Abstract
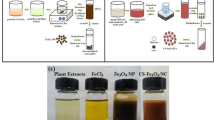
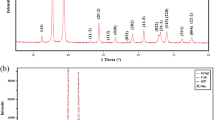
In the present study, we hypothesized that novel nanocomposites of chitosan-coated cerium oxide (CS/CeO2 NCs) derived from aqueous extracts of tea polyphenols would be stabilized and reduced by using green chemistry. The UV–visible spectrum of the synthesized material revealed an SPR peak at 279 nm, and the morphological characteristics of nanoparticles (NPs) as a uniformly distributed spherical shape with a size range of 20 nm were confirmed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectrum illustrated the amino groups of chitosan-coated with CeO2 NPs on the surface. While, the hydrodynamic size (376 nm) and surface charge (+ 25.0 mV) of particles were assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS), and the existence of oxidation state elements Ce 3d, O 1 s, and C 1 s was identified by employing X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). A cubic fluorite polycrystalline structure with a crystallite size of (5.24 nm) NPs was determined using an X-ray Diffractometer (XRD). The developed CS/CeO2 NCs demonstrated excellent antibacterial and antifungal efficacy against foodborne pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Botrytis cinerea with zone of inhibition of 13.5 ± 0.2 and 11.7 ± 0.2 mm, respectively. The results elucidated the potential of biosynthesized CS/CeO2 NCs could be utilized as potent antimicrobial agents in the food and agriculture industries.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahluwalia V, Elumalai S, Kumar V, Kumar S, Sangwan RS (2018) Nano silver particle synthesis using Swertia paniculata herbal extract and its antimicrobial activity. Microb Pathog 114:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.052
Ahmed HE, Iqbal Y, Aziz MH, Atif M, Batool Z, Hanif A, Yaqub N, Farooq WA, Ahmad S, Fatehmulla A, Ahmad H (2021) Green synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles from the Abelmoschus esculentus extract: evaluation of antioxidant, anticancer, antibacterial, and wound-healing activities. Molecules 26:4659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154659
Altaf M, Manoharadas S, Zeyad MD (2021) Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Acorus calamus extract and their antibiofilm activity against bacterial pathogens. Microsc Res Tech 84:1638–1648. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23724
Amin F, Fozia KB, Alotaibi A, Qasim M, Ahmad I, Ullah R, Bourhia M, Gul A, Zahoor S, Ahmad R (2021) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Aerva javanica leaf extract and their characterization and investigation of in vitro antimicrobial potential and cytotoxic activities. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2021:5589703. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5589703
Amini R, Brar SK, Cledon M, Surampalli RY (2016) Intertechnique comparisons for nanoparticle size measurements and shape distribution. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 20:B4015004. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000286
Andersson DA, Simak SI, Skorodumova NV, Abrikosov IA, Johansson B (2006) Optimization of ionic conductivity in doped ceria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3518–3521. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509537103
Arshad H, Sami MA, Sadaf S, Hassan U (2021) Salvadora persica mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial efcacy. Sci Rep 11:5996. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85584-w
Arumugam A, Karthikeyan C, Hameed ASH, Gopinath K, Gowri S, Karthika V (2015) Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Eng C 49:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.042
Babu S, Cho JH, Dowding JM, Heckert E, Komanski C, Das S, Colon J, Baker CH, Bass M, Self WT, Seal S (2010) Multicolored redox active upconverter cerium oxide nanoparticle for bio-imaging and therapeutics. Chem Commun 46:6915–6917. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01832E
Baldea I, Florea A, Olteanu D, Clichici S, David L, Moldovan B, Cenariu M, Achim M, Suharoschi R, Danescu S, Vulcu A, Filip GA (2020) Effects of silver and gold nanoparticles phytosynthesized with Cornus mas extract on oral dysplastic human cells. Nanomedicine 15:55–75. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2019-0290
Bandi S, Hastak V, Peshwe DR, Srivastav AK (2018) In-situ TiO2–rGO nanocomposites for CO gas sensing. Bull Mater Sci 41:115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-018-1632-0
Berne BJ, Pecora R (1976) Dynamic light scattering: with applications to chemistry, biology, and physics. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Briffa SM, Lynch I, Trouillet V, Bruns M, Hapiuk D, Liu J, Palmerc RE, Valsami-Jones E (2017) Development of scalable and versatile nanomaterial libraries for nanosafety studies: polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) capped metal oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 7:3894–3906. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra25064e
Carneiro J, Tedim J, Fernandes SCM, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Gandini A, Ferreira MGS, Zheludkevich ML (2012) Chitosan-based self-healing protective coatings doped with cerium nitrate for corrosion protection of aluminum alloy 2024. Prog Org Coat 75:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2012.02.012
