Abstract
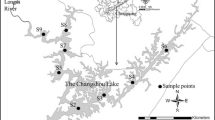
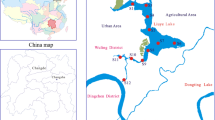
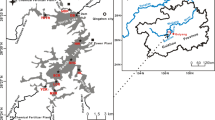
Much attention has been paid to the heavy metal contamination of lake sediments in rapidly developing regions. In this study, heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Co, Ni, Mn, Pb, As, Cu, and Zn) concentrations in sediment surface samples and cores from the Nansi Lake were investigated to ascertain the potential sources and environmental risks of heavy metals. The average concentration of heavy metals was 0.16–16.04 times background concentrations. The enrichment factor, Tomlinson pollution load index, geo accumulation index, positive definite matrix factor analysis (PMF), and potential ecological risk index were used to assess heavy metal concentrations and explore the evolution of heavy metal sources, and result indicated that Cd reached moderate pollution levels, which is the most polluted heavy metal in the history and present, while the remaining heavy metals are at low or no pollution levels. The contribution of Cd to RI exceeded 76%, which is the decisive factor in the ecological risk of Nansi Lake. The result of ecological risk showed that the risk level for most of Nansi Lake is medium, and some areas of Zhaoyang Lake and Weishan Lake reach high levels. The PMF results showed that there are four main factors influencing heavy metal concentrations in Nansi Lake sediments, including industrial sources, fertilizers, and herbicides used in agricultural production, traffic-related emissions, and mineral mining. Among these factors, industrial and mineral mining sources were found to be the most important, and the highest contribution rate occurred in the −10cm (1960s). Although the contribution of fertilizers and herbicides is lower than that of other sources, increasing trend should be a warning sign that Cd has reached a high ecological risk level in Nansi Lake sediments.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are true and valid and can use general repositories saving.
References
Aghadadashi V, Neyestani MR, Mehdinia A, Riyahi Bakhtiari A, Molaei S, Farhangi M, Esmaili M, Rezai Marnani H, Gerivani H (2019) Spatial distribution and vertical profile of heavy metals in marine sediments around Iran’s special economic energy zone; arsenic as an enriched contaminant. Mar Pollut Bull 138:437–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.033
Ahmed I, Mostefa B, Bernard A, Olivier R (2018) Levels and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of fishing grounds along Algerian coast. Mar Pollut Bull 136:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.029
Arfaeinia H, Dobaradaran S, Moradi M, Pasalari H, Mehrizi EA, Taghizadeh F, Esmaili A, Ansarizadeh M (2019) The effect of land use configurations on concentration, spatial distribution, and ecological risk of heavy metals in coastal sediments of northern part along the Persian Gulf. Sci Total Environ 653:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.009
Barcena JF, Claramunt I, Garcia-Alba J, Perez ML, Garcia A (2017) A method to assess the evolution and recovery of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments: Past history, present situation and future perspectives. Mar Pollut Bull 124:421–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.07.070
Bhuiyan MAH, Dampare SB, Islam MA, Suzuki S (2014) Source apportionment and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in water and sediments of Buriganga River, Bangladesh, using multivariate analysis and pollution evaluation indices. Environ Monit Assess 187:4075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4075-0
Bulut E, Aksoy A (2008) Impact of fertilizer usage on phosphorus loads to Lake Uluabat. Desalination 226:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.02.112
Cao Q, Song Y, Zhang Y (2017) Risk analysis on heavy metal contamination in sediments of rivers flowing into Nansi Lake. Envison Sci Pollut Res 24(35):26910–26918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4655-8
Chen Y, Jiang Y, Huang H, Mou L, Ru J, Zhao J, Xiao S (2018) Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci Total Environ 637-638:1400–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.109
Chen M, Ding S, Gao S, Fu Z, Tang W, Wu Y, Gong M, Wang D, Wang Y (2019) Efficacy of dredging engineering as a means to remove heavy metals from lake sediments. Sci Total Environ 665:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.057
Ciazela J, Siepak M, Wojtowicz P (2018) Tracking heavy metal contamination in a complex river-oxbow lake system: Middle Odra Valley, Germany/Poland. Sci Total Environ 616-617:996–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.219
Comero S, Locoro G, Free G, Vaccaro S, De Capitani L, Gawlik BM (2011) Characterization of Alpine lake sediments using multivariate statistical techniques. Chemometri Intell Lab 107:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2011.01.002
Conrad CF, Fugate D, Daus J (2007) Assessment of the historical trace metal contamination of sediments in the Elizabeth River, Virginia. Mar Pollut Bull 54:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.11.005
Dai L, Wang L, Li L, Liang T, Zhang Y, Ma C (2017) Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang lake in China. Sci Total Environ S0048969717327882:1433–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.085
Dhivert E, Grosbois C, Coynel A (2015) Influences of major flood sediment inputs on sedimentary and geochemical signals archived in a reservoir core (Upper Loire Basin, France). Catena 126:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.030
Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2016) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ Pollut 219:1077–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.008
Feng Y, Cheng L, Bowen W (2019) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the sediment of Poyang Lake based on stochastic geo-accumulation model (SGM). Sci Total Environ 659:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.311
