Abstract
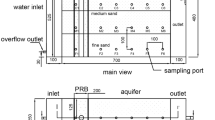
Cr(VI), which is highly toxic and soluble, is one of the most challenging groundwater contaminants. Previous work has indicated that emulsified vegetable oil (EVO) is an effective in situ amendment for removing Cr(VI) from groundwater. However, the spatial and temporal changes in geological parameters and microbial community structures throughout the remediation period are poorly understood. In this study, a large laboratory-scale sand-packed chamber (reactive zone of 100 × 50 × 30 cm) was used to simulate the bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated aquifer by EVO over a 512-day period. Various geological parameters and microbial communities were monitored during both the establishment and remediation stages. The results indicate that several biogeochemical reactions occurred in a specific sequence following the injection of EVO, creating an acidic and reducing environment. A shift in the community structure and a decrease in the community diversity were observed. The abundance of microbes involved in the degradation of EVO and reduction of electron acceptors significantly increased. Then, the EVO reactive zone was flushed with Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater. Biogeochemical reactions were inhibited after the inflow of Cr(VI) and subsequently recovered a month later. The pH of the aquifer returned to the initial neutral condition (approximately 7.2). The EVO reactive zone could remediate Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater at an efficiency exceeding 97% over 480 days. Biogeochemistry played a major role in the early period (0~75 days). In the later period (240~480 days), the remediation of Cr(VI) in the reactive zone depended mostly on bio-reduction by Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MZ, Malik A (2008) Chromate resistance, transport and bioreduction by Exiguobacterium sp ZM-2 isolated from agricultural soil irrigated with tannery effluent. J Basic Microbiol 48:416–420
Anderson RT, Vrionis HA, Ortiz-Bernad I, Resch CT, Long PE, Dayvault R, Karp K, Marutzky S, Metzler DR, Peacock A, White DC, Lowe M, Lovley DR (2003) Stimulating the in situ activity of Geobacter species to remove uranium from the groundwater of a uranium-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5884–5891
Bao P, Hu ZY, Wang XJ, Chen J, Ba YX, Hua J, Zhu CY, Zhong M, Wu CY (2012) Dechlorination of p,p '-DDTs coupled with sulfate reduction by novel sulfate-reducing bacterium Clostridium sp BXM. Environ Pollut 162:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.037
Borden RC (2007) Concurrent bioremediation of perchlorate and 1,1,1-trichloroethane in an EVO barrier. J Contam Hydrol 94:13–33
Borden RC, Beckwith WJ, Lieberman MT, Akladiss N, Hill SR (2007) Enhanced anaerobic bioremediation of a TCE source at the Tarheel Army Missile Plant using EOS. Remediat J 17:5–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.20130
Borden RC, Rodriguez BX (2006) Evaluation of slow release substrates for anaerobic bioremediation. Bioremed J 10:59–69
Brodie EL, Joyner DC, Faybishenko B, Conrad ME, Rios-Velazquez C, Malave J, Martinez R, Mork B, Willett A, Koenigsberg S, Herman DJ, Firestone MK, Hazen TC (2011) Microbial community response to addition of polylactate compounds to stimulate hexavalent chromium reduction in groundwater. Chemosphere 85:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.021
Chang DH, Lee JB, Lee GH, Rhee MS, Lee H, Bae KS, Park DS, Kim BC (2013) Sunxiuqinia dokdonensis sp nov., isolated from deep sub-seafloor sediment. J Microbiol 51:741–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-3492-z
Chen MJ, Liu CS, Chen PC, Tong H, Li FB, Qiao JT, Lan Q (2016) Dynamics of the microbial community and Fe(III)-reducing and dechlorinating microorganisms in response to pentachlorophenol transformation in paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 312:97–105
Chen MJ, Tong H, Liu CS, Chen DD, Li FB, Qiao JT (2016) A humic substance analogue AQDS stimulates Geobacter sp abundance and enhances pentachlorophenol transformation in a paddy soil. Chemosphere 160:141–148
Divyasree P, Braun JJ, Subramanian S (2014) Comparative studies on the bioremediation of hexavalent and trivalent chromium using Citrobacter freundii: part I-effect of parameters controlling biosorption. Int J Environ Res 8:1127–1134
Dogan NM, Kantar C, Gulcan S, Dodge CJ, Yilmaz BC, Mazmanci MA (2011) Chromium(VI) bioremoval by Pseudomonas acteria: role of microbial exudates for natural attenuation and biotreatment of Cr(VI) contamination. Environ Sci Technol 45:2278–2285
Dong J, Li BW, Bao QBR (2017) In situ reactive zone with modified Mg(OH)(2) for remediation of heavy metal polluted groundwater: immobilization and interaction of Cr(III), Pb(II) and Cd(II). J Contam Hydrol 199:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.02.005
