Abstract
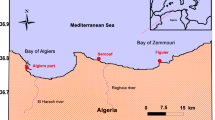
The green mussel (Perna viridis) is widely distributed in the coastal waters of Asia and is used in mussel watch programmes for monitoring environmental contaminants throughout the region. Green mussels representing different size groups and habitats were sampled from their natural beds at 28 locations in the inshore waters of Karnataka (southwest coast of India) to analyze the tissue concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn. Tissue concentrations of Cr, Cu, Fe, and Pb were significantly higher in smaller mussels than in the larger size group. Significantly higher concentrations of Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, and Ni were observed in mussels sampled from intertidal beds when compared to mussels from the subtidal beds. The sampling sites were categorized into industrial sites (IS), urban sites (US), and nonurban sites (NS) based on principal component analysis of metal concentrations in mussel. Spatial variations in tissue concentrations of all metals were observed except for Zn. Generally, the levels of toxic trace metals like Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cr in the whole tissue of P. viridis were within safe limits throughout the coast of Karnataka. However, relatively high concentrations of Cd, Cr, and Pb were observed in the whole tissue of green mussels collected from the industrial sites (IS), which may be derived from a variety of anthropogenic activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appukuttan KK, Kripa V, Velayudhan TS, Mohamed KS, Victor ACC, Kuriakose PS, Laxmilatha P, Muthiah P (2000) Bivalve Mariculture in India: a success story in coastal ecosystem development. In: Pillai VN (ed) Asia Pacific Association of Agricultural Research Institutions, FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok (APAARI Publication 2000/1), 56 pp
Airas S (2003) Trace metal concentration in blue mussels Mytilus edulis (L.) in Byfjorden and the coastal areas of Bergen. Master Thesis, Institute for Fisheries and Marine Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 59 pp
Borg H, Jonsson P (1996) Large-scale metal distribution in Baltic Sea sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 32:8–21
Brix H, Lyngby JE (1985) The influence of size upon the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb and Zn in the common mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). In: Salánki J (ed) Heavy metals in water organisms. Symposia Biologia Hungarica. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest 29:253–271
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) (1996) Coastal Pollution. Central Pollution Control Board, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Govt. of India, New Delhi, India pp 30
Cobelo-Garcia A, Prego R, Labandeira A (2004) Land inputs of trace metals, major elements, particulate organic carbon and suspended solids to an industrial coastal bay of NE Atlantic. Water Res 38:1753–1764
Fowler SW, Oregioni B (1976) Trace metals in mussels from the N.W. Mediterranean. Mar Pollut Bull 7:26–29
Fowler SW (2002) Non-oil industry. The gulf ecosystem: Health and sustainability. In: Khan NY, Munawar M, Price ARG (eds) Ecovision World Monograph Series, Backhuys Publ., Leiden, The Netherlands, pp 157–172
Glynn D, McHugh LTB, Rowe A, Costello J, McGovern E (2003) Trace metal and chlorinated hydrocarbon concentration in shellfish from Irish waters, 2000. Marine Environmental and Health Series, 7. Marine Institute, Marine Environment and Food Safety Services Abbotstown, Dublin, 15 pp
Krishnakumar PK, Pillai VK (1990) Mercury near a caustic soda plant at Karwar, India. Mar Pollut Bull 21:304–307
Krishnakumar PK, Pillai VK, Valsala KK (1990) Bioaccumulation of trace metals by marine flora and fauna near a caustic soda plant (Karwar, India). Ind J Fish 37:129–137
