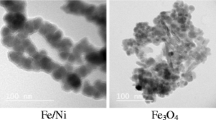
Abstract
Soil pollution by polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) arising from the crude disposal and recycling of electronic and electrical waste (e-waste) is a serious issue, and effective remediation technologies are urgently needed. Nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) and bimetallic systems have been shown to promote successfully the destruction of halogenated organic compounds. In the present study, nZVI and Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized by chemical deposition were used to remove 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl from deionized water, and then applied to PCBs contaminated soil collected from an e-waste recycling area. The results indicated that the hydrodechlorination of 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl by nZVI and Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles followed pseudo-first-order kinetics and Pd loading was beneficial to the hydrodechlorination process. It was also found that the removal efficiencies of PCBs from soil achieved using Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles were higher than that achieved using nZVI and that PCBs degradation might be affected by the soil properties. Finally, the potential challenges of nZVI application to in situ remediation were explored.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Agarwal S, Al-Abed SR, Dionysiou DD (2007) Enhanced corrosion-based Pd/Mg bimetallic systems for dechlorination of PCBs. Environ Sci Technol 41(10):3722–3727. doi:10.1021/es062886y
Chen JL, Al-Abed SR, Ryan JA, Li Z (2001) Effects of pH on dechlorination of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 83(3):243–254. doi:10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00193-5
Chen YX, Tang XJ, Cheema SA, Liu WL, Shen CF (2010) Beta-cyclodextrin enhanced phytoremediation of aged PCBs-contaminated soil from e-waste recycling area. J Environ Monit 12(7):1482–1489. doi:10.1039/c0em00029a
Chuang FW, Larson RA, Wessman MS (1995) Zero-valent iron-promoted dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Sci Technol 29(9):2460–2463. doi:10.1021/es00009a044
Cogliano VJ (1998) Assessing the cancer risk from environmental PCBs. Environ Health Perspect 106(6):317–323
Cundy AB, Hopkinson L, Whitby RLD (2008) Use of iron-based technologies in contaminated land and groundwater remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 400(1–3):42–51. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.07.002
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ (2012) Ecotoxicological effects on earthworms of fresh and aged nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil. Chemosphere 89(1):76–82. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.020
Fang Y, Al-Abed SR (2008) Dechlorination kinetics of monochlorobiphenyls by Fe/Pd: effects of solvent, temperature, and PCB concentration. Appl Catal B: Environ 78(3–4):371–380. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.09.009
Gomes HI, Dias-Ferreira C, Ribeiro AB (2013) Overview of in situ and ex situ remediation technologies for PCB-contaminated soils and sediments and obstacles for full-scale application. Sci Total Environ 445–446:237–260. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.098
Grittini C, Malcomson M, Fernando Q, Korte N (1995) Rapid dechlorination of polychlorinated-biphenyls on the surface of a Pd/Fe bimetallic system. Environ Sci Technol 29(11):2898–2900. doi:10.1021/es00011a029
Hadnagy E, Rauch LM, Gardner KH (2007) Dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls, naphthalenes and dibenzo-p-dioxins by magnesium/palladium bimetallic particles. J Environ Sci Health Part A 42(6):685–695. doi:10.1080/10934520701326222
He F, Zhao D, Paul C (2010) Field assessment of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles for in situ destruction of chlorinated solvents in source zones. Water Res 44(7):2360–2370. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.041
He F, Zhao DY (2005) Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water. Environ Sci Technol 39(9):3314–3320. doi:10.1021/es048743y
He F, Zhao DY, Liu JC, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe-Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(1):29–34. doi:10.1021/ie0610896
He N, Li P, Zhou Y, Ren W, Fan S, Verkhozina VA (2009) Catalytic dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil by palladium-iron bimetallic catalyst. J Hazard Mater 164(1):126–132. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.149
Karn B, Kuiken T, Otto M (2009) Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: a review of the benefits and potential risks. Environ Heal Perspect 117(12):1823–1831. doi:10.1289/ehp.0900793
Kim YH, Carraway ER (2000) Dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by zero valent iron and modified zero valent irons. Environ Health Perspect 34(10):2014–2017. doi:10.1021/es991129f
Kirschling TL, Gregory KB, Minkley EG, Lowry GV, Tilton RD (2010) Impact of nanoscale zero valent iron on geochemistry and microbial populations in trichloroethylene contaminated aquifer materials. Environ Sci Technol 44(9):3474–3480. doi:10.1021/es903744f
Kluyev N, Cheleptchikov A, Brodsky E, Soyfer V, Zhilnikov V (2002) Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins by zerovalent iron in subcritical water. Chemosphere 46(9–10):1293–1296. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(01)00276-4
Kume A, Monguchi Y, Hattori K, Nagase H, Sajiki H (2008) Pd/C-catalyzed practical degradation of PCBs at room temperature. Appl Catal B Environ 81(3–4):274–282. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.12.019
Leung AOW, Zheng J, Yu CK, Liu WK, Wong CKC, Cai Z, Wong MH (2011) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in surface dust at an e-waste processing site in southeast China. Environ Sci Technol 45(13):5775–5782. doi:10.1021/es103915w
Liu H, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Cai Z, Jiang G (2008) E-waste recycling induced polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzo-furans pollution in the ambient environment. Environ Int 34(1):67–72. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.07.008
Liu YQ, Lowry GV (2006) Effect of particle age (Fe0 content) and solution pH on NZVI reactivity: H2 evolution and TCE dechlorination. Environ Int 40(19):6085–6090. doi:10.1021/es060685o
Luo Y, Luo XJ, Lin Z, Chen SJ, Liu J, Mai BX, Yang ZY (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in road and farmland soils from an e-waste recycling region in Southern China: Concentrations, source profiles, and potential dispersion and deposition. Sci Total Environ 407(3):1105–1113. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.044
