Abstract
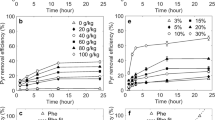
The remediation of dioxin-contaminated soil of a specific coastal area previously employed for the manufacture of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in southern Taiwan’s Tainan City has attracted much attention of researchers there. This work addresses the possibility of providing an effective and environmentally friendly option for removing PCDD/Fs from soil in that field. Soil screening/sieving was first conducted to assess particle distribution. Fine sand was observed to be the major component of the soil, accounting for more than 60% of the total mass. A combination of ultrasonification and mechanical double-blade agitation was used to facilitate the washing of the soil using the biosurfactant anaerobic compost tea. More than 85 and 95% of total removal efficiencies were achieved for moderately and highly contaminated soils after 6 and 10 washing cycles, respectively, under ambient temperature, a soil/liquid ratio 1:2.5, 700 rpm, and over a relatively short duration. These results were achieved through the collision and penetration effects of this combined treatment as well as PCDD/F partitioning between the particles and anaerobic compost tea. This study represents the first to report the use of anaerobic compost tea solvent to wash soil highly contaminated by dioxin. It was concluded that anaerobic compost tea, rich in non-toxic bio-surfactants (e.g., alcohols, humic acids), can be used to improve bioavailability and bioactivity of the soil making bio-attenuation and full remediation more efficient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn CK, Kim YM, Woo SH, Park JM (2008) Soil washing using various nonionic surfactants and their recovery by selective adsorption with activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):153–160
Anderson R, Rasor E, Van Ryn F (1999) Particle size separation via soil washing to obtain volume reduction. J Hazard Mater 66(1–2):89–98
Asakura Y, Nishida T, Matsuoka T, Koda S (2008) Effects of ultrasonic frequency and liquid height on sonochemical efficiency of large-scale sonochemical reactors. Ultrason Sonochem 15(3):244–250
Birkett JW, Lester JN (2003) Endocrine disrupters in wastewater and sludge treatment processes. Lewis Pub, Boca Raton
Boening DW (1998) Toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to several ecological receptor groups: a short review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 39(3):155–163
Cao M, Ye Y, Chen J, Lu X (2016) Remediation of arsenic contaminated soil by coupling oxalate washing with subsequent ZVI/Air treatment. Chemosphere 144:1313–1318
Chen F, Tan M, Ma J, Li G, Qu J (2016) Restoration of manufactured gas plant site soil through combined ultrasound-assisted soil washing and bioaugmentation. Chemosphere 146:289–299
Cheng SF, Chang JH, Huang CY (2007) Particle separation to enhance the efficiency of soil acid washing—case study on the removal of cadmium from contaminated soil in southwestern Taiwan. Environ Technol 28(10):1163–1171
Collings AF, Farmer AD, Gwan PB, Pintos APS, Leo CJ (2006) Processing contaminated soils and sediments by high power ultrasound. Miner Eng 19(5):450–453
Conte P, Zena A, Pilidis G, Piccolo A (2001) Increased retention of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils induced by soil treatment with humic substances. Environ Pollut 112(1):27–31
Conte P, Agretto A, Spaccini R, Piccolo A (2005) Soil remediation: humic acids as natural surfactants in the washings of highly contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 135(3):515–522
Czerwinski F (2004a) The generation of Mg–Al–Zn alloys by semisolid state mixing of particulate precursors. Acta Mater 52(17):5057–5069
Czerwinski F (2004b) Magnesium alloy particulates for Thixomolding applications manufactured by rapid solidification. Mater Sci Eng A 367(1–2):261–271
Fava F, Piccolo A (2002) Effects of humic substances on the bioavailability and aerobic biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in a model soil. Biotechnol Bioeng 77(2):204–211
Feng D, Aldrich C (2000) Sonochemical treatment of simulated soil contaminated with diesel. Adv Environ Res 4(2):103–112
Gogate PR, Mujumdar S, Pandit AB (2003) Large-scale sonochemical reactors for process intensification: design and experimental validation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 78(6):685–693
Gogate PR, Sutkar VS, Pandit AB (2011) Sonochemical reactors: important design and scale up considerations with a special emphasis on heterogeneous systems. Chem Eng J 166(3):1066–1082
Habe H, Ide K, Yotsumoto M, Tsuji H, Hirano H, Widada J, Yoshida T, Nojiri H, Omori T (2001) Preliminary examinations for applying a carbazole-degrader, Pseudomonas sp strain CA10, to dioxin-contaminated soil remediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56(5–6):788–795
Harjanto S, Kasai E, Terui T, Nakamura T (2002) Behavior of dioxin during thermal remediation in the zone combustion process. Chemosphere 47(7):687–693
Holman H-YN, Nieman K, Sorensen DL, Miller CD, Martin MC, Borch T, Mckinney WR, Sims RC (2002) Catalysis of PAH biodegradation by humic acid shown in synchrotron infrared studies. Environ Sci Technol 36(6):1276–1280