Ellis DE, Lutz EJ, Odom JM, Buchanan RJ, Bartlett CL, Lee MD, Harkness MR, Deweerd KA (2000) Bioaugmentation for accelerated in situ anaerobic bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 34:2254–2260. https://doi.org/10.1021/es990638e
Faybishenko B, Hazen TC, Long PE, Brodie EL, Conrad ME, Hubbard SS, Christensen JN, Joyner D, Borglin SE, Chakraborty R, Williams KH, Peterson JE, Chen J, Brown ST, Tokunaga TK, Wan J, Firestone M, Newcomer DR, Resch CT, Cantrell KJ, Willett A, Koenigsberg S (2008) In situ long-term reductive bioimmobilization of Cr(VI) in groundwater using hydrogen release compound. Environ Sci Technol 42:8478–8485. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801383r
Fu F, Hu M, Tang B, Han W, Cheng Z (2015) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater using acid-washed zero-valent iron catalyzed by polyoxometalate under acid conditions: efficacy, reaction mechanism and influencing factors. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 47:177–181
Gihring TM, Zhang GX, Brandt CC, Brooks SC, Campbell JH, Carroll S, Criddle CS, Green SJ, Jardine P, Kostka JE, Lowe K, Mehlhorn TL, Overholt W, Watson DB, Yang ZM, Wu WM, Schadt CW (2011) A limited microbial consortium is responsible for extended bioreduction of uranium in a contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5955–5965
Harkness M, Fisher A (2013) Use of emulsified vegetable oil to support bioremediation of TCE DNAPL in soil columns. J Contam Hydrol 151:16–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.04.002
Hunter WJ (2001) Use of vegetable oil in a pilot-scale denitrifying barrier. J Contam Hydrol 53:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(01)00137-1
Kao CM, Liao HY, Chien CC, Tseng YK, Tang P, Lin CE, Chen SC (2016) The change of microbial community from chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater after biostimulation using the metagenome analysis. J Hazard Mater 302:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.047
Kotik M, Davidová A, Voříšková J, Baldrian P (2013) Bacterial communities in tetrachloroethene-polluted groundwaters: a case study. Sci Total Environ 454-455:517–527
Li J, Chen Z, Shen J, Wang B, Fan L (2017) Influence of phosphate, citrate and nitrilotriacetic acid on the removal of aqueous hexavalent chromium by zero-valent iron at circumneutral pH. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:269–275
Liang SH, Kuo YC, Chen SH, Chen CY, Kao CM (2013) Development of a slow polycolloid-releasing substrate (SPRS) biobarrier to remediate TCE-contaminated aquifers. J Hazard Mater 254:107–115
Lindow NL, Borden RC (2005) Anaerobic bioremediation of acid mine drainage using emulsified soybean oil. Mine Water Environ 24:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-005-0096-9
Lovley DR, Anderson RT (2000) Influence of dissimilatory metal reduction on fate of organic and metal contaminants in the subsurface. Hydrogeol J 8:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010974
Mitchell AL, Scheremetjew M, Denise H, Potter S, Tarkowska A, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Pesseat S, Boland MA, Hunter Fiona MI, ten Hoopen P, Alako B, Amid C, Wilkinson DJ, Curtis TP, Cochrane G, Finn RD (2018) EBI metagenomics in 2017: enriching the analysis of microbial communities, from sequence reads to assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res 46:726–735
Okemgbo AA, Hill HH, Metcalf SG, Bachelor M (1999) Metal ion interferences in reverse polarity capillary zone electrophoretic analysis of Hanford Defense Waste for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and n-hydroxyethylethylenediaminetriacetic acid (HEDTA ). Anal Chim Acta 396:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00449-3
Qu LY, Zhu FL, Hong XG, Gao W, Chen JH, Sun XQ (2011) Sunxiuqinia elliptica gen. nov., sp nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from sediment in a sea cucumber farm. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2885–2889
Sarangi A, Krishnan C (2008) Comparison of in vitro Cr(VI) reduction by CFEs of chromate resistant bacteria isolated from chromate contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 99:4130–4137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.059
Sattley WM, Jung DO, Madigan MT (2008) Psychrosinus fermentans gen. nov., sp nov., a lactate-fermenting bacterium from near-freezing oxycline waters of a meromictic Antarctic lake. FEMS Microbiol Lett 287:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01300.x
Shah V, Zakrzewski M, Wibberg D, Eikmeyer F, Schlüter A, Madamwar D (2013) Taxonomic profiling and metagenome analysis of a microbial community from a habitat contaminated with industrial discharges. Microb Ecol 66:533–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0253-9