Krishnakumar PK, Casillas E, Varanasi U (1994) Effects of environmental contaminants on the health of Mytilus edulis from Puget sound, Washington, USA. I. Cytochemical measures of lysosomal responses in the digestive cells using automatic image analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 106:249–261
Krishnakumar PK, Casillas E, Varanasi U (1995) Effects of environmental contaminants on the health of Mytilus edulis from Puget sound, Washington, USA. II. Cytochemical detection of subcellular changes in the digestive cells. Mar Biol 124:251–259
Krishnakumar PK, Casillas E, Varanasi U (1997) Cytochemical responses in Mytilus edulis exposed to microencapsulated PAHs and PCBs. Comp Biochem Physiol 118C:11–18
Krishnakumar PK, Bhat GS, Vaidya NG, Pillai VK (1998) Heavy metal distribution in the coastal waters of Karnataka, west coast of India. Ind J Mar Sci 27:201–205
Lakshmanan PT, Nambisan PNK (1983) Seasonal variations in trace metal content in bivalve mollusks, Villorita cyprinoids var. cochinensis (Hanley), Meretrix casta (Chemnitz) & Perna viridis (Linnaeus). Ind J Mar Sci 12:100–103
Liu JH, Kueh CSW (2005) Biomonitoring of heavy metals and trace organics using the intertidal mussel Perna viridis in Hong Kong coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 51:857‐875
Mohamed KS, Muthiah C, Nagaraja D, Kumar GS (1998) Initiation of marine mussel culture activities in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka. Mar Fish Inform Serv T & E Ser 155:10–15
Monirith I, Ueno, Takahashi S, Nakata H, Sudaryanto A, Subramanian A, Kauppiah S, Ishmail A, Muchtar M, Zheng J, Richardson BJ, Prudente M, Hue ND, Tana TS, Tkalin AV, Tanabe S (2003) Asia-Pacific mussel watch: monitoring contamination of persistent organochlorine compounds in coastal waters of Asian countries. Mar Pollut Bull 46:281–300
Mohankumar MB, Katti RJ, Moorthy KSV, D’Souza RK (2003) Selected heavy metals in the sediment and macrobenthos of the coastal waters off Mangalore Indian J Fish 50(2):263–268
Nayar KN, Mahadevan S, Alagaraswami K, Sundaram PTM (eds) (1980) Coastal aquaculture, mussel farming progress and prospects. CMFRI Bull 29:1–56
Nicholson S, Szefer P (2003) Accumulation of metals in the soft tissues, byssus and shell of the mytilid mussel Perna viridis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) from polluted and uncontaminated locations in Hong Kong coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1039–1043
O’Conner T (1992) Recent trends in coastal environmental quality: Results from the first five years of the NOAA Mussel Watch Project. NOAA, Department of Commerce, 1305 East-West Highway, Silver Spring, MD 20910, 46 pp
Otchere FA (2003) Heavy metals concentration and burden in the bivalves (Anadara (Senilia) senilis, Crasostrea ntulipa and Perna perna) from lagoons in Ghana: Model to describe mechanism of accumulation/excretion. Afr J Biotechnol 2(9):280–287
Pempkowiak J, Beldowski J, Pazdro K, Staniszewski A, Zaborska A, Leipe T, Emeis K (2005) Factors influencing fluffy layer suspended matter (FLSM) properties in the Odra River, Pomeranian Bay, Arkona Deep System (Baltic Sea) as derived by principal components analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis (CA). Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 9:67–80
Phillips DJH (1976a) The common mussel Mytilus edulis as an indicator of pollution by Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper. 1. Effects of environmental variables on uptake of metals. Mar Biol 38(1):59–69
Phillips DJH (1976b) The common mussel Mytilus edulis as an indicator of pollution by Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper. II. Relationship of metals in the mussel to those discharged by industry. Mar Biol 38:71–80
Radhakrishnan AG (1993). Studies on the trace metal content of fish and shellfish including bivalves. In: Devadasan K (ed) Nutrients and bioactive substances in aquatic organisms. Society of Fisheries Technologists (India), Cochin, pp 271–275
Rajendran N, Tagore J, Kasinathan R (1988) Heavy metal concentrations in oyster, Crassostrea madrasensis (Preston) of Cuddalore backwaters, southeast coast of India. Ind J Mar Sci 17:174–175
