Abstract
This study examines the spatial impact of FDI on ecological footprint of 31 African countries. In achieving this, the study uses the Driscoll-Kraay (1998) random effect model, fixed-effect instrumental variable regression, and the spatial Durbin model. There are three main important findings from this empirical study. First, FDI has a nonlinear impact on ecological footprint in Africa. At the initial stage, FDI reduces ecological footprint up to a threshold of $404.75–$669.96 million, before the impact increases ecological degradation. This result is robust to the instrumental regression model. Second, the results further reveal a significant spatial spillover of FDI on ecological footprint in Africa. Third, the empirical results provide evidence of both direct and spillover effects of environmental degradation determinant in Africa. This denotes that environmental quality of a particular country influences the environmental quality of other neighbouring countries. While it is important to attract significant amount of foreign investment to Africa, this study recommends that African governments need to improve their environmental regulations and laws to achieve transfer of energy-saving technology from foreign investors.

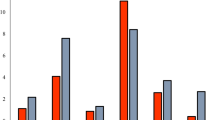
Source: UNCTAD (2021)Query

Source: Global Footprint Network (GFN)

Source: Authors’ calculation using Global Footprint Network Database

Source: Authors’ computation using data from Global Footprint Network Database

Source: Authors’ computation using data from Global Footprint Network and UNCTAD Database
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
Quadrant A in Fig. 3 are countries with negative spatial clustering of low ecological footprint, while B indicates countries with positive spatial clustering of high ecological footprint, C indicates positive spatial cluster of countries with low ecological footprint, and D is negative spatial cluster of high ecological footprint.
The selected countries account for 91% of total stock of FDI inflows in Africa in 2017. This makes our sample more representative.
The fixed-effect instrumental regression is used to address endogeneity in the model. Lagged FDI was used as instruments in the model.
This study empirically confirms the presence of spatial autocorrelation in Eq. (2) with the Moran \(Ii\) test. This is done through the residual of the pooled regression (not reported in this study but available on request).
See Elhorst (2014) for more on the mathematical derivation.
References
Abdo, A, Li, B, Zhang, X, Lu, J and Rasheed, A. (2020). Influence of FDI on environmental pollution in selected Arab countries: a spatial econometric analysis perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(22): 28222–28246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08810-4
Adekola O, Mitchell G, Grainger A (2015) Inequality and ecosystem services: the value and social distribution of Niger Delta wetland services. Ecosyst Serv 12:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2015.01.005
Aghasafari H, Aminizadeh M, Karbasi A, Calisti R (2021) CO2 emissions, export and foreign direct investment: empirical evidence from Middle East and North African Region. J Int Trade Econ Dev 30(7):1054–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638199.2021.1934087
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Majeed A, Raza MY (2020a) Does financial development and foreign direct investment improve environmental quality? Evidence from belt and road countries. Environ Sci Pollut R 27(19):23586–23601
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Majeed A, Umar M, Khan Z, Muhammad S (2020b) The dynamic impact of natural resources, technological innovations and economic growth on ecological footprint: an advanced panel data estimation. Resour Policy 69:101817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101817
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Murshed M, Shehzad K, Akram R, Cui L, Khan Z (2021) Modelling the dynamic linkages between eco-innovation, urbanization, economic growth and ecological footprints for G7 countries: does financial globalization matter? Sustain Cities Soc 70:102881
Akinlo AE (2004) Foreign direct investment and growth in Nigeria: an empirical investigation. J Policy Model 26(2):627–639
Akinlo AE (2003) Globalization, international investment and stock market growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Visiting Research Fellow Monograph Series, (382).
Al-mulali U (2012) Factors affecting CO2 emission in the Middle East: A panel data analysis. Energy 44(1):564–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.05.045
Al-Mulali U, Tang CF (2013) Investigating the validity of pollution haven hypothesis in the gulf cooperation council (GCC) countries. Energ Policy 60:813–819
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.139
Anselin L (1988) Spatial econometrics: methods and models. Springer, Netherlands
Anselin L (2009) Spatial regression. SAGE Handb Spat Anal 1:255–276
Anselin L, Bera A (1998) Spatial dependence in linear regression models with an introduction to spatial econometrics. In: Ullah A, Giles DEA (eds) Handbook of Applied Economic Statistics. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 237–289
Anselin L, Le Gallo J (2006) Interpolation of air quality measures in hedonic house price models: spatial aspects. Spat Econ Anal 1(1):31–52
Anyanwu J C (2012) Why does foreign direct investment go where it goes?: New evidence from African countries. Ann Econ Financ 13(2):425–462
Arogundade S, Biyase M, Eita JH (2021) Foreign direct investment and inclusive human development in sub-Saharan African countries: domestic conditions matter. Economia Internazionale/International Economics 74(4):463–498
Aremo AG, Ojeyinka TA (2018) Foreign direct investment, energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Nigeria (1970–2014): an aggregate empirical analysis. Int J Green Econ 12(3–4):209–227. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGE.2018.097868
Ashraf A, Doytch N, Uctum M (2020) Foreign direct investment and the environment: disentangling the impact of greenfield investment and merger and acquisition sales. Sustain Account Manag Policy J
Ayanlade A, Proske U (2015) Assessing wetland degradation and loss of ecosystem services in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Marine and Freshwater Research, 67(6): 828-836. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF15066
Baek J (2016) A new look at the FDI–income–energy–environment nexus: dynamic panel data analysis of ASEAN. Energy Pol 91:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.12.045
Baloch A, Ozturk I, Bekun V, Khan D (2020) Modeling the dynamic linkage between financial development, energy innovation, and environmental quality: Does globalization matter? Bus Strat Environ 30(1):176–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2615
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energ Policy 113:356–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.10.050
Behera SR, Dash DP (2017) The effect of urbanization, energy consumption, and foreign direct investment on the carbon dioxide emission in the SSEA (south and southeast Asian) region. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:96–106
Burridge P (1980) On the Cliff-Ord test for spatial correlation. J Roy Stat Soc: Ser B (methodol) 42(1):107–108
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:138-154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.031
Chowdhury MAF, Shanto PA, Ahmed A, Rumana RH (2021) Does foreign direct investment impair the ecological footprint? New evidence from the panel quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut R 28:14372–14385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11518-0
Cole MA, Elliott RJ, Zhang J (2011) Growth, foreign direct investment, and the environment: evidence from Chinese cities. J Reg Sci 51(1):121–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2010.00674.x
Cramer W, Guiot J, Fader M, Garrabou J, Gattuso JP et al (2018) Climate change and interconnected risks to sustainable development in the Mediterranean. Nat Clim Change 8(11): 972-980. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0299-2
Cumming GS, Von Cramon-Taubadel S (2018) Linking economic growth pathways and environmental sustainability by understanding development as alternate social-ecological regimes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(38):9533–9538. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1807026115
Danish Baloch MA, Mahmood N, Zhang JW (2019) Effect of natural resources, renewable energy and economic development on CO2 emissions in BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 678:632–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.028
Danish, Wang Z (2018) Dynamic relationship between tourism, economic growth, and environmental quality. J Sustain Tour 26(11):1928–1943
DeFries RS, Rudel T, Uriarte M, Hansen M (2010) Deforestation driven by urban population growth and agricultural trade in the twenty-first century. Nat Geosci 3(3):178
Destek MA, Okumus I (2019) Does pollution haven hypothesis hold in newly industrialized countries? Evidence from ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23689–23695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05614-z
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.017
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.011
Doytch N, Ashraf A (2021) The ecological footprints of greenfield FDI and cross-border M&A Sales. Environ Model Assess 1–17.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-021-09777-3
Doytch N, Uctum M (2016) Globalization and the environmental impact of sectoral FDI. Econ Syst 40(4):582–594
Driscoll JC, Kraay AC (1998) Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev Econ Stat 80:549–560
Eskeland G S, Harrison AE (2003) Moving to greener pastures? Multinationals and the pollution haven hypothesis. J Dev Econ 70(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3878(02)00084-6
Fakher HA (2019) Investigating the determinant factors of environmental quality (based on ecological carbon footprint index). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(10):10276–10291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14470-9
GFN (2018) Global footprint network. http://data.footprintnetwork.org/.
GFN (2020) Global footprint network. http://data.footprintnetwork.org/.
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Hakimi A, Hamdi H (2016) Trade liberalization, FDI inflows, environmental quality and economic growth: a comparative analysis between Tunisia and Morocco. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:1445–1456
Hassan A, Meyer D (2021) Financial development–income inequality nexus in South Africa: A nonlinear analysis. Int J Econ Financ 12:15–25
Hassan ST, Xia E, Khan NH, Mohsin S, Shah A (2018) Economic growth, natural resources and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2929–2938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3803-3
He J (2006) Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol Econ 60(1):228–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.12.008
Iheonu CO, Anyanwu OC, Odo OK, Nathaniel SP (2021) Does economic growth, international trade, and urbanization uphold environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa? Insights from quantile and causality procedures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:28222–28233
Kelejian HH, Tavlas GS, Hondroyiannis G (2006) A spatial modelling approach to contagion among emerging economies. Open Econ Rev 17(4):423–441
Khan D, Ulucak R (2020) How do environmental technologies affect green growth? Evidence from BRICS economies. Sci Total Environ, 712, 136504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136504
Khan A (2007) Foreign direct investment and economic growth: the role of domestic financial sector. Pakistan Institute of Development Economics (PIDE) Working Paper.
