Abstract
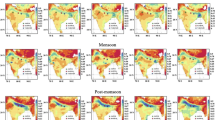
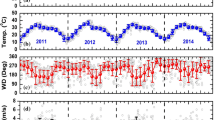
We analysed aerosol optical and physical properties in an urban environment (Kolkata) during winter monsoon pollution transport from nearby and far-off regions. Prevailing meteorological conditions, viz. low temperature and wind speed, and a strong downdraft of air mass, indicated weak dispersion and inhibition of vertical mixing of aerosols. Spectral features of WinMon aerosol optical depth (AOD) showed larger variability (0.68–1.13) in monthly mean AOD at short-wavelength (SW) channels (0.34–0.5 μm) compared to that (0.28–0.37) at long-wavelength (LW) channels (0.87–1.02 μm), thereby indicating sensitivity of WinMon AOD to fine aerosol constituents and the predominant contribution from fine aerosol constituents to WinMon AOD. WinMon AOD at 0.5 μm (AOD 0. 5) and Angstrom parameter ( α) were 0.68–0.82 and 1.14–1.32, respectively, with their highest value in December. Consistent with inference from spectral features of AOD, surface aerosol loading was primarily constituted of fine aerosols (size 0.23–3 μm) which was 60–70 % of aerosol 10- μm (size 0.23–10 μm) concentration. Three distinct modes of aerosol distribution were obtained, with the highest WinMon concentration at a mass median diameter (MMD) of 0.3 μm during December, thereby indicating characteristics of primary contribution related to anthropogenic pollutants that were inferred to be mostly due to contribution from air mass originating in nearby region having predominant emissions from biofuel and fossil fuel combustion. A relatively higher contribution from aerosols in the upper atmospheric layers than at the surface to WinMon AOD was inferred during February compared to other months and was attributed to predominant contribution from open burning emissions arising from nearby and far-off regions. A comparison of ground-based measurements with Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data showed an underestimation of MODIS AOD and α values for most of the days. Discrepancy in relative distribution of fine and coarse mode of MODIS AOD was also inferred.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angstrom A (1964) The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 16:64–75
Arino O, Simon M, Piccolini I, Rosaz JM (2001) The ERS-ATSR 2 World Fire Atlas and the ERS 2 ATSR 2 World Burnt Surface Atlas projects. Paper presented at 8th ISPRS conference on physical measurement and signatures in remote sensing, Europe Space Agency, Aussois
Babu SS, Gogoi MM, Kumar VHA, Nair VS, Moorthy KK (2012) Radiative properties of Bay of Bengal aerosols: spatial distinctiveness and source impacts. J Geophys Res 17:D06213. doi:10.1029/2011JD017355
Babu SS, Satheesh SK, Moorthy KK (2002) Aerosol radiative forcing due to enhanced black carbon at an urban site in India. Geophys Res Lett 29(18):1880. doi:10.1029/2002GL015826
Benas N, Chrysoulakis N, Giannakopoulou G (2013) Validation of MERIS/AATSR synergy algorithm for aerosol retrieval against globally distributed AERONET observations and comparison with MODIS aerosol product. Atmos Res 132-133:102–113
Burkart J, Steiner G, Reischl G, Moshammer H, Neuberger M, Hitzenberger R (2010) Characterizing the performance of two optical particle counters (Grimm OPC1.108 and OPC1.109) under urban aerosol conditions. J Aerosol Sci 41:953–962
Chakraborty A, Satheesh SK, Nanjundiah RS, Srinivasan J (2004) Impact of absorbing aerosols on the simulation of climate over the Indian region in an atmospheric general circulation model. Ann Geophys 22:1421–1434
Charlson RJ, Schwartz SE, Hales JM, Cess RD, Coakley JD, Hansen JE, Hofmann DJ (1992) Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 255:423–430
Choudhry P, Misra A, Tripathi SN (2012) Study of MODIS derived AOD at three different locations in the Indo Gangetic Plain: Kanpur, Gandhi College and Nainital. Ann Geophys 30:1479–1493. doi:10.5194/angeo-30-1479-2012
Das SK, Jayaraman A, Misra A (2008) Fog-induced variations in aerosol optical and physical properties over the Indo-Gangetic Basin and impact to aerosol radiative forcing. Ann Geophys 26:1345–1354
