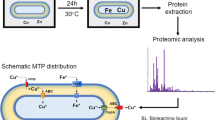
Abstract
There has been alarming depletion of manganese (Mn) reserves owing to the ongoing extensive mining operations for catering the massive industrial demand of this element. Moreover, the mining operations have been leading to the generation of Mn-rich waste, thereby contaminating both terrestrial and aquatic bodies. The current scenario necessitates the development of alternative processes for bioremediation as well as economic recovery of Mn from mining wastes. The present investigation aims to report the bioleaching of Mn by Lysinibacillus sp. from mining waste residues in the context of mine waste remediation. Results confirmed that the native isolate had a high Mn biosolubilization potential with a solubilizing efficiency of 84% at the end of a 21-day study under optimized conditions of pulp density 2% (< 150-μm particle size), pH 6.5, and temperature 30 °C. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) studies followed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis were used to ascertain the change in microbial protein conformation, configuration, and protein identification. The results revealed the expression of heat shock proteins (HSP) from the family HSP which is predominantly expressed in bacteria during stress conditions. This study represents the application of native bacterial strain in Mn biosolubilization. We foresee the utility of proteomics-based studies to provide a methodological framework to the underlying mechanism of metal solubilization, thereby facilitating the two-tier benefit of recovery of Mn from alternative sources as well as bioremediation of waste having high manganese content.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abhilash GA, Pandey BD (2015) Bioleaching of low-grade granitic chalcopyrite ore by hyperthermophiles: elucidation of kinetics-mechanism. Metall Res Technol 112(506):1–14
Acharya C, Kar RN, Sukla LB, Misra VN (2004) Fungal leaching of manganese ore. Trans Indian Inst Metals 57(5):501–508
Bajestani MI, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA (2014) Bioleaching of heavy metals from spent household batteries using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: statistical evaluation and optimization. Sep Purif Technol 132:309–316
Barik S, Park K, Parhi P, Park J, Nam C (2012) Extraction of metal values from waste spent petroleum catalyst using acidic solutions. Sep Purif Technol 101:85–90
Beolichini VF, Gasbarro A, Toro L, Ubaldini S, Abbruzzese C (1997) Batch and semi-continuous tests in bioleaching of manganiferous minerals by heterotrophic mixed microorganisms. Int J Miner Process 50:255–273
Bellenberg S, Huynh D, Poetsch A, Sand W, Vera M (2019) Proteomics reveal enhanced oxidative stress responses and metabolic adaptation in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans biofilm cells on pyrite. Front Microbiol 29
Bergey DH, Breed RS (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Am J Public Health Nations Health 1:416–417
Beveridge TJ, Doyle RJ (1989) Metal ions and bacteria. Wiley, New York
Brandl H, Faramarzi MA (2006) Microbe-metal-interactions for the biotechnological treatment of metal containing solid waste. China Particuology 4(2):93–97
Buciuman F, Patcas F, Craciun R, Zahn DRT (1999) Vibrational spectroscopy of bulk and supported manganese oxides. Phys Chem Chem Phys 1:185–190
Chen P et al (2011) Bioleaching of realgar by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using ferrous iron and elemental sulphur as the sole and mixed energy sources. Bioresour Technol 102:3260–3267
Cui J, Zhang L (2008) Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: a review. J Hazard Mater 158:228–256
Das AP, Ghosh S, Mohanty S, Sukla LB (2015a) Advances in manganese pollution and its bioremediation. Environ Microbial Biotechnol Soil Biol 45
Das AP, Ghosh S, Mohanty S, Sukla LB (2015b) Consequences of manganese compounds: a review. Toxicol Environ Chem 96:981–997
Das AP, Pradhan N, Sukla LB (2012) Microbial recovery of manganese using Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int J Nonferrous Metall 1:9–12
