Abstract
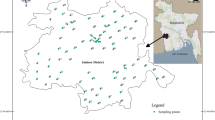
Safe drinking water is directly linked to good human health. An excessive amount of manganese (Mn) in drinking water supplies causes people show symptoms of neurotoxicity. In this study, the level of Mn in potable water sourced from tube wells located in 9 (nine) districts of Bangladesh was monitored. In total, 170 (one hundred and seventy) water samples were collected and Mn was quantified by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). The levels of Mn found in the tube well water samples of Sirajganj, Meherpur, Chuadanga, Jhenaidah, Magura, Faridpur, Jashore, Satkhira, and Khulna were 0.37–1.86, 0.10–4.11, 0.30–0.76, 0.26–0.94, 0.01–0.18, 0.21–1.78, 0.08–1.23, 0.05–0.27, and 0.01–2.11 mg/L, respectively. Results revealed that Mn level was beyond the highest contaminated levels of 0.1 mg/L and 0.4 mg/L, which are recommended by Bangladesh Drinking Standard (BDS) and World Health Organization (WHO), respectively. The maximum Mn contaminated level reached up to 4.11 mg/L (mean, 0.53 mg/L). The Mn level in tube well water exceeded 51.1% and 75.9% set by the recommended value of WHO and BDS, respectively. Furthermore, the calculated hazard quotient (HQ) value for Mn was observed to be greater than unity, indicating both children and adults risked potential non-carcinogenic health issues. The water supply authorities should take steps to provide Mn-free drinking water for communities.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aktaruzzaman M, Hossain MS, Fakhruddin ANM, Uddin MJ, Rahman SH, Chowdhury MAZ, Alam MK, Fardous Z, Hossain MA (2013) Water and bottom sediments quality of brackish water shrimp farms in Kaliganj Upazila, Satkhira, Bangladesh. Soil Environ 32:29–35
Akter MS, Islam MN, Fardous Z, Khan MH, Rahman MA (2010) Assessment of heavy metals in handloom cottage, dyeing and printing industrial effluents in Belkuchi, Sirajganj. J Appl Sci Technol 7:85–90
Ali MH, Bhattacharya B, Islam AKMS, Islam GMT, Hossain MS, Khan AS (2019) Challenges for flood risk management in flood-prone Sirajganj region of Bangladesh. J Flood Risk Manag 12. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12450
Aschner JL, Aschner M (2005) Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol Asp Med 26:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2005.07.003
Aschner M, Guilarte TR, Schneider JS, Zheng W (2007) Manganese: recent advances in understanding its transport and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221:131–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2007.03.001
ATSDR (2012) Toxicological Profile for Formaldehyde. US Department of Health and Human Services. Public Health Service, and the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Atlanta, GA
Avila DS, Puntel RL, Aschner M (2013) Manganese in health and disease.Met Ions Life Sci 13:199–227
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, BBS (2013) Statistics and Informatics Division (SID) Ministry of Planning Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. District Statistics 2011
Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, BBS (2015) Population density and vulnerability: a challenge for sustainable development of Bangladesh. Statistics and Informatics Division (SID), Ministry of Planning
Bhuiyan MAH, Bodrud-Doza M, Islam ARMT, Rakib MA, Rahman MS, Ramanathan A (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality of Lakshimpur district of Bangladesh using water quality indices, geostatistical methods, and multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 75:1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5823-y
Bouchard M, Laforest F, Vandelac L, Bellinger D, Mergler D (2007) Hair manganese and hyperactive behaviors: Pilot study of school-age children exposed through tap water. Environ Health Perspect 115(1):122–127. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9504
Bouchard MF, Surette C, Cormier P, Foucher D (2018) Low level exposure to manganese from drinking water and cognition in school-age children. Neurotoxicol 64:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2017.07.024
Bowler RM, Gysens S, Diamond E, Nakagawa S, Drezgic M, Roels HA (2006) Manganese exposure: neuropsychological and neurological symptoms and effects in welders. Neurotoxicol 27:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2005.10.007
Brown MT, Foos B (2009) Assessing children’s exposures and risks to drinking water contaminants: a manganese case study. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 15(5):923–947
Bureau of Indian Standard, BIS (2012) Drinking water-specification (1st Rev.) IS-10500. New Delhi, India
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Das B, Murrill M, Dey S, Mukherjee SC, Dhar RK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury UK, Roy S, Sorif S (2010) Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: a 14-year study report. Water Res 44(19):5789–5802
Chen P, Bornhorst J, Aschner MA (2018) Manganese metabolism in humans. Front Biosci 23:1655–1679
Cotruvo JA (2017) 2017 WHO guidelines for drinking water quality: first addendum to the fourth edition. J Am Water Works Assoc 109(7):44–51