Draxler RR, Hess GD (1998) An overview of the HYSPLIT-4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion and deposition. Aust Meteorol Mag 47:295–308
Eck TF, Holben BN, Reid JS, Dubovik O, Smirnov A, O’Neill NT, Slutsker I, Kinne S (1999) Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J Geophys Res 104:31333–31349. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00093-5
Erwin KL (2009) Wetlands and global climate change: the role of wetland restoration in a changing world. Wetl Ecol Manag 17:71–84
Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Artaxo P, Berntsen T, Betts R, Fahey DW, Haywood J, Lean J, Lowe DC, Myhre G, Nganga J, Prinn R, Raga G, Schulz M, Dorland RV (2007) Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 186–217
Ganguly D, Jayaraman A, Gadhavi H (2006a) Physical and optical properties of aerosols over an urban location in western India: seasonal variabilities. J Geophys Res 111:D24. doi:10.1029/2006JD007392
Ganguly D, Jayaraman A, Rajesh TA, Gadhavi H (2006b) Wintertime aerosol properties during foggy and nonfoggy days over urban center Delhi and their implications for shortwave radiative forcing. J Geophys Res 111:D15217. doi:10.1029/2005JD007029
Ge JM, Su J, Fu Q, Ackerman TP, Huang JP (2011) Dust aerosol forward scattering effects on ground-based aerosol optical depth retrievals. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 112:310–319
Gerasopoulos E, Koulouri E, Kalivitis N, Kouvarakis G, Saarikoski S, Makela T, Hillamo R, Mihalopoulos N (2007) Size-segregated mass distributions of aerosols over Eastern Mediterranean: seasonal variability and comparison with AERONET columnar size-distributions. Atmos Chem Phys 7:2551–2561
Grimm H, Eatough DJ (2009) Aerosol measurement: the use of optical light scattering for the determination of particulate size distribution, and particulate mass, including the semi-volatile fraction. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 59:101–107. doi:10.3155/1047-3289.59.1.101
Hegerl GC, Cubasch U (1996) Greenhouse gas induced climate change. Environ Sci Pollut Res 3:99–102. doi:10.1007/BF02985499
Hess M, Koepke P, Schult I (1998) Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: the software package OPAC. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:831–844
Hinds WC (1999) Aerosol technology: properties, behavior, and measurement of airborne particles, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Ichoku C, Levy R, Kaufman YJ, Remer LA, Li R-R, Martins VJ, Holben BN, Abuhassan N, Slutsker I, Eck TF, Pietras C (2002) Analysis of the performance characteristics of the five-channel Microtops II Sun photometer for measuring aerosol optical thickness and precipitable water vapor. J Geophys Res 107:AAC5-1–AAC5-17. doi:10.1029/2001JD001302
Ichoku C, Remer LA, Kaufman YJ, Levy R, Chu DA, Tanre D, Holben BN (2003) MODIS observation of aerosols and estimation of aerosol radiative forcing over southern Africa during SAFARI 2000. J Geophys Res 108:16. doi:10.1029/2002JD002366
Jethva H, Satheesh SK, Srinivasan J (2007) Assessment of second-generation MODIS aerosol retrieval (collection 005) at Kanpur, India. Geophys Res Lett 34:L19802. doi:10.1029/2007GL029647
Kaufman YJ, Tanre D, Boucher O (2002) A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 419:215–223
Kaufman YJ, Tanre D, Remer L, Vermote E, Chu A, Holben BN (1997) Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J Geophys Res 102:17051–17067
Kedia S, Ramachandran S, Kumar A, Sarin MM (2010) Spatiotemporal gradients in aerosol radiative forcing and heating rate over Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea derived on the basis of optical, physical, and chemical properties. J Geophys Res 115:16. doi:10.1029/2009JD013136
King MD, Kaufman YJ, Tanre D, Nakajima T (1999) Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: past, present, and future. Bull Amer Meteorol Soc 80:2229–2259
Krishnamurti TN, Chakraborty A, Martin A, Lau WK, Kim K-M, Sud Y, Walker G (2009) Impact of Arabian Sea pollution on the Bay of Bengal winter monsoon rains. J Geophys Res 114:D06213. doi:10.1029/2008JD010679
