Abstract
Slow and random transfer of pollutants and photo-induced carriers on photocatalysts causes loss of efficiency in photodegradation of contaminants. Enhancing and directing mass transfer of them are considered as two major methods for improving the photodegradation of pollutants over photocatalysts. Here in this work, we focused on the design of a novel photocatalyst which not only accelerated the transfer rate of Cr(VI) and electrons but also provided specific transfer routes for them. By careful characterizations, it is indicated that 2-((2-(2-aminoethylamino)ethylimino)methyl)phenol (AEMP) was covalently attached onto activated carbon (AC), which enhanced Cr(VI) transfer from bulk solution to AC through electrostatic or coordinative interactions. The external mass transfer coefficient (Kf) of Cr(VI) over TiO2/AC-AEMP was estimated as 1.75 × 10−6 m s−1, which was ~ 12.79 and ~ 5.96 times that of TiO2 and TiO2/AC, respectively. Dense and homogeneous heterojunctions between AC and TiO2 were acquired synchronically by forming Ti–O–C linkages, which increased traveling of electrons from TiO2 to AC. Accordingly, Cr(VI) can capture photo-induced electrons on the surface of AC via concrete routes and then be reduced efficiently. The results showed that the photoreduction rate of Cr(VI) on TiO2/AC-AEMP reached to ~ 92.7%, and the overall photocatalytic activity of this well-designed TiO2/AC-AEMP has been enhanced significantly by 5.5 times compared to TiO2/AC. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/AC-AEMP was mainly attributed to an improved synergetic process of mass transfer–induced adsorption–photoreduction by forming specific transfer routes for accelerative motion of Cr(VI) and electrons. This work provides a feasible strategy to improve the photoactivity of photocatalysts for the degradation of pollutants by effective mass transfer.

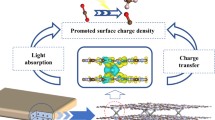
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ghouti MA, Khraisheh MAM (2009) Adsorption behaviour of methylene blue onto Jordanian diatomite: a kinetic study. J Hazard Mater 165:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.018
Amieśnik J, Rabajczyk A (2012) Speciation analysis of chromium in environmental samples. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:327–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.518517
Ao YH, B JQ, W PF (2016) Bismuth oxychloride modified titanium phosphate nanoplates: a new p-n heterostructured photocatalysts with high activity for the degradation of different kinds of organic pollutants. J Colloid Interface Sci 476:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.05.021
Azeez F, Al-Hetlani E, Arafa M (2018) The effect of surface charge on photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using chargeable titania nanoparticles. 8:7104–7113. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25673-5
Baek MH, Jung WC, Yoon JW (2013) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity evaluation of micro- and mesoporous TiO2/spherical activated carbon. J Ind Eng Chem 19:469–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.08.026
Bashir S, Washab AK, Idriss H (2015) Synergism and photocatalytic water splitting to hydrogen over M/TiO2 catalysts: effect of initial particle size of TiO2. Catal Today 240:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.05.034
Bhattacharyya KG, Sharma A (2004) Azadirachta indica leaf powder as an effective biosorbent for dyes: a case study with aqueous Congo red solutions. J Environ Manag 71:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2004.03.002
Blanes PS, Bordom ME, Gonzalez JC (2016) Application of soy hull biomass in removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated waters. Kinetic, thermodynamic and continuous sorption studies. J Environ Chem Eng 4:516–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.008
Boyd GE, Adamson AW, Myers LS (1947) The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II: kinetics. J Am Chem Soc 69:2836–2848. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01203a066
Chabot V, Higgins D, Yu A, Xiao X (2014) A review of graphene and graphene oxide sponge: material synthesis and applications to energy and the environment. Energy Environ Sci 7:1564–1596. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee43385d
Deng Y, Tang L, Zeng G (2017) Insight into highly efficient simultaneous photocatalytic removal of Cr (VI) and 2,4-diclorophenol under visible light irradiation by phosphorus doped porous ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheets from aqueous media: performance and reaction mechanism. Appl Catal B Environ 203:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.046
Dural MU, Cavas L (2011) Methylene blue adsorption on activated carbon prepared from Posidonia oceanica (L.) dead leaves: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chem Eng J 168:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.038
Feng HJ, Zhang MH, Yu LY (2013) Phosphorus-doped TiO2 catalysts with stable anatase–brookite biphase structure: synthesis and photocatalytic performance. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 13:4981–4989. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2013.7606
Fu P, Luan Y (2004) Preparation of activated carbon fibers supported TiO2 photocatalyst and evaluation of its photocatalytic reactivity. J Mol Catal A Chem 221:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2004.06.018
