S (2014) Assessment of trace metal contamination in water and sediment of some rivers in Bangladesh. J Water Environ Technol 12:109–121. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.2014.109
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M et al (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Ind 48:282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016
Jafarabadi AR, Raudonyte-Svirbutaviciene E, Toosi AS, Bakhitari AR (2021) Positive matrix factorization receptor model and dynamics in fingerprinting of potentially toxic metals in coastal ecosystem sediments at a large scale (Persian Gulf, Iran). Water Res 188:116509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116509
Jahan S, Strezov V (2018) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of seaports of NSW, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 128:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.036
Jeong H, Choi YJ, Lim J, Shim JW, Kim YO, Ra K (2020) Characterization of the contribution of road deposited sediments to the contamination of the close marine environment with trace metals: case of the port city of Busan (South Korea). Mar Pollut Bull 161:111717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111717
Kaya H, Erginal G, Çakır Ç, Gazioğlu C, Erginal A (2017) Ecological risk evaluation of sediment core samples, Lake Tortum (Erzurum, NE Turkey) using environmental indices. Int J Environ Geoinformatics 4:227–239. https://doi.org/10.30897/ijegeo.348826
Kang X, Song J, Yuan H et al (2017) Speciation of heavy metals in different grain sizes of Jiaozhou Bay sediments: Bioavailability, ecological risk assessment and source analysis on a centennial timescale. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.036
Ke X, Gui S, Huang H et al (2017) Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 175:473–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.029
Kontaş A, Kucuksezgin F, Altay O, Uluturhan E (2004) Monitoring of eutrophication and nutrient limitation in the İzmir Bay (Turkey) before and after Wastewater Treatment Plant. Environ Int 29:1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00098-9
Kükrer S, Erginal AE, Kılıç Ş, Bay Ö, Akarsu T, Öztura E (2020) Ecological risk assessment of surface sediments of Çardak Lagoon along a human disturbance gradient. Environ Monit Asses. 192https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08336-9
Küçüksezgin F (2001) Distribution of heavy metals in the surficial sediments of Izmir Bay (Turkey). Toxicol Environ Chem 80:203–207. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240109359010
Li Y, Qu X, Zhang M, Peng W, Yu Y, Gao B (2018) Anthropogenic impact and ecological risk assessment of thallium and cobalt in Poyang Lake using the geochemical baseline. Water 10:1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111703
Liu J, Xu Y, Cheng Y, Zhao Y, Pan Y, Fu G, Dai Y (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River. China Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:2711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8044-8
Liu J-J, Ni Z-X, Diao Z-H et al (2018) Contamination level, chemical fraction and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from Daya Bay, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 128:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.021
Looi LJ, Aris AZ, Yusoff F, Mohd N, Haris IH (2019) Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environ Geochem Health 41:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0149-1
Lu G, Zhu A, Fang H, Dang Y, Wang WX (2019) Establishing baseline trace metals in marine bivalves in China and worldwide: meta-analysis and modeling approach. Sci Total Environ 669:746–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.164
MacDonald DD, Carr RS, Calder FD (1997) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Oceanogr Lit Rev 6:638
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010075
Martin DF (1972) Marine Chemistry: Theory and Applications, First U.S. Edition. ed. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1973.18.1.0181a
Matthiesen H (1998) Phosphate release from marine sediments: by diffusion, advection and resuspension. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Chemistry, University of Aarhus, Denmark
Maurya P, Kumari R (2021) Toxic metals distribution, seasonal variations and environmental risk assessment in surficial sediment and mangrove plants (A marina), Gulf of Kachchh (India). J Hazard Mater 413:125345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125345
Merhaby D, Ouddane B, Net S, Halvani J (2018) Assessment of trace metals contamination in surficial sediments along Lebanese Coastal Zone. Mar Pollut Bull 113:881–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.031
Muhammad S, Shah MT, Khan S (2011) Heavy metal concentrations in soil and wild plants growing around Pb-Zn sulfide terrain in the Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem J 99:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2011.03.012
Nowrouzi M, Pourkhabbaz A (2014) Application of Geoaccumulation Index and Enrichment Factor for Assessing Metal Contamination in the Sediments of Hara Biosphere Reserve. Iran Chem Speciat Bioavailab 26:99–105. https://doi.org/10.3184/095422914X13951584546986
Oliveira TS, Xavier D, Santos LD, França EJ, Sanders C.J, Passos TU, Barcellos RL (2020) Geochemical background indicators within a tropical estuarine system influenced by a port-industrial complex. Mar Pollut Bull. 111794https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111794
Özkan EY, Büyükışık B (2012) Geochemical and statistical approach for assessing heavy metal accumulation in the Southern Black Sea Sediments. Ecology 21:11–24 https://app.trdizin.gov.tr/makale/TVRNek56VTRPQT09/geochemical-and-statistical-approach-for-assessing-heavy-metal-accumulation-in-the-southern-black-sea-sediments-
Özkan EY, Büyükışık HB, Kontaş A, Türkdoğan M (2017) A survey of metal concentrations in marine sediment cores in the vicinity of an old mercury-mining area in Karaburun, Aegean Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:13823–13836 https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11356-017-8792-0.pdf
Panagos A, Papadopoulos N, Alexandropoulou S, Synetos S, Varnavas S (1989) Geochemical study of sediments from deposits. Mar Geol 110:93–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(93)90108-8
Palas S (2020) Investigation of heavy metal accumulation in Late Quaternary-Contemporary surface sediments of Aliağa Bay, M.T.A. Nat Resour Econ Bull 29:29–48