Ridgwig J, Breward N, Langston WJ, Lister R, Rees JG, Rowlatt SM, (2003) Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources of metals entering the Irish Sea. Appl Geochem 18:283–309
Riget F, Johansen P, Asmund G (1996) Influence of Length on Element Concentrations in Blue Mussels (Mytilus edulis). Mar Pollut Bull 32(10):745–751
Robisch PA, Clark RC (1993) Sample preparation and analyses of trace metals by atomic absorption spectroscopy. In: Lauenstein GG, Cantillo AY (eds) Sampling and analytical methods of the National Status and Trends Program, National Benthic Surveillance Program, and Mussel Watch Project 1984–1992. Vol. III. Comprehensive description of elemental analytical methods. NOAA Tech. Memo. NOS ORCA 71, NOAA, Springfield, VA, pp 111–150
Sankaranarayanan VN, Purushan KS, Rao TSS (1978) Concentration of some of the heavy metals in the oyster Crassostrea madrasensis from the Cochin region. Ind J Mar Sci 7:130–131
Schulz-Baldes M (1974) Lead uptake from sea water and food, and lead loss in the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Biol 25:177–193
Sentilnathan S, Balasubrmanian T, Venugopalan VK (1998) Metal concentration in mussel, Perna viridis (Bivalvia/Anisomyaria) and Oysters, Crassostrea madrasensis from some parts in southeast coast of India. Ind J Mar Sci 27:206–210
Szefer P, Kim BS, Kim CK, Kim EH, Lee CB (2004) Distribution and coassociations of trace elements of trace elements in whole tissue and byssus of Mytilus galloprovincialis relative to the surrounding seawater and suspended matter of the southern part of Korean Peninsula. Environ Pollut 129:209–228
Tata Energy Research Institute (TERI) (1999) Measuring, monitoring and managing the sustainability: the coastal dimension. Report No. 1998/WR/41 submitted to European Economic Union. TERI, New Delhi
Tewari A, Joshi HV, Raghunathan C, SravanKumar VG, Kotiwar OS (2000) New record of Mytilus viridis Linn., its density, growth and accumulation of heavy metals on Saurashtra coast, Arabian sea. Curr Sci 78:97–102
Tewari A, Joshi HV, Raghunathan C, SravanKumar VG, Khambhaty Y (2001) Effect of heavy metal pollution on growth, carotenoid content and bacterial flora in the gut of Perna viridis (L.) in in situ condition. Curr Sci 81:819–828
WHO (World Health Organisation) (1972) Evaluation of certain food additives and the contaminants mercury, lead, cadmium. 16th Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Technical Report Series 505, Geneva
WHO (World Health Organisation) (1987) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. 33rd Report of the joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. WHO Technical Report Series 776, Geneva, 80 pp
Zingde MD, Singbal SYS, Moraes CF, Reddy CVG (1976) Arsenic, copper, zinc and manganese in the marine flora and fauna of coastal estuarine waters around Goa. Indian J Mar Sci 5:212–217
Acknowledgments
We are extremely grateful to our Director, Prof. (Dr) Mohan Joseph Modayil, for his encouragement and for facilities provided. We are thankful to Dr. K. K. Appukutan, Head of MF Division; Dr. M. Rajagopalan, Head of FEM Division, Dr. C. Muthiah, Scientist-in-Charge, RC of CMFRI, Mangalore; Dr. Kakati, Scientist-in-Charge, RC of CMFRI, Karwar; and Dr. Prathibha Rohit, Senior Scientist, RC of CMFRI, Mangalore, for their encouragement. We are also thankful to Shri. D. Nagaraja, G. Sampathkumar, Shri. Maruthi Naik, and Smt. Uma S. Bhat for their helpful technical assistance and Dr. Chandra Mohan, Chemical Oceanography Division, School of Marine Sciences, Cochin University of Science and Technology, for AAS facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikumar, G., Krishnakumar, P. & Bhat, G. Monitoring Trace Metal Contaminants in Green Mussel, Perna viridis from the Coastal Waters of Karnataka, Southwest Coast of India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51, 206–214 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0055-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0055-2