Abstract
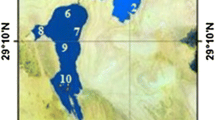
Core and surface sediment samples were collected from three sub-lakes (Lake Nanyang, Lake Dushan and Lake Zhaoyang) in the Lake Nansi Basin, Shandong Province. In order to reveal the characteristics of spatial and historical distribution of heavy metals in different sublakes of the Upper Lake Nansi, heavy metal (As, Cr, Cu, Hg, K, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, Al, Fe, Ti and V) concentrations of sediment samples were investigated. Based on the activity of137Cs in the sediments, the modern accumulation rate of Lake Nansi sediments is 3.5 mm/a. Our results show that the whole Upper Lake Nansi has been already polluted by heavy metals, among which Lake Nanyang has been polluted seriously by mercury, as well as by lead and arsenic, while Lake Dushan has been most seriously polluted by lead and arsenic. Historical variation of heavy metal (Cr, Cu, K, Ni, Zn, Al, Fe, Ti and V) concentrations shows an abrupt shift in 1962, resulting in a division of two periods: from 1957 to 1962 when metal enrichment increased with time, and from 1962 to 2000 when it decreased with time, while that of some anthropogenic elements such as Hg, Pb and Mn tend to increase toward the surface. However, the variation trend of As in the sediments is different from that of Hg, Pb and Mn, with its maximum value appearing in 1982. Since 1982 the concentrations of As have decreased due to the forbidden use of arsenite pesticides. This variation trend revealed changes in manner of human activity (coal combustion, waste discharges from both industries and urban sewage) within the catchment during different periods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby, P. G., P. G. Noian, and D. W. Gifford, 1986,210Pb dating by low background gamma counting [J]: Hydrobiologia, v. 141, p. 21–27.
Appleby, P. G., N. Richardson, and P. G. Noian, 1992, Self-absorption corrections for well-type germanium detectors [J]: Nuclear Institute & Methods (B), v. 71, p. 228–233.
Chen Jingan, Wan Guojiang, and Huang Ronggui, 1998, Geochemical phases and pollution history of heavy metals in sediments of Lake Erhai [J]: Geology-Geochemistry, v. 26, p. 1–8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Förstner, U., 1989, Contaminated sediments, in: Lecture notes in Earth sciences [A]: Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, p. 157.
Förstner, U. and G. T. W. Wittmann, 1983, Metal pollution in the aquatic environment [M]: Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, p. 247–269.
Gibbs, R., 1977, Transport phases of transition metals in the Amazon and Yukon Rivers [J]: Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., v. 88, p. 829–843.
Guo Ruixia, Yang Jianli, and Liu Dongyan, 2002, Transformation of Na, K, Pb and Mn during pyrolysis of coal [J]: Environmental Science, v. 23, n. 5, p. 100–104 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Irabien, M. J. and F. Velasco, 1999, Heavy metals in Oka River sediments (Urdaibai National Biosphere Reserve, northern Spain): Lithogenic and anthropogenic effects [J]: Environ. Geol., v. 37, p. 54–63.
Lacey, E. M., J. W. King, and J. G. Quinn, 2001, Sediment quality in Burlington Harbor, Lake Champlain, U. S. A. [J]: Water Air Soil Pollution, v. 126, p. 96–120.
Nriagu, J. O. and J. M. Pacyna, 1988, Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals [J]: Nature, v. 333, p. 134–140.
Qu Wenchun, M. Dickman, and Wang Sumin, 2001, Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in sediments of Taihu Lake, China [J]: Hydrobiolgia, v. 450, p. 83–89.
Ren Jianli, Zhou Jinsong, and Luo Zhongyang, 2002, Study of mercury emission during coal combustion [J]: Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, v. 22, n. 3, p. 289–293 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rognerud, S. and E. Fjeld, 2001, Trace element contamination of Norwegian Lake sediments [J]: Ambio, v. 30, n. 1, p. 11–19.
Salomons, W. and U. Forstner, 1984, Metals in the hydrocycle [M]: New York, Springer-Verlag, p. 349.
Shen Ji, Zhang Zulu, and Sun Qingyi, 1998, Character and paleoenvironmental significance of the pigment and organic δ13C in sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]: Journal of Lake Science, v. 10, n. 2, p. 17–22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Von H. R. Gunten, M. Sturm, and R. N. Moser, 1997, 200-year record of metals in lake sediments and natural background concentrations [J]: Environ. Sci. Technol., v. 31, p. 2193–2197.
Wan Guojiang, 1999,137Cs dating by annual distinguish for recent sedimentation: samples from Erhai Lake and Hongfeng Lake [J]: Quaternary Science, v. 1, p. 73–80 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wan Guojiang, Lin Wenzhu, and Huang Ronggui, 1991, Dating characteristics and erosion traces of the137Cs vertical profiles in Hongfeng Lake sediments [J]: Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 36, n. 8, p. 674–677.
Zhang Zulu, Niu Zhenguo, and Sun Qingyi, 1999, Pollution of sediment and its changing process of Nansihu Lake [J]: China Environmental Science, v. 19, n. 1, p. 29–32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zulu, Shen Ji, and Sun Qingyi, 2002, Formation and water environments evolution of the Nansihu Lake [J]: Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, v. 33, n. 3, p. 314–321 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Chaosheng, Zhang Shen, and Wang Lijun, 1998, Geochemistry of metals in sediments from Changjiang River and Huanghe River and their comparison [J]: Acta Geographica Sinica, v. 53, n. 4, p. 314–322 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yiyang and Yan Mingcai, 1992, A comparison of chemical elements abundances in sediments between Huanghe River, Changjiang River and China shallow sea district [J]: Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 37, n. 13, p. 1202–1204 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Liping, Chen Ling, Li Bingyuan, Li Yuanfang, Xia Weilan, and Li Jianguo, 2002, Environmental changes reflected by the lake sediments of the South Hongshan Lake, Northwest Tibet [J]: Science in China (Series D), v. 45, n. 5, p. 430–439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was financially supported jointly by the Knowledge Innovation Project of Nanjing Institute of Geography & Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CXNIGLAS-A02-04), and the National Key Project for Basic Research on the Processes of Lake Eutrophication and the Mechanism of Cyanobacterial Blooming (2002CB412300).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Shen, J., Zhang, Z. et al. Human influence on heavy metal distribution in the Upper Lake Nansi sediments, Shandong Province, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 23, 177–185 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02868982
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02868982