Gao BF, Yap PS, Lim TM (2011) Adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of acid red 88 by supported TiO2: effect of activated carbon support and aqueous anions. Chem Eng J 171:1098–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.006
Ge MZ, Cai JS (2017) A review of TiO2 nanostructured catalysts for sustainable H2 generation. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:8418–8449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.052
Guo JZ, Li B, Liu L, Lv KL (2014) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by chemically modified bamboo. Chemosphere 11:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.118
Hu R, Dai S, Shao D (2015) Efficient removal of phenol and aniline from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide/polypyrrole composites. J Mol Liq 203:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.12.046
Huo PP, Zhao P, Wang Y (2018) An effective utilization of solar energy: enhanced photodegradation efficiency of TiO2/graphene-based composite. 11:630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030630
Jiang F, Zheng Z, Xu ZY (2006) Aqueous Cr(VI) photo-reduction catalyzed by TiO2 and sulfated TiO2. J Hazard Mater 134:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.041
Kal S, Louis AM, Dinolfo PH (2014) Evidence for catalytic water oxidation by a dimanganese tetrakis-Schiff base macrocycle. Inorg Chim Acta 423:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2014.08.007
Kaul S, Kumar A, Sain B (2002) A simple and convenient one-pot synthesis of fatty acid esters from hindered alcohols using N,N-dimeehylchloro-sulfitemethaniminium chloride as dehydrating agent. Synth Commun 33:2885–2891. https://doi.org/10.1081/SCC-120006474
Kuo CS, Lin CF (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of methamphetamine by UV/TiO2—kinetics, intermediates and products. Water Res 74:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.01.043
Li N, Bai R (2006) Development of chitosan-based granular adsorbents for enhanced and selective adsorption performance in heavy metal removal. Water Sci Technol 54:103–113. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2006.736
Li JB, Liu XW (2013) Silica-gel supported V complexes: preparation, characterization and catalytic oxidative desulfurization. J China Chem Eng 21:860–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(13)60558-3
Li ZH, Chang XJ, Hu Z (2009) Zincon-modified activated carbon for solid-phase extraction and preconcentration of trace lead and chromium from environmental samples. J Hazard Mater 166:133–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.006
Li HM, Zeng YS, Huang TC (2012) Hierarchical TiO2 nanospheres with dominant {001} facets: facile synthesis, growth mechanism, and photocatalytic activity. Chem. 18:7525–7532. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201103087
Li Y, Cui WQ, Liu L (2016) Removal of Cr(VI) by 3D TiO2-graphene hydrogel via adsorption enriched with photocatalytic reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 199:412–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.053
Lim TT, Yap PS, Srinivasan M, Fane AG (2011) TiO2/AC composites for synergistic adsorption-photocatalysis processes: present challenges and further developments for water treatment and reclamation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:1173–1230. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380903488664
Liu SX, Chen XY, Chen XA (2007) TiO2/AC composite photocatalyst with high activity and easy separation prepared by a hydrothermal method. J Hazard Mater 143:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.026
Liu TX, Li FB, Li XZ (2008) TiO2 hydrosols with high activity for photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde in a gaseous phase. J Hazard Mater 152:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.003
Liu J, Li WY, Liu YG (2014a) Titanium(IV) hydrate based on chitosan template for defluoridation from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 293:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.050
Liu W, Ni J, Yin X (2014b) Synergy of photocatalysis and adsorption for simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) with TiO2 and titanate nanotubes. Water Res 53:12–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.12.043
Liu J, Jing LQ, Gao GF (2017) Ag2S quantum dots in situ coupled to hexagonal SnS2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity for MO and Cr(VI) removal. RSC Adv 7:46823–46831. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra08369f
Lu HT, Dong HF, Fan WH (2017) Aging and behavior of functional TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous environment. J Hazard Mater 325:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/jhazmat.2016.11.013
Malasha GF, El-Khaiary MI (2010) Piecewise linear regression: a statistical method for the analysis of experimental adsorption data by the intraparticle-diffusion models. Chem Eng J 163:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.059
Min H, Girard-Lauriault PL (2012) Ambient-ageing processes in amine self-assembled monolayers on microarray slides as studied by ToF-SIMS with principal component analysis, XPS, and NEXAFS spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:613–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5862-5
Moffitt M, Eisenberg A (1995) Size control of nanoparticles in semiconductor-polymer composites. 1. Control via multiplet aggregation numbers in styrene-based random ionomers. Chem Mater 7:1185–1192. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00054a018