Chen C, Hu J, Shao D, Li J, Wang X (2009) Adsorption behavior of multiwall carbon nanotube/iron oxide magnetic composites for Ni(II) and Sr(II). J Hazard Mater 164:923–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.089
Corral-Diaz B, Peralta-Videa JR, Alvarez-Parrilla E, Rodrigo-García J, Morales MI, Osuna-Avila P, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Cerium oxide nanoparticles alter the antioxidant capacity but do not impact tuber ionome in Raphanus sativus (L). Plant Physiol Biochem 84:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.09.018
Corsi F, Caputo F, Traversa E, Ghibelli L (2018) Not only redox: the multifaceted activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in cancer prevention and therapy. Front Oncol 8:309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00309
Dutta D, Mukherjee R, Patra P, Banik M, Dasgupta R, Mukherjee M, Basu T (2016) Green synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticle: a prospective drug against oxidative harm. Colloids Surf B 147:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.07.045
Egodawatte S, Datt A, Burns EA, Larsen SC (2015) Chemical insight into the adsorption of chromium (III) on iron oxide/mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Langmuir 31:7553–7562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01483
Fang X, Song H (2019) Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles loaded on chitosan for enhanced auto-catalytic regenerative ability and biocompatibility for the spinal cord injury repair. J Photochem Photobiol b: Biol 191:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.11.016
Fernandes M, Singh KRB, Sarkar T, Singh P, Singh RP (2020) Recent applications of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles in various domains. Adv Mater Lett 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2020.081543
Fu Q, Saltsburg H, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2003) Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 301:935–938. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1085721
Gao F, Zheng D, Tanaka H, Zhan F, Yuan X, Gao F, Wang Q (2015) An electrochemical sensor for gallic acid based on Fe2O3/electro-reduced graphene oxide composite: estimation for the antioxidant capacity index of wines. Mater Sci Eng C 57:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.025
George S, Pokhrel S, Xia T, Gilbert B, Ji Z, Schowalter M, Rosenauer A, Damoiseaux R, Bradley KA, Mädler L, Nel AE (2010) Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping. ACS Nano 26:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn901503q
Gong JL, Wang B, Zeng GM, Yang CP, Niu CG, Niu QY, Zhou WJ, Liang Y (2009) Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 164:1517–1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.072
Haldorai Y, Shim JJ (2013) Multifunctional chitosan copper oxide hybrid material: photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Int J Photoenergy 2013:245646. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/245646
Hao R, Li D, Zhang J, Jiao T (2021) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using green tea and its removal of hexavalent chromium. Nanomaterials 11:650. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030650
Hassannejad H, Nouri A (2016) Synthesis and evaluation of self-healing cerium-doped chitosan nanocomposite coatings on AA5083-H321. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:2106–2118
Hu C, Lu T, Chen F, Zhang R (2013) A brief review of graphene–metal oxide composites synthesis and applications in photocatalysis. J Chin Adv Mater Soc 1:21–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/22243682.2013.771917
Inbasekar C, Fathima NN (2020) Collagen stabilization using ionic liquid functionalised cerium oxide nanoparticle. Int J Biol Macromol 147:24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.271
Jan H, Shah M, Andleeb A, Faisal S, Khattak A, Rizwan M, Drouet S, Hano C, Abbasi BH (2021) Plant-based synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using aqueous leaf extract of Aquilegia pubiflora: their antiproliferative activity against HepG2 cells inducing reactive oxygen species and other in vitro properties. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2021:4786227. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4786227
Kannan SK, Sundrarajan M (2014) A green approach for the synthesis of a cerium oxide nanoparticle: characterization and antibacterial activity. Int J Nanosci 13:1450018. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X14500185
Kaushik A, Pratima R, Solanki MK, Pandey AS, Malhotra BD (2009) Cerium oxide-chitosan based nanobiocomposite for food borne mycotoxin detection. Appl Phys Lett 95:173703. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3249586
Kaygusuz H, Erim FB (2021) Biopolymer-assisted green synthesis of functional cerium oxide nanoparticles. Chem Zvesti 74:2357–2363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01084-7
Kaygusuz H, Torlak E, Akın-Evingür G, Özen İ, von Klitzing R, Erim FB (2017) Antimicrobial cerium ion-chitosan crosslinked alginate biopolymer flms: a novel and potential wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol 105:1161–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.144
