Abstract
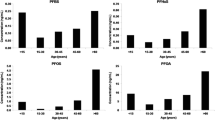
Severe perfluoroalkyl acid (PFAA) contamination resulting from the fast-growing semiconductor, electrochemical, and optoelectronic industries has been determined in the river water in the vicinity of the Taipei area, Taiwan, during recent years. However, little is known about body burdens of the PFAA contaminations in local residents, especially children living in the Taipei area recently. In this study, ten target PFAA analytes consisted of three perfluorosulfonates (PFSAs) and seven perfluorocarboxylates (PFCAs) in the blood serum samples, collected from 225 healthy children with an average age of 13.6 years in the Taipei area from 2009 to 2010, were analyzed via high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS). As the dominant PFAA contaminant in the blood serum samples from Taiwanese children, perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) contributed 86 % of all the target PFAA analytes, while the other nine analytes contributed less than 5 % individually. PFOS showed the highest median up to 29 ng/mL, ranging from 0.03 to 148 ng/mL, which was higher than that observed in the serum samples collected from Taiwanese children between 2006 and 2008. Statistically, serum concentrations of perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS), perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS), and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) had significantly positive correlations with ages of children (p < 0.05). Furthermore, serum PFBS, PFHxS, and PFOA concentrations in the male children were considerably higher than those in the female children (p = 0.049, p = 0.000, p = 0.000).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao J, Liu W, Liu L, Jin Y, Dai J, Ran X, Zhang Z, Tsuda S (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in the environment and the blood of residents living near fluorochemical plants in Fuxin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:8075–8080
Chen MH, Ha EH, Wen TW, Su YN, Lien GW, Chen CY, Chen PC, Hsieh WS (2012) Perfluorinated compounds in umbilical cord blood and adverse birth outcomes. PLoS One 7:e42474
Chimeddulam D, Wu KY (2013) River water contaminated with perfluorinated compounds potentially posing the greatest risk to young children. Chemosphere 90:1617–1624
D'eon JC, Mabury SA (2011) Exploring indirect sources of human exposure to perfluoroalkyl carboxylates (PFCAs): evaluating uptake, elimination, and biotransformation of polyfluoroalkyl phosphate esters (PAPs) in the rat. Environ Health Perspect 119:344–350
Fromme H, Schlummer M, Möller A, Gruber L, Wolz G, Ungewiss J, Böhmer S, Dekant W, Mayer R, Liebl B, Twardella D (2007) Exposure of an adult population to perfluorinated substances using duplicate diet portions and biomonitoring data. Environ Sci Technol 41:7928–7933
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2001) Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 35:1339–1342
Grandjean P, Andersen EW, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Nielsen F, Mølbak K, Weihe P, Heilmann C (2012) Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. JAMA 307:391–397
Hansen KJ, Clemen LA, Ellefson ME, Johnson HO (2001) Compound-specific, quantitative characterization of organic fluorochemicals in biological matrices. Environ Sci Technol 35:766–770
Hölzer J, Midasch O, Rauchfuss K, Kraft M, Reupert R, Angerer J, Kleeschulte P, Marschall N, Wilhelm M (2008) Biomonitoring of perfluorinated compounds in children and adults exposed to perfluorooctanoate-contaminated drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 116:651–657
Houde M, Martin JW, Letcher RJ, Solomon KR, Muir DC (2006) Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40:3463–3473
Houde M, De Silva AO, Muir DC, Letcher RJ (2011) Monitoring of perfluorinated compounds in aquatic biota: an updated review. Environ Sci Technol 45:7962–7973
Kannan K, Corsolini S, Falandysz J, Fillman G, Kumar KS, Loganathan BG, Mohd MA, Olivero J, van Wouwe N, Yang JH, Aldous KM (2004) Perfluorooctanesulfonate and related fluorochemicals in human blood from several countries. Environ Sci Technol 38:4489–4495
Kissa E (2001) Fluorinated surfactants and repellents (2nd ed). Marcel Dekker, New York
Lau C, Butenhoff J, Rogers JM (2004) The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:231–241
Lau C, Anitole K, Hodes C, Lai D, Pfahles-Hutchens A, Seed J (2007) Perfluoroalkyl acids: a review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol Sci 99:366–394
Lin CY, Wen LL, Lin LY, Wen TW, Lien GW, Chen CY, Hsu SH, Chien KL, Sung FC, Chen PC, Su TC (2011) Associations between levels of serum perfluorinated chemicals and adiponectin in a young hypertension cohort in Taiwan. Environ Sci Technol 45:10691–10698
Lopez-Espinosa MJ, Mondal D, Armstrong B, Bloom MS, Fletcher T (2012) Thyroid function and perfluoroalkyl acids in children living near a chemical plant. Environ Health Perspect 20:1036–1041
Martin JW, Whittle DM, Muir DCG, Mabury SA (2004) Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in a food web from Lake Ontario. Environ Sci Technol 38:5379–5385
Nilsson H, Kärrman A, Rotander A, van Bavel B, Lindström G, Westberg H (2010) Inhalation exposure to fluorotelomer alcohols yield perfluorocarboxylates in human blood? Environ Sci Technol 44:7717–7722
OECD (2002) Hazard assessment of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and its salts
Schecter A, Malik-Bass N, Calafat AM, Kato K, Colacino JA, Gent TL, Hynan LS, Harris TR, Malla S, Birnbaum L (2012) Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in Texas children from birth through 12 years of age. Environ Health Perspect 120:590–594
Stein CR, Savitz DA (2011) Serum perfluorinated compound concentration and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children 5–18 years of age. Environ Health Perspect 119:1466–1471
Strynar MJ, Lindstrom AB (2008) Perfluorinated compounds in house dust from Ohio and North Carolina, USA. Environ Sci Technol 42:3751–3756
Toms LM, Calafat AM, Kato K, Thompson J, Harden F, Hobson P, Sjödin A, Mueller JF (2009) Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in pooled blood serum from infants, children, and adults in Australia. Environ Sci Technol 43:4194–4199
Tsai CH, Huang JH, Hwang BF, Lee YL (2010) Household environmental tobacco smoke and risks of asthma, wheeze and bronchitic symptoms among children in Taiwan. Respir Res 11:11
UNEP (2009) Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants (POPs). http://chm.pops.int/Portals/0/Repository/convention_text/UNEP-POPS-COP-CONVTEXT-FULL.English.PDF
Zhang T, Wu Q, Sun HW, Zhang XZ, Yun SH, Kannan K (2010) Perfluorinated compounds in whole blood samples from infants, children, and adults in China. Environ Sci Technol 44:4341–4347
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant no. 81172630 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and grant no. 98-2314-B-002-138-MY3 from the National Science Council in Taiwan. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the funding source. The funding source had no role in the design or analysis of the study publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Leif Kronberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, J., Lee, Y.L., Chen, PC. et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in blood serum samples from children in Taiwan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 7650–7655 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2594-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2594-4