Abstract
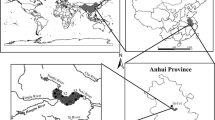
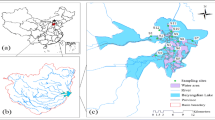
In this study, 15 representative surface waters and sediments and seven typical fish were collected during the wet season in 2016 to explore the occurrence, chemical fractionation, and ecological risk of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr, Hg, As, and Ni) in aquatic ecosystems of Dongting Lake in China. In surface water, the concentrations of all elements were lower than the third grade of the surface water quality standards (GB3838-2002). The highest concentrations of Zn, Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cu were found in the outlet of Dongting Lake, whereas As and Cr were highest in the Xiangjiang River Delta area. In surface sediments, the concentration decreased in the order of Zn > Cr > Pb > Cu > Ni > As>Cd > Hg; the highest concentration of all elements, except for Hg, was located in the Xiangjiang River Delta area; for chemical fractionation, Cr, Hg, Zn, As, Ni, and Cu were mainly residual fractionation; and Pb and Cd were mainly in a reducible state and fraction soluble in acid, respectively. In fish muscle, the concentrations of all elements were lower than relevant standards; the highest concentration appeared in fish living in the middle-lower and demersal layers. As for the feeding habits of fish, the average concentration decreased in the order of carnivorous > omnivorous > herbivorous fish. The potential ecological risk and the ratio of secondary phase to primary phase assessment showed that Cd and Hg had the highest ecological risk and that Cd and Pb had a high risk of secondary release. A health risk assessment showed that drinking water and fish for consumption in urban and rural areas around Dongting Lake were in the acceptable level.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthemidis A., Zachariadis G., Voutsa D., et al. (2002) Variation of heavy metals and other toxic element concentrations in surface water of Macedonia[C]. Proceedings of 1st Environmental Conference of Macedonia, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp, 104–109
Bo L, Wang D, Li T et al (2015) Accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic organisms in rural rivers in the Taihu Lake region, China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(9):6721–6731
Bonanno G, Giudice RL (2010) Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the organs of Phragmites australis, (common reed) and their potential use as contamination indicators[J]. Ecol Indic 10(3):639–645
Chen Y, Li T, Ma J et al (2016) Health risk assessment of heavy metal accumulation in soil and groundwater in a typical high cancer incidence area of Huai River basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae(in Chinese) 36(12):4537–4545
Chen J, Wang S, Lin W et al (2005) Development and resource status of China chrome industry in the 21th century.[J]. Ferro-Alloy (inChinese) 36(2):39–41
Chi Thanh V, Giang V, Tuan H (2017) Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and water of a contaminated river in Taiwan[J]. Ecol Indic 82:32–42
Fang Binbin, Yu Yang, Jiang Weili et al (2017) Spatio-Temporal distribution of Heavy Metals in the Surface Water and Sediment of the Lake Taihu Basin and Assessment of Their Potential Ecological Risks[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment (in Chinese) 33(3):215–224
Fu J, Hu X, Tao X et al (2013) Risk and toxicity assessments of heavy metals in sediments and fishes from the Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, China[J]. Chemosphere 93(9):1887–1895
Fu Z, Wu F, Chen L et al (2016) Copper and zinc, but not other priority toxic metals, pose risks to native aquatic species in a large urban lake in Eastern China.[J]. Environ Pollut 219:1069
Fu Zhiyou, Guo Wenjing, Dang Zhi et al (2017) Refocusing on Nonpriority Toxic Metals in the Aquatic Environment in China.[J]. Environ Sci Technol 51(6):3117-3118
Guo J, Li L, Huang D et al (2016) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment of Dongting Lake[J]. Res Environ Sci(in Chinese) 29(1):44–51
Guo W, Huo S, Xi B et al (2015) Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: distribution, bioavailability, and risk[J]. Ecol Eng 81:243–255
Huang R, Zhang Y, Bozzetti C et al (2014) High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China.[J]. Nature 514(7521):218–222
He W, Bai Z, Liu W et al (2016) Occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in surface sediments from a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu)[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(11):10335–10348
Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Res, 1980, 14(8), 975–1001.
