Abstract
Introduction
Regular exercise is confirmed as a lifestyle treatment option for all obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients. It has beneficial effects other than weight loss, although the mechanisms remain unclear. Autonomic function imbalance plays an important role in OSA, so that it is meaningful to observe the effect of exercise on autonomic function.
Methods
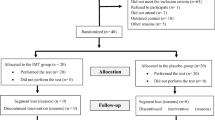
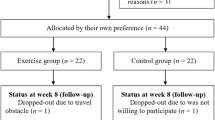
Seventy mild to moderate OSA patients were divided into two groups. The exercise group received a 12-week exercise program prescribed according to their first cardiopulmonary exercise tests, while the control group kept previous lifestyle. All patients underwent blood tests, cardiopulmonary exercise tests, and polysomnography studies at enrollment and at the 12-week’s follow-up.
Results
At the end of 12 weeks, three patients of the exercise group did not complete the program due to lack of adherence. The current study showed 12-week aerobic exercises could improve body mass index (27.6 ± 4.7 kg/m2 vs. 24.5 ± 4.2 kg/m2, P < 0.05), exercise capacities, apnea-hypopnea index (total AHI 20.2 ± 7.5 vs. 16.4 ± 5.2, P < 0.05; supine AHI 22.1 ± 6.3 vs. 18.3 ± 4.9, P < 0.05), average oxyhemoglobin saturation (AverSpO2), time/percentage SpO2 below 90%, and heart rate recovery (HRR) of OSA patients. Moreover, AverSpO2 change was significantly associated with HRR change in the exercise group.
Conclusions
Our findings suggested regular aerobic exercise had beneficial effects on body mass index, functional capacity, intermittent hypoxia, and parasympathetic tone of OSA patients, and whether parasympathetic tone modification plays a role in improving intermittent hypoxia or not deserves further exploration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laratta CR, Ayas NT, Povitz M, Pendharkar SR (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. CMAJ 189(48):E1481–E1488
Lévy P, Kohler M, McNicholas WT, Barbé F, McEvoy RD, Somers VK, Lavie L, Pépin JL (2015) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15015
Patinkin ZW, Feinn R, Santos M (2017) Metabolic consequences of obstructive sleep apnea in adolescents with obesity: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Child Obes 13(2):102–110
Schaefer CA, Adam L, Weisser-Thomas J, Pingel S, Vogel G, Klarmann-Schulz U, Nickenig G, Pizarro C, Skowasch D (2015) High prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin Res Cardiol 104(9):719–726
Turnbull CD (2018) Intermittent hypoxia, cardiovascular disease and obstructive sleep apnoea. J Thorac Dis 10(Suppl 1):S33–S39
Drager LF, McEvoy RD, Barbe F, Lorenzi-Filho G, Redline S, INCOSACT Initiative (International Collaboration of Sleep Apnea Cardiovascular Trialists) (2017) Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: lessons from recent trials and need for team science. Circulation 136(9):1840–1850
Dobrosielski DA, Papandreou C, Patil SP, Salas-Salvadó J (2017) Diet and exercise in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur Respir Rev 26(144). https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0110-2016
Awad KM, Malhotra A, Barnet JH, Quan SF, Peppard PE (2012) Exercise is associated with a reduced incidence of sleep-disordered breathing. Am J Med 125(5):485–490
Alves ES, Lira FS, Santos RV, Tufik S, de Mello MT (2011) Obesity, diabetes and OSAS induce of sleep disorders: exercise as therapy. Lipids Health Dis 10:148
Alves Eda S, Ackel-D'Elia C, Luz GP, Cunha TC, Carneiro G, Tufik S, Bittencourt LR, de Mello MT (2013) Does physical exercise reduce excessive daytime sleepiness by improving inflammatory profiles in obstructive sleep apnea patients? Sleep Breath 17(2):505–510
Andrade FM, Pedrosa RP (2016) The role of physical exercise in obstructive sleep apnea. J Bras Pneumol 42(6):457–464
Korkmaz B, Benbir Şenel G, Kızıltan ME, Karadeniz D (2016) Demonstration of sympathetic dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome by measuring sympathetic skin responses from the neck. Sleep Med 25:13–15
Hamaoka T, Murai H, Kaneko S, Usui S, Okabe Y, Tokuhisa H, Kato T, Furusho H, Sugiyama Y, Nakatsumi Y, Takata S, Takamura M (2016) Single-unit muscle sympathetic nerve activity reflects sleep apnea severity, especially in severe obstructive sleep apnea patients. Front Physiol 7:66
Gammoudi N, Ben Cheikh R, Saafi MA, Sakly G, Dogui M (2015) Cardiac autonomic control in the obstructive sleep apnea. Libyan J Med 10:26989
Maeder MT, Münzer T, Rickli H, Schoch OD, Korte W, Hürny C, Ammann P (2008) Association between heart rate recovery and severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med 9(7):753–761
Georgoulias P, Orfanakis A, Demakopoulos N, Xaplanteris P, Mortzos G, Vardas P, Karkavitsas N (2003) Abnormal heart rate recovery immediately after treadmill testing: correlation with clinical, exercise testing, and myocardial perfusion parameters. J Nucl Cardiol 10(5):498–505
