Abstract
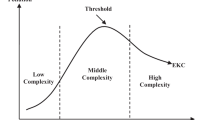
This study aims to investigate the effect of economic globalization and technological changes on the environmental degradation of the South Asian countries over the time span of 1975–2017. Westerlund (Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69:709–748, 2007) cointegration test is employed to estimate the presence of long-run relationship between globalization, technological changes, and environmental degradation. To determine the validity of the Environmental Kuznets Curve, this study employs panel autoregressive distributional lag (ARDL) model. Empirical findings of this study yield the inverted U-shaped association between globalization, technological changes, and environmental degradation which validate that EKC holds in the South Asian countries. The results indicate that the measures of globalization such as FDI, trade openness, and KOF index have positive and statistically significant effect on ecological footprint. However, technological changes measured as patents registered by residents have an insignificant impact on environmental quality. This study infers that the globalization has increased environmental degradation through unsustainable economic development in South Asian countries. These countries should shift to renewable energy resources to protect the environment and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar S, Aşıcı AA (2016) Does income growth relocate ecological footprint? Ecol Indic 61(2):707–714
Al-Mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, Mohammed AH (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Andersson JO, Lindroth M (2001) Ecologically unsustainable trade. Ecol Econ 37:113–122
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Indic 52:16–22
Aşıcı AA, Acar S (2018) How does environmental regulation affect production location of non-carbon ecological footprint? J Clean Prod 178:927–936
Asongu S, El Montasser G, Toumi H (2016) Testing the relationships between energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in 24 African countries: a panel ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(7):6563–6573
Baek J, Kim HS (2013) Is economic growth good or bad for the environment? Empirical evidence from Korea. Energy Econ 36:744–749
Bagliani M, Bravo G, Dalmazzone S (2008) A consumption-based approach to environmental Kuznets curves using the ecological footprint indicator. Ecol Econ 65(3):650–661
Borghesi S, Vercelli A (2003) Sustainable globalization. Ecol Econ 44(1):77–89
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47:239–253
Chandran VGR, Tang CF (2013) The impacts of transport energy consumption, foreign direct investment and income on CO2 emissions in ASEAN-5 economies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 24:445–453
Charfeddine L (2017) The impact of energy consumption and economic development on Ecological Footprint and CO 2 emissions: evidence from a Markov switching equilibrium correction model. Energy Econ 65:355–374
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 76:138–154
Cho CH, Chu YP, Yang HY (2014) An Environment Kuznets Curve for GHG emissions: a panel cointegration analysis. Energy Sources B Econ Plan Policy 9(2):20–129
Copeland B, Taylor M (2004) Trade, growth and the environment. J Econ Lit 42(1):7–71
Danish, Zhang B, Wang B, Wang Z (2017) Role of renewable energy and non-renewable energy consumption on EKC: evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 156:855–864
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl Econ 38:1091–1110
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156
Frankel JA (2003) The environment and globalization (No. w10090). National Bureau of Economic Research
Gallagher KP (2009) Economic globalization and the environment. Annu Rev Environ Resour 34:279–304
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. NBER, Working Paper Series No. 3914, 1–57
Kanjilal K, Ghosh S (2013) Environmental Kuznets curve for India: evidence from tests for cointegration with unknown structural breaks. Energy Policy 56:509–515
Katircioğlu ST (2014) Testing the tourism-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Singapore. Econ Model 41:383–391
Khwaja MA, Umer F, Shaheen N, Sherazi A, Shaheen FH (2012) Air pollution reduction and control in South Asia, Working paper series 121. Sustainable Development Policy Institute (SDPI) Islamabad
Kuznets S (1955) Economic growth and income inequality. Am Econ Rev 45:1–28
Liddle B (2015) What are the carbon emissions elasticities for income and population? Bridging STIRPAT and EKC via robust heterogeneous panel estimates. Glob Environ Chang 31:62–73
Managi S, Hibiki A, Tetsuya T (2008) Does trade liberalization reduce pollution emissions? Discussion Papers 08013, Research Institute of Economy, Trade and Industry (RIETI
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2017) Testing the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:1366–1375
Narayan PK, Narayan S (2010) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: panel data evidence from developing countries. Energy Policy 38(1):661–666
Nasir M, Ur Rehman F (2011) Environmental Kuznets Curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: an empirical investigation. Energy Policy 39(3):1857–1864
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(9):3220–3225
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2015) Investigating the validity of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Cambodia. Ecol Indic 57:324–330
Ozturk I, Bilgili F (2015) Economic growth and biomass consumption nexus: dynamic panel analysis for Sub-Sahara African countries. Appl Energy 137:110–116
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U, Saboori B (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1916–1928
Pablo-Romero MDP, Sánchez-Braza A (2017) The changing of the relationships between carbon footprints and final demand: panel data evidence for 40 major countries. Energy Econ 61:8–20
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development, working paper WP238, Technology and Employment Program, Geneva: International Labor Office
Pao HT, Tsai CM (2011) Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 36(1):685–693
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312
Pesaran MH, Smith R (1995) Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Econ 68(1):79–113
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RP (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Stat Assoc 94(446):621–634
Rudolph A, Figge L (2017) Determinants of Ecological Footprints: what is the role of globalization? Ecol Indic 81:348–361
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191
Sephton P, Mann J (2013) Further evidence of an Environmental Kuznets Curve in Spain. Energy Econ 36:177–181
Shahbaz M, Ozturk I, Afza T, Ali A (2013a) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in a global economy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:494–502
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK, Nasir M (2013b) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Indic 52:379–393
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62(4):929–957
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018a) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New Threshold Analysis. Environ Model Assess 23(5):557–568
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2018b) How strong is the causal relationship between globalization and energy consumption in developed economies? A country-specific time-series and panel analysis. Appl Econ 50(13):1479–1494
Shahbaz M, Mahalik MK, Shahzad SJH, Hammoudeh S (2019) Does the environment Kuznets curve exist between globalization and energy consumption? Global evidence from the cross-correlation method. Int J Financ Econ 24(1):540–557
Sinha A, Bhattacharya J (2017) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for SO 2 emission: a case of Indian cities. Ecol Indic 72:881–894
Srinivasan PV (2013) Dynamics of structural transformation in South Asia. Asia Pac Dev J 20(2):53–88
Stern DI (2004) The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev 32:1419–1439
Thompson A (2012) Water abundance and an EKC for water pollution. Econ Lett 117:423–425
Ulucak R, Bilgili F (2018) A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. J Clean Prod 188:144–157
Weinzettel J, Hertwich EG, Peters GP, Steen-Olsen K, Galli A (2013) Affluence drives the global displacement of land use. Glob Environ Chang 23(2):433–438
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabir, S., Gorus, M.S. The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from the South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 33387–33398 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06458-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06458-3