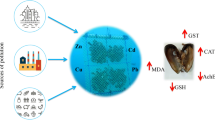
Abstract
Despite the nutritional benefits, bivalves like mussels are also an excellent aquatic heavy metal biomonitoring agent due to their high tolerance to varying levels of temperature, salinity and oxygen, as well as pollutants. Although the accumulated toxic heavy metals may not exert direct negative impacts on the mussels, such toxicants in mussel tissues can give harmful effects on human body when consumed in toxic quantities and/or over prolonged period. The booming of urban and industrial activities, and consequently the increment of runoffs, as well as wastewater effluents and leaching, further exacerbated the magnitude of this issue. Hence, continuous monitoring of heavy metal contents in mussels is vital to ensure its compliance with food safety regulations, protecting consumers at large. This review paper discusses the occurrence of heavy metals in mussels especially that of Perna viridis in Malaysia and other parts of the world since year 2000 until 2021. Heavy metal concentration data and patterns from various coastal and/or estuaries were compared. Where applicable, statistical data that indicate variations between sampling sites, sampling months or years and chemical treatments for heavy metal removal were critically reviewed. Health risk assessment findings were also discussed. More importantly, related chemical-based interventions to minimize and/or eliminate toxic heavy metals from mussels are also reviewed.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abderrahmani K, Boulahdid M, Bendou N, Aissani A (2020) Seasonal distribution of cadmium, lead, nickel, and magnesium in several tissues of mussels from the Algerian coasts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:22547–22567
Abdullah F, Yusoff ARM, Bakar W, Ismail R, Hadiyanto DP (2014a) Removal of selected heavy metals from green mussel via catalytic oxidation. Malaysian J Anal Sci 18:271–283
Abdullah N, Tair R, Abdullah MH (2014b) Heavy metals concentration relationship with Perna viridis physical properties in Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah. Malaysia Pak J Biol Sci 17:62–67
Azelee IW, Ismail R, Bakar WAWA, Ali R, Mohamed R, Samsudin NA, Baharin H (2013) Catalyzed trisodium citrate as a medium for heavy metals treatment in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis). Mod Res Cat 2:50–56
Azelee IW, Ismail R, Ali R, Bakar W (2014) Chelation technique for the removal of heavy metals (As, Pb, Cd and Ni) from green mussel, Perna viridis. Indian J Geo-Mar Sci 43:372–376
Azizi G, Akodad M, Baghour M, Layachi M, Moumen A (2018) The use of Mytilus spp. mussels as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in the coastal environment. A review. J Mater Environ Sci 9:1170–1181
Baltas H, Sirin M, Dalgic G, Bayrak EY, Akdeniz A (2017) Assessment of metal concentrations (Cu, Zn, and Pb) in seawater, sediment and biota samples in the coastal area of Eastern Black Sea. Turkey Mar Pollut Bull 122:475–482
Bhattacharyya A, Chattopadhyay R, Mitra S, Crowe SE (2014) Oxidative stress: an essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiol Rev 94:329–354
Chang-Yen I, Guppy M, Agard J (1999): Perna viridis: potential as a novel food source and sentinel organism, Institute of Marine Affairs 6th Annual Symposium, Trinidad, Caribbean
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867
De Astudillo LR, Yen IC, Agard J, Bekele I, Hubbard R (2002) Heavy metals in green mussel (Perna viridis) and oysters (Crassostrea sp.) from Trinidad and Venezuela. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:410–415
de Souza MMM, da Boa Morte ES, Cardoso LG, Nunes DV, de Souza CO, Druzian JI, Cardoso RCV (2021) Nutritional contribution of shellfish from the biodiversity of Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil. J Food Compos Anal 102:1–8
Denil DJ, Ransangan J, Soon TK, Fui Fui C (2017) Seasonal variation of heavy metals (Cu, Mn, Ni and Zn) in farmed green mussel (Perna viridis) in Marudu Bay, Sabah. Malaysia Int J of Aquatic Science 8:51–60
El Nemr A, El-Said GF, Ragab S, Khaled A, El-Sikaily A (2016) The distribution, contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and shellfish from the Red Sea coast. Egypt Chemosphere 165:369–380
FAO/WHO, (1972) Evaluation of certain food additives and the contaminants mercury, lead, and cadmium: 16th report of the Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. World Health Organization, Geneva
FAO, WHO, (2011) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants: 73rd report of the Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. World Health Organization, Geneva
Feng X, Zhang G (2020) New insights into the spatial confinement mechanism of nucleation of biogenic aragonite crystals from bivalve nacre. CrystEngComm 22:6596–6602
Firth DC, Salie K, O’Neill B, Hoffman LC (2019) Monitoring of trace metal accumulation in two South African farmed mussel species, Mytilus galloprovincialis and Choromytilus meridionalis. Mar Pollut Bull 141:529–534
Gbogbo F, Arthur-Yartel A, Bondzie JA, Dorleku W-P, Dadzie S, Kwansa-Bentum B, Ewool J, Billah MK, Lamptey AM (2018): Risk of heavy metal ingestion from the consumption of two commercially valuable species of fish from the fresh and coastal waters of Ghana. Plos One 13, e0194682
Gobin J, Agard J, Madera J, Mohammed A (2013) The asian green mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus 1758): 20 years after its introduction in Trinidad and Tobago. Open J Mar Sci 3:62–65
Guendouzi Y, Soualili DL, Fowler SW, Boulahdid M (2020): Environmental and human health risk assessment of trace metals in the mussel ecosystem from the Southwestern Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 151, 110820
Gundacker C (2000) Comparison of heavy metal bioaccumulation in freshwater molluscs of urban river habitats in Vienna. Environ Pollut 110:61–71
Gupta A, Rai DK, Pandey RS, Sharma B (2009) Analysis of some heavy metals in the riverine water, sediments and fish from river Ganges at Allahabad. Environ Monit Assess 157:449–458
Gupta VK, Singh S, Agrawal A, Siddiqi NJ, Sharma B (2015) Phytochemicals mediated remediation of neurotoxicity induced by heavy metals. Biochem Res Int 2015:1–10
Hamin S, Bakar WAWA (2017): Demetallization of heavy metals in clam, Corbicula fluminea utilizing catalytic chelation technique. eProceedings Chemistry 2, 142–147
Harsono NDBD, Ransangan J, Denil DJ, Tan KS (2017) Heavy metals in marsh clam (Polymesoda expansa) and green mussel (Perna viridis) along the northwest coast of Sabah, Malaysia. BJoMSA 1:25–32
He L, He T, Farrar S, Ji L, Liu T, Ma X (2017) Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:532–553
Hou D, He J, Lü C, Ren L, Fan Q, Wang J, Xie Z (2013) Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd) in water and sediments from Lake Dalinouer. China Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 93:135–144
Indonesia (1989): Regulation of the Minister of Health No. 382/MENKES/PER/VI/1989 on the registrations of food. Minister of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, Jakarta
Johor BPEN (2017) Basic data on the state of Johor: major fishery production by type in Johor state (metric tonnes), 2013–2017, Iskandar Puteri
Kamaruzzaman B, Ong M, Zaleha K, Shahbudin S (2008) Levels of heavy metals in green-lipped mussel Perna veridis (Linnaeus) from Muar Estuary, Johore. Malaysia Pak J Biol Sci 11:2249–2253
Kamaruzzaman B, Mohd Zahir M, Akbar B, Jalal K, Shahbudin S, Al-Barwani S, Goddard J (2011) Bioaccumulation of some metals by green mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus 1758) from Pekan, Pahang. Malaysia Int J Biol Chem 5:54–60
Karsli B (2021) Determination of metal content in anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) from Turkey, Georgia and Abkhazia coasts of the Black Sea: evaluation of potential risks associated with human consumption. Mar Pollut Bull 165:1–8
Khan MI, Khisroon M, Khan A, Gulfam N, Siraj M, Zaidi F, Fatima SH, Noreen S, Shah ZA, Qadir F (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in water, sediments, and tissues and their histopathological effects on Anodonta cygnea (Linea, 1876) in Kabul River, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Pakistan Biomed Res Int 2018:1–10
Len JS, Koh WSD, Tan S-X (2019) The roles of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in cryopreservation. Biosci Rep 39:1–25
Li J, Huang ZY, Hu Y, Yang H (2013) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals by consuming shellfish collected from Xiamen. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2937–2947
Lu G-Y, Wang W-X (2018) Trace metals and macroelements in mussels from Chinese coastal waters: national spatial patterns and normalization. Sci Total Environ 626:307–318
Maadin FS, Rahman MFA, Zawawi MAA, Azman S, Oladokun S (2016) Copper and zinc accumulation in sediment at straits of Johor. Malays J Civ Eng 28:314–322
Maar M, Larsen MM, Tørring D, Petersen JK (2018) Bioaccumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn) in suspended cultures of blue mussels exposed to different environmental conditions. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 201:185–197
Mahat NA, Muktar NK, Ismail R, Razak FIA, Wahab RA, Abdul Keyon AS (2018) Toxic metals in Perna viridis mussel and surface seawater in Pasir Gudang coastal area, Malaysia, and its health implications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30224–30235
Malaysia (2017): Food Act 1983 (act 281) and regulations. International Law Book Services, Petaling Jaya