Watanabe J, Thamilarasan M, Blackstone EH, Thomas JD, Lauer MS (2001) Heart rate recovery immediately after treadmill exercise and left ventricular systolic dysfunction as predictors of mortality: the case of stress echocardiography. Circulation 104(16):1911–1916
Libman E, Bailes S, Fichten CS, Rizzo D, Creti L, Baltzan M, Grad R, Pavilanis A, Tran DL, Conrod K, Amsel R (2017) CPAP treatment adherence in women with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Disord 5:1–8
Olsen S, Smith S, Oei T, Douglas J (2008) Health belief model predicts adherence to CPAP before experience with CPAP. Eur Respir J 32(3):710–717
Kline CE, Crowley EP, Ewing GB, Burch JB, Blair SN, Durstine JL, Davis JM, Youngstedt SD (2013) Blunted heart rate recovery is improved following exercise training in overweight adults with obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Cardiol 167(4):1610–1615
Kline CE, Crowley EP, Ewing GB, Burch JB, Blair SN, Durstine JL, Davis JM, Youngstedt SD (2011) The effect of exercise training on obstructive sleep apnea and sleep quality: a randomized controlled trial. Sleep 34(12):1631–1640
Aiello KD, Caughey WG, Nelluri B, Sharma A, Mookadam F, Mookadam M (2016) Effect of exercise training on sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med 116:85–92
Norman JF, Von Essen SG, Fuchs RH, McElligott M (2000) Exercise training effect on obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Res Online 3(3):121–129
Ackel-D'Elia C, da Silva AC, Silva RS, Truksinas E, Sousa BS, Tufik S, de Mello MT, Bittencourt LR (2012) Effects of exercise training associated with continuous positive airway pressure treatment in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 16(3):723–735
Servantes DM, Pelcerman A, Salvetti XM, Salles AF, de Albuquerque PF, de Salles FC, Lopes C, de Mello MT, Almeida DR, Filho JA (2012) Effects of home-based exercise training for patients with chronic heart failure and sleep apnoea: a randomized comparison of two different programmes. Clin Rehabil 26(1):45–57
Jurysta F, Kempenaers C, Lanquart JP, Noseda A, van de Borne P, Linkowski P (2013) Long-term CPAP treatment partially improves the link between cardiac vagal influence and delta sleep. BMC Pulm Med 13(1):1–11
Chrysostomakis SI, Simantirakis EN, Schiza SE, Karalis IK, Klapsinos NC, Siafakas NM, Vardas PE (2006) Continuous positive airway pressure therapy lowers vagal tone in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome. Hell J Cardiol 47(1):13–20
Maser RE, Lenhard MJ, Rizzo AA, Vasile AA (2008) Continuous positive airway pressure therapy improves cardiovascular autonomic function for persons with sleep-disordered breathing. Chest 133:86–91
Pinto P, Bárbara C, Montserrat JM, Patarrão RS, Guarino MP, Carmo MM, Macedo MP, Martinho C, Dias R, Gomes MJ (2013) Effects of CPAP on nitrate and norepinephrine levels in severe and mild-moderate sleep apnea. BMC Pulm Med 13:13
Lachman S, Terbraak MS, Limpens J, Jorstad H, Lucas C, Scholte Op Reimer W, Boekholdt SM, Ter Riet G, Peters RJG (2018) The prognostic value of heart rate recovery in patients with coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am Heart J 199:163–169
Peçanha T, Silva-Júnior ND, Forjaz CL (2014) Heart rate recovery: autonomic determinants, methods of assessment and association with mortality and cardiovascular diseases. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 34(5):327–339
Mohammed J, Derom E, Van Oosterwijck J, Da Silva H, Calders P (2018) Evidence for aerobic exercise training on the autonomic function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a systematic review. Physiotherapy 104(1):36–45
Bhati P, Shenoy S, Hussain ME (2018) Exercise training and cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Syndr 12(1):69–78
Dimopoulos S (2015) Abnormal heart rate recovery in patients with heart failure: an important target for exercise training treatment. Anatol J Cardiol 15(9):735–736
Chaidas K, Tsaoussoglou M, Theodorou E, Lianou L, Chrousos G, Kaditis AG (2014) Poincare plot width, morning urine norepinephrine levels, and autonomic imbalance in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Pediatr Neurol 51(2):246–251
Levendowski DJ, Zack N, Rao S, Wong K, Gendreau M, Kranzler J, Zavora T, Westbrook PR (2009) Assessment of the test-retest reliability of laboratory polysomnography. Sleep Breath 13(2):163–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Huan Zheng received a research grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Award Number: 81400206). Other authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee Review Board of Tongji Hospital (Shanghai, China).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Liu, Y., Zheng, H. et al. Effects of 12 weeks of regular aerobic exercises on autonomic nervous system in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients. Sleep Breath 22, 1189–1195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1736-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1736-1