Suthersan SS, Payne FC (2005) In situ remediation engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 511
Takai K, Abe M, Miyazaki M, Koide O, Nunoura T, Imachi H, Inagaki F, Kobayashi T (2013) Sunxiuqinia faeciviva sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic organoheterotroph of the Bacteroidetes isolated from deep subseafloor sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1602–1609. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.044065-0
Tang GP, Watson DB, Wu WM, Schadt CW, Parker JC, Brooks SC (2013) U(VI) bioreduction with emulsified vegetable oil as the electron donor - model application to a field test. Environ Sci Technol 47:3218–3225
Tang GP, Wu WM, Watson DB, Parker JC, Schadt CW, Shi XQ, Brooks SC (2013) U(VI) bioreduction with emulsified vegetable oil as the electron donor - microcosm tests and model development. Environ Sci Technol 47:3209–3217
Wang ZC, Gao MC, She ZL, Jin CJ, Zhao YG, Yang SY, Guo L, Wang S (2015) Effects of hexavalent chromium on performance and microbial community of an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4575–4586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3704-z
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07 http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/misc/resources.jsp. Accessed Nov 2016
Wang XM, Li ZF, Zhou XQ, Wang QQ, Wu YG, Saino MY, Bai X (2016) Study on the bio-methane yield and microbial community structure in enzyme enhanced anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and corn straw. Bioresour Technol 219:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.116
Wang XR, Yan XH, Wang Q (2011) Case study of demonstration project of typical chrome contaminated sites remediation. In: International Conference on Contaminated Sites Remediation 2011 International Forum (RCST) 2011), Chongqing, China, p 203–213
Watson DB, Wu WM, Mehlhorn T, Tang GP, Earles J, Lowe K, Gihring TM, Zhang GX, Phillips J, Boyanov MI, Spalding BP, Schadt C, Kemner KM, Criddle CS, Jardine PM, Brooks SC (2013) In situ bioremediation of uranium with emulsified vegetable oil as the electron donor. Environ Sci Technol 47:6440–6448. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3033555
Wen CY, Sheng H, Ren LM, Dong Y, Dong J (2017) Study on the removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated groundwater using emulsified vegetable oil. Process Saf Environ 109:599–608
Xu WH, Liu YG, Zeng GM, Li X, Song HX, Peng QQ (2009) Characterization of Cr(VI) resistance and reduction by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 19:1336–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60446-X
Xu S, Lu WJ, Liu YT, Ming ZY, Liu YJ, Meng RH, Wang HT (2017) Structure and diversity of bacterial communities in two large sanitary landfills in China as revealed by high-throughput sequencing (MiSeq). Waste Manag 63:41–48
Xu D, Xiao ER, Xu P, Zhou Y, He F, Zhou QH, Xu D, Wu ZB (2017) Performance and microbial communities of completely autotrophic denitrification in a bioelectrochemically-assisted constructed wetland system for nitrate removal. Bioresour Technol 228:39–46
Yin Z, Zhang JC, Liao SL, Ma Q, Wang QG, Zhang JF (2015) Research and application of the remediation technology for the chromium contaminated site. Environ Eng 01:159–162 (in Chinese)
Zhang P, Van Nostrand JD, He ZL, Chakraborty R, Deng Y, Curtis D, Fields MW, Hazen TC, Arkin AP, Zhou JZ (2015) A slow-release substrate stimulates groundwater microbial communities for long-term in situ Cr(VI) reduction. Environ Sci Technol 49:12922–12931. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00024
Zhang JB, Wu PX, Hao B, Yu ZN (2011) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by the bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001. Bioresour Technol 102:9866–9869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.118
Funding
This research was financially funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41572214, 41772241 and 41602252), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (No. 20130101027JC), and “The 12th Five-Year Plan” science and technology research projects of the Education Department of Jilin Province (No. 2014B012); the work was supported by the Key Laboratory of Groundwater Resources and Environment, Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Diane Purchase
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 215 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, J., Yu, J. & Bao, Q. Simulated reactive zone with emulsified vegetable oil for the long-term remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated aquifer: dynamic evolution of geological parameters and groundwater microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 34392–34402 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3386-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3386-z