Phillips DJH, Rainbow PS (1993) Biomonitoring of aquatic trace contaminants. Part of the Environmental Management Series book series (EMISS, volume 37), London Chapman and Hall
Quinton JN, Catt JA (2007) Enrichment of Heavy Metals in Sediment Resulting from Soil Erosion on Agricultural Fields. Environ Sci Technol 41:3495–3500. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062147h
Ratnaike RN (2003) Acute and chronic arsenic toxicity. Postgrad Med J 79:391–396. https://doi.org/10.1136/pmj.79.933.391
Roberts DA, Birchenough SN, Lewis C, Sanders MB, Bolam T, Sheahan D (2013) Ocean acidification increases the toxicity of contaminated sediments. Glob Change Biol 19:340–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12048
Rodríguez-Espinosa PF, Shruti VC, Jonathan MP, Martinez-Tavera E (2018) Metal concentrations and their potential ecological risks in fluvial sediments of Atoyac River basin, Central Mexico: Volcanic and anthropogenic influences. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:1020–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.068
Rumisha C, Elskens M, Leermakers M, Kochzius M (2012) Trace metal pollution and its influence on the community structure of soft bottom molluscs in intertidal areas of the Dar es Salaam coast, Tanzania. Mar Pollut Bull 64:521–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.12.025
Siddiquee NA, Ahmed MK, Quddus MMA, Parween S, Islam MH (2006) Trace metal concentration in sediments of Chittagong ship breaking area. The Journal of Noami 23:23–30
Singovszka E, Balintova M (2019) Enrichment Factor and Geo-Accumulation Index of Trace Metals in Sediments in the River Hornad. Slovakia IOP Conf Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/222/1/012023
Schiff KC, Weisberg SB (1999) Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in Southern California coast shelf sediments. Mar Environ Res 48:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00033-1
Shil S, Singh UK (2019) Health risk assessment and spatial variations of dissolved heavy metals and metalloids in a tropical river basin system. Ecol Ind 106:105455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105455
Strickland J, Parsons T (1972) A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. FISHERIES RESEARCH BOARD OF CANADA, Ottawa, p 328p
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii Environ Geol 39:611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Sun Z, Mou X, Tong C, Wang C, Xie Z, Song H, Sun W, Lv Y (2015) Spatial variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in intertidal zone of the Yellow River estuary, China. CATENA 126:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.037
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang H, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Nan R, Zhu X (2014) Heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of representative limnetic ecosystems in eastern China. Sci Rep 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07152
Tunca E, Aydın M, Şahin ÜA (2018) An ecological risk investigation of marine sediment from the northern Mediterranean coasts (Aegean Sea) using multiple methods of pollution determination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7487–7503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0984-0
Ustaoğlu F (2020) Ecotoxicological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Çömlekci stream, Giresun, Turkey. Environ Forensics 22:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2020.1806148
Ustaoğlu F, Islam MS (2020) Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: a preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol Ind 113:106237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106237
Varnavas SP (1989) Metal Pollution of the Kalloni Bay,Lesvos Greece. Proceedings of the conference. Environmental Science and Technology. Lesvos, Greece. 211–220
Viard B, Pihan F, Promeyrat S, Pihan JC (2004) Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd) highway pollution: bioaccumulation in soil, Graminaceae and land snails. Chemosphere 55:1349–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.003
Williams JA, Antoine J (2020) Evaluation of the elemental pollution status of Jamaican surface sediments using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, ecological risk and potential ecological risk index. Mar Pollut Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111288
Xiao R, Bai J, Lu Q, Zhao Q, Gao Z, Wen X, Liu X (2015) Fractionation, transfer, and ecological risks of heavy metals in riparian and ditch wetlands across a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in an estuary of China. Sci Total Environ 517:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.052
Zahir F, Rizwi SJ, Haq SK, Khan RH (2005) Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 20:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.007
Zhang L, Ye X, Feng H et al (2007) Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China. Mar Pollut Bull 54:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.02.010
Zhang G, Bai J, Zhao Q (2016) Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronose quence in the Yellow River Delta of China: Levels, sources and toxic risks. Ecol Ind 69:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.04.042
Acknowledgements
We thank TUBITAK for their support and Mr. Graham Lee for proof-reading the text.
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) within the scope of project 114Y419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EYÖ, conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, project administration, writing—original draft. Ş.F, conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, software, writing—original draft, visualization. S.K, Conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, resources, writing—review and editing. HBB, Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, validation, writing—review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All authors approve the publication of the article in your journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkan, E.Y., Fural, Ş., Kükrer, S. et al. Seasonal and spatial variations of ecological risk from potential toxic elements in the southern littoral zone of İzmir Inner Gulf, Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 62669–62689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19987-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19987-1