Hsueh KA, Chang FC, Wang HP, Wang HC, Huang YJ, Huang HL, Tuan YJ (2013) Enhanced extraction of PAHs hindered in fly ashes with supercritical water. J Supercrit Fluids 73:116–119
Huang R, Huang K-L, Lin Z-Y, Wang J-W, Lin C, Kuo Y-M (2013) Recovery of valuable metals from electroplating sludge with reducing additives via vitrification. J Environ Manag 129:586–592
Huang WY, Hung WT, Vu CT, Chen WT, Lai JW, Lin CT (2016) Green and sustainable remediation (GSR) evaluation: framework, standards, and tool. A case study in Taiwan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(21):21712–21725
Impellitteri CA, Lu Y, Saxe JK, Allen HE, Peijnenburg WJGM (2002) Correlation of the partitioning of dissolved organic matter fractions with the desorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from 18 Dutch soils. Environ Int 28(5):401–410
Islam MN, Jo Y-T, Park J-H (2012) Remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by extraction using subcritical water. J Ind Eng Chem 18(5):1689–1693
Janzen RA, Xing B, Gomez CC, Salloum MJ, Drijber RA, Mcgill WB (1996) Compost extract enhances desorption of α-naphthol and naphthalene from pristine and contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 28(8):1089–1098
Jonsson S, Lind H, Lundstedt S, Haglund P, Tysklind M (2010) Dioxin removal from contaminated soils by ethanol washing. J Hazard Mater 179(1–3):393–399
Kapp RW Jr (2014) CERCLA; revised as the superfund amendments reauthorization act (SARA). In: WEXLER P (ed) Encyclopedia of toxicology (third edition). Academic Press, Oxford
Kasai E, Harjanto S, Terui T, Nakamura T, Waseda Y (2000) Thermal remediation of PCDD/Fs contaminated soil by zone combustion process. Chemosphere 41(6):857–864
Khodadoust AP, Suidan MT, Acheson CM, Brenner RC (1999) Solvent extraction of pentachlorophenol from contaminated soils using water-ethanol mixtures. Chemosphere 38:2681–2693
Khodadoust AP, Bagchi R, Suidan MT, Brenner RC, Sellers NG (2000) Removal of PAHs from highly contaminated soils found at prior manufactured gas operations. J Hazard Mater 80(1–3):159–174
Kim Y, Lee D (2002) Solubility enhancement of PCDD/F in the presence of dissolved humic matter. J Hazard Mater 91(1–3):113–127
Kulkarni PS, Crespo JG, Afonso CAM (2008) Dioxins sources and current remediation technologies—a review. Environ Int 34(1):139–153
Kuokka S, Rantalainen AL, Häggblom MM (2014) Anaerobic reductive dechlorination of 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin- and dibenzofuran-contaminated sediments of the Kymijoki River, Finland. Chemosphere 98:58–65
Laha S, Tansel B, Ussawarujikulchai A (2009) Surfactant–soil interactions during surfactant-amended remediation of contaminated soils by hydrophobic organic compounds: a review. J Environ Manag 90(1):95–100
Lee C-C, Guo YL, Kuei C-H, Chang H-Y, Hsu J-F, Wang S-T, Liao P-C (2006) Human PCDD/PCDF levels near a pentachlorophenol contamination site in Tainan, Taiwan. Chemosphere 65(3):436–448
Liao X, Li Y, Yan X (2015) Removal of heavy metals and arsenic from a co-contaminated soil by sieving combined with washing process. J Environ Sci
Lin C (2008) A negative-pressure aeration system for composting food wastes. Bioresour Technol 99(16):7651–7656
Lin CT, Sheu DS, Lin TC, Kao CM, Grasso D (2012) Thermophilic biodegradation of diesel oil in food waste composting processes without bioaugmentation. Environ Eng Sci 29(2):117–123
Lin C, Wei CC, Tsai CC (2016) Prediction of influential operational compost parameters for monitoring composting process. Environ Eng Sci 33(7):494–506
Mitrou PI, Dimitriadis G, Raptis SA (2001) Toxic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds. Eur J Intern Med 12(5):406–411
Pant AP, Radovich TJK, Hue NV, Paull RE (2012) Biochemical properties of compost tea associated with compost quality and effects on pak choi growth. Sci Hortic 148:138–146
Park B, Son Y (2017) Ultrasonic and mechanical soil washing processes for the removal of heavy metals from soils. Ultrason Sonochem 35(Part B):640–645
Peng S, Wu W, Chen J (2011) Removal of PAHs with surfactant-enhanced soil washing: influencing factors and removal effectiveness. Chemosphere 82(8):1173–1177
Sany SBT, Hashim R, Rezayi M, Rahman MA, Razavizadeh BBM, Abouzari-Lotf E, Karlen DJ (2015a) Integrated ecological risk assessment of dioxin compounds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(15):11193–11208
Sany SBT, Hashim R, Salleh A, Rezayi M, Karlen DJ, Razavizadeh BBM, Abouzari-Lotf E (2015b) Dioxin risk assessment: mechanisms of action and possible toxicity in human health. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(24):19434–19450
Sheets RG, Bergquist BA (1999) Laboratory treatability testing of soils contaminated with lead and PCBs using particle-size separation and soil washing. J Hazard Mater 66(1–2):137–150
Singh DN, Shah PH (2004) A simple methodology for determining electrical conductivity of soils. J ASTM Int 1(5)
Son Y, Cha J, Lim M, Ashokkumar M, Khim J (2011) Comparison of ultrasonic and conventional mechanical soil-washing processes for diesel-contaminated sand. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(4):2400–2407
Son Y, Nam S, Ashokkumar M, Khim J (2012) Comparison of energy consumptions between ultrasonic, mechanical, and combined soil washing processes. Ultrason Sonochem 19(3):395–398
