Abstract
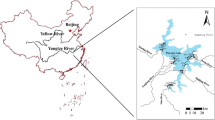
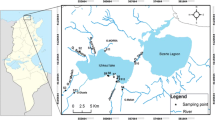
The pollution levels of lakes vary in quantity and type of contaminants accumulated in their sediment and water. The second Chinese capital city will be built around Baiyangdian Lake in the near future, and thus, it is important to monitor pollution status of Baiyangdian Lake. This study mainly focused on the accumulated heavy metal concentrations in the surface sediment and in variety of fish bodies. Sediment pollution status and ecological risk were evaluated through geo-accumulation (I-geo), contamination factor (CF), pollution load index (PLI), potential ecological risk (\( {E}_r^i \)), and mean probable effect concentration quotient (mPEC-Q). In addition, human health risks via fish consumption were also evaluated. Based on the results, the average sediment trace As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn concentrations were 9.53, 0.35, 56.37, 32.33, 617.05, 30.18, 19.17, and 84.24 mg/kg dry wt, respectively. Both I-geo and \( {E}_r^i \) inferred low pollution levels and low ecological risks from all assessed trace metals except Cd. Cd posed moderate to high ecological risks. Based on sediment quality guidelines (SQGs), average Ni and Cr concentrations exceeded the threshold effect concentrations (TEC), but their \( {E}_r^i \) are low as their average concentrations is below Hebei province pre-contaminations (30.8 mg/kg for Ni and 68.3 mg/kg for Cr). There is no cumulative toxicity from all the metals through mPEC-Q. Omnivorous fish accumulated statistically insignificantly higher amounts of metals than carnivorous fish, except for Hg. The intake of 12.22 g/person/day fish muscle for the entire life is safe from noncarcinogenic human health problems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, J., Cui, B., Chen, B., Zhang, K., Deng, W., Gao, H., & Xiao, R. (2011). Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecological Modelling, 222(2), 301–306.
Briggs, P. (2002) The determination of forty elements in geological and botanical samples by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry in analytical methods for chemical analysis of geologic and other materials. US Geological Survey.
Burger, J., Gaines, K. F., Boring, C. S., Stephens, W. L., Snodgrass, J., Dixon, C., McMahon, M., Shukla, S., Shukla, T., & Gochfeld, M. (2002). Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: Potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environmental Research, 89(1), 85–97.
Cao, Y., Wang, W., & Zhang, Y. (2003). Present situation of fish stocks in Baiyangdian Lake. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 38(3), 65–69.
Chakravarty, M., & Patgiri, A. D. (2009). Metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Dikrong River, NE India. Journal of Human Ecology, 27(1), 63–67.
Chen, C. Y., Pickhardt, P. C., Xu, M. Q., & Folt, C. L. (2008). Mercury and arsenic bioaccumulation and eutrophication in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 190(1–4), 115–127.
Chen, S., Fath, B. D., & Chen, B. (2011). Information-based network environ analysis: a system perspective for ecological risk assessment. Ecological Indicators, 11(6), 1664–1672.
Lu C.X., & Cheng J.M. (2011). Speciation of heavy metals in the sediments from different eutrophic lakes of China. Procedia Engineering, 18, 318-323.
Chi, Q. Q., Zhu, G. W., & Langdon, A. (2007). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fishes from Taihu Lake, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(12), 1500–1504.
Dai, G. H., Liu, X. H., Liang, G., Xu, M. Z., Han, X., & Shi, L. (2011). Health risk assessment of organochlorine contaminants in fish from a major Lake (Baiyangdian lake) in North China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87(1), 58–64.
Dai, L., Wang, L., Li, L., Liang, T., Zhang, Y., Ma, C., & Xing, B. (2017). Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 1433–1444.
Doyle, J., Solberg, T., Tiefenthaler, J., O’Brien, G., Behnke, H., Poulson, H., Ela, J., & Willett, S. (2003). Consensus-based sediment quality guidelines; recommendations for use and application interim guidance. WT: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources.
Fidan, A. F., Ciğerci, İ. H., Konuk, M., Küçükkurt, İ., Aslan, R., & Dündar, Y. (2008). Determination of some heavy metal levels and oxidative status in Carassius carassius L., 1758 from Eber Lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 147(1–3), 35–41.
Forstner, U., & Muller, G. (1981). Concentrations of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river sediments: geochemical background, man's influence and environmental impact. GeoJournal, 5(5), 417.
Gao, F., Guo, W., Wang, J., & Zhao, X. (2015). Historical record of trace elements input and risk in the shallow freshwater lake, North China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 155, 26–32.
Gao, H., Bai, J., Xiao, R., Liu, P., Jiang, W., & Wang, J. (2012). Levels, sources and risk assessment of trace elements in wetland soils of a typical shallow freshwater lake, China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 27(1), 275–284.
Gäbler, H. E. (1997). Mobility of heavy metals as a function of pH of samples from an overbank sediment profile contaminated by mining activities. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 58(2–3), 185–194.
Gu, Y. G., Lin, Q., Wang, X. H., Du, F. Y., Yu, Z. L., & Huang, H. H. (2015a). Heavy metal concentrations in wild fishes captured from the South China Sea and associated health risks. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96(1–2), 508–512.
Gu, Y. G., Lin, Q., Yu, Z. L., Wang, X. N., Ke, C. L., & Ning, J. J. (2015b). Speciation and risk of heavy metals in sediments and human health implications of heavy metals in edible nekton in Beibu Gulf, China: A case study of Qinzhou Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(2), 852–859.
Guo, W., Pei, Y., Yang, Z., & Chen, H. (2011). Historical changes in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) input in Lake Baiyangdian related to regional socio-economic development. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 187(1–3), 441–449.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Hao, Y., Chen, L., Zhang, X., Zhang, D., Zhang, X., Yu, Y., & Fu, J. (2013). Trace elements in fish from Taihu Lake, China: Levels, associated risks, and trophic transfer. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 90, 89–97.
Harikumar, P. S., Nasir, U. P., & Rahman, M. M. (2009). Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 6(2), 225–232.
Hu, G., Luo, X., Li, F., Dai, J., Guo, J., Chen, S., et al. (2010). Organochlorine compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediment from Baiyangdian Lake, North China: Concentrations, sources profiles and potential risk. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(2), 176–183.
Iwegbue, C. M. (2015). Metal concentrations in selected brands of canned fish in Nigeria: Estimation of dietary intakes and target hazard quotients. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 85.
Jia, Y., Wang, L., Qu, Z., Wang, C., & Yang, Z. (2017). Effects on heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fishes: Species, tissues, and sizes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(10), 9379–9386.
Ji, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Huang, C., & Pei, Y. (2019). Fraction spatial distributions and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 174, 417–428.
Ju, Y. R., Chen, C. W., Chen, C. F., Chuang, X. Y., & Dong, C. D. (2017). Assessment of heavy metals in aquaculture fishes collected from southwest coast of Taiwan and human consumption risk. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 124, 314–325.
Kankılıç, G. B., Tüzün, İ., & Kadıoğlu, Y. K. (2013). Assessment of heavy metal levels in sediment samples of Kapulukaya dam Lake (Kirikkale) and lower catchment area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(8), 6739–6750.
Kaya, G., & Turkoglu, S. (2017). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in various tissues of some fish species and green tiger shrimp (Penaeus semisulcatus) from İskenderun bay, Turkey, and risk assessment for human health. Biological Trace Element Research, 180(2), 314–326.
Kumar, B., Virendra Kumar, V., Ashish Kumar, N., Paromita, C., & Rita, S. (2013). Human health hazard due to metal uptake via fish consumption from coastal and fresh water waters in eastern India along the bay of Bengal. Jouranl of Marine Biology Oceanography, 2(3), 2.
Li, F. J., Cui, B. S., Lan, Y., Lin, W. T., Liu, Y., & Tong, Y. L. (2013, January). Heavy metal pollution in different types of land use in Baiyangdian Lake. In 2013 Third International Conference on Intelligent System Design and Engineering Applications (pp. 811-815). IEEE.
Li, W., Shi, Y., Gao, L., Liu, J., & Cai, Y. (2012). Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere, 89(11), 1307–1315.
Lin, Q., Liu, E., Zhang, E., Li, K., & Shen, J. (2016). Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in Southwest China. Catena, 145, 193–203.
Linnik, P. M., & Zubenko, I. B. (2000). Role of bottom sediments in the secondary pollution of aquatic environments by heavy-metal compounds. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 5(1), 11–21.
Liu, Y., Liu, G., Yuan, Z., Liu, H., & Lam, P. K. (2018). Heavy metals (as, hg and V) and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in fish from Yellow River estuary, China. Science of the Total Environment, 613, 462–471.
Lü, C., He, J., Fan, Q., & Xue, H. (2011). Accumulation of heavy metals in wild commercial fish from the Baotou urban section of the Yellow River, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(4), 679–696.
Maanan, M., Saddik, M., Maanan, M., Chaibi, M., Assobhei, O., & Zourarah, B. (2015). Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecological Indicators, 48, 616–626.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31.
Malik, N., Biswas, A. K., Qureshi, T. A., Borana, K., & Virha, R. (2010). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish tissues of a freshwater lake of Bhopal. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1–4), 267–276.
Mamat, Z., Haximu, S., & yong Zhang, Z., & Aji, R. (2016). An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, Northwest China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(8), 7255–7265.
Miri, M., Akbari, E., Amrane, A., Jafari, S. J., Eslami, H., Hoseinzadeh, E., Zarrabi, M., Salimi, J., Sayyad-Arbabi, M., & Taghavi, M. (2017). Health risk assessment of heavy metal intake due to fish consumption in the Sistan region, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(11), 583.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, 2, 108-118.
NYDEC. (2014).(New York State Department of Environmental Conservation), Screening and Assessment of Contaminated Sediment, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Fish, Wildlife and Marine Resources Bureau of Habitat.
Ra, K., Bang, J. H., Lee, J. M., Kim, K. T., & Kim, E. S. (2011). The extent and historical trend of metal pollution recorded in core sediments from the artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(8), 1814–1821.
Siraj, M., Shaheen, M., Sthanadar, A. A., Khan, A., Chivers, D. P., & Yousafzai, A. M. (2014). A comparative study of bioaccumulation of heavy metals in two fresh water species, Aorichthys seenghala and Ompok bimaculatous at river Kabul, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences, 4(3), 40–54.
Su, L., Liu, J., & Christensen, P. (2011). Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of metals in sediments of Baiyangdian wetland ecosystem. Ecotoxicology, 20(5), 1107–1116.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1), 566.
USEPA. (1986). Environmental protection agency. Guidelines for the health risk assessment of chemical mixtures. Federal Register, 51, 34014–34025.
USEPA. (2008). A review of the reference dose and reference concentration processes. Washington, DC: Risk Assessment Forum U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Velusamy, A., Kumar, P. S., Ram, A., & Chinnadurai, S. (2014). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in commercially important marine fishes from Mumbai Harbor, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 81(1), 218–224.
Wang, L., Cui, X., Cheng, H., Chen, F., Wang, J., Zhao, X., Lin, C., & Pu, X. (2015a). A review of soil cadmium contamination in China including a health risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(21), 16441–16452.
Wang, Q., & Chen, X. J. (2015). Biological characteristics and propagative Technologies of Rhodeus Sinensis. Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology, 7(9), 668–675.
Wang, Y., Yang, L., Kong, L., Liu, E., Wang, L., & Zhu, J. (2015b). Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena, 125, 200–205.
Wenning, R. J. (Ed.). (2005). Use of sediment quality guidelines and related tools for the assessment of contaminated sediments. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC).
Xu, F., Yang, Z. F., Chen, B., & Zhao, Y. W. (2013). Impact of submerged plants on ecosystem health of the plant-dominated Baiyangdian Lake, China. Ecological Modelling, 252, 167–175.
Xu, Y., Wu, Y., Han, J., & Li, P. (2017). The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: Pollution and ecological risk assessment. Ecology and Evolution, 7(14), 5454–5466.
Yang, J., Chen, L., Liu, L. Z., Shi, W. L., & Meng, X. Z. (2014). Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 102, 129–135.
Yang, Y., Chen, H., & Yang, Z. (2010). Assessing changes of trophic interactions during once anthropogenic water supplement in Baiyangdian Lake. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 1169–1179.
Yang, Z., Li, B., Li, G., & Wang, W. (2007). Nutrient elements and heavy metals in the sediment of Baiyangdian and Taihu Lakes: a comparative analysis of pollution trends. Frontiers of Agriculture in China, 1(2), 203–209.
Yang, Z., Li, G. B., Wang, D. W., Gui, H. M., & Shang, T. Z. (2005). Pollution and the potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment of Baiyangdian Lake. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 24(5), 945–951.
Yi, Y., Tang, C., Yi, T., Yang, Z., & Zhang, S. (2017). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in fish and accumulation patterns in food web in the upper Yangtze River, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 145, 295–302.
Yi, Y., Yang, Z., & Zhang, S. (2011). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environmental Pollution, 159, 2575–2585.
Yi, Y. J., Sun, J., Tang, C. H., & Zhang, S. H. (2016). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment in the upper reach of the Yangtze River. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(11), 11002–11013.
Yi, Y. J., & Zhang, S. H. (2012). The relationships between fish heavy metal concentrations and fish size in the upper and middle reach of Yangtze River. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 1699–1707.
Zeng, J., Yang, L., Wang, X., Wang, W. X., & Wu, Q. L. (2012). Metal accumulation in fish from different zones of a large, shallow freshwater lake. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 86, 116–124.
Zhang, C., Shan, B., Zhao, Y., Song, Z., & Tang, W. (2018). Spatial distribution, fractionation, toxicity and risk assessment of surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake in northern China. Ecological Indicators, 90, 633–642.
Zhang, L., & Liu, J. (2014). In situ relationships between spatial–temporal variations in potential ecological risk indexes for metals and the short-term effects on periphyton in a macrophyte-dominated lake: A comparison of structural and functional metrics. Ecotoxicology, 23(4), 553–566.
Zhao, S., Feng, C., Quan, W., Chen, X., Niu, J., & Shen, Z. (2012a). Role of living environments in the accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in fishes and crabs in the Yangtze River estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(6), 1163–1171.
Zhao, Y., Xia, X. H., Yang, Z. F., & Wang, F. (2012b). Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 1213–1226.
Zheng, N. A., Wang, Q., Liang, Z., & Zheng, D. (2008). Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environmental Pollution, 154(1), 135–142.
Zhong, W., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., Yang, R., Chen, X., Yang, J., & Zhu, L. (2018). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in freshwater fish in the central and eastern North China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 157, 343–349.
Zhou, Q., Xie, P., Xu, J., Liang, X., Qin, J., Cao, T., & Chen, F. (2011). Seasonal trophic shift of littoral consumers in eutrophic Lake Taihu (China) revealed by a two-source mixing model. The Scientific World Journal, 11, 1442–1454.
Zhu, F., Qu, L., Fan, W., Wang, A., Hao, H., Li, X., & Yao, S. (2015). Study on heavy metal levels and its health risk assessment in some edible fishes from Nansi Lake, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(4), 161.
Zhu, H., Xu, Y., Yan, B., Guan, J., Zhou, Q., & Liang, Y. (2016). Risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediment and aquatic animals in downstream waters affected by historical gold extraction in Northeast China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 22(3), 693–705.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51722901), the National Key Research & Development Program of China (2018YFC0407403), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (JQ19034), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zerizghi, T., Yang, Y., Wang, W. et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal concentrations in sediment and fish of a shallow lake: a case study of Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Environ Monit Assess 192, 154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8078-8