Kishe MA, Machiwa JF (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Mwanza Gulf of Lake Victoria, Tanzania[J]. Environ Int 28(7):619–625
Ke X, Gui S, Huang H et al (2017) Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China[J]. Chemosphere 175:473–481
Liu Y, Peng Y, Yue D et al (2015) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment, bioavailability, and controlling factors in sediments of Taihu Lake, China[J]. J Soil Contam 24(3):262–275
Lalah JO, Ochieng EZ, Wandiga SO (2008) Sources of heavy metal input into Winam Gulf, Kenya[J]. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81(3):277–284
Li L, Wang C, Zhang Y et al (2016a) Study of macrozoobenthos and heavy metals of surface sediment in Dongting Lake [J]. Ecol Environ Sci(in Chinese) 25(2):286–291
Lin AY, Panchangam SC, Ciou PS (2010) High levels of perfluorochemicals in Taiwan’s wastewater treatment plants and downstream rivers pose great risk to local aquatic ecosystems[J]. Chemosphere 80(10):1167–1174
Liu M, Zhong J, Zheng X et al (2018) Fraction distribution and leaching behavior of heavy metals in dredged sediment disposal sites around Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu (China).[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 7:1–8
Li Y, Zhang L, Wang S et al (2016b) Composition, structural characteristics and indication of water quality of dissolved organic matter in Dongting Lake sediments[J]. Ecol Eng 97:370–380
Li Yuelong, Rao Q.2013 Water ecology and its causes in Dongting Lake Area.[C]. 2013 Dongting Lake Development Forum(in Chinese)
Liang J, Liu J, Yuan X et al (2015) Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metal risk and source in sediments of Dongting Lake wetland, mid-south China[J]. J Environ Sci Health, Part A 50(1):100–108
Malferrari D, Brigatti MF, Laurora A et al (2009) Heavy metals in sediments from canals for water supplying and drainage: mobilization and control strategies[J]. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):723–729
Ma R, Wang B, Lu S et al (2016) Characterization of pharmaceutically active compounds in Dongting Lake, China: occurrence, chiral profiling and environmental risk[J]. Sci Total Environ 557:268–275
Makokha VA, Qi Y, Shen Y, Wang J (2016) Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China[J]. Expo Health 8(1):31–41
Mendil D, Uluözlü ÖD, Hasdemir E et al (2005) Determination of trace metal levels in seven fish species in lakes in Tokat, Turkey[J]. Food Chem 90(1–2):175–179
Opfer SE, Farver JR, Miner JG, Krieger K (2011) Heavy metals in sediments and uptake by burrowing mayflies in western Lake Erie basin[J]. J Great Lakes Res 37(1):1–8
Qiao Y, Yang Y, Gu J et al (2013) Distribution and geochemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments from coastal area suffered rapid urbanization, a case study of Shantou Bay, China[J]. Mar Pollut Bull 68(1):140–146
Qian X, Li X (1988) Geochemical background value of sediments in the Dongting Lake water system [J]. Sci Bull(in Chinese) 6:458–462
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X et al (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China.[J]. Chemosphere 191(4):626–638
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials[J]. J Environ Monit 1(1):57–61
Shyleshchandran MN, Mohan M, Ramasamy EV (2017) Risk assessment of heavy metals in Vembanad Lake sediments (south-west coast of India), based on acid-volatile sulfide (AVS)-simultaneously extracted metal (SEM) approach[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 8:1–13
Muhannad S, Javed I, Gulraiz A et al (2018) Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan[J]. J Geochem Explor 184:199–208
US EPA (2005) Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment. Risk Assessment Forum[R].USEPA /630 / P-03 /001F.Washington DC: US EPA
US EPA (2000a) Risk-based concentration table. Philadelphia PA: United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC
USEPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency (2013) The risk assessment information system. RAIS. Available at: 〈http://rais.ornl.gov/〉 http://rais.ornl.gov/〉. Last accessed:1004.2014;
USGS, 1995–2013. Mineral commodity summaries
Wang M, Webber M, Finlayson B et al (2008) Rural industries and water pollution in China.[J]. J Environ Manag 86(4):648–659