Didar-Ul Islam SM, Bhuiyan MA, Ramanathan AL (2015) Climate change impacts and vulnerability assessment in coastal region of Bangladesh: a case study on Shyamnagar upazila of Satkhira district. J Clim Chang 1:37–45
Environment Conservation Rules (ECR), Ministry of Environment & Forests (MoEF), Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, 1997
Ericson JE, Crinella FM, Clarke-Stewart KA, Allhusen VD, Chan T, Robertson RT (2007) Prenatal manganese levels linked to childhood behavioral disinhibition. Neurotoxicol Teratol 29:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2006.09.020
Erikson KM, Aschner M (2003) Manganese neurotoxicity and glutamate-GABA interaction. Neurochem Int 43:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-0186(03)00037-8
Erikson KM, Dorman DC, Lash LH, Aschner M (2005) Persistent alterations in biomarkers of oxidative stress resulting from combined in utero and neonatal manganese inhalation. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:104:2:151
Frisbie SH, Mitchell EJ, Dustin H, Maynard DM, Sarkar B (2012) World Health Organization discontinues its drinking-water guideline for manganese. Environ Health Perspect 120:775–778. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104693
Ghosh GC, Khan MJH, Chakraborty TK, Zaman S, Kabir AE, Tanaka H (2020) Human health risk assessment of elevated and variable iron and manganese intake with arsenic-safe groundwater in Jashore, Bangladesh. Sci Rep 10:1–9
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69665-7
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2014) Neurobehavioural effects of developmental toxicity. Lancet Neurol 13(3):330–338
Groschen GE, Arnold TL, Morrow WS, Warner KL (2009) Occurrence and distribution of iron, manganese, and selected trace elements in ground water in the glacial aquifer system of the Northern United States. US Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2009-5006. Available: http://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2009/5006/
Guilarte TR, Chen MK (2007) Manganese inhibits NMDA receptor channel function: implications to psychiatric and cognitive effects. Neurotoxicol 28:1147–1152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2007.06.005
Hafeman D, Factor-Litvak P, Cheng Z, van Geen A, Ahsan H (2007) Association between manganese exposure through drinking water and infant mortality in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 115:1107–1112. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10051
Hasan S, Ali MA (2010) Occurrence of manganese in groundwater of Bangladesh and its implications on safe water supply. J Civ Eng (IEB) 38:121–128
Hasan MM, Ahmed KM, Sultana S, Rahman MS, Ghosh SK, Ravenscroft P (2018) Investigations on groundwater buffering in Khulna-Satkhira Coastal Belt using managed aquifer recharge. In: Groundwater of South Asia. Springer, Singapore, pp 453–462
Henn BC, Schnaas L, Ettinger AS, Schwartz J, Lamadrid-Figueroa H, Hernàndez-Avila M, Amarasiriwardena C, Hu H, Bellinger DC, Wright RO, Téllez-Rojo MM (2011) Associations of early childhood manganese and lead coexposure with neurodevelopment. Environ Health Perspect 120:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1003300
Hossain MA, Rahman MM, Murrill M, Das B, Roy B, Dey S, Maity D, Chakraborti D (2013) Water consumption patterns and factors contributing to water consumption in arsenic affected population of rural West Bengal, India. Sci Total Environ 463:1217–1224
Hossain ML, Hossain MK, Das SR (2014) Vulnerability of Bangladesh to natural and anthropogenic disasters. Pothi.com publisher, India
Hou Q, Zhang Q, Huang G, Liu C, Zhang Y (2020) Elevated manganese concentrations in shallow groundwater of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized delta, south China. Sci Total Environ 701:134777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134777
Islam AT, Shen S, Bodrud-Doza M, Rahman MA, Das S (2017) Assessment of trace elements of groundwater and their spatial distribution in Rangpur district, Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2886-3
Islam MS, Mohanta SC, Siddique MAB, Al-Mamun MA, Hossain N, Bithi UH (2018) Physico-chemical assessment of water quality parameters in Rupsha river of Khulna region, Bangladesh. Int J Eng Sci (IJES) 7:73–78
Islam MA, Akber MA, Rahman MA, Islam MA, Kabir MP (2019) Evaluation of harvested rainwater quality at primary schools of southwest coastal Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 191:80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7217-6
Islam ARMT, Siddiqua MT, Zahid A, Tasnim SS, Rahman MM (2020) Drinking appraisal of coastal groundwater in Bangladesh: an approach of multi-hazards towards water security and health safety. Chemosphere 255:126933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126933
Iyare PU (2019) The effects of manganese exposure from drinking water on school-age children: a systematic review. Neurotoxicol 73:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.013
Keen CL, Ensunsa JL, Lonnerdal B, Zidenberg-Cherr S (2013) Manganese. Encyclopedia of human nutrition (3rd ed.) Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp. 148