Marshall WD, Kubatova A, Lagadec AJM, Miller DJ, Hawthorne SB (2002) Zero-valent metal accelerators for the dechlorination of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in subcritical water. Green Chem 4(1):17–23. doi:10.1039/b108337f
Mitoma Y, Egashira N, Simion C (2009) Highly effective degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil mediated by a Ca/Rh bicatalytic system. Chemosphere 74(7):968–973. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.034
Mueller N, Braun J, Bruns J, Černík M, Rissing P, Rickerby D, Nowack B (2012) Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (NZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(2):550–558. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0576-3
O’Carroll D, Sleep B, Krol M, Boparai H, Kocur C (2013) Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv Water Resour 51:104–122. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.02.005
Pawlett M, Ritz K, Dorey R, Rocks S, Ramsden J, Harris J (2013) The impact of zero-valent iron nanoparticles upon soil microbial communities is context dependent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(2):1041–1049. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1196-2
Safe S (1993) Toxicology, structure-function relationship, and human and environmental health impacts of polychlorinated biphenyls: progress and problems. Environ Health Perspect 100:259–268
Schrick B, Blough JL, Jones AD, Mallouk TE (2002) Hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene to hydrocarbons using bimetallic nickel–iron nanoparticles. Chem Mater 14(12):5140–5147. doi:10.1021/cm020737i
Shen CF, Chen YX, Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Yu CN, Qiao M, Xu YP, Setty K, Zhang JY, Zhu YF, Lin Q (2009a) Dioxin-like compounds in agricultural soils near e-waste recycling sites from Taizhou area, China: chemical and bioanalytical characterization. Environ Int 35(1):50–55. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.005
Shen CF, Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Qiao M, Tang XJ, Yu CN, Shi DZ, Zhu YF, Shi JY, Chen XC, Setty K, Chen YX (2008) Identification of Ah receptor agonists in soil of E-waste recycling sites from Taizhou area in China. Environ Sci Technol 42(1):49–55. doi:10.1021/es071162z
Shen CF, Tang XJ, Cheema SA, Zhang CK, Khan MI, Liang F, Chen XC, Zhu YF, Lin Q, Chen YX (2009b) Enhanced phytoremediation potential of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated soil from e-waste recycling area in the presence of randomly methylated-beta-cyclodextrins. J Hazard Mater 172(2–3):1671–1676. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.064
Shih Y, Chen YC, Chen MY, Tai YT, Tso CP (2009) Dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene by using nanoscale Fe and nanoscale Pd/Fe bimetallic particles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 332(2–3):84–89. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.09.031
Tang X, Shen C, Shi D, Cheema SA, Khan MI, Zhang C, Chen Y (2010a) Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination in soil from Wenling: An emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area, China. J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):653–660. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.134
Tang XJ, Shen CF, Chen L, Xiao X, Wu JY, Khan MI, Dou CM, Chen YX (2010b) Inorganic and organic pollution in agricultural soil from an emerging e-waste recycling town in Taizhou area, China. J J Soils Sediments 10(5):895–906. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0252-0
Varanasi P, Fullana A, Sidhu S (2007) Remediation of PCB contaminated soils using iron nano-particles. Chemosphere 66(6):1031–1038. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.036
Wang CB, Zhang WX (1997) Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ Sci Technol 31(7):2154–2156. doi:10.1021/es970039c
Wang Y, Zhou D, Wang L, Cang L (2012) Automatic pH control system enhances the dechlorination of 2,4,4′-trichlorobiphenyl and extracted PCBs from contaminated soil by nanoscale Fe and Pd/Fe. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(2):448–457. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0587-0
Xu Y, Zhang WX (2000) Subcolloidal Fe/Ag particles for eeductive dehalogenation of chlorinated benzenes. Ind Eng Chem Res 39(7):2238–2244. doi:10.1021/ie9903588
Ye X, Jianguo J, Yong Y, Guolong G (2011) Base-catalyzed destruction of hexachlorobenzene with zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 173(2):415–421. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.082
Zhang M, He F, Zhao D, Hao X (2011) Degradation of soil-sorbed trichloroethylene by stabilized zero valent iron nanoparticles: effects of sorption, surfactants, and natural organic matter. Water Res 45(7):2401–2414. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.01.028
Zhang WX (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanopart Res 5(3):323–332. doi:10.1023/a:1025520116015
Zhang WX, Wang CB, Lien HL (1998) Treatment of chlorinated organic contaminants with nanoscale bimetallic particles. Catal Today 40(4):387–395. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00067-4
Zhou H, Han J, Baig SA, Xu X (2011) Dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized Pd/Fe nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 198:7–12. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.002
Zhu BW, Lim TT (2007) Catalytic reduction of chlorobenzenes with Pd/Fe nanoparticles: reactive sites, catalyst stability, particle aging, and regeneration. Environ Sci Technol 41(21):7523–7529. doi:10.1021/es0712625
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (2009C13003), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA06A203), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41271334 and 81001475) and the Science and Technology Development Foundation of Hangzhou (20101131N05).We thank Ms. Lijuan Mao, the technician of the 985-Institute of Agrobiology and Environmental Sciences of Zhejiang University, for her contributions in determining the specific surface area of nZVI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hongwen Sun
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Yao, X., Yu, C. et al. Hydrodechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in contaminated soil from an e-waste recycling area, using nanoscale zerovalent iron and Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 5201–5210 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2089-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2089-8