Abstract
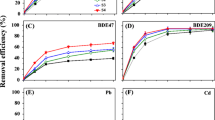
Laboratorial scale experiments were performed to evaluate the efficacy of a washing process using the combination of methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MCD) and tea saponin (TS) for simultaneous desorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants (HOCs) and heavy metals from an electronic waste (e-waste) site. Ultrasonically aided mixing of the field contaminated soil with a combination of MCD and TS solutions simultaneously mobilizes most of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and the analyte metal (Pb, Cu, and Ni) burdens. It is found that 15 g/L MCD and 10 g/L TS is an efficient reagent combination reconciling extraction performance and reagent costs. Under these conditions, the removal efficiencies of HOCs and heavy metals are 93.5 and 91.2 %, respectively, after 2 cycles of 60-min ultrasound-assisted washing cycles. By contrast, 86.3 % of HOCs and 88.4 % of metals are removed from the soil in the absence of ultrasound after 3 cycles of 120-min washing. The ultrasound-assisted soil washing could generate high removal efficiency and decrease the operating time significantly. Finally, the feasibility of regenerating and reusing the spent washing solution in extracting pollutants from the soil is also demonstrated. By application of this integrated technology, it is possible to recycle the washing solution for a purpose to reduce the consumption of surfactant solutions. Collectively, it has provided an effective and economic treatment of e-waste-polluted soil.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao M, Hu Y, Sun Q, Wang L, Chen J, Lu X (2013) Enhanced desorption of PCB and trace metal elements (Pb and Cu) from contaminated soils by saponin and EDDS mixed solution. Environ Pollut 174:93–99. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.015
Chigbo C, Batty L, Bartlett R (2013) Interactions of copper and pyrene on phytoremediation potential of Brassica juncea in copper–pyrene co-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 90:2542–2548. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.007
Flaherty RJ, Nshime B, DeLaMarre M, DeJong S, Scott P, Lantz AW (2013) Cyclodextrins as complexation and extraction agents for pesticides from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 91:912–920. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.005
Fonseca B, Pazos M, Figueiredo H, Tavares T, Sanromán MA (2011) Desorption kinetics of phenanthrene and lead from historically contaminated soil. Chem Eng J 167:84–90. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.004
Gusiatin ZM, Klimiuk E (2012) Metal (Cu, Cd and Zn) removal and stabilization during multiple soil washing by saponin. Chemosphere 86:383–391. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.10.027
Maity JP, Huang YM, Hsu CM, Wu CI, Chen CC, Li CY, Jean JS, Chang YF, Chen CY (2013) Removal of Cu, Pb and Zn by foam fractionation and a soil washing process from contaminated industrial soils using soapberry-derived saponin: a comparative effectiveness assessment. Chemosphere 92:1286–1293. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.060
Mao Y, Sun M, Yang X, Wei H, Song Y, Jiang X (2013) Remediation of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) contaminated soil by successive hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and peanut oil enhanced soil washing–nutrient addition: a laboratory evaluation. J Soil Sediment 13:403–412. doi:10.1007/s11368-012-0628-4
Mao X, Jiang R, Xiao W, Yu J (2015) Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: a review. J Hazard Mater 285:419–435. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.009
Rivero-Huguet M, Marshall WD (2011) Scaling up a treatment to simultaneously remove persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 83:668–673. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.007
Shang H, Wang P, Wang T, Wang Y, Zhang H, Fu J, Ren D, Chen W, Zhang Q, Jiang G (2013) Bioaccumulation of PCDD/Fs, PCBs and PBDEs by earthworms in field soils of an E-waste dismantling area in China. Environ Int 54:50–58. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.01.006
Son Y, Cha J, Lim M, Ashokkumar M, Khim J (2011) Comparison of ultrasonic and conventional mechanical soil-washing processes for diesel-contaminated sand. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:2400–2407. doi:10.1021/ie1016688
Sun M, Luo Y, Teng Y, Jia Z, Li Z, Deng S (2013) Remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and metal-contaminated soil by successive methyl-β-cyclodextrin-enhanced soil washing-microbial augmentation: a laboratory evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:976–986. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1064-0
Thangavadivel K, Megharaj M, Smart RSC, Lesniewski PJ, Bates D, Naidu R (2011) Ultrasonic enhanced desorption of DDT from contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Poll 217:115–125. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0572-0
Trellu C, Mousset E, Pechaud Y, Huguenot D, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2016) Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 306:149–174. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.008
Von Lau E, Gan S, Ng HK, Poh PE (2014) Extraction agents for the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil in soil washing technologies. Environ Pollut 184:640–649. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.010
Wang Y, Luo C, Li J, Yin H, Li X, Zhang G (2011) Characterization of PBDEs in soils and vegetations near an e-waste recycling site in South China. Environ Pollut 159:2443–2448. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.030
Wen Y, Marshall WD (2011) Simultaneous mobilization of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compounds from soil with a nonionic surfactant and [S, S]-EDDS in admixture: metals. J Hazard Mater 197:361–368. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.09.097
Ye M, Sun M, Kengara FO, Wang J, Ni N, Wang L, Song Y, Yang X, Li H, Hu F, Jiang X (2014a) Evaluation of soil washing process with carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin and carboxymethyl chitosan for recovery of PAHs/heavy metals/fluorine from metallurgic plant site. J Environ Sci 26:1661–1672. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2014.06.006.
Ye M, Sun M, Hu F, Kengara FO, Jiang X, Luo Y, Yang X (2014b) Remediation of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) contaminated site by successive methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MCD) and sunflower oil enhanced soil washing-portulaca oleracea L. cultivation. Chemosphere 105:119–125. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.058.
Ye M, Sun M, Wan J, Fang G, Li H, Hu F, Jiang X, Orori Kengara F (2015) Evaluation of enhanced soil washing process with tea saponin in a peanut oil–water solvent system for the extraction of PBDEs/PCBs/PAHs and heavy metals from an electronic waste site followed by vetiver grass phytoremediation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:2027–2035. doi:10.1002/jctb.4512
Zhang WH, Wu YX, Simonnot MO (2012) Soil contamination due to e-waste disposal and recycling activities: a review with special focus on China. Pedosphere 22:434–455. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(12)60030-7
Zhou W, Yang J, Lou L, Zhu L (2011) Solubilization properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by saponin, a plant-derived biosurfactant. Environ Pollut 159:1198–1204. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.001
Zhou W, Wang X, Chen C, Zhu L (2013) Enhanced soil washing of phenanthrene by a plant-derived natural biosurfactant, Sapindus saponin. Colloid Surface A 425:122–128. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.055
Zou Z, Qiu R, Zhang W, Dong H, Zhao Z, Zhang T, Wei X, Cai X (2009) The study of operating variables in soil washing with EDTA. Environ Pollut 157:229–236. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.07.009
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the 13th Five-year Plan Period (2015BAD06B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Yang, B., Ma, J. et al. Decontamination of electronic waste-polluted soil by ultrasound-assisted soil washing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 20331–20340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7271-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7271-3