Latha KM, Badarinath K (2004) Characterization of aerosols and its radiative impacts over urban and rural environments—a case study from Hyderabad and Srisailam. Environ Pollut 132:463–468. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.010
Leon J-F, Chazette P, Dulac F, Pelon J, Flamant C, Bonazzola M, Foret G, Alfaro S, Cachier H, Cautenet S, Hamonou E, Gaudichet A, Gomes L, Rajot J, Lavenu F, Inamdar S, Sarode P, Kadadevarmath J (2001) Large scale advection of continental aerosols during INDOEX. J Geophys Res 106:28,427–28,440
Levy R, Remer L, Martins JV, Kaufman YJ, Plana-Fattori A, Redemann J, Wenny B (2005) Evaluation of the MODIS aerosol retrievals over ocean and land during CLAMS. J Atmos Sci 62:974–992. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00093-5
Levy R, Remer L, Dubovik O (2007) Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J Geophys Res 112:D13210. doi:10.1029/2006JD0078151
Levy RC, Remer LA, Kleidman RG, Mattoo S, Ichoku C, Kahn R, Eck TF (2010) Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos Chem Phys 10:10399–10420. doi:10.5194/acp-10-10399-2010
Liousse C, Penner JE, Chuang C, Walton JJ, Eddleman H, Cachier H (1996) A global three-dimensional model study of carbonaceous aerosols. J Geophys Res 101:19411–19432
Mischenko MI, Geogdzhayev IV, Cairns B, Rossow WB, Lacis AA (1999) Aerosols retrievals over the oceans by use of channels 1 and 2 AVHRR data: sensitivity analysis and preliminary results. Appl Opt 38:7325–7341
Misra A, Jayaraman A, Ganguly D (2008) Validation of MODIS derived aerosol optical depth over Western India. J Geophys Res 113:D04203. doi:10.1029/2007JD009075
Moorthy KK, Saha A, Prasad B, Niranjan K, Jhurry D, Pillai PS (2001) Aerosol optical depths over peninsular India and adjoining oceans during the INDOEX campaign: spatial, temporal, and spectral characteristics. J Geophys Res 106:28539–28554
Morys M, Mims FM III, Hagerup S, Anderson SE, Baker A, Kia J, Walkup T (2001) Design, calibration, and performance of MICROTOPS II handheld ozone monitor and Sun photometer. J Geophys Res 106:14573–14582
Nair VS, et al. (2007) Wintertime aerosol characteristics over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP): impacts of local boundary layer processes and long-range transport. J Geophys Res 112:D13205. doi:10.1029/2006JD008099
Niranjan K, Sreekanth V, Madhavan BL, Moorthy KK (2006) Wintertime aerosol characteristics at a north Indian site Kharagpur in the Indo-Gangetic plains located at the outflow region into Bay of Bengal. J Geophys Res 111:D24209. doi:10.1029/2006JD007635
Penner J, Hegg D, Leaitch R (2001) Unraveling the role of aerosols in climate change. Environ Sci Technol 35:332A–340A
Pilinis C, Pandis SN, Seinfeld JH (1995) Sensitivity of direct climate forcing by atmospheric aerosols to aerosol size and composition. J Geophys Res 100:18739–18754
Prasad AK, Singh RP (2007) Comparison of MISR-MODIS aerosol optical depth over the Indo-Gangetic basin during the winter and summer seasons (2000-2005). Remote Sens Environ 107:109–119
Ramachandran S, Jayaraman A (2002) Premonsoon aerosol mass loadings and size distributions over the Arabian Sea and the Tropical Indian Ocean. J Geophys Res 107:4738. doi:10.1029/2002JD002386
Ramachandran S, Kedia S (2012) Radiative effects of aerosols over Indo-Gangetic plain: environmental (urban vs. rural) and seasonal variations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2159–2171. doi:10.1007/s1356-011-0715-x
Ramanathan V, Carmichael G (2008) Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat Geosci 1:221–227. doi:10.1038/ngeo156
Ramanathan V, Li F, Ramana MV, Praveen PS, Kim D, Corrigan CE, Nguyen H, Stone EA, Schauer JJ, Carmichael GR, Adhikary B, Yoon SC (2007) Atmospheric brown clouds: hemispherical and regional variations in long-range transport, absorption, and radiative forcing. J Geophys Res 112:D22S21. doi:10.1029/2006JD008124
Ramaswamy V, Boucher O, Haigh J, Haywood DHJ, Myhre G, Nakajima T, Shi GY, Solomon S, et al (2001) Radiative forcing of climate change. Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. In: Houghton JT, et al (eds) Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 349–416