Mejdoub Z, Zaid Y, Hmimid F, Kabine M (2018) Assessment of metals bioaccumulation and bioavailability in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to outfalls pollution in coastal areas of Casablanca. J Trace Elem Med Bio 48:30–37
Mok JS, Yoo HD, Kim PH, Yoon HD, Park YC, Lee T, Kwon JY, Son KT, Lee HJ, Ha KS (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in the Changseon area, Korea, and assessment of potential risk to human health. Fish Aquat Sci 17:313–318
Molinero-Abad B, Izquierdo D, Pérez L, Escudero I, Arcos-Martínez M (2018) Comparison of backing materials of screen printed electrochemical sensors for direct determination of the sub-nanomolar concentration of lead in seawater. Talanta 182:549–557
Montojo UM, Baldoza BJS, Cambia FD, Benitez KCD, Perelonia KBS, Rivera ATF (2021): Levels and health risk assessment of mercury, cadmium, and lead in green mussel (Perna viridis) and oyster (Crassostrea iredalei) harvested around Manila Bay, Philippines. Food Control 124, 107890
Morroni L, Pinsino A, Pellegrini D, Regoli F (2018) Reversibility of trace metals effects on sea urchin embryonic development. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:923–929
Nosaka Y, Nosaka AY (2017) Generation and detection of reactive oxygen species in photocatalysis. Chem Rev 117:11302–11336
Pasupulety N, Gunda K, Liu Y, Rempel GL, Ng FT (2013) Production of biodiesel from soybean oil on CaO/Al2O3 solid base catalysts. Appl Catal a: Gen 452:189–202
Paul D (2017) Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: a review. Ann Agrar Sci 15:278–286
Ponnusamy K, Sivaperumal P, Suresh M, Arularasan S, Munilkumar S, Pal A (2014) Heavy metal concentration from biologically important edible species of bivalves (Perna viridis and Modiolus metcalfei) from vellar estuary, south east coast of India. J Aquac Res Development 5:1–5
Putri LSE, Prasetyo AD, Arifin Z (2012) Green mussel (Perna viridis L.) as bioindicator of heavy metals pollution at Kamal estuary, Jakarta Bay. Indonesia J Environ Res Dev 6:389–396
Qiao J, Arthur JF, Gardiner EE, Andrews RK, Zeng L, Xu K (2018) Regulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation by reactive oxygen species. Redox Biol 14:126–130
Ray PD, Huang B-W, Tsuji Y (2012) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal 24:981–990
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. BBA-Mol Cell Res 1863:2977–2992
Regoli F, Orlando E (1994) Seasonal variation of trace metal concentrations in the digestive gland of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: comparison between a polluted and a non-polluted site. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27:36–43
Regulation CE (2006): Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union, Geneva
Ruiz MD, Iriel A, Yusseppone MS, Ortiz N, Di Salvatore P, Cirelli AF, de Molina MR, Calcagno J, Sabatini SE (2018) Trace metals and oxidative status in soft tissues of caged mussels (Aulacomya atra) on the North Patagonian coastline. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 155:152–161
Sadeghi P, Loghmani M, Frokhzad S (2020) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of commercial marine fish (Thunnus albacares, Euthynnus affinis, and Katsuwonus pelamis) in Oman Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:14944–14952
Saritha K, Mary D, Patterson J (2015) Nutritional status of green mussel Perna viridis at Tamil Nadu, Southwest Coast of India. J Nutr Food Sci 14:1–4
Sasikumar G, Krishnakumar P, Bhat G (2006) Monitoring trace metal contaminants in green mussel, Perna viridis from the coastal waters of Karnataka, southwest coast of India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:206–214
Sharma B, Singh S, Siddiqi NJ (2014) Biomedical implications of heavy metals induced imbalances in redox systems. Biomed Res Int 2014:1–26
Singh N, Gupta VK, Kumar A, Sharma B (2017) Synergistic effects of heavy metals and pesticides in living systems. Front Chem 5:1–9
Song S, Han Y, Zhang Y, Ma H, Zhang L, Huo J, Wang P, Liang M, Gao M (2019) Protective role of citric acid against oxidative stress induced by heavy metals in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:36820–36831
Spada L, Annicchiarico C, Cardellicchio N, Giandomenico S, Di Leo A (2013) Heavy metals monitoring in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Apulian coasts (Southern Italy). Mediterr Mar Sci 14:99–108
Stankovic S, Kalaba P, Stankovic AR (2014) Biota as toxic metal indicators. Environ Chem Lett 12:63–84
Suprapti NH, Bambang AN, Swastawati F, Kurniasih RA (2016) Removal of heavy metals from a contaminated green mussel [Perna viridis (Linneaus, 1758)] using acetic acid as chelating agents. Aquat Procedia 7:154–159
Suprapto D, Suryanti S, Latifah N (2018): Content heavy metal pb, cd in Perna viridis and sediments in Semarang bay, IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, pp. 1–7