Nibou D, Mekatel H (2010) Adsorption of Zn2+ ions onto NaA and NaX zeolites: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 173:637–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.132
Ong CW, Zhao XA, Tsang YC (1996) Effects of substrate temperature on the structure and properties of reactive pulsed laser deposited CNx films. Thin Solid Films 280:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/004-6090(96)00853-x
Qin G, McGuiRe MJ, Blute NK (2005) Hexavalent chromium removal by reduction with ferrous sulfate, coagulation, and filtration: a pilot-scale study. Environ Sci Technol 39:6321–6327. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050486p
Rani JS, Ramakrishnan V (2013) Interaction of Schiff base ligand with tin dioxide nanoparticles: optical studies. Spectrochim Acta A 114:170–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.05.037
Reichenberg D (1953) Properties of ion exchange resins in relation to their structure. III. Kinetics of exchange. J Am Chem Soc 75:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01099a022
Shah KA, Tali BA (2016) Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by catalytic chemical vapour deposition: a review on carbon sources, catalysts and substrates. Mater Sci Semicond Process 41:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.08.013
Slimen H, Houas A, Nogier JP (2011) Elaboration of stable anatase TiO2 through activated carbon addition with high photocatalytic activity under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 221:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.04.013
Tauc J, Menth A (1972) States in the gap. J Non-Cryst Solids 8:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(72)90194-9
Vieira EFS, Cestari AR (2006) Measurement of cation binding to immobilized vanillin by isothermal calorimetry. J Colloid Interface Sci 298:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.12.021
Wang B, Ma HZ (2001) Chiroptical lanthanide(III) schiff base complexes derived from p-nitrophenyl-hydrazine and d-camphor-β-sulphonic acid. Inorg Chem Commun 4:248–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1387-7003(01)00173-3
Wang XJ, Hu ZH, Chen YJ (2009) A novel approach towards high-performance composite photocatalyst of TiO2 deposited on activated carbon. Appl Surf Sci 255:3953–3958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.10.083
Wang Y, Zhu L, Ba NN (2017) Effects of NH4F quantity on N-doping level, photodegradation and photocatalytic H2 production activities of N-doped TiO2 nanotube array films. Mater Res Bull 86:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.10.031
Wang J, Zhang DK, Deng JK (2018) Fabrication of phosphorus nanostructures/TiO2 composite photocatalyst with enhancing photodegradation and hydrogen production from water under visible light. 516:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.003
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–59
Xiao Q, Zhang J, Xiao C (2008) Solar photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in carbon-doped TiO2 nanoparticles suspension. Sol Energy 82:706–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2008.02.006
Yang J, Bai H, Tan XC (2006) IR and XPS investigation of visible-light photocatalysis-nitrogen-carbon-doped TiO2 film. Appl Surf Sci 253:1988–1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.03.078
Yao CC, Chen TJ (2015) A new simplified method for estimating film msaa transfer and surface diffusion coefficients from batch adsorption kinetic data. Chem Eng J 265:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.005
Zhang XW, Lei LC (2008) Effect of preparation methods on the structure and catalytic performance of TiO2/AC photocatalysts. J Hazard Mater 153:827–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.052
Zhao Y, Zhao DL, Chen CL (2013) Enhanced photo-reduction and removal of Cr(VI) on reduced graphene oxide decorated with TiO2 nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 405:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.05.004
Zhou Z, Li YH, Lv KL (2018) Fabrication of walnut-like BiVO4@Bi2S3 heterojunction for efficient visible photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Mater Sci Semicond Process 75:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.11.011
Zhu JZ, Deng BL, Yang J (2009) Modifying activated carbon with hybrid ligands for enhancing aqueous mercury removal. Carbon 47:2014–2025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.03.047
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate the financial support from the Foundation of National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of China (No. 2014YQ060773), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20180148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A TiO2/AC-AEMP photocatalyst was obtained through a multi-step chemical process.
• Dense and homogeneous heterojunctions were formed between TiO2 and functionalized activated carbon (AC-AEMP).
• Significant adsorptive–photocatalytic performance of TiO2/AC-AEMP in Cr(VI) reduction was achieved.
• A synergy in the mass transfer of Cr(VI) and photo-induced electrons was proposed.
• The mass transfer coefficient of Cr(VI) was calculated quantitatively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Yang, H., Fu, X. et al. Efficient photoreduction of Cr(VI) on TiO2/functionalized activated carbon (TiO2/AC-AEMP): improved adsorption of Cr(VI) and induced transfer of electrons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 17446–17457 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05374-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05374-w