Abstract
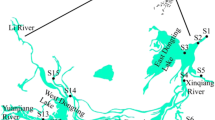
In this study, the concentrations of seven heavy metals (As, Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in the water, sediments, and nine tissues of eight fish species in Chaohu Lake were detected. And the ecological risk of sediments and food safety caused by heavy metals were evaluated. The mean concentrations of metals (As: 8.21, Cd: 0.58, Cu: 2.56, Cr: 0.50, Ni: 26.47, Pb: 3.51, Zn: 23.05 μg/L) in the water were found lower than the threshold values for the first-grade water quality (China environmental quality standards for surface water). The mean concentrations of Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the sediments were 41.79, 19.31, 7.61, 7.09, and 102.85 μg/g, respectively, while the concentration of As and Cd was recorded below the detection limit. The ecological risk assessment demonstrated that metals in the sediments posed low ecological risk. The bioaccumulation of metals in fish tissues showed relatively high concentrations in liver, brain, kidney, and intestines while low levels of metals were detected in muscle. A fascinating phenomenon was firstly noticed that all metals highly existed in fish brain and exhibited an especially significant positive correlation with the metal concentrations in sediment, indicating a health risk for Chinese due to their consumption favor of fish head.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim GMS, Parker RJ (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136:227–238
Adams SM (2002) Biological indicators of aquatic ecosystem stress. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda
Ahmed MK, Baki MA, Islam MS, Kundu GK, Habibullah Al Mamun M, Sarkar SK, Hossain MM (2015) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in tropical fish and shellfish collected from the river Buriganga, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:15880–15890
Bhuyan MS, Bakar MA (2017) Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water and sediments in the Halda River, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:27587–27600
Bhuyan MS, Bakar MA, Akhtar A, Islam MS (2016) Heavy metals status in some commercially important fishes of Meghna River adjacent to Narsingdi district, Bangladesh: health risk assessment. Am J Life Sci 4:60–70
Bhuyan MS, Bakar MA, Akhtar A, Hossain MB, Ali MM, Islam MS (2017) Heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediment of the Meghna River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 8:273–279
Braune B, Muir D, DeMarch B, Gamberg M, Poole K, Currie R, Dodd M, Duschenko W, Eamer J, Elkin B, Evans M, Grundy S, Hebert C, Johnstone R, Kidd K, Koenig B, Lockhart L, Marshall H, Reimer K, Sanderson J, Shutt L (1999) Spatial and temporal trends of contaminants in Canadian Arctic freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems: a review. Sci Total Environ 230:145–207
Chen TB, Zheng YM, Lei M, Huang ZC, Wu HT, Chen H, Fan KK, Yu K, Wu X, Tian QZ (2005) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60:542–551
CSEPA (China State Environmental Protection Administration) and CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Center) (1990) China soil element background value. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 330–378 (in Chinese)
Cui B, Zhang Q, Zhang K, Liu X, Zhang H (2011) Analyzing trophic transfer of heavy metals for food webs in the newly-formed wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ Pollut 159:1297–1306
Dhanakumar S, Solaraj G, Mohanraj R (2015) Heavy metal partitioning in sediments and bioaccumulation in commercial fish species of three major reservoirs of river Cauvery delta region, India. Ecotox Environ Safe 113:145–151
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi Khansari M, Jafarzadeh N (2004) Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the Karoon waterway river. Iran Toxicol Lett 151:63–68
Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2016) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ Pollut 219:1077–1091
Environmental quality standard for surface water (GB3838-2002) (2002) China Environmental Science Press. Beijing, China (in Chinese)
European Food Safety Authority (2010) European food safety authority panel on contaminants in the food China (CONTAM). Scientific opinion on lead in food. EFSA J 8:1570
Fang T, Lu W, Li J, Zhao X, Yang K (2017) Levels and risk assessment of metals in sediment and fish from Chaohu Lake, Anhui Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:15390–15400