Das AP, Sukla LB, Pradhan N, Nayek S (2011) Mn biomining: a review. Bioresour Technol 102:7381–7387
Das AP, Mishra S (2010) Biodegradation of the metallic carcinogen hexavalent chromium Cr (VI) by an indigenously isolated bacterial strain. J Carcinog 9:6
De vrind JPM, Boogerd FC, de Vrind-de Jong EW (1986) Manganese reduction by a marine Bacillus species. J Bacteriol 167:30–34
Dick GJ, Justin W, Terry J, Bradley MT (2008) Direct identification of a bacterial manganese (II) oxidase, the multicopper oxidase mnxg, from spores of several different marine Bacillus Species. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(5):1527–1534
Durve A, Naphade S, Bhot M, Varghese J, Chandra N (2013) Plasmid curing and protein profiling of heavy metal tolerating bacterial isolates. Arch Appl Sci Res 5(4):46–54
Easton JA, Thompson P (2006) Crowder MW Time-dependent translational response of E. coli to excess Zn(II). J Biomol Tech 17:303–307
Felicioa AP, Garcia O, Bertolinia C, Ottobonib LMM, Novoa MTM (2003) The effects of copper ions on the synthesis of periplasmic and membrane proteins in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans as analyzed by SDS-PAGE and 2D-PAGE. Hydrometallurgy 71:165–171
Gao H et al (2004) Global transcriptome analysis of the heat shock response of Shewanella oneidensis. J Bacteriol 186:7796–7803
Ghiorse WC (1984) Biology of iron- and manganese-depositing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:515–550
Ghosh S, Das AP (2018) Metagenomic insights into the microbial diversity in manganese-contaminated mine tailings and their role in biogeochemical cycling of manganese. Sci Rep 8:8257
Ghosh S, Das AP (2017) Bioleaching of manganese from mining waste residues using Acinetobacter sp. Geol Ecol Landscapes 1(2):77–83
Ghosh S, Mohanty S, Akcil A, Sukla LB, Das AP (2016) A greener approach for resource recycling: manganese bioleaching. Chemosphere 154:628–639
Ghosh S, Das AP (2015) Modified titanium oxide (TiO2) nanocomposites and its array of applications: a review. Toxicol Environ Chem 97(5):491–514
Ghosh S, Mohanty S, Nayak S, Sukla LB, Das AP (2015) Molecular identification of indigenous manganese solubilising bacterial biodiversity from manganese mining deposits. J Basic Microbiol 55:1–9
Gottesman S (1996) Proteases and their targets in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet 30:465–506
Haghshenas DF, Bonakdarpour B, Alamdari E, Nasernejad B (2012) Optimization of physicochemical parameters for bioleaching of sphalerite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using shaking bioreactors. Hydrometallurgy. 111:22–28
Kumar MD, Das AP (2017) Emerging nanotechnology based strategies for diagnosis and therapeutics of urinary tract infections: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 249:63–65
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larsson L, Olsson G, Hoist O, Karlsson HT (1990) Pyrite oxidation by thermophilic Archaebacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:697–701
Li HL et al (2009) Study on bioleaching of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue. Chin J Environ Eng 3:1667–1672
Liu S, Zheng Y, Ma Y, Sarwar A, Zhao X, Luo T, Yang Z (2019) Evaluation and proteomic analysis of lead adsorption by lactic acid bacteria. Int J Mol Sci 20(22):5540
Liu H, Song Y, Chen F, Zheng S, Wang G (2013) Lysinibacillus manganicus sp. nov., isolated from manganese mining soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(10):3568–3573
Li Y, Zuo W, Li Y, Wang X (2012) Cloning of multicopper oxidase gene from Ochrobactrum sp. 531 and characterization of its alkaline laccase activity towards phenolic substrates. Adv Biol Chem 2:248–255
Leverrier P, Vissers JP, Rouault A, Boyaval P, Jan G (2004) Mass spectrometry proteomic analysis of stress adaptation reveals both common and distinct response pathways in Propionibacterium freudenreichii. Arch Microbiol 181:215–230
Mejía ER, Ospina JD, Osorno L, Márquez MA, Morales AL (2015) Mineralogical characterization of chalcopyrite bioleaching, Fourier transform-signal processing and physical sciences, Dr.Ing. Salih Salih (Ed.), InTech, DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/59489.
