Abstract
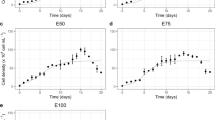
The growth of two species of macrophytes (Lemna minor and Salvinia auriculata) under the effect of a mixture of amoxicillin, caffeine, carbamazepine, dipyrone, ibuprofen, losartan, omeprazole, and tenivastatin was investigated by bioassay. Three concentration levels were utilized in this study (10, 200, and 500 μg L−1) using a growth inhibition test based on the OECD 221/2006 guidelines. The frond number, total area, and chlorophyll a level were selected as suitable end points. For L. minor, at all concentrations, a significant difference in the total frond number was observed and the growth inhibition varied from 30 to 70% at the low and high concentrations, respectively. No significant growth change was observed to S. auriculata exposed to the mixture of drugs. Thus, individual drug tests were performed for L. minor which demonstrated stimulation in growth, when exposed to most drugs individually, except tenivastatin which was identified as the drug responsible for the significant growth inhibition seen in the mixture. The L. minor enhanced growth was probably caused by N molecule transformation to ammonium and nitrate, essential nutrients for plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The raw data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aguirre-Martinez GV, Owuor MA, Garrido-Pérez C, Salamanca MJ, Del Valls TA, Martín-Díaz ML (2015) Are standard tests sensitive enough to evaluate effects of human pharmaceuticals in aquatic biota? Facing changes in research approaches when performing risk assessment of drugs. Chemosphere 120:75–85
Alkimin GD, Daniel D, Frankenbach S, Serôdio J, Soares AMVM, Barata C, Nunes B (2019) Evaluation of pharmaceutical toxic effects of non-standard endpoints of the macrophyte species Lemna minor and Lemna gibba. Sci Total Environ 657:926–937
Almeida, G. A. Identificação de poluentes orgânicos na represa Billings - São Paulo, São Paulo, SP. 2003 [Identification of organic pollutants at the Billings dam - São Paulo, São Paulo, SP]. PhD Thesis in Analytical Chemistry by University of Sao Paulo, 176 p.
Américo JHPA, Isique WD, Minillo A, Carvalho SL (2012) Fármacos em Uma Estação de Tratamento de Esgoto na Região Centro-Oeste do Brasil e os Riscos aos Recursos Hídricos.[Drugs in a sewage treatment plant in the midwest region of Brazil and the risks to water resources]. Rev Bras Recur Hidr 17(3):61–67
Aznar R, Albero B, Sánchez-Brunete C, Miguel E, Martín-Girela I, Tadeo JL (2017) Simultaneous determination of multiclass emerging contaminants in aquatic plants by ultrasound-assisted matrix solid-phase dispersion and GC-MS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7911–7920
Bertoldi AD, Arrais PSD, Tavares NUL, Ramos LR, Luiza VL, Mengue SS, Dal-Pizzol TS, Farias MR, Oliveira MA (2016) Use of generic medicines by the Brazilian population: an evaluation of PNAUM 2014. Rev Saúde Pública 50(suppl 2):1s–11s
Carvalho PN, Basto MCP, Almeida CMR, Brix H (2010) A review of plant-pharmaceutical interactions: from uptake and effects in crop plants to phytoremediation in constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:11729–11763
Coelho LHG, Jesus TA, Kohatsu MY, Poccia GT, Chicarolli V, Helwig K, Hunter C, Roberts J, Teedon P, Pahl O (2020) Estrogenic hormones in São Paulo waters (Brazil) and their relationship with environmental variables and Sinapis alba phytotoxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04477-2
Connon RE, Geist J, Werner I (2012) Effect-based tools for monitoring and predicting the ecotoxicological effects of chemicals in the aquatic environment. Sensors 12:12741–12771
Costa, C. O. 2009. Metodologias para determinação de fármacos, metabólitos e disruptores endócrinos em água de abastecimento público utilizando técnicas de separação em meio líquido (CE/UV, CE-MS, LC-MS/MS), São Paulo, SP. [Methodologies for the determination of drugs, metabolites and endocrine disruptors in public water supply using liquid separation techniques (CE / UV, CE-MS, LC-MS / MS), São Paulo, SP]. PhD Thesis in Analytical Chemistry by University of Campinas, SP, 294 p.
