Abstract
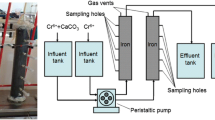
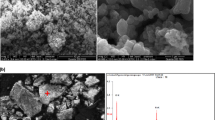
Zero-valent iron (Fe0) has been widely used for Cr(VI) removal; however, the removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution under complex hydrogeochemical conditions were poorly understood. In this research, the mixed materials containing cast iron and activated carbon were packed in columns for the treatment of aqueous Cr(VI)-Cr(III) in groundwater with high concentration of Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3 −, NO3 −, and SO4 2−. We investigate the influences of those ions on Cr(VI) removal, especially emphasizing on the reaction mechanisms and associated precipitations which may lead to porosity loss by using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. The results show that the precipitations accumulated on the material surface were (Fe/Cr) (oxy)hydroxide, mixed Fe(III)-Cr(III) (oxy)hydroxides, Fe2O3, CaCO3, and MgCO3. During these reactions, the Cr(VI) was reduced to Cr(III) coupled with the oxidated Fe0 to Fe(II) through the galvanic corrosion formed by the Fe0-C and/or the direct electron transfer between Fe0 and Cr(VI). In addition, Cr(VI) could be reduced by aqueous Fe(II), which dominated the whole removal efficiency. The primary aqueous Cr(III) was completely removed together with Cr(III) reduced from Cr(VI) even when Cr(VI) was detected in the effluent, which meant that the aqueous Cr(III) could occupy the adsorption sites. In general, the combined system was useful for the Cr(VI)-Cr(III) treatment based on galvanic corrosion, and the hardness ions had a negative effect on Cr(VI) removal by forming the carbonates which might promote the passivation of materials and decrease the removal capacity of the system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner RA (1975) The role of magnesium in the crystal growth of calcite and aragonite from sea water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:489–504
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL (1997) In-situ remediation of chromate contaminated groundwater using permeable reactive walls: laboratory studies. Environ Sci Technol 31:3348–3357
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Benner SG et al (2000) Treatment of inorganic contaminants using permeable reactive barriers. J Contam Hydrol 45(1–2):123–137
Chen SS, Hsu BC, Hung LW et al (2008) Chromate reduction by waste iron from electroplating wastewater using plug flow reactor. J Hazard Mater 152:1092–1097
Dinda D, Gupta A, Saha S (2013) Removal of toxic Cr(VI) by UV-active functionalized graphene oxide for water purification. J Mater Chem 1:11221–11228
Doyle CS, Kendelewicz T, Bostick BC et al (2004) Soft X-ray spectroscopic studies of the reaction of fractured pyrite surfaces with Cr(VI)-containing aqueous solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(21):4287–4299
Eary LE, Rai D (1988) Chromate removal from aqueous wastes by reduction with ferrous ion. Environ Sci Technol 22:972–977
EI-Shazly AH, Mubarak AA, Konsowa AH (2005) Hexavalent chromium reduction using a fixed bed of scrap bearing iron spheres. Desalination 185:307–316
Fendorf S, Wielinga B, Hansel C (2001) Chromium transformations in natural environments: the role of biological and abiological processes in chromium(VI) reduction. Int Geol Rev 42:691–701
Fiúza A, Silva A, Carvalho G et al (2010) Heterogeneous kinetics of the reduction of chromium (VI) by elemental iron. J Hazard Mater 175:1042–1047
Flury B, Eggenberger U, Mäder U et al (2009) First results of operating and monitoring an innovative design of a permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of chromate contaminated groundwater. J Appl Geochem 24:687–696
Fu FL, Han WJ, Huang CJ et al (2013) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by supported nanoscale zero-valent iron on granular activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 51:13–15
Gallios GP, Vaclavikova M (2008) Removal of chromium(VI) from water streams: a thermodynamic study. Environ Chem Lett 6:235–240
Geng B, Jin Z, Li T et al (2009) Preparation of chitosan-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Sci Total Environ 407:4994–5000
Gheju M (2011) Hexavalent chromium reduction with zero-valent iron (ZVI) in aquatic systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 222:103–148
Gheju M, Balcu I (2010) Hexavalent chromium reduction with scrap iron in continuous-flow system. Part 2: effect of scrap iron shape and size. J Hazard Mater 182:484–493
Gu B, Phelps TJ, Liang L et al (1999) Biogeochemical dynamics in zero-valent iron columns: implications for permeable reactive barriers. Environ Sci Technol 33:2170–2177
Henderson AD, Demond AH (2011) Impact of solids formation and gas production on the permeability of ZVI PRBs. J Environ Eng 137:689–696
Jamieson-Hanes JH, Lentz AM, Amos RT et al (2014) Examination of Cr(VI) treatment by zero-valent iron using in situ, real-time X-ray absorption spectroscopy and Cr isotope measurements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 142:299–313
Kakavandi B, Kalantary RR, Farzadkia M et al (2014) Enhanced chromium (VI) removal using activated carbon modified by zero valent iron and silver bimetallic nanoparticles. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:115–124
Kantar C, Ari C, Keskin S et al (2015) Cr(VI) removal from aqueous systems using pyrite as the reducing agent: batch, spectroscopic and column experiments. J Contam Hydrol 174C:28–38
Kotaś J, Stasicka Z (2000) Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ Pollut 107:263–283
Lai KC, Lo IM (2008) Removal of chromium (VI) by acid-washed zero-valent iron under various groundwater geochemistry conditions. Environ Sci Technol 42:1238–1244
Lee JW, Cha DK, Oh YK et al (2010) Wastewater screening method for evaluating applicability of zero-valent iron to industrial wastewater. J Hazard Mater 180:354–360
Legrand L, Figuigui AE, Florence Mercier A et al (2004) Reduction of aqueous chromate by Fe(II)/Fe(III) carbonate green rust: kinetic and mechanistic studies. Environ Sci Technol 38:4587–4595
Li H, Pereira TR, Teppen BJ et al (2007) Ionic strength-induced formation of smectite quasicrystals enhances nitroaromatic compound sorption. Environ Sci Technol 41:1251–1256
Li X, Cao J, Zhang W et al (2008) Stoichiometry of Cr(VI) immobilization using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI): a study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). Ind Eng Chem Res 47:2131–2139
Li S, Yan W, Zhang WX (2009) Solvent-free production of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with precision milling. Green Chem 11:1618–1626
Li Y, Zhu S, Liu Q et al (2013) N-doped porous carbon with magnetic particles formed in situ for enhanced Cr(VI) removal. Water Res 47(12):4188–4197
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF et al (2015) Building a new and sustainable “silk road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270
Li X, Ai L, Jiang J (2016) Nanoscale zerovalent iron decorated on graphene nanosheets for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution: surface corrosion retard induced the enhanced performance. Chem Eng J 288:789–797
Liu T, Lo IM (2011) Influences of humic acid on Cr(VI) removal by zero-valent iron from groundwater with various constituents: implication for long-term PRB performance. Water Air Soil Pollut 261:473–483
Liu BP, Terano M (2001) Investigation of the physico-chemical state and aggregation mechanism of surface Cr species on a Phillips CrOx/SiO2 catalysis by XPS and EPMA. J Mol Catal 172:227–240
Lo IM, Lam CS, Lai KC (2006) Hardness and carbonate effects on the reactivity of zero-valent iron for Cr(VI) removal. Water Res 40:595–605
Lu X, Li M, Tang C et al (2012) Electrochemical depassivation for recovering Fe0 reactivity by Cr(VI) removal with a permeable reactive barrier system. J Hazard Mater 213-214:355–360
Lv X, Xu JG, Xu X (2011) Removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles supported on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 85:1204–1209
Manning BA, Kiser JR, Kwon H et al (2007) Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(III)-and Cr(VI)-treated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 41:586–592
Meng FS, Wang YY (2013) Remediation of hexavalent chromium polluted ground water by PRB. Adv Mater Res 726-731:1724–1731
Meng FS, Wang YY, Bai LP (2015) Remediation of nitrate and chromium contaminated groundwater by zero-valent iron PRB. Front Environ Sci 2:39–45
MOHC (2006) Standards for drinking water quality (GB5749-2006). Ministry of Health of the P.R. China, Beijing
Myneni SCB, Tokunaga TK (1997) Abiotic selenium redox transformation in the presence of Fe(II,III) oxides. Science 278:1106–1109
Noubactep C (2007) Processes of contaminant removal in “Fe0-H2O” systems revisited: the importance of coprecipitaion. Open Environ Sci 1(1):9–13
Noubactep C (2010) Metallic iron for safe drinking water worldwide. Chem Eng J 165(2):740–749
Olowe AA, Génin JMR (1991) The mechanism of oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in sulfated aqueous media: importance of the initial ratio of the reactants. Corros Sci 32:965–984
Park DH, Yun YS, Lim SR et al (2006) Kinetic analysis and mathematical modeling of Cr(VI) removal in a differential reactor packed with Ecklonia biomass. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:1720–1727
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Mallouk TE (2000) Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 34:2564–2569
Qiu SR, Lai HF, Roberson MJ et al (2000) Removal of contaminants from aqueous solution by reaction with iron surfaces. Langmuir 16:2230–2236
Rao JM, Sivaprasad A, Rao PS et al (1999) A comparative study of bulk and supported chromia catalysis for the fluorination of trichloroethylene. J Catal 184:105–111
Reardon EJ (2005) Zerovalent irons: styles of corrosion and inorganic control on hydrogen pressure buildup. Environ Sci Technol 39:7311–7317
Roh Y, Lee SY, Elless MP (2000) Characterization of corrosion products in the permeable reactive barriers. Environ Geol 40:184–194
Scherer MM, Richter S, Valentine RL et al (2000) Chemistry and microbiology of reactive barriers for in situ groundwater cleanup. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30:363–411
Simon L, Génin JMR, Refait P (1997) Standard free enthalpy of formation of Fe(II)-Fe(III) hydroxysulphite green rust one and its oxidation into hydroxysulfate green rust two. Corros Sci 39:1673–1685
Tang L, Yang GD, Zeng GM et al (2014) Synergistic effect of iron doped ordered mesoporous carbon on adsorption-coupled reduction of hexavalent chromium and the relative mechanism study. Chem Eng J 239:114–122
Vaca MM, López CR, Gehr R et al (2001) Heavy metal removal with Mexican clinoptilolite multi-component ionic exchange. Water Res 35(2):373–378
Vega A, Fiuza A, Guimarães F (2010) Insight into the phenomenology of the Cr(VI) reduction by metallic iron using an electron probe microanalyzer. Langmuir 26:11980–11986
Wang Q, Qian H, Yang Y et al (2010) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Contam Hydrol 114:35–42
Wu P, Li S, Ju L et al (2012) Mechanism of the reduction of hexavalent chromium by organo-montmorillonite supported iron nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 219-220:283–288
Wu LM, Liao L, Lv G et al (2013) Micro-electrolysis of Cr(VI) in the nanoscale zero-valent iron loaded activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 254-255:277–283
Yim SD, Nam IS (2004) Characteristics of chromium oxides supported on TiO2 and Al2O3 for the decompositon of perchloroethylene. J Catal 221:601–611
Zhang YL, Li Y, Li J et al (2012) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by using the mixture of pillared bentonite and zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 185-186:243–249
Zhou H, He Y, Lan Y et al (2008) Influence of complex reagents on removal of chromium (VI) by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 72:870–887
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China University of Geosciences, Beijing (CUGB) (No. 53200859616), and China Geological Survey (CGS) (DD20160310). We thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions which have helped us to considerably improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Wang, G., Li, Z. et al. Investigation of the removal mechanism of Cr(VI) in groundwater using activated carbon and cast iron combined system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18341–18354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9453-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9453-z