Abstract
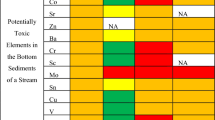
Sediment can accumulate trace elements in the environment. This study profiled the magnitude of As, Ba, Cd, Co, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, Se, and Zn pollution in surface sediments of the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Trace elements were digested using aqua regia and were analyzed using the inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The extent of elemental pollution was evaluated using with the enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo). This study found that the elemental distribution in the sediment in descending order was Zn > Ba > Cr > Pb > Cu > As > Ni > Co > Se > Cd. Zn concentrations in all samples were below the interim sediment quality guideline (ISQG) (124 mg/kg). In contrast, Cd concentrations (2.34 ± 0.01 mg/kg) at Station 31 (Merlimau) exceeded the ISQG (0.70 mg/kg), and the concentrations of As in the samples from Station 9 (Tanjung Dawai) exceeded the probable effect level (41.60 mg/kg). The Igeo and EF revealed that Station 9 and Station 31 were extremely enriched with Se and Cd, respectively. All stations posed low ecological risk, except Station 31, which had moderate ecological risk. The outputs from this study are expected to provide the background levels of pollutants and help develop regional sediment quality guideline values. This study is also important in aiding relevant authorities to set priorities for resources management and policy implementation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, N. A., Shazili, N. A. M., Yaacob, R., & Yunus, K. (2014). Grain size and metallic trace element contents in sediments of Kemaman Coast, Terengganu, Malaysia, South China Sea. Journal of Earth Science and Engineering, 4, 80–87.
Al-Shami, S. A., Rawi, C. S. M., Hassan Ahmad, A., & Nor, S. A. M. (2010). Distribution of Chironomidae (Insecta: Diptera) in polluted rivers of the Juru River basin, Penang, Malaysia. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22, 1718–1727.
Amin, B., Ismail, A., Arshad, A., Yap, C. K., & Kamarudin, M. S. (2009). Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 148, 291–305.
Barbieri, M. (2016). The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (I geo) to evaluate the soil contamination. Geology & Geophysics, 5(1), 1–4.
Bashir, F. H., Othman, M. S., Mazlan, A. G., Rahim, S. M., & Simon, K. D. (2013). Heavy metal concentration in fishes from the coastal waters of Kapar and Mersing, Malaysia. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 13, 375–382.
Buhari, T. R., & Ismail, A. (2016). Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in surface sediments of west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, 7, 750–756.
Burger, J., Jeitner, C., Donio, M., Pittfield, T., & Gochfeld, M. (2013). Mercury and selenium levels, and selenium:mercury molar ratios of brain, muscle, and other tissues in bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) from New Jersey, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 278–286.
Capello, M., Cutroneo, L., Consani, S., Dinelli, E., Vagge, G., & Carbone, C. (2016). Marine sediment contamination and dynamics at the mouth of a contaminated torrent: The case of the Gromolo Torrent (Sestri Levante, north-western Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 109(1), 128–141.
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment). (2001). Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: Summary tables. In: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, 1999, updated 2001, Winnipeg.
Chen, C.-M., & Liu, M.-C. (2006). Ecological risk assessment on a cadmium contaminated soil landfill—A preliminary evaluation based on toxicity tests on local species and site-specific information. Science of the Total Environment, 359, 120–129.
Cheng, W. H., & Yap, C. K. (2015). Potential human health risks from toxic metals via mangrove snail consumption and their ecological risk assessments in the habitat sediment from Peninsular Malaysia. Chemosphere, 135, 156–165.
Department of Statistics Malaysia. (2017). Current population estimates Malaysia 2017. Putrajaya: Department of Statistics Malaysia.
Elias, M. S., Ibrahim, S., Samuding, K., Rahman, S. A., Wo, Y. M., & Daung, J. A. D. (2018). Multivariate analysis for source identification of pollution in sediment of Linggi River, Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 2–16.
Hajeb, P., Christianus, A., Ismail, A., Zadeh, S. S., & Saad, C. R. (2009). Heavy metal concentration in Horseshoe Crab (Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda and Tachypleus gigas) eggs from Malaysian Coastline. In J. Tanacredi, M. Botton, & D. Smith (Eds.), Biology and conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (pp. 455–463). Boston, MA: Springer.
Håkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentary approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Haris, H., & Aris, A. Z. (2013). The geo-accumulation index and enrichment factor of mercury in mangrove sediment of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6, 4119–4128.