Di Baccio D, Pietrini F, Bertolotto P, Pérez P, Barcelò D, Zacchini M, Donati E (2017) Response of Lemna gibba L. to high and environmentally relevant Cs of ibuprofen: removal, metabolismo and morpho-physiological traits for biomonitoring of emerging contaminants. Sci Total Environ 584-585:363–373
Ekperusi AO, Sikoki FD, Nwachukwu EO (2019) Application of common duckweed (Lemna minor) in phytoremediation of chemicals in the environment: State and future perspective. Chemosphere 223:285–309
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution using UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2/TiO2 photocatalysis. Desalination 252:46–52
Escher BI, Baumgartner R, Koller M, Treyer K, Lienert J, McArdell CS (2011) Environmental toxicology and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals from hospital wastewater. Water Res 45(1):75–92
Fekete-Kertész I, Kunglné-Nagy Z, Gruiz K, Magyar Á, Farkas É, Molnár M (2015) Assessing toxicity of organic aquatic micropollutants based on the total chlorophyll content of Lemna minor as a sensitive endpoint. Period Polytech Chem Eng 59(4):262–271
Ghiselli, G. 2006. Avaliação da qualidade das águas destinadas ao abastecimento público na região de Campinas: ocorrência e determinação dos interferentes endócrinos (IE) e produtos farmacêuticos e de higiene pessoal (PFHP), Campinas, São Paulo. [Evaluation of the quality of water used for public supply in the region of Campinas: occurrence and determination of endocrine interferences (IE) and pharmaceutical and personal hygiene products (PFHP), Campinas, São Paulo]. PhD Thesis in Analytical Chemistry by University of Campinas, SP, 181 p.
Godoy AA, Kummrow F, Pamplin PAZ (2015) Ecotoxicological evaluation of propranolol hydrochloride and losartan potassium to Lemna minor L. (1753) individually and in binary mixtures. Ecotoxicology 24:1112–1123
González-Pleiter M, Gonzalo S, Rodea-Palomares I, Leganés F, Rosal R, Boltes K, Marco E, Fernández-Piñas F (2013) Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res 47(6):2050–2064
Herklotz PA, Gurung P, Heuvel BV, Kinney CA (2010) Uptake of human pharmaceuticals by plants grown under hydroponic conditions. Chemosphere 78:1416–1421
Jakimska A, Kot-Wasik A, Namiesnik J (2014) The current state-of-the-art in the determination of pharmaceutical residues in environmental matrices using hyphenated techniques. Crit Rev Anal Chem 44(3):277–298. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2013.835244
Khetan SK, Collins TJ (2007) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a challenge to green chemistry. Chem Rev 107:2319–2364
Klauson D, Babkina J, Stepanova K, Krichevskaya M, Preis S (2010) Aqueous photocatalytic oxidation of amoxicillin. Catal Today 151:39–45
Kummerova M, Zezelka S, Babula P, Triska J (2016) Possible ecological risk of two pharmaceuticals diclofenac and paracetamol demonstrated on a model plant Lemna minor. J Hazard Mater 302:351–361
Low GKC, McEvoy SR, Matthews RW (1991) Formation of nitrate and ammonium ions in titanium dioxide mediated photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds containing nitrogen atoms. Environ Sci Technol 25:460–467
Montagner CC, Jardim WF (2011) Spatial and seasonal variations of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in the Atibaia River, Sao Paulo State (Brazil). J Braz Chem Soc 22(8):1452–1462
Noguera-Oviedo A, Aga DS (2016) Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment. J Hazard Mater 316:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.058
Nunes B, Pinto G, Martins L, Gonçalves F, Antunes SC (2014) Biochemical and standard toxic effects of acetaminophen on the macrophytes species Lemna minor and Lemna gibba. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10815–11822
Obinna IB, Ebere EC (2019) Phytoremediation of polluted waterbodies with aquatic plants: recent progress on heavy metal and organic pollutants. Anal Methods Environ Chem J 2:66–104
OECD guideline 221, 2006. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals: revised proposal for a new guideline 221, Lemna sp. growth inhibition test. Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development Paris, France.
Orias F, Perrodin Y (2013) Characterisation of the ecotoxicity of hospital effluents: a review. Sci Total Environ 454:250–276
Pereira, J. H. O. S. 2014. Solar photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics: chemical, ecotoxicologial and biodegradability assessment. PhD Thesis in Environmental Engineering by University of Porto, 176 p.