Wang H, Fang F, Xie H (2010) Research situation and outlook on heavy metal pollution in water environment of China[J]. Guangdong Trace Elem Sci (in Chinese) 17(1):14–18
Wan Q, Li F, Zhu H et al (2011) Distribution characteristics, pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of East Dongting Lake. [J]. Env Sci Res (in Chinese) 24(12):1378–1384
Wan Xiantao. (1989). Assessment of Water Environmental Quality and Water Quality in Dongting Lake Water System.[J]. Water Resources Protection(in Chinese), (2):71–78
Wu Lei, Liu Guijian, Zhou Chuncai et al (2018) Temporal-spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Dissolved Heavy Metals in Chaohu Lake[J]. Environ Sci (in Chinese) 2:738–747
Xu Simin, Wang Jianhui, Liu Yongle, et al. Review on current situation of harmful residual of freshwater fish in Dongting Lake region.[J]. Food & Machinery, 2016(5):220–224
Yao Z, Bao Z, Gao P (2006) Environmental assessments of trace metals in sediments from Dongting Lake, Central China[J]. J China Univ Geosci 17(4):310–319
Yao Z (2008) Comparison between BCR sequential extraction and geo-accumulation method to evaluate metal mobility in sediments of Dongting Lake, Central China[J]. Chin J Oceanol Limnol(in Chinese) 26(1):14
Yang M, Fu X, Li Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution status in Xiangjiang river and its effect on food chain.[J]. Food & Machinery, 2014(5):103–106
Yi Y, Tang C, Yi T et al (2017) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in fish and accumulation patterns in food web in the upper Yangtze River, China.[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:295–302
Yu Y. Characteristics of heavy metals pollution of fish from three gorges reservoir during the initial impoundment.[D]. China Institute of Water Resources & Hydropower Research (IWHR), 2013
Zhang G (2015a) Pollution characteristics, sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongting Lake.[J]. Environ Monitoring in China (in Chinese) 31(6):58–63
Zhang G, Tian Q, Guo J. Heavy metal ecological risk of surface sediments in Dongting Lake and its tread.[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology ( in Chinese),2015a, 10( 3) : 184–191
Zhang G (2015b) Characterization and ecological risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of Dongting Lake[J]. J Hydroecol(in Chinese) 36(2):25–31
Zhang G, Tian Q, Guo J (2015b) Study on the ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments and their changing trends [J]. Chin J Ecotoxicol(in Chinese) 10(3):184–191
Zhang G. Health risk assessment of the water environment of Dongting Lake [J]. Wetland Sci Manag (in Chinese), 2013(4):26–29
Zhang Y, Tian Y, Shen M et al (2018a) Heavy metals in soils and sediments from Dongting Lake in China: occurrence, sources, and spatial distribution by multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 145:1–10
Zhang C, Shan B, Zhao Y et al (2018b) Spatial distribution, fractionation, toxicity and risk assessment of surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake in northern China[J]. Ecol Indic 90:633–642
Zhang D, Luo L, Zhang L et al (2014) Speciation and potential ecological risk assessment of As and heavy metals in surface sediments of Poyang Lake[J]. Res Environ The Yangtze Basin 23(8):1132–1138
Zhong X, Zhou S, Zhu Q et al (2011) Fraction distribution and bioavailability of soil heavy metals in the Yangtze River Delta--a case study of Kunshan City in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. J Hazard Mater 198(2):13–21
Zhong W, Zhang Y, Wu Z et al (2018) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in freshwater fish in the central and eastern North China.[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:343–349
Zhu Y, Jiang J, Huang Q et al (2007) Levels and ecological evaluation of heavy metals in organisms in Datong Lake and Dongting Lake area [J]. Lake University(in Chinese) 19(6):690–697
Zhu C et al (2017) The heavy metal pollution situation and control in Hongze Lake. J Nanjing Forestry University
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2015FY110900) and the National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant of CRAES (Grant No. 2012-YSKY-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, B., Liu, X., Guo, X. et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 34076–34090 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3329-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3329-8