Sponza DT, Gök O (2010) Effect of rhamnolipid on the aerobic removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and COD components from petrochemical wastewater. Bioresour Technol 101(3):914–924
Sponza DT, Oztekin R (2011) Removals of some hydrophobic poly aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Daphnia magna acute toxicity in a petrochemical industry wastewater with ultrasound in Izmir-Turkey. Sep Purif Technol 77(3):301–311
Stalling DL, Norstrom RJ, Smith LM, Simon M (1985) Patterns of PCDD, PCDF, and PCB contamination in Great Lakes fish and birds and their characterization by principal components analysis. Chemosphere 14(6–7):627–643
Sun XL, Kido T, Honma S, Okamoto R, Manh HD, Maruzeni S, Nishijo M, Nakagawa H, Nakano T, Koh E, Takasuga T, Nhu DD, Hung NN, Son LK (2016) Influence of dioxin exposure upon levels of prostate-specific antigen and steroid hormones in Vietnamese men. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7807–7813
Takeda N, Takaoka M (2013) An assessment of dioxin contamination from the intermittent operation of a municipal waste incinerator in Japan and associated remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(4):2070–2080
Tanaka F, Fukushima M, Kikuchi A, Yabuta H, Ichikawa H, Tatsumi K (2005) Influence of chemical characteristics of humic substances on the partition coefficient of a chlorinated dioxin. Chemosphere 58(10):1319–1326
Trellu C, Mousset E, Pechaud Y, Huguenot D, Van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2016) Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 306:149–174
Tuyet-Hanh TT, Minh NH, Vu-Anh L, Dunne M, Toms L-M, Tenkate T, Thi M-HN, Harden F (2015) Environmental health risk assessment of dioxin in foods at the two most severe dioxin hot spots in Vietnam. Int J Hyg Environ Health 218(5):471–478
Ukisu Y, Miyadera T (2003) Hydrogen-transfer hydrodechlorination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans catalyzed by supported palladium catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 40(2):141–149
Vallejo M, Fresnedo San Román M, Ortiz I, Irabien A (2015) Overview of the PCDD/Fs degradation potential and formation risk in the application of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) to wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 118:44–56
Van Den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld ATC, Brunstrom B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, Van Leeuwen FXR, Liem AKD, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waern F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106(12):775–792
Van Den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93(2):223–241
Viglianti C, Hanna K, De Brauer C, Germain P (2006) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aged-contaminated soil using cyclodextrins: experimental study. Environ Pollut 140(3):427–435
Wang P, Keller AA (2008) Particle-size dependent sorption and desorption of pesticides within a water−soil−nonionic surfactant system. Environ Sci Technol 42(9):3381–3387
Wang M, Liu GR, Jiang XX, Xiao K, Zheng MH (2015) Formation and potential mechanisms of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans on fly ash from a secondary copper smelting process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(11):8747–8755
Xiao N, Liu R, Jin C, Dai Y (2015) Efficiency of five ornamental plant species in the phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-contaminated soil. Ecol Eng 75:384–391
Yang HY, Jia RB, Chen B, Li L (2014) Degradation of recalcitrant aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons by a dioxin-degrader Rhodococcus sp strain p52. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(18):11086–11093
Zhang F, Chen J, Zhang H, Ni Y, Zhang Q, Liang X (2008) Dechlorination of dioxins with Pd/C in ethanol–water solution under mild conditions. Sep Purif Technol 59(2):164–168
Zhang Y-f, Liu Y-b, Cao Z-y, Zhang L (2010) Microstructure transformation of deformed AZ91D during isothermal holding. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 20(1):14–21
Zhao D, Zheng Y, Li M, Baig SA, Wu D, Xu X (2014) Catalytic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Ni/Fe nanoparticles prepared in the presence of ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason Sonochem 21(5):1714–1721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Highlights
• Anaerobic compost tea (solvent) was used to wash the aged soil of a field highly contaminated with dioxins.
• The biosurfactant, anaerobic compost tea, consisted mostly of non-toxic alcohol and acidic ingredients.
• Double-blade propeller and ultrasonication added attrition, agitation, and penetration to the washing process.
• Removal efficiencies reached as high as 96% for most contaminated soil.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, W., Huang, WY., Lin, C. et al. The use of ultrasound-assisted anaerobic compost tea washing to remove poly-chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzo-furans (PCDFs) from highly contaminated field soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18936–18945 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9517-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9517-0