Remer LA, Kaufman YJ, Tanre D, Mattoo S, Chu DA, Martins JV, Li R-R, Ichoku C, Levy RC, Kleidman RG, Eck TF, Vermote E, Holben BN (2005) The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J Atmos Sci 62:947–973
Remer LA, Kleidman RG, Levy RC, Kaufman YJ, Tanre D, Mattoo S, Martins JV, Ichoku C, Koren I, Yu H, Holben BN (2008) Global aerosol climatology from the MODIS satellite sensors. J Geophys Res 113:D14S07. doi:10.1029/2007JD009661
Rose D, Wehner B, Ketzel M, Engler C, Voigtlander J, Tuch T, Wiedensohler A (2006) Atmospheric number size distributions of soot particles and estimation of emission factors. Atmos Chem Phys 6:1021–1031
Schuster GL, Dubovik O, Holben BN (2006) Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J Geophys Res 111:D07207. doi:10.1029/2005JD006328
Tanre D, Kaufman YJ, Herman M, Mattoo S (1997) Remote sensing of aerosol properties over oceans using the MODIS/EOS spectral radiances. J Geophys Res 102:16971– 16988
Tripathi SN, Dey S, Chandel A, Srivastava S, Singh RP, Holben BN (2005a) Comparison of MODIS and AERONET derived aerosol optical depth over the Ganga Basin, India. Ann Geophys 23:1093–1101
Tripathi SN, Dey S, Tare V (2005b) Aerosol black carbon radiative forcing at an industrial city in northern India. Geophys Res Lett 32:L08802. doi:10.1029/2005GL022515
Tsigaridis K, Krol M, Dentener FJ, Balkanski Y, Lathiere J, Metzger S, Hauglustaine DA, Kanakidou M (2006) Change in global aerosol composition since preindustrial times. Atmos Chem Phys 6:5143–5162. doi:10.5194/acp-6-5143-2006
Verma S, Venkataraman C, Boucher O, Ramachandran S (2007) Source evaluation of aerosols measured during the Indian Ocean Experiment using combined chemical transport and back trajectory modeling. J Geophys Res 112:D11210. doi:10.1029/2006JD007698
Verma S, Venkataraman C, Boucher O (2008) Origin of surface and columnar INDOEX aerosols using source- and region-tagged emissions transport in a general circulation model. J Geophys Res 113:D24211. doi:10.1029/2007JD009538
Verma S, Venkataraman C, Boucher O (2011) Attribution of aerosol radiative forcing over India during the winter monsoon to emissions from source categories and geographical regions. Atmos Environ 45:4398–4407
Wang C, Liu Q, Ying N, Wang X, Ma J (2013) Air quality evaluation on an urban scale based on MODIS satellite images. Atmos Res 132–133:22–34. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.04.011
Xie Y, Zhang Y, Xiong X, Qu J, Che H (2011) Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth product over China using CARSNET measurements. Atmos Res 45:5970–5978. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.08.002
Xiong X, Sun J, Bames W, Salomonson V, Esposito J, Erives H, Guenther B (2007) Multiyear On-Orbit calibration and performance of Terra MODIS reflective solar bands. IEEE T Geosci Remote 45:879–889
Xiong X, Sun J, Wu A, Chiang K, Esposito J, Erives H, Guenther B (2005) Terra and Aqua MODIS calibration algorithms and uncertainty analysis, sensors, systems, and next-generation satellites IX. In: Proceedings of SPIE, p 5978
Zhao M, Heinsch FA, Nemani RR, Running SW (2005) Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens Environ 95:164–176
Acknowledgments
Computing resources and experimental work at Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur were supported through a grant received from the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India. D. Bharath Kumar and Priyadharshini B, research scholars, Civil Engineering Department, IIT-KGP, are acknowledged for their help in extracting fire count data and refining Fig. 1. We acknowledge the support from ECMWF for providing wind field data. The MODIS data used in this study are downloaded from the Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (LAADS), a part of the NASA’s Goddard Earth Sciences (GES) Data and Information Services Center (DISC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Bhanja, S.N., Pani, S.K. et al. Aerosol optical and physical properties during winter monsoon pollution transport in an urban environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 4977–4994 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2383-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2383-5