Gholizadeh M, Patimar R (2018) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Gorgan Bay, Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 137:662–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.009
Gibbs RJ (1973) Mechanisms of trace metal transport in rivers. Science 180:71–73. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.180.4081.71
Hahn J, Opp C, Evgrafova A, Groll M, Zitzer N, Laufenberg G (2018) Impacts of dam draining on the mobility of heavy metals and arsenic in water and basin bottom sediments of three studied dams in Germany. Sci Total Environ 640–641:1072–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.295
Harikrishnan N, Ravisankar R, Chandrasekaran A, Suresh Gandhi M, Kanagasabapathy KV, Prasad MVR, Satapathy KK (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of east coast of Tamil Nadu affected by different pollution sources. Mar Pollut Bull 121:418–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.05.047
Hu C, Yang X, Dong J, Zhang X (2018) Heavy metal concentrations and chemical fractions in sediment from Swan Lagoon, China: their relation to the physiochemical properties of sediment. Chemosphere 209:848–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.113
Huang SS, Liao QL, Hua M, Wu XM, Bi KS, Yan CY, Chen B, Zhang XY (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67:2148–2155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.043
Ji Z, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Huang C, Pei Y (2019) Fraction spatial distributions and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.062
Jiang Q, He J, Ye G, Christakos G (2018) Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the East Zhejiang coastal area during 2012-2015. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:444–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.107
Lan B, Zhang D, Yang Y (2018) Lacustrine sediment chronology defined by 137 Cs, 210 Pb and 14 C and the hydrological evolution of Lake Ailike during 1901–2013, northern Xinjiang, China. Catena 161:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.020
Lanzerstorfer C (2018) Heavy metals in the finest size fractions of road-deposited sediments. Environ Pollut 239:522–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.063
Li ZJ, Yue Q, Gao B (2011) Fractionation and potential risk of heavy metals in surface sediment of Nansi Lake, China. Desalin Water Treat 32:10–18. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2011.2419
Li F, Huang J, Zeng G, Yuan X, Li X, Liang J, Wang X, Tang X, Bai B (2013) Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J Geochem Explor 132:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.05.007
Li HM, Wang JH, Wang QG, Yu Q, Meng Y, Feng YL, Hao L, Cheng W (2015a) Chemical fractionation of arsenic and heavy metals in fine particle matter and its implications for risk assessment: a case study in Nanjing, China. Atmos Environ 103:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.065
Li P, Zhang J, Xie H, Liu C, Liang S, Ren Y (2015b) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and health hazard assessment for three fish species from Nansi lake, china. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94(4):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1475-y
Li F, Zhang J, Liu C, Xiao M, Wu Z (2018) Distribution, bioavailability and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Honghu Lake, China. Process Saf Environ 116:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.02.007
Li R, Tang C, Li X, Jiang T, Shi Y, Cao Y (2019) Reconstructing the historical pollution levels and ecological risks over the past sixty years in sediments of the Beijiang River, South China. Sci Total Environ 649:448–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.283
Lin Q, Liu E, Zhang E, Li K, Shen J (2016) Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena 145:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.003
Lintern A, Leahy PJ, Heijnis H, Zawadzki A, Gadd P, Jacobsen G, Deletic A, McCarthy DT (2016) Identifying heavy metal levels in historical flood water deposits using sediment cores. Water Res 105:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.041
Malvandi H (2017) Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 117:547–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.02.035
Müller J, Ruppert H, Muramatsu Y, Schneider J (2000) Reservoir sediments–a witness of mining and industrial development (Malter Reservoir, eastern Erzgebirge, Germany). Environ Geol 39:1341–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000117
Omwene PI, Oncel MS, Celen M, Kobya M (2018) Heavy metal pollution and spatial distribution in surface sediments of Mustafakemalpasa stream located in the world’s largest borate basin (Turkey). Chemosphere 208:782–792. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EM00063H
Ontiveros-Cuadras JF, Ruiz-Fernandez AC, Sanchez-Cabeza JA, Perez-Bernal LH, Sericano JL, Preda M, Wee Kwong LL, Paez-Osuna F (2014) Trace element fluxes and natural potential risks from 210Pb-dated sediment cores in lacustrine environments at the Central Mexican Plateau. Sci Total Environ 468–469:677–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.071
Paatero P, Tapper U (1994) Positive matrix factorisation: a non-negative factor model with optimal utilisation of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 5:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/env.3170050203
Palleiro L, Patinha C, Rodríguez BML (2016) Metal fractionation in top soils and bed sediments in the Mero River rural basin: bioavailability and relationship with soil and sediment properties. Catena 144:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.04.019
Pathak AK, Yadav S, Kumar P, Kumar R (2013) Source apportionment and spatial-temporal variations in the metal content of surface dust collected from an industrial area adjoining Delhi, India. Sci Total Environ 443:662–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.030
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ravikumar B, Bai G, Li X (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 191:626–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.078
Rinklebe J, Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Rosche O, Altermann M (2019) Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Environ Int 126:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.011
Sert I, Eftelioglu M, Ozel FE (2017) Historical evolution of heavy metal pollution and recent records in Lake Karagöl sediment cores using 210Pb models, western Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314:2155–2169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5627-x
Shen J, Zhang ZL, Yang LY, Sun QY (2008) Nansi Lake: environment and Resource Research. Seismological Press, Beijing. isbn:978-7-5028-3308-4
Shi J, Li X, He T, Wang J, Wang Z, Li P, Lai Y, Sanganyado E, Liu W (2018) Integrated assessment of heavy metal pollution using transplanted mussels in eastern Guangdong, China. Environ Pollut 243:601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.006
Statistics Bureau of Shandong Province (1978-2017) Shandong Statistical Yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Sun X, Fan D, Liu M, Tian Y, Pang Y, Liao H (2018) Source identification, geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ Pollut 241:938–949
Tian Y, Shi G, Han S, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Liu G, Gao L, Wu J, Zhu T (2013) Vertical characteristics of levels and potential sources of water-soluble ions in PM10 in a Chinese megacity. Sci Total Environ 447:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.071
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of pollution index. Helgolnder Meeresun 33:566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780
Wang Y, Hu J, Xiong K, Huang X, Duan S (2012) Distribution of heavy metals in core sediments from Baihua Lake. Procedia Environ Sci 16:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.008
Wang LF, Yang LY, Kong LH, Li S, Zhu JR, Wang YQ (2014) Spatial distribution, source identification and pollution assessment of metal content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake, China. J Geochem Explor 140:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.02.008
Wang JZ, Yang LY, Wang YQ, Wang BH (2015a) Research on the relationship between economic growth and heavy metals pollution of lake sediments in Nansi Lake Basin. Adv Mater Res 1092-1093:1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1092-1093.1017
Wang SP, Wang YH, Zhang RJ (2015b) Historical levels of heavy metals reconstructed from sedimentary record in the Hejiang River, located in a typical mining region of Southern China. Sci Total Environ 532:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.035
Wang Y, Yang L, Kong L, Liu E, Wang L, Zhu J (2015c) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 125:200–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.023
Wang S, Wang W, Chen J, Zhao L, Zhang B, Jiang X (2019) Geochemical baseline establishment and pollution source determination of heavy metals in lake sediments: a case study in Lihu Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 657:978–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.098
Yang LY, Shen J, Zhang ZL, Zhu YX, Sun QY (2003) Distribution and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in superficial sediments of Nansihu Lake. J Lake Sci 15:252–256. https://doi.org/10.18307/2003.0309
Yang L, Shen J, Zhang Z (2004) Human influence on heavy metal distribution in the Upper Lake Nansi sediments, Shandong Province, China. Chin J Geochem 23(2):185. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02868982
Yin H, Tan NH, Liu CP, Wang JJ, Liang XL, Qu MK (2016) The associations of heavy metals with crystalline iron oxides in the polluted soils around the mining areas in Guangdong Province, China. Chemosphere 161:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.018
Zhang ZL, Shen J, Liu EF, Sun QY, Jiang LG, Wang L (2002) Formation and water environmental evolution of the Nansihu Lake. J Geogr Ences 13:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837464
Zhang H, Huo S, Yeager KM, Xi B, Zhang J, He Z, Ma C, Wu F (2018a) Accumulation of arsenic, mercury and heavy metals in lacustrine sediment in relation to eutrophication: impacts of sources and climate change. Ecol Indic 93:771–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.059
Zhang Z, Lu Y, Li H, Tu Y, Liu B, Yang Z (2018b) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 645:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026
Zhang M, He P, Qiao G, Huang J, Yuan X, Li Q (2019) Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere 223:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.058
Zhu F, Li FW, Wang A, Hao H, Li X (2015) Study on heavy metal levels and its health risk assessment in some edible fishes from Nansi lake, china. Environ Monit Assess 187(4):161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4355-3
Zoller WH, Gladney ES, Duce RA (1974) Atmospheric concentrations and sources of trace metals at the South Pole. Science 183(4121):198–200. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.183.4121.198
Zu Z, Juan S, Lin W (2004) Pollution of bed sediments and its changing process of Nansihu Lake. J Geogr Ences 14(1):121–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02873099
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on this paper.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.41671033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Sen Guo, Junhong Ling, Baojian Chang, and Guanglei Zhao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sen Guo. Yizhang Zhang, Jieying Xiao, and Qiuying Zhang make contribution to this manuscript by editing, supervision, and validation. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, in whole or in part.
Consent to participate
All the authors listed consent to participate
Consent for publication
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 698 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Zhang, Y., Xiao, J. et al. Assessment of heavy metal content, distribution, and sources in Nansi Lake sediments, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 30929–30942 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12729-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12729-9