Kirkulak B, Qiu B, Yin W (2011) The impact of FDI on air quality: evidence from China. J Chinese Econ Foreign Trade Stud. https://doi.org/10.1108/17544401111143436
Kissinger M, Rees WE (2010) Importing terrestrial biocapacity: The U.S. case and global implications. Land Use Policy 27(2):589–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2009.07.014
Lambin EF, Meyfroidt P (2011) Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(9):3465–3472
LeSage J, Pace R K (2009) Introduction to spatial econometrics(1st ed.). Chapman and Hall/CRC. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420064254
LeSage JP, Pace RK (2010) Spatial econometric models. In Handbook of applied spatial analysis (pp. 355–376). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
LeSage J, Pace RK (2009b) Introduction to spatial econometrics. Chapman and Hall, CRC
Maddison D (2006) Environmental Kuznets curves: a spatial econometric approach. J Environ Econ Manag 51:218–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2005.07.002
Mahmood H, Alkhateeb Y, Furqan M (2020) Exports, imports, foreign direct investment and CO2 emissions in North Africa: spatial analysis. Energy Rep 6:2403–2409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.08.038
Nathaniel S, Nwodo O, Adediran A, Sharma G, Shah M, Adeleye N (2019) Ecological footprint, urbanization, and energy consumption in South Africa: including the excluded. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(26):27168–27179
Nathaniel SP, Barua S, Ahmed Z (2021a) What drives ecological footprint in top ten tourist destinations? Evidence from advanced panel techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1–10
Nathaniel SP, Murshed M, Bassim M (2021) The nexus between economic growth, energy use, international trade and ecological footprints: the role of environmental regulations in N11 countries. Ener, Eco and Environ. 6(6): 496-512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-020-00205-y
Nathaniel SP, Yalciner K, Bekun FV (2021). Assessing the environmental sustainability corridor: Linking natural resources, renewable energy, human capital, and ecological footprint in BRICS. Res Pol, 70, 101924.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101924
Nunnenkamp P (2004) To what extent can foreign direct investment help achieve international development goals?. World Econ 27(5):657–677. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0378-5920.2004.00620
Omri A, Nguyen DK, Rault C (2014) Causal interactions between CO2 emissions, FDI, and economic growth: evidence from dynamic simultaneous-equation models. Econ Model 42:382–389
Ozcan B, Tzeremes PG, Tzeremes NG (2020) Energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in OECD countries. Econ Model 84:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2019.04.010
Pao HT, Tsai CM (2011) Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 36(1):685–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.09.041
Pazienza P (2015) The relationship between CO2 and foreign direct investment in the agriculture and fishing sector of OECD countries: evidence and policy considerations. Intellectual Economics 9(1):55–66
Ragoubi H, El Harbi S (2018) Entrepreneurship and income inequality: a spatial panel data analysis. Int Rev Appl Econ 32(3):374–422. https://doi.org/10.2478/tekhne-2019-0012
Rappaport J (2000) How does openness to capital flows affect growth?. FRB of Kansas City Research Working Paper No. 00-11.
Sabir S, Qayyum U, Majeed T (2020) FDI and environmental degradation: the role of political institutions in South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(26):32544–32553
Sapkota P, Bastola U (2017) Foreign direct investment, income, and environmental pollution in developing countries: panel data analysis of Latin America. Energy Econ 64:206–212
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019) Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 646:862–871
Seker F, Ertugrul HM, Cetin M (2015) The impact of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: a bounds testing and causality analysis for Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:347–356
Shaari M S, Hussain N E, Abdullah H, Kamil S (2014) Relationship among foreign direct investment, economic growth and CO2 emission: a panel data analysis. International J Energy Econ Policy 4(4):706–715
Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019a) Foreign direct Investment-CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Prod 217:603–614
Shahbaz M, Destek MA, Okumus I, Sinha A (2019b) An empirical note on comparison between resource abundance and resource dependence in resource abundant countries. Resour Policy 60:47–55
Shahbaz M, Raghutla C, Song M, Zameer H, Jiao Z (2020) Public-private partnerships investment in energy as new determinant of CO2 emissions: the role of technological innovations in China. Energy Econ 86:104664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104664
Sharma SS (2011) Determinants of carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from 69 countries Appl. Energy 88:376–382
Shen J, Wei YD, Yang Z (2017) The impact of environmental regulations on the location of pollution-intensive industries in China. J Clean Prod 148:785–794
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Musah I, Ozturk I (2017) Investigating the pollution haven hypothesis in Ghana: an empirical investigation. Energy 124:706–719
Sun C, Zhang F, Xu M (2017) Investigation of pollution haven hypothesis for China: an ARDL approach with breakpoint unit root tests. J Clean Prod 161:153–164
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ 32(1):137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.04.004
Tang CF, Tan BW (2015) The impact of energy consumption, income and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 79:447–454
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37(1):246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.025
Tian X (2007) Accounting for sources of FDI technology spillovers: Evidence from China. J Int Bus Stud 38(1):147–159. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400245
Tilman D, Socolow R, Foley JA, Hill J, Larson E, Lynd L et al (2009) Beneficial biofuels—the food, energy, and environment trilemma. Science 325(5938):270–271
Tobler WR (1970) A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ Geogr 46:234–240
Udemba EN (2020b) Ecological implication of offshored economic activities in Turkey: foreign direct investment perspective. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:38015–38028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09629-9
Udemba EN, Magazzino C, Bekun FV (2020) Modeling the nexus between pollutant emission, energy consumption, foreign direct investment, and economic growth: new insights from China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(15): 17831-17842 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08180-x
Udemba EN (2020a) A sustainable study of economic growth and development amidst ecological footprint: new insight from Nigerian perspective. Sci Total Environ. 732, 139270 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139270
Ugwuegbe SU, Modebe NJ (2014) The impact and foreign direct investment on capital formation in Nigeria: a cointegration approach. Int J Econ Financ Manag Sci 2(2):188–196
Ulph A (1992) The choice of environmental policy instruments and strategic international trade. In Conflicts and cooperation in managing environmental resources (111-132). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Ulucak R, Khan SUD (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain Cities Soc 54:101996
Ulucak R, Khan S (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sust Citi and Soci 54:101996
Ulucak R, Lin D (2017) Persistence of policy shocks to ecological footprint of the USA. Ecol Indic 80:337–343
UNCTAD (1999) Foreign direct investment in Africa: performance and potential. https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/poiteiitm15.pdf. Accessed 28 October 2021
UNCTAD (2021) Foreign direct investment: inward and outward flows and stock, annual. Accessed 28 October 2021 https://unctadstat.unctad.org
Usman O, Rafindadi AA, Sarkodie SA (2021) Conflicts and ecological footprint in MENA countries: implications for sustainable terrestrial ecosystem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(42):59988–59999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14931-1
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1998) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth 720:9. New Society Publishers.
Wang DT, Chen WY (2014) Foreign direct investment, institutional development, and environmental externalities: Evidence from China. J Environmental Manag 135:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.013
Wang Y, Zhao T (2015) Impacts of energy-related CO2 emissions: evidence from under developed, developing and highly developed regions in China. Ecol Indic 50:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.010
Wang Z, Ye X (2017) Re-examining environmental Kuznets curve for China’s city level carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Spat Stat 21:377–389
Wang L, Vo XV, Shahbaz M, Ak A (2020) Globalization and carbon emissions: is there any role of agriculture value-added, financial development, and natural resource rent in the aftermath of COP21? J Environ Manage 268:110712
Weinzettel J, Hertwich EG, Peters GP, Steen-Olsen K, Galli A (2013) Affluence drives the global displacement of land use. Global Environ Chang 23(2):433–438
Zafar MW, Zaidi SAH, Khan NR, Mizra FM, Hou F, Kirmani SAS (2019) The impact of natural resources, human capital and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: the case of the United States. Resour Policy 63:101428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101428
Zakarya GY, Mostefa B, Abbes SM, Seghir GM (2015) Factors affecting CO2 emissions in the BRICS countries: a panel data analysis. Procedia Econ Financ 26:114–125
Zhang Z, Zhu K, Hewings GJD (2017) A multi-regional input–output analysis of the pollution haven hypothesis from the perspective of global production fragmentation. Energy Econ 64:13–23
Zhao J, Zhao Z, Zhang H (2019) The impact of growth, energy and financial development on environmental pollution in China: new evidence from a spatial econometric analysis. Energ Econ 93: 104506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104506
Zhu H, Duan L, Guo Y, Yu K (2016) The effects of FDI, economic growth and energy consumption on carbon emissions in ASEAN-5: evidence from panel quantile regression. Econ Model 58:237–248
Zhu L, Gan Q, Liu Y, Yan Z (2017) The impact of foreign direct investment on SO2 emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region: a spatial econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 166:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.032
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sodiq Arogundade conceptualized the major idea of this research paper. He prepared the methodology, data collection, analysis, interpretation, and conclusion section. Adewale Hassan prepared the introduction, and Biyase Mduduzi prepared the literature review. The three authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arogundade, S., Mduduzi, B. & Hassan, A.S. Spatial impact of foreign direct investment on ecological footprint in Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 51589–51608 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18831-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18831-w