FAO (2005) Statistical databases. http://faostat.fao.org
Farkas A, Salanki J, Specziar A (2003) Age- and size-specific patterns of heavy metals in the organs of freshwater fish Abramis brama L. populating a low-contaminated site. Water Res 37:959–964
Fukushima T (1999) Metals in aquatic ecosystems: mechanisms of uptake, accumulation and release-Ecotoxicological perspectives. Int J Environ Stud 56:385–417
Fuller CC, Davis JA, Cain DJ, Lamothe PJ, Fries TL, Fernandez G, Vargas JA, Murillo MM (1990) Distribution and transport of sediment-bound metal contaminants in the rio grande de tarcoles, costa rica (Central America). Water Res 24:805–812
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hallenbeck WH, Breen SP, Brenniman GR (1993) Cancer risk assessment for the inhalation of metals from municipal solid waste incinerators impacting Chicago. B Environ Contam Tox 51:165–170
He W, Bai ZL, Liu WX, Kong XZ, Yang B, Yang C, Jorgensen SE, Xu FL (2016) Occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in surface sediments from a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Chaohu Lake). Environ Sci Pollut R 23:10335–10348
Hong H, Zhou Y, Wu H, Luo Y, Shen H (2014) Lipid content and fatty acid profile of muscle, brain and eyes of seven freshwater fish: a comparative study. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91:795–804
Huo S, Xi B, Yu X, Su J, Zan F, Zhao G (2013) Application of equilibrium partitioning approach to derive sediment quality criteria for heavy metals in a shallow eutrophic lake, Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 69:2275–2285
Islam GMR, Khan FE, Hoque MM, Jolly YN (2014) Consumption of unsafe food in the adjacent area of Hazaribag tannery campus and Buriganga River embankments of Bangladesh: heavy metal contamination. Environ Monit Assess 186:7233–7244
Jiang Y, Yang Y, Wu Y, Tao J, Cheng B (2017) Microcystin bioaccumulation in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Chaohu Lake, China. B Environ Contam Tox 99:69–74
Karri V, Schuhmacher M, Kumar V (2016) Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: a general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain. Environ Toxicol Phar 48:203–213
Kera NH, Bhaumik M, Pillay K, Ray SS, Maity A (2017) Selective removal of toxic Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption combined with reduction at a magnetic nanocomposite surface. J Colloid Interf Sci 503:214–228
Kong M, Dong Z, Chao J, Zhang Y, Yin H (2015) Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake. China Environ Sci 35:1223–1229
Leblanc GA (1995) Trophic-level differences in the bioconcentration of chemicals: implications in assessing environmental biomagnification. Environ Sci Technol 29:154–160
Li F, Fan Z, Xiao P, Oh K, Ma X, Hou W (2009) Contamination, chemical speciation and vertical distribution of heavy metals in soils of an old and large industrial zone in Northeast China. Environ Geol 57:1815–1823
Li G, Liu G, Zhou C, Chou CL, Zheng L, Wang J (2012) Spatial distribution and multiple sources of heavy metals in the water of Chaohu Lake, Anhui, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:2763–2773
Li G, Liu G, Zhou C, Kang Y, Yuan W, Xie F (2013) Mobility, binding behavior and potential risks of trace metals in the sediments of the fifth largest freshwater lake, China. Water Sci Technol 67:2503–2510
Liang P, Wu SC, Zhang J, Cao Y, Yu S, Wong MH (2016) The effects of mariculture on heavy metal distribution in sediments and cultured fish around the Pearl River Delta region, south China. Chemosphere 148:171–177
Ling MP, Wu CC, Yang KR, Hsu HT (2013) Differential accumulation of trace elements in ventral and dorsal muscle tissues in tilapia and milkfish with different feeding habits from the same cultured fishery pond. Ecotox Environ Safe 89:222–230
Manoj K, Padhy PK (2014) Distribution, enrichment and ecological risk assessment of six elements in bed sediments of a Tropical River, Chottanagpur Plateau: a spatial and temporal appraisal. J Environ Prot 5:1419–1434
Morgano MA, Rabonato LC, Milani RE, Miyagusku L, Balian SC (2011) Assessment of trace elements in fishes of Japanese foods marketed in Sao Paulo (Brazil). Food Control 22:778–785
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. J Geol 2:108–118
