Abstract
Purpose
The emerging recycling of electronic and electric waste (e-waste) is causing critical levels of soil pollution in those relatively poor towns surrounding the central cities, which have been involved in recycling activities for quite some time. Agricultural soil is of great importance due to its direct impact on food and human health. The objective of this study was to provide a systematic investigation of the contamination in agricultural soil for a range of inorganic compounds (Cr, Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu, and Ni) and organic compounds (PAHs and PCBs) in town A, an emerging e-waste recycling town in China.
Materials and methods
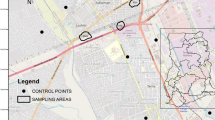
A total of 20 agricultural soil samples were collected from three sampling locations throughout town A. Levels of inorganic compounds (Cr, Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu, and Ni) and organic compounds (PAHs and PCBs) were determined by AAS, GC/MS, and GC/electron capture detector, respectively. Data was processed with SPSS 13 and Arcview 3.3 GIS software.
Results and discussion
The findings demonstrate that agricultural soil was contaminated to various extents by inorganic and/or organic pollutants. Comparison among the three sampling areas indicated that the soil was highly contaminated in the agricultural area near e-waste recycling workshops. Moreover, the contaminants (Cu, Pb, PAHs, and PCBs) may be connected through a common source as found in the Pearson correlations and cluster analysis.
Conclusions
There exists a heightened sense of awareness concerning the hazardous implications of current emerging e-waste recycling issues in the agricultural soil of those areas close to the central city in Taizhou.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi X, Chu S, Meng Q, Xu X (2002) Movement and retention of polychlorinated biphenyls in a paddy field of WenTai area in China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 89:241–252
Blake L, Goulding KWT (2002) Effects of atmospheric deposition, soil pH and acidification on heavy metal contents in soils and vegetation of semi-natural ecosystems at Rothamsted Experimental Station, UK. Plant Soil 240:235–251
Boruvka L, Vacek O, Jehlicka J (2005) Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils. Geoderma 128:289–300
Chen B, Xuan X, Zhu L, Wang J, Gao Y, Yang K, Shen X, Lou B (2004) Distributions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface waters, sediments and soils of Hangzhou city, China. Water Res 38:3558–3568
Chen L, Ran Y, Xing B, Mai B, He J, Wei X, Fu J, Sheng G (2005) Contents and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in vegetable soils of Guangzhou, China. Chemosphere 60:879–890
Choi SD, Beak SY, Chang YS, Wania F, Ikonomou MG, Yoon YJ, Park BK, Hong SM (2008) Passive air sampling of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides at the Korean Arctic and Antarctic research stations: implications for long-range transport and local pollution. Environ Sci Technol 42:7125–7713
Cobbing M (2008) Toxic Tech: Not in Our Backyard. Uncovering the Hidden Flows of e-waste. Report from Greenpeace International. http://www.greenpeace.org/raw/content/belgium/fr/press/reports/toxic-tech.pdf, Amsterdam
Cousins IT, Gevao B, Jones KC (1999) Measuring and modeling the vertical distribution of semi-volatile organic compounds in soils. I: PCB and PAH soil core data. Chemosphere 39:2507–2518
Fabietti G, Biasioli M, Barberis R, Ajmone-Marsan F (2010) Soil contamination by organic and inorganic pollutants at the regional scale: the case of Piedmont, Italy. J Soils Sediments 10(2):290–300
Fu JJ, Zhou QF, Liu JM, Liu W, Wang T, Zhang QH, Jiang GB (2008) High levels of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from a typical E-waste recycling area in southeast China and its potential risk to human health. Chemosphere 71:1269–1275
Gouin T, Mackay D, Jones KC, Harner T, Meijer SN (2004) Evidence for the “grasshopper” effect and fractionation during long-range atmospheric transport of organic contaminants. Environ Pollut 128:139–148
Heywood E, Wright J, Wienburg CL, Black HIJ, Long SM, Osborn D, Spurgeon DJ (2006) Factors influencing the national distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in British soils. Environ Sci Technol 40:7629–7635
Howsam M, Jones KC, Ineson P (2000) PAHs in the soils of a mature, mixed-deciduous (quercus-fraxinus) woodland and the surrounding pasture. Water Air Soil Pollut 121:379–398
Huang SS, Liao QL, Hua M, Wu XM, Bi KS, Yan CY, Chen B, Zhang XY (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67:2148–2155
Ladou J, Lovegrove S (2008) Export of electronics equipment waste. Int J Occup Environ Health 14:1–10
Leung A, Cai ZW, Wong MH (2006) Environmental contamination from electronic waste recycling at Guiyu, southeast China. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 8:21–33
Ma LQ, Rao GN (1997) Chemical fractionation of cadmium, copper, nickel and zinc in contaminated soils. J Environ Qual 26:259–264
Maliszewska-Kordybach B, Smreczak B, Klimkowicz-Pawlas A (2009) Concentrations, sources, and spatial distribution of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soils in the Eastern part of the EU: Poland as a case study. Sci Total Environ 407:3746–3753
Meijer SN, Ockenden WA, Sweetman A, Breivik K, Grimalt JO, Jones KC (2003) Global distribution and budget of PCBs and HCB in background surface soils: implications or sources and environmental processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:667–672
Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2004) Levels of PAHs in soil and vegetation samples from Tarragona County, Spain. Environ Pollut 132:1–11
Nemeth-Konda L, Füleky G, Morovjan G, Csokan P (2002) Sorption behavior of acetochlor, atrazine, carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere 48:545–552
Ren NQ, Que MX, Li YF, Liu YF, Wan XN, Xu DD, Sverko E, Ma J (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinese surface soils. Environ Sci Technol l41:3871–3876
Robinson BH (2009) E-waste: an assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ 408:183–191
Shen CF, Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Qiao M, Tang XJ, Yu CN, Shi DZ, Zhu YF, Shi JY, Chen XC, Setty K, Chen YX (2008) Identification of Ah receptor agonists in soil of E-waste recycling sites from Taizhou area in China. Environ Sci Technol 42:49–55
Shen CF, Chen YX, Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Yu CN, Qiao M, Xu M, Setty K, Zhang JY, Lin Q (2009) Dioxin-like compounds in agricultural soils near e-waste recycling sites from Taizhou area, China: chemical and bioanalytical characterization. Environ Int 35:50–55
Shepherd KD, Walsh MG (2002) Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:988–998
State Environmental Protection Administration of China, SEPA (1995) Environmental quality standards for soils (GB15618-1995). www.sepa.gov.cn/english/index.php3
Tang XJ, Shen CF, Shi DZ, Cheema SA, Khan MI, Zhang CK, Chen YX (2010) Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination in soil from Wenling: an emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area, China. J Hazard Mater 173:653–660
The Basel Action Network, Silicon Valley Toxics Coalition (2002) Exporting harm: the high-tech trashing of Asia. http://ban.org
UNEP (2009) Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal. United Nations Environment Programme. http://www.basel.int/
USEPA (1996a) Method 3540C: soxhlet extraction. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
USEPA (1996b) Method 3620B: Florisil cleanup. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
VROM (1994) Intervention values and target values: soil quality standards. Netherlands Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment. The Hague, Netherlands: Department of Soil Protection
Wang DG, Yang M, Jia HL, Zhou L, Li FY (2008) Levels, distributions and profiles of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface soils of Dalian, China. Chemosphere 73:38–42
Wei FS (1990) Background concentrations of elements in soils of China. Beijing
Wilcke W, Krauss M, Safronov G, Fokin AD, Kaupenjohann M (2006) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in soils of the Moscow region: concentrations and small-scale distribution along an urban-rural transect. Environ Pollut 141:327–335
Wong SC, Li XD, Zhang G (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 119:33–44
Wong MH, Wu SC, Deng WJ, Yu XZ, Luo Q, Leung AO, Wong CSC, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS (2007) Export of toxic chemicals—a review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ Pollut 149:131–140
Yin Y, Impellitteri CA, You SJ, Allen HE (2002) The importance of organic matter distribution and extract soil: solution ratio on the desorption of heavy metals from soils. Sci Total Environ 287:107–119
Yin CQ, Jiang X, Yang XL, Bian YR, Wang F (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils in the vicinity of Nanjing, China. Chemosphere 73:389–394
Yu XZ, Gao Y, Wu SC, Zhang HB, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2006) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils at Guiyu area of China, affected by recycling of electronic waste using primitive technologies. Chemosphere 65:1500–1509
Zhang CS (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142:501–511
Zhang JM, Ming H (2009) Eco-toxicity and metal contamination of paddy soil in an e-wastes recycling area. J Hazard Mater 165:744–750
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wong MH, Zhao QG, Zhang GL (2006) Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils. Environ Pollut 141:107–114
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wong MH, Zhao QG, Zhang GL (2007) Concentrations and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in the soils of Hong Kong. Geoderma 138:244–251
Zhao GF, Xu Y, Han GG, Ling B (2006) Biotransfer of persistent organic pollutants from a large site in China used for the disassembly of electronic and electrical waste. Environ Geochem Health 28:341–351
Zhao GF, Xu Y, Li W, Han GG, Ling B (2007) PCBs and OCPs in human milk and selected foods from Luqiao and Pingqiao in Zhejiang, China. Sci Total Environ 378:281–292
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Science and Technology Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (2009C13003), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (20080441246 and 200902636) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (40901153). The authors would like to acknowledge Professor Jianming Xu and other organizers of International Symposium of Molecular Environmental Soil Science at the Interfaces in the Earth’s Critical Zone (ISMESS 2009). Special thanks to Dr. Jianying Zhang of Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Zhejiang University for her great assistance during our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ji-Zheng He
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Shen, C., Chen, L. et al. Inorganic and organic pollution in agricultural soil from an emerging e-waste recycling town in Taizhou area, China. J Soils Sediments 10, 895–906 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0252-0