Mohanty S, Ghosh S, Bsl B Das AP (2018) A review of biotechnology process applied for manganese recovery from wastes. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 17(4):791–811
Mohanty S, Ghosh S, Nayak S, Das AP (2017) Bioleaching of manganese by Aspergillus sp. isolated from mining deposits. Chemosphere 172:302–309
Mohanty S, Ghosh S, Nayak S, Das AP (2016) Isolation, identification and screening of manganese solubilizing fungi from low grade manganese ore deposits. Geomicrobiol J. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2016.1189016
Mohapatra S, Bohidar S, Pradhan N, Kar RN, Sukla LB (2007) Microbial extraction of nickel from Sukinda chromite overburden by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Aspergillus strains. Hydrometallurgy 85(1):1–8
Sethurajan M, van Hullebusch ED, Nancharaiah YV (2018) Biotechnology in the management and resource recovery from metal bearing solid wastes: recent advances. J Environ Manag 211:138–153
Nemati M, Lowenadler J, Harrison S (2000) Particle size effects in bioleaching of pyrite by acidophilic thermophile Sulfolobusmetallicus (BC). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53(173):173–179
Parikh SJ, Chorover J (2005) FTIR Spectroscopic study of biogenic Mn-oxide formation by Pseudomonas putida GB-1. Geomicrobiol J 22:207–218
Prakash JW, Marimuthu J, Antonisamy Jeeva S (2011) Antimicrobial activity of certain fresh water microalgae from Thamirabarani River, Tamil Nadu, South India Asian Pacific. Journal of Tropical Biomedicine:S170–S173
Rawlings DE (2005) Characteristics and adaptability of iron and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates. Microb Cell Factories 4:13
Ribeiro DA et al (2011) The small heat shock proteins from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: gene expression, phylogenetic analysis, and structural modeling. BMC Microbiol 11:259
Richmond CS, Glasner JD, Mau R, Jin H, Blattner FR (1999) Genome-wide expression profiling in Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res 27:3821–3835
Sanket AS, Ghosh S, Sahoo R, Nayak S, Das AP (2016) Molecular identification of acidophilic Manganese (Mn) solubilizing bacteria from mining effluents and their application in mineral beneficiation. Geomicrobiol J 34. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2016.1141340
Singh S, Sukla LB, Mishra BK (2011) Extraction of copper from Malanjkhand low-grade Ore by Bacillus stearothermophilus. Indian J Microbiol 51:477–481
Stintzi A (2003) Gene expression profile of Campylobacter jejuni in response to growth temperature variation. J Bacteriol 185:2009–2016
Srichandan H, Singh S, Pathak A, Kim DJ, Lee SW, Heyes G (2014) Bioleaching of metals from spent refinery petroleum catalyst using moderately thermophilic bacteria: effect of particle size. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 49(7):807–818
Suzuki M et al (2012) Iodide oxidation by a novel multicopper oxidase from the Alphaproteobacterium strain Q-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(11):3941–3949
Sawhney SK, Singh R (2011) Introductory practical biochemistry. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi
Tang W, Gong J, Wu L, Li Y, Zhang M, Zeng X (2016) DGGE diversity of manganese mine samples and isolation of a Lysinibacillus sp. efficient in removal of high Mn (II) concentrations. Chemosphere 165:277–283
Vera M, Schippers A, Sand W (2013) Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation-part A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7529–7541
Watling HR (2006) The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides-a review. Hydrometallurgy 84:81–108
Wang J, Bai J, Xu J, Liang B (2009) Bioleaching of metals from printed wire boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and their mixture. J Hazard Mater 172:1100–1105
Wang A, Crowley DE (2005) Global gene expression responses to cadmium toxicity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:3259–3266
Xiao S et al (2009) Real-time PCR Analysis of the Heat-Shock Response of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270. Folia Biol (Praha) 55:1–6
Xin B, Jiang W, Li X, Zhang K, Liu C, Wang R, Wang Y (2012a) Analysis of reasons for decline of bioleaching efficiency of spent Zn–Mn batteries at high pulp densities and exploration measure for improving performance. Bioresour Technol 112(2):186–192
Xin B, Chen B, Duan N, Zhou C (2010) Extraction of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by bioleaching. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.107
Xin B et al (2012b) Bioleaching of zinc and manganese from spent Zn-Mn batteries and mechanism exploration. Bioresour Technol 106:147–153
Yang Y et al (2014) Bioleaching waste printed circuit boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its kinetics aspect. J Biotechnol 173:24–30
Yang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Huang Q, Xin Y, Xin B (2016) Screening bioleaching systems and operational conditions for optimal Ni recovery from dry electroplating sludge and exploration of the leaching mechanisms involved. Geomicrobiol J 33:179–184
Zhang Y et al (2008) Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by pure and mixed culture. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 18:1491–1496
Zhang WW, Culley DE, Hogan M, Vitiritti L, Brockman FJ (2006) Oxidative stress and heat-shock response in Desulfovibrio vulgaris by genome-wide transcriptomic analysis. Anton Leeuw 90:41–55
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (SP/YO/031/2016) and to SAIF, IIT Bombay, for the ICP-AES and LC-MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shreya Ghosh and Alok Prasad Das: carried out the research work and prepared the manuscript. Mayuri Gandhi: mentored the ICP-AES and LC-MS analysis carried out at SAIF, IIT Bombay. Eric D. van Hullebusch: manuscript preparation and proofreading.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to publish
All authors have given their consent to publish this research article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Gandhi, M., van Hullebusch, E.D. et al. Proteomic insights into Lysinibacillus sp.-mediated biosolubilization of manganese. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 40249–40263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10863-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10863-4