Khan SA, Ahmad A (2014) Fungus mediated synthesis of biomedically important CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 48:4134–4138
Kim CK, Kim T, Choi I, Soh M, Kim D, Kim Y, Jang H, Yang HS, Kim JY, Park HK, Park SP, Park S, Yu T, Yoon BW, Lee SH, Hyeon T (2012) Ceria nanoparticles that can protect against ischemic stroke. Angew Chemie Int Ed. Wiley Online Library 51:11039–11043. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201203780
Kim DK, Mikhaylova M, Wang FH, Kehr J, Bjelke B, Zhang Y, Tsakalakos T, Muhammed M (2003) Starch-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles as MR contrast agents. Chem Mater 15:4343–4351. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm031104m
Kızılkonca E, Torlak E, Bedia Erim F (2021) Preparation and characterization of antibacterial nano cerium oxide/chitosan/hydroxyethylcellulose/polyethylene glycol composite films. Int J Bio Macromol 177:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.139
Kokila K, Elavarasan N, Sujatha V (2017) Diospyros montana leaf extract mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their biological applications. New J Chem 41:7481–7490. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ01124E
Kumar E, Selvarajan P, Balasubramanian K (2010) Preparation and studies of cerium dioxide (CeO2) nanoparticles by microwave-assisted solution method. Recent Res Sci Technol 2:37–41
Lamba R, Umar A, Mehta SK, Kumar Kansal S (2015) Well-crystalline porous ZnO-SnO2 nanosheets: an effective visible-light driven photocatalyst and highly sensitive smart sensor material. Talanta 131:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.07.096
Lebaschi S, Hekmati M, Veisi H (2017) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles mediated by black tea leaves (Camellia Sinensis) Extract: Catalytic Activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction under ligand-free conditions. J Colloid Interface Sci 485:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.09.027
Li X, Qi M, Li C, Dong B, Wang L, Weir MD, Imazato S, Du L, Lynch CD, Xu L, Zhou Y, Wang L, Xu HHK (2019a) Novel nanoparticles of cerium-doped zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with dual benefits of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory functions against periodontitis. J Mater Chem B 7:6955–6971. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB01743G
Li X, Qi M, Sun X, Weir MD, Tay FR, Oates TW, Dong B, Zhou Y, Wanga L, Xu HHK (2019b) Surface treatments on titanium implants via nanostructured ceria for antibacterial and anti-inflammatory capabilities. Acta Biomater 94:627–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2019.06.023
Li X, Sun C, Luo L, He Y (2015) Determination of tea polyphenols content by infrared spectroscopy coupled with iPLS and random frog techniques. Comput Electron Agric 112:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.01.005
Liang J, Li F, Fang Y, Yang W, An X, Zhao L, Xin Z, Cao L, Hu Q (2011) Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity studies of chitosan-coated tea polyphenols nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 82:297–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.08.045
Mallick S, Singh KRB, Nayak V, Singh J, Singh RB (2022) Potentialities of core@shell nanomaterials for biosensor technologies. Mater Lett 306:130912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130912
Manikandan A, Sathiyabama M (2015) Green synthesis of copper chitosan nanoparticles and study of its antibacterial activity. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 6:1. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000251
Maqbool Q, Nazar M, Naz S, Hussain T, Jabeen N, Kausar R, Anwaar S, Abbas F, Jan T (2016) Antimicrobial potential of green synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles from Olea europaea leaf extract. Int J Nanomed 11:5015–5025. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S113508
Masui T, Ozaki T, Machida K, Adachi G (2000) Preparation of ceria–zirconia sub-catalysts for automotive exhaust cleaning. J Alloys Compd 303:49–55
Mohammad F, Arfin T, Al-Lohedan HA (2017) Enhanced biological activity and biosorption performance of trimethyl chitosan-loaded cerium oxide particles. J Ind Eng Chem 45:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.08.029
Morales MI, Rico CM, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Nunez JE, Barrios AC, Tafoya A, Flores-Marges JP, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2013) Toxicity assessment of cerium oxide nanoparticles in cilantro (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grown in organic soil. J Agric Food Chem 61:6224–6230. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf401628v
Naidi SN, Khan F, Tan AL, Harunsani MH, Kim YM, Khan MM (2021) Photoantioxidant and antibiofilm studies of green synthesized Sn-doped CeO2 nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extracts of Pometia pinnata. New J Chem 45:7816–7829. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ00416F
Nasiri A, Shariaty-Niasar MSN, Akbari Z (2012) Synthesis of LDPE/nano TiO2 nanocomposite for 792 packaging applications. Int J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:165–170
Nguyet NT, Yen LTH, Doan VY, Hoang NL, Van Thu Vu, lan H, Trung T, Pham VH, Tam PD, (2019) A label-free and highly sensitive DNA biosensor based on the core-shell structured CeO2-NR@Ppy nanocomposite for salmonella detection. Mater Sci Eng C 96:790–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.059
Nishanthi R, Malathi S, John Paul S, Palani P (2019) Green synthesis and characterization of bioinspired silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles and evaluation of their synergistic antibacterial activity after combining with different classes of antibiotics. Mater Sci Eng C 96:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.050
Onazi WAA, Ali MHH (2021) Synthesis and characterization of cerium oxide hybrid with chitosan nanoparticles for enhancing the photodegradation of Congo Red dye. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:12017–12030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05832-7
Pelletier DA, Suresh AK, Holton GA, McKeown CK, Wang W, Gu B, Mortensen NP, Allison DP, Joy DC, Allison MR, Brown SD, Phelps TJ, Doktycz MJ (2010) Effects of engineered cerium oxide nanoparticles on bacterial growth and viability. Appl Environ Microb 76:7981–7989. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00650-10
Qi M, Li W, Zheng X, Li X, Sun Y, Wang Y, Li C, Wang L (2020) Cerium and its oxidant-based nanomaterials for antibacterial applications: a state-of-the-art review. Front Mater 7:213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00213
Rajan A, Rajan A, John A, Philip D (2019) Green synthesis of CeO2 nanostructures by using Morus nigra fruit extract and its antidiabetic activity. AIP Conf Proc 2105:020008. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5100693
Rajeshkumar S, Naik P (2018) Synthesis and biomedical applications of cerium oxide nanoparticles-a review. Biotechnol Rep 17:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.11.008
Ramli M, Rossani RB, Nadia Y, Darmawan TB, Febriani S, Ismail YS (2019) Nanoparticle fabrication of calcium oxide (CaO) mediated by the extract of red dragon fruit peels (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) and its application as inorganic–anti-microorganism materials. IOP Conf Series: Mater Sci Eng 509:012090. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/509/1/012090
Romer I, Briffa SM, Arroyo Rojas Dasilva Y, Hapiuk D, Trouillet V, Palmer RE, Valsami-Jones E (2019) Impact of particle size, oxidation state and capping agent of different cerium dioxide nanoparticles on the phosphate-induced transformations at different pH and concentration. PLoS ONE 14:e0217483. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217483
Senthilkumar P, Bhuvaneshwaria V, Ranjithkumarb R, Sathiyavimala S, Malayamanc V, Chandarshekar B (2017) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of hybridchitosan-cerium oxide nanoparticles: as a bionanomaterials. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1746–1752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.139
Sharmila G, Muthukumaran C, Saraswathi H, Sangeetha E, Soundarya S, Manoj Kumar N (2019) Green synthesis, characterization and biological activities of nanoceria. Ceram Int 45:12382–12386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.164
Singh KRB, Nayak V, Jay Singh J, Singh AK, Singh RP (2021a) Potentialities of bioinspired metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in biomedical sciences. RSC Adv 1:24722–24746. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04273D
Singh P, Singh KR, Singh J, Das SN, Singh RP (2021b) Tunable electrochemistry and efficient antibacterial activity of plant-mediated copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Annona squamosa seed extract for agricultural utility. RSC Adv 11:18050–18060. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA02382A
Singh KRB, Nayak V, Sarkar T, Singh RP (2020) Cerium oxide nanoparticles: properties, biosynthesis and biomedical application. RSC Adv 10:27194–27214. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA04736H
Singh P, Kim YJ, Zhang D, Yang DC (2016) Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 34:588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.006
Singh P, Singh KRB, Verma R, Singh J, Singh RP (2022) Efficient electro-optical characteristics of bioinspired iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Terminalia chebula dried seed extract. Mater Lett 307:131053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131053
Srinivasan R, Bose AC (2010) Structural properties of Sm3+ doped cerium oxide nanorods synthesized by hydrolysis assisted co-precipitation method. Mater Lett 64:1954–1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2010.06.023
Sumaoka J, Azuma Y, Komiyama M (1998) Enzymatic manipulation of the fragments obtained by cerium(IV)-induced DNA scission: characterization of hydrolytic termini. Chem Eur J 4:205–209
Sun Y, Sun X, Li X, Li W, Li C, Zhou Y, Wang L, Dong B (2021) A versatile nanocomposite based on nanoceria for antibacterial enhancement and protection from aPDT-aggravated inflammation via modulation of macrophage polarization. Biomaterials 268:120614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120614