Pietrini F, Di Baccio D, Aceña J, Pérez S, Barceló D, Zacchini M (2015) Ibuprofen exposure in Lemna gibba L.: evaluation of growth and phytotoxic indicators, detection of ibuprofen and identification of its metabolites in plant and in the medium. J Hazard Mater 300:189–193
Pomati F, Netting AG, Calamari D, Neilan BA (2004) Effects of erythromycin, tetracycline and ibuprofen on the growth of Synechocystis sp and Lemna minor. Aquat Toxicol 67:387–396
Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, Jelic A, Llorca M, Farré M, Caminal G, Petrovic M, Barceló D, Vicent T (2011) Solid-phase treatment with the fungus Trametes versicolor substantially reduces pharmaceutical Cs and toxicity from sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:5602–5608
Sanchez SM, Prado EL, do, Ferreira IM, Braga HF, Vieira EM, (2012) Presença da toxina microcistina em água, impactos na saúde pública e medidas de controle. Rev Ciênc Farm Básica Apl 33(2):181–187
Santos LHMLM, Araújo AN, Fachini A, Pena A, Delerue-Matos C, Montenegro MCBSM (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95
Santos NBC, Arruda ECP, Pinna GFAM, Neto AGB, Oliveira AFM (2020) Assessing the effects of water quality on leaf morphoanatomy, ultrastructure and photosynthetic pigment content of Salvinia auriculata Aubl. (Salvinaceae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110061
Shihomatsu, H. M. 2015. Desenvolvimento e validação de metodologia SPE-LC-MS/MS para a determinação de fármacos e droga de abuso nas águas da represa Guarapiranga - São Paulo/SP, Brasil, São Paulo, SP. [Development and validation of SPE-LC-MS/MS methodology for the determination of drugs and drugs of abuse in the waters of the Guarapiranga dam - São Paulo / SP, Brazil, São Paulo, SP]. PhD Thesis in Science by University of Sao Paulo, 224 p.
Sodré FF, Montagner CC, Locatelli MAF (2007) Ocorrência de Interferentes Endócrinos e Produtos Farmacêuticos em Águas Superficiais da Região de Campinas (SP, Brasil). J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 2(2):187–196
Stumpf M, Ternes TA, Wilken R-D, Rodrigues SV, Baumann W (1999) Polar drug residues in sewage and natural waters in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 225:135–141
Sumanta N, Haque CI, Nishika J, Suprakash R (2014) Spectrophotometric analysis of chlorophylls and carotenoids from commonly grown fern species by using various extracting solvents. Res J Chem Sci 4(9):63–69
Tanoue R, Sato Y, Motoyama M, Nakagawa S, Shinohara R, Nomiyama K (2012) Plant uptake of pharmaceutical chemicals detected in recycled organic manure and reclaimed wastewater. J Agric Food Chem 60:10203–10211. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf303142t
Taylor-Smith, A. 2015. Pharmaceutical compounds in land-applied sludge and plant uptake: a review. Master dissertation in Environmental assessment by North Carolina State University, 32 p.
Thomas KV, Silva FMA, Langford KH, Souza ADL, Nizzeto L, Waichman AV (2014) Screening for selected human pharmaceuticals and cocaine in the urban streams of Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. Jawra, 50(2):302–308
Trine E, Tone NA, Kari G, Victor H (2011) Uptake and translocation of metformin, ciprofloxacin and narasin in forage- and crop plants. Chemosphere 85(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.041
Tundisi, J. G. 2014. Recursos Hídricos no Brasil: problemas, desafios e estratégias para o futuro. Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil.
Tundisi, J. G., Tundisi, T. M., 2008. Limnologia. Oficina de Textos, 631 p.
UN, 2019. 17 goals to transform our world. Available at <URL https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/development-agenda/>. Accessed January 18th, 2019.
UNEP, 2016. A snapshot of the world’s water quality: towards a global assessment. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi, Kenya. 162 pp. Nairobi, Kenia, p. 162. URL https://uneplive.unep.org/media/docs/assessments/unep_wwqa_report_web.pdf
Wang W, Li R, Zhu Q, Tang X, Zhao Q (2016) Transcriptomic and physiological analysis of common duckweed Lemna minor responses to NH4+ toxicity. BMC Plant Biol 16:92
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD, Fang M, Czajkowski KP (2010) Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 44(16):6157–6161. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1011115
Acknowledgements
We thank our colleagues from Glasgow Caledonian University, Universidade Federal do ABC and PUC Paraná who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted with the interdisciplinarity of the project. We also thank Dr. Fanny Costa for her research to define a priority list of pharmaceutical compounds of this study. And a special thanks to GCU for laboratory and office facilities and for the opportunity to develop the research abroad from Brazil. We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers that contributed significantly to improve this manuscript providing valuable comments, suggestions, and corrections particularly to our statistical approach.
Funding
This research is funded by British Council, Newton Fund and CAPES (Coordination for Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) (process number 004/16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by JIO, CH, JR, and KH. The statistical analysis was performed by LRM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JIO and LRM, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikebe Otomo, J., Araujo de Jesus, T., Gomes Coelho, L.H. et al. Effect of eight common Brazilian drugs on Lemna minor and Salvinia auriculata growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 43747–43762 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13795-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13795-9