Khan K, Wasserman GA, Liu X, Ahmed E, Parvez F, Slavkovich V, Levy D, Mey J, van Geen A, Graziano JH, Litvak PF (2012) Manganese exposure from drinking water and children’s academic achievement. Neurotoxicol 33:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2011.12.002
Kim Y, Kim BN, Hong YC, Shin MS, Yoo HJ, Kim JW, Bhang SY, Cho SC (2009) Co-exposure to environmental lead and manganese affects the intelligence of school-aged children. Neurotoxicol 30:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2009.03.012
Kohl PM, Medlar S J (2006) Occurrence of manganese in drinking water and manganese control. American Water Research Foundation, American Water Works Association and IWA Publishing, Denver
Kullar SS, Shao K, Surette C, Foucher D, Mergler D, Cormier P, Bellinger DC, Barbeau B, Sauvé S, Bouchard MF (2019) A benchmark concentration analysis for manganese in drinking water and IQ deficits in children. Environ Int 130:104889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.083
Ljung K, Vahter M (2007) Time to re-evaluate the guideline value for manganese in drinking water? Environ Health Perspect 115(11):1533–1538
Lucchini R, Placidi D, Cagna G, Fedrighi C, Oppini M, Peli M, Zoni S (2017) Manganese and developmental neurotoxicity. Adv Neurobiol 18:13–34
McMillan DE (1999) A brief history of the neurobehavioral toxicity of manganese: some unanswered questions. Neurotoxicol 20(2-3):499–507
Menezes-Filho JA, Novaes Cde O, Moreira JC, Sarcinelli PN, Mergler D (2011) Elevated manganese and cognitive performance in school-aged children and their mothers. Environ Res 111:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2010.09.006
Mohana AA, Rahman MA, Islam MR (2020) Deep and shallow tubewell water from an arsenic-contaminated area in rural Bangladesh: risk-based status. Int J Energy Water Res 4(2):163–179
National Center for Health Statistics, NCHS (2000) In collaboration with the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts; accessed at: https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/data/set1clinical/cj41l021.pdf
O’Neal SL, Zheng W (2015) Manganese toxicity upon overexposure: a decade in review. Curr Environ Health Rep 2:315–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-015-0056-x
Rahman A, Rahaman H (2018) Contamination of arsenic, manganese and coliform bacteria in groundwater at Kushtia District, Bangladesh: human health vulnerabilities. J Water Health 16(5):782–795
Rahman MM, Dong Z, Naidu R (2015) Concentrations of arsenic and other elements in groundwater of Bangladesh and West Bengal, India: potential cancer risk. Chemosphere 139:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.05
Rahman MA, Hashem MA, Nur-A-Tomal MS (2016) Potable water quality monitoring of primary schools in Magura district, Bangladesh: children’s health risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 188:680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5692-6
Rahman MA, Kumar S, Mohana AA, Islam R, Hashem MA, Chuanxiu L (2019) Coliform bacteria and trace metals in drinking water, southwest Bangladesh: multivariate and human health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res 13:395–408
Riojas-Rodriguez H, Solis-Vivanco R, Schilmann A, Montes S, Rodriguez S, Rios C, Rodríguez-Agudelo Y (2010) Intellectual function in Mexican children living in a mining area and environmentally exposed to manganese. Environ Health Perspect 118:1465–1470. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901229
Rodríguez-Barranco M, Lacasaña M, Aguilar-Garduño C, Alguacil J, Gil F, González-Alzaga B, Rojas-García A (2013) Association of arsenic, cadmium and manganese exposure with neurodevelopment and behavioural disorders in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 454:562–577
Roels HA, Bowler RM, Kim Y, Henn BC, Mergler D, Hoet P, Téllez-Rojo MM (2012) Manganese exposure and cognitive deficits: a growing concern for manganese neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol 33(4):872–880
Sahni V, Léger Y, Panaro L, Allen M, Giffin S, Fury D, Hamm N (2007) Case report: a metabolic disorder presenting as pediatric manganism. Environ Health Perspect 115(12):1776–1779
Spangler JG, Reid JC (2010) Environmental manganese and cancer mortality rates by county in North Carolina: an ecological study. Biol Trace Elem Res 133:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8415-9
Spangler AH, Spangler JG (2009) Groundwater manganese and infant mortality rate by county in North Carolina: an ecological analysis. Ecohealth 6:596–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-010-0291-4
Stokes P, Campbell P, Schroeder W, Trick C, France R, Puckett K, Donaldson J (1988) Manganese in the Canadian environment. NRCC No. 26193. Natl. Res. Council of Canada, Assoc. Committee on Scientific Criteria for Environ. Quality, Ottawa, ON
Uddin MZ, Rahman MA, Ahmed I, Mohiuddin KM (2019) Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation usages in Kazipur upazila under Sirajganj district of Bangladesh. J Bangladesh Agric Univ 17:309–318
USEPA (2004) Drinking water health advisory for manganese. US Environmental Protection Agency (accessed at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-09/documents/support_cc1_magnese_dwreport_0.pdf)
USEPA (2011) Exposure factors handbook. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC (EPA/600/R-09/052F).