Swapna P, Ravinder R (2015) Proximate, amino acid, fatty acid and mineral analysis of bivalve Parreysia cylindrica from Waddepally and Kaleshwaram Lake. World J Pharm Sci 4:1388–1401
Velammal A, Saritha K, Immaculate J, Jamila P (2017) Food safety and shelf life of cooked meat of brown mussel, Perna perna (Linnaeus, 1758) stored under different temperatures. Int Food Res J 24:2609–2615
Venugopal V, Gopakumar K (2017) Shellfish: nutritive value, health benefits, and consumer safety. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16:1219–1242
Volpe CMO, Villar-Delfino PH, dos Anjos PMF, Nogueira-Machado JA (2018) Cellular death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis 9:1–9
Wu R, Lau T (1996) Polymer-ligands: a novel chemical device for monitoring heavy metals in the aquatic environment? Mar Pollut Bull 32:391–396
Yap C, Ismail A, Tan S (2003) Background concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus) from Peninsular Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1044–1048
Yap C, Ismail A, Tan S, Ismail AR (2004) Assessment of different soft tissues of the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus) as biomonitoring agents of Pb: field and laboratory studies. Water Air Soil Pollut 153:253–268
Yap C, Cheng W, Tan S, Rahim Ismail A (2005a) Tissue distribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis from Nenasi and Kuala Pontian, east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci 28:13
Yap C, Ismail A, Tan S (2005b): Cadmium, copper, lead and zinc levels in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (l.) from the west coast of peninsular malaysia: safe as food? Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 28, 41
Yap C, Edward F, Tan S, UPM43400 S (2007) Determination of heavy metal distribution in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis as bioindicators of heavy metal contamination in the Johore Straits and Senggarang, Peninsular Malaysia. Trends in Applied Sciences Research 2:284–294
Yap C, Ismail A, Tan S (2009) Effect of body size on heavy metal contents and concentrations in green-lipped mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus) from Malaysian coastal waters. Pertanika J Sci Technol 17:61–68
Yap C, Al-Barwani S (2012) A comparative study of condition indices and heavy metals in Perna viridis populations at Sebatu and Muar, Peninsular Malaysia. Sains Malaysiana 41:1063–1069
Yap C, Shahbazi A, Zakaria M (2012) Concentrations of heavy metals (Cu, Cd, Zn and Ni) and PAHs in Perna viridis collected from seaport and non-seaport waters in the Straits of Johore. B Environ Contam Tox 89:1205–1210
Yigit M, Celikkol B, Yilmaz S, Bulut M, Ozalp B, Dwyer RL, Maita M, Kizilkaya B, Yigit Ü, Ergün S (2018) Bioaccumulation of trace metals in Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from a fish farm with copper-alloy mesh pens and potential risk assessment. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24:465–481
Yulianto B, Radjasa OK, Soegianto A (2020a) Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn) in green mussel ( Perna viridis) and health risk analysis on residents of Semarang Coastal Waters, Central Java, Indonesia. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 17:71–76
Yulianto B, Radjasa OK, Soegianto A (2020b) Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn) in green mussel (Perna viridis) and health risk analysis on residents of Semarang Coastal Waters, Central Java, Indonesia. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 17:71–76
Funding
We are grateful for the financial support of the work by Universiti Teknologi Malaysia via Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Fundamental Research grant (UTMFR, Q.J130000.2554.20H98, reference number PY/2019/02057) and UTMShine grant (Q.J130000.2454.09G30, reference number PY/2020/03555).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TAG reviewed the collected papers and wrote the main content of the manuscript. NAM contributed to the conception and design of the work, wrote the Introduction and Outlook of the review paper, as well as the approval of the final version. ASAK is the corresponding author who drafted the framework of the review paper and critically revised students’ writing on important intellectual content.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Philippe Garrigues.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, T.G., Abdul Keyon, A.S. & Mahat, N.A. Occurrence of heavy metals and their removal in Perna viridis mussels using chemical methods: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 4803–4821 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17343-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17343-3