Nemerow NL (1991) Stream, lake, estuary, and ocean pollution. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Qian Y, Chen C, Zhang Q, Li Y, Chen Z, Li M (2010) Concentrations of cadmium, lead, mercury and arsenic in Chinese market milled rice and associated population health risk. Food Control 21:1757–1763
Qin D, Jiang H, Bai S, Tang S, Mou Z (2015) Determination of 28 trace elements in three farmed cyprinid fish species from Northeast China. Food Control 50:1–8
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Shah MH (2015) Geochemical speciation, anthropogenic contamination, risk assessment and source identification of selected metals in freshwater sediments—a case study from Mangla Lake, Pakistan. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 4:27–36
Shinn C, Dauba F, Grenouillet G, Guenard G, Lek S (2009) Temporal variation of heavy metal contamination in fish of the river lot in southern France. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:1957–1965
Socha K, Karpinska E, Kochanowicz J, Soroczynska J, Jakoniuk M, Wilkiel M, Mariak ZD, Borawska MH (2017) Dietary habits; concentration of copper, zinc, and Cu-to-Zn ratio in serum and ability status of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Nutrition 39–40:76–81
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu R (2010) Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174:455–462
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in assessment of heavy metals in estuaries and the formation of pollution index. Helgoland Mar Res 33:566–575
USEPA (1999) United States Environmental Protection Agency: screening level ecological risk assessment protocol for hazardous waste combustion facilities. Appendix E Toxicity Ref Values 3
USEPA (2017) United States Environmental Protection Agency: regional screening levels (RSLs)-genetic tables (June 2017). http://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables-june-2017
Van AE, Blust R, Bervoets L (2017) Metals in the Scheldt estuary: from environmental concentrations to bioaccumulation. Environ Pollut 228:82–91
Wan L, Xu L, Fu Y (2016) Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals in lake bed sediment of a large lake scenic area in China. Inter J Env Res Pub Heal 13:741
Wang JZ, Peng SC, Chen TH, Zhang L (2016) Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:307–314
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization. http://www.doc88.com/p-333730829736.html
Xu Z, Ji J, Shi C (2011) Water geochemistry of the Chaohu Lake Basin rivers, China: chemical weathering and anthropogenic inputs. Appl Geochem 26:S379–S383
Xu FL, Yang C, He W, He QS, Li YL, Kang L, Liu WX, Xiong YQ, Xing B (2017) Bias and association of sediment organic matter source apportionment indicators: a case study in a eutrophic Chaohu Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 581:874–884
Yang Y, Zhou ZC, Bai YY, Cai YM, Chen WP (2016) Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Fenghe River by the fuzzy synthetic evaluation model and multivariate statistical methods. Pedosphere 26:326–334
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Yin H, Deng J, Shao S, Gao F, Gao J, Fan C (2011) Distribution characteristics and toxicity assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 179:431–442
Zan F, Huo S, Xi B, Su J, Li X, Zhang J, Yeager KM (2011) A 100 year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in a shallow eutrophic lake, Chaohu Lake, China. J Environ Monit 13:2788–2797
Zhang L, Liao Q, Shao S, Zhang N, Shen Q, Liu C (2015) Heavy metal pollution, fractionation, and potential ecological risks in sediments from Chaohu Lake (Eastern China) and the surrounding rivers. Inter J Env Res Pub Heal 12:14115–14131
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zhang X, Zheng D, Zhang Z, Zhang S (2007) Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China. Sci Total Environ 387:96–104
Zohra BS, Habib A (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels and toxicity in sediments and fishes from the Mediterranean Sea (southern coast of Sfax, Tunisia). Environ Sci Pollut R 23:13954–13963
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (Grant No. 201503108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Liu, Q., Wang, L. et al. The distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and fish of Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 77, 97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7276-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7276-y