USEPA (2017) Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) and federal facilities: enforcement. https://www.epa.gov/enforcement/safe-drinking-water-act-sdwa-and-federal-facilities. Accessed 25 July 2017
USEPA (2020) Regional Screening Level (RSL) Resident Tapwater Table (TR = 1E-06, HQ = 1) May 2020 (corrected) [WWW Document]. URL 9Accessed at: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/HQ/200055.pdf)
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Levy D, Litvak PF, Kline J, van Geen A, Slavkovich V, LoIacono NJ, Cheng Z, Zheng Y, Graziano JH (2006) Water manganese exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 114:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8030
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd ed. Geneva, Switzerland
WHO (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: incorporating the1st addendum. World Health Organization, Geneva
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality (4th ed.). WHO Press, Geneva
William-Johnson M, World Health Organization (1999) Manganese and its compounds. Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 12. World health organization. (accessed at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42184/924153012X.pdf)
Woolf A, Wright R, Amarasiriwardena C, Bellinger D (2002) A child with chronic manganese exposure from drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 110(6):613–616
World Health Organization (2020) Manganese in drinking-water: background document for development of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization (accessed at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/gdwq-manganese-background-document-for-public-review.pdf?sfvrsn=9296741f_5)
Wright RO, Amarasiriwardena C, Woolf AD, Jim R, Bellinger DC (2006) Neuropsychological correlates of hair arsenic, manganese, and cadmium levels in school-age children residing near a hazardous waste site. Neurotoxicol 27:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2005.10.001
Yousef S, Adem A, Zoubeidi T, Kosanovic M, Mabrouk AA, Eapen V (2011) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and environmental toxic metal exposure in the United Arab Emirates. J Trop Pediatr 57:457–460. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmq121
Zhang S, Tian Y, Guo Y, Shan J, Liu R (2020) Manganese release from corrosion products of cast iron pipes in drinking water distribution systems: effect of water temperature, pH, alkalinity, SO42- concentration and disinfectants. Chemosphere 262:127904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127904
Zota AR, Ettinger AS, Bouchard M, Amarasiriwardena C, Schwartz J, Hu H, Wrighta RO (2009) Maternal blood manganese levels and infant birth weight. Epidemiology 20:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e31819b93c
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge the Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE), Zonal Laboratory Khulna, Jhenaidah, and Bogura for providing the laboratory facilities. We are also thankful to the field workers for their assistance in the sampling process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aminur Rahman: visualization/conceptualization, investigation, methodology, and writing-review, and editing. Abul Hashem: investigation, methodology, supervision, data managing-organizing, writing-original draft, writing-review, and editing. Sohel Rana: sampling and data collection. Rashidul Islam: review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that the submitted manuscript is original. Authors also acknowledge that the current research has been conducted ethically and the final shape of the research has been agreed by all authors. Authors declared that this manuscript does not involve researching about humans or animals.
Consent to participate
The authors consent to participate in this research study.
Consent to publish
The authors consent to publish the current research in ESPR journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Seventy-six percent of tube well water manganese level exceeds Bangladesh drinking water standard.
• Compared to WHO guideline 51% tube well water manganese exceeds permissible level.
• Hazard quotient of Mn was greater than unity, potentially non-carcinogenic health risks.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.A., Hashem, M.A., Rana, M.S. et al. Manganese in potable water of nine districts, Bangladesh: human health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 45663–45675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14016-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14016-z