Haris, H., & Aris, A. Z. (2015). Distribution of metals and quality of intertidal surface sediment near commercial ports and estuaries of urbanized rivers in Port Klang, Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73, 7205–7218.
Haris, H., Looi, L. J., Mokhtar, N. F., Ayob, N. A. A., Yusoff, F. M., Salleh, A. B., et al. (2017). Geo-accumulation index and contamination factors of heavy metals (Zn and Pb) in urban river sediment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39, 1–13.
Hasan, A. R., & Nair, P. L. (2014). Urbanisation and growth of metropolitan centres in Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Economic Studies, 51, 87–101.
Hossen, M. F., Hamdan, S., & Rahman, M. R. (2015). Review on the risk assessment of heavy metals in Malaysian clams. The Scientific World Journal, 2015, 1–7.
Hu, B., Li, G., Li, J., Bi, J., Zhao, J., & Bu, R. (2013). Spatial distribution and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the southern Bohai Bay, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 4099–4110.
Kasilingam, K., Suresh Gandhi, M., Krishnakumar, S., & Magesh, N. S. (2016). Trace element concentration in surface sediment of Palk Strait, southeast coast of Tamil Nadu, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1–2), 500–508.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., & Sharifi, R. (2017). Ecotoxicological and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in short-neck clam (Paphia undulata) and contaminated sediments in Malacca Strait, Malaysia. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 73(3), 474–487.
Khodami, S., Surif, M., Wan Maznah, W. O., & Daryanabard, R. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Bayan Lepas area, Penang, Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114, 615–622.
Kowalska, J., Mazurek, R., Gąsiorek, M., Setlak, M., Zaleski, T., & Waroszewski, J. (2016). Soil pollution indices conditioned by medieval metallurgical activity—A case study from Krakow (Poland). Environmental Pollution, 218, 1023–1036.
Lemly, A. D. (2002). Symptoms and implications of selenium toxicity in fish: The Belews Lake case example. Aquatic Toxicology, 57, 39–49.
Li, X., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Luo, G., Chen, X., Yang, X., et al. (2012). Integrated assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments from a coastal industrial basin, NE China. PLoS ONE, 7(6), 1–10.
Lim, W. Y., Aris, A. Z., & Zakaria, M. P. (2012). Spatial variability of metals in surface water and sediment in the Langat river and geochemical factors that influence their water–sediment interactions. The Scientific World Journal, 2012, 1–14.
Liu, R., Men, C., Liu, Y., Yu, W., Xu, F., & Shen, Z. (2016). Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in Yangtze estuary sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1), 564–571.
Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Haris, H., Yusoff, F. M., & Hashim, Z. (2015). Mercury contamination in the estuaries and coastal sediments of the Strait of Malacca. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(4099), 1–15.
Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Haris, H., Yusoff, F. M., & Hashim, Z. (2016). The levels of mercury, methylmercury, and selenium and the selenium health benefit value in grey-eel catfish (Plotosus canius) and gaint mudskipper (Periothalmodon schlosseri) from the Strait of Malacca. Chemosphere, 152, 265–273.
Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Wan Johari, W. L., Yusoff, F. M., & Hashim, Z. (2013). Baseline metals pollution profile of tropical estuaries and coastal waters of the straits of Malacca. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 74, 471–476.
Lopes, G., Ávila, F. W., & Guilherme, L. R. G. (2017). Review: Selenium behavior in the soil environment and its implication for human health. Ciência e Agrotecnologia, 41, 605–615.
Machado, K. S., Ferreira, P. A., Rizzi, J., Figueira, R., & Froehner, S. (2016). Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metals contamination in recent sediments from Barigui river basin, South Brazil. Environment Pollution and Climate Change, 1, 1–9.
Magesh, N. S., Chandrasekar, N., Krishna Kumar, S., & Glory, M. (2013). Trace element contamination in the estuarine sediments along Tuticorin coast—Gulf of Mannar, southeast coast of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 73, 355–361.
Mir, S. I., Karim, M. A., Ali, M. I., & Ramli, N. I. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal contents in surface sediment of the Tungguk River surrounding the industrial complex of Gebeng City. Bioresearch Communications, 3(1), 362–371.
Molamohyeddin, N., Ghafourin, H., & Sadatipour, S. M. (2017). Contamination assessment of mercury, lead, cadmium and arsenic in surface sediments of Chabahar Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124(1), 521–525.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. The Journal of Geology, 2, 108–118.
Nilin, J., Moreira, L. B., Aguiar, J. E., Marins, R., Moledode Souza Abessa, D., Cruz Lotufo, T. M. D., et al. (2013). Sediment quality assessment in a tropical estuary: The case of Ceará River, Northeastern Brazil. Marine Environmental Research, 91, 89–96.
Noronha-D’Mello, C., & Nayak, G. N. (2016). Assessment of metal enrichment and their bioavailability in sediment and pneumatophores bioaccumulation by mangrove plant in a tropical (Zuari) estuary, west coast of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1), 221–230.
Ordonez, C., Lougheed, V. L., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., & Bain, L. J. (2011). Impact of metals on macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Forgotten stretch of the Rio Grande. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 426–436.
Poh, S.-C., & Tahir, N. M. (2017). The common pitfall of using enrichment factor in assessing soil heavy metal pollution. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 21, 52–59.
Praveena, S. M., Ong, W. K., & Aris, A. Z. (2012). Effect of data pre-treatment procedures on principal component analysis: A case study for mangrove surface sediment datasets. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 6855–6868.
Price, M. H. H. (2013). Sub-lethal metal toxicity effects on salmonoids: A review. Smithers, BC: Report prepared for Skeena Wild Conservation Trust.
Radojević, M., & Bashkin, V. N. (2006). Practical environmental analysis (2nd ed.). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Redzwan, G., Halim, H. A., Alias, S. A., & Rahman, M. M. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal contamination at west and east coastal area of Peninsular Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Science, 33, 23–31.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Science of Total Environment, 337, 91–107.
Rudnick, R. L., & Gao, S. (2003). Composition of the continental crust. In R. L. Rudnick (Ed.), The crust (Vol. 3, pp. 1–64). New York: Elsevier.
Rumisha, C., Mdegela, R. H., Kochzius, M., Leermakers, M., & Elskens, M. (2016). Trace metals in the giant tiger prawn Penaeus monodon and mangrove sediments of the Tanzania coast: Is there a risk to marine fauna and public health? Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 132, 77–86.
Sany, S. B. T., Salleh, A., Rezayi, M., Saadati, N., Narimany, L., & Tehrani, G. M. (2013). Distribution and contamination of heavy metal in the coastal sediments of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 224, 2–18.
Sany, B. T., Sulaiman, A. H., Monazami, G. H., & Salleh, A. (2011). Assessment of sediment quality according to heavy metal status in the west port of Malaysia. International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation, 5, 111–115.
Shafie, N. A., Aris, A. Z., Zakaria, M. P., Haris, H., Lim, W. Y., & Isa, N. M. (2013). Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factors on the assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 48, 182–190.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Tang, W., Shan, B., Zhang, H., Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., Ding, Y., et al. (2014). Heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of representative limnetic ecosystems in eastern China. Scientific Reports, 4(7152), 1–7.
Turner, A. (2010). Marine pollution from antifouling paint particles. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60, 159–171.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (1995). Method 3052: Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. In USEPA-SW-846 (Ed.), Test methods for evaluating solid waste (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Wang, A. J., Bong, C. W., Xu, Y. H., Hassan, M. H. A., Ye, X., Bakar, A. F. A., et al. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments from a tropical river-estuary-shelf system: A case study of Kelantan River, Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 125(1–2), 492–500.
Xu, X., Cao, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, R., & Hu, B. (2016). Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1), 596–602.
Yang, K., & Cattle, S. R. (2016). Comtemporary sources and levels of heavy metal contamination in urban soil of Broken Hill, Australia after ad hoc land remediation. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 32(1), 1–17.
Zhao, X.-M., Yao, L.-A., Ma, Q.-L., Zhou, G.-J., Wang, L., Fang, Q.-L., et al. (2018). Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: Implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere, 194, 107–116.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS, Project No. FRGS/1/11/STWN/UPM/02/32) from Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia and Putra Grant (GP, Project No. GP/2017/9574800) from Universiti Putra Malaysia. The authors would wish to thank Ng Tzu Shan, Lim Wan Ying, Farhah Amalya Ismail, and Lim Ai Phing for their help during field sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Looi, L.J., Aris, A.Z., Yusoff, F.M. et al. Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environ Geochem Health 41, 27–42 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0149-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0149-1