Sun Z, Shi C, Wang X, Fang Q, Huang J (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activities of sulfonated chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 155:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.069
Suresh R, Ponnuswamy V, Mariappan R (2013) Effect of annealing temperature on the microstructural, optical and electrical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method. Appl Surf Sci 273:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.062
Tammineni S, Roopan S (2016) Photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of phytosynthesized of CeO2 NPs using Moringa oleifera peel extract. J Photochem Photobiol B 161:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.019
Thill A, Zeyons O, Spalla O, Chauvat F, Rose J, Auffan M, Flank AM (2006) Cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles for Escherichia coli. Physico-chemical insight of the cytotoxicity mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 40:6151–6156. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060999b
Unsoy G, Yalcin S, Khodadust R, Gunduz G, Gunduz U (2012) Synthesis optimization and characterization of chitosan coated iron oxide nanoparticles produced for biomedical applications. J Nanopart Res 14:964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0964-8
Veisi H, Ghorbani F (2017) Iron oxide nanoparticles coated with green tea extract as a novel magnetite reductant and stabilizer sorbent for silver ions: synthetic application of Fe3O4@green tea/Ag nanoparticles as magnetically separable and reusable nanocatalyst for reduction of 4-. Appl Organomet Chem 31:e3711. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3711
Wang H, Chen L, Weng LL, Zhang MY, Shen Q (2014) Surface properties and dissolution kinetics of tea polyphenols. J Adhes Sci Technol 28:2416–2423. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2014.968420
Wang W, Zhang Z (2007) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of carbohydrate microspheres coated with magnetic nanoparticles. J Dispers Sci Technol 28:557–561. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690701277294
Wang Y, Ho CT (2009) Polyphenols chemistry of tea and coffee: a century of progress. J Agric Food Chem 57:8109–8114. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf804025c
Wang Y, Li C, Wan Y, Qi M, Chen Q, Sun Y, Sun X, Fang J, Fu L, Xu L, Dong B, Wang L (2021) Quercetin-loaded ceria nanocomposite potentiate dual-directional immunoregulation via macrophage polarization against periodontal inflammation. Small 17:2101505. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202101505
Wang Y, Shi Z, Yin J (2011) Facile synthesis of soluble graphene via a green reduction of graphene oxide in tea solution and its biocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1021/am1012613
Wang Z, Huang Y, Dongcan LV, Jiang G, Zhang F, Song A (2019) Tea polyphenol-assisted green synthesis of Ag-nanodiamond hybrid and its catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction. Green Chem Lett Rev 12:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2019.1624836
Yabe S, Sato T (2003) Cerium oxide for sunscreen cosmetics. J Solid State Chem 171:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-4596(02)00139-1
Zhai Y, Zhou K, Xue Y, Qin F, Yang L, Yao X (2013) Synthesis of water-soluble chitosan-coated nanoceria with excellent antioxidant properties. RSC Adv 3:6833. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA22251A
Zhang JH, Zhu YF (2014) Synthesis and characterization of CeO2-incorporated mesoporous calcium-silicate materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 197:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.06.018
Zhang M, Zhang C, Zhai X, Luo F, Du Y, Yan C (2019) Antibacterial mechanism and activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Sci China Mater 62:1727–1739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-019-9471-7
Zhao L, Sun Y, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Hong J, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea NGM, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2015) Monitoring the environmental effects of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles through the life cycle of corn (Zea mays) plants and in situ μ-XRF mapping of nutrients in kernels. Environ Sci Technol 49:2921–2928. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5060226
Acknowledgements
We thank the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (2017C32008) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY20B040001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: Conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, writing-original draft, and preparation. HW: Formal analysis and investigation. HC: Methodology and investigation. JH: Conceptualization, supervision, visualization, and writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Appu, M., Wu, H., Chen, H. et al. Tea polyphenols mediated biogenic synthesis of chitosan-coated cerium oxide (CS/CeO2) nanocomposites and their potent antimicrobial capabilities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 42575–42586 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19349-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19349-x