Abstract
Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) merits increasing attention as cardiovascular risk factor. Whereas carotid and coronary artery disease have been associated with OSA, occurrence of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in OSA remains undefined.
Methods
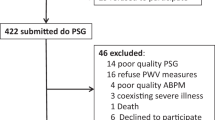
We screened 100 patients with suspected OSA for PAD. After polysomnography, each patient underwent standardized angiological testing including ankle-brachial index (ABI), central pulse wave velocity, pulse wave index and duplex sonography.
Results
Among total study population, PAD prevalence accounted for 88 %, of those 68 % had asymptomatic plaques and 20 % were symptomatic Fontaine ≥IIa. In confirmed OSA, prevalence raised up to 98 %. Except for smoking habits, distribution of established risk factors did not differ between OSA groups (patients without, mild, intermediate and severe OSA). Presence of plaque, Fontaine PAD stages and intermittent claudication exhibited significant gain with increasing AHI. A logistic regression model revealed that age (OR = 1.199, 95 % CI [1.066; 1.348]) and the logarithmically transformed AHI (OR = 5.426, 95 % CI [1.068; 27.567]) had the strongest influence on plaque presence. Central pulse wave velocity as marker of arterial stiffness was positively correlated with AHI.
Conclusion
OSA is associated with a high prevalence of PAD. This implies substantial disease´s under-recognition and a presumable atherogenic role of OSA in the pathogenesis of PAD. However, vasoprotective impact of OSA treatment remains to be determined.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Punjabi NM (2008) The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnoea. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:136–143
Narkiewicz K, Somers VK (2003) Sympathetic nerve activity in obstructive sleep apnoea. Acta Physiol Scand 177:385–390
Okcay A, Somers VK, Caples SM (2008) Obstructive sleep apnoea and hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 10:549–555
Narkiewicz K, Wolf J, Lopez-Jimenez F, Somers VK (2005) Obstructive sleep apnoea and hypertension. Curr Cardiol Rep 7:435–440
Jelic S, Padeletti M, Kawut SM et al (2008) Inflammation, oxidative stress, and repair capacity of the vascular endothelium in obstructive sleep apnoea. Circulation 117:2270–2278
Davignon J, Ganz P (2004) Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 109:III27–32
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Lanfranchi P et al (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Circulation 105:2462–2464
Svatikova A, Wolk R, Shamsuzzaman AS, Kara T, Olson EJ, Somers VK (2003) Serum amyloid a in obstructive sleep apnoea. Circulation 108:1451–1454
Ohga E, Tomita T, Wada H, Yamamoto H, Nagase T, Ouchi Y (2003) Effects of obstructive sleep apnoea on circulating ICAM-1, IL-8, and MCP-1. J Appl Physiol 94:179–184
Knutson KL, Van Cauter E (2008) Associations between sleep loss and increased risk of obesity and diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1129:287–304
Calvin AD, Albuquerque FN, Lopez-Jimenez F, Somers VK (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea, inflammation, and the metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 7:271–278
Tuleta I, Pabst S, Juergens UR, Nickenig G, Skowasch D (2011) Obstructive sleep apnoea as a risk factor for atherosclerosis—implication for preventive and personalised treatment. EPMA J 2:39–47
Mooe T, Franklin KA, Holmstrom K, Rabben T, Wiklund U (2001) Sleep-disordered breathing and coronary artery disease: long-term prognosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1910–1913
Schafer H, Koehler U, Ewig S, Hasper E, Tasci S, Luderitz B (1999) Obstructive sleep apnoea as a risk marker in coronary artery disease. Cardiology 92:79–84
Somers VK, White DP, Amin R et al (2008) Sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease: an American Heart Association/American College Of Cardiology Foundation Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association Council for High Blood Pressure Research Professional Education Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke Council, and Council On Cardiovascular Nursing. In collaboration with the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Center on Sleep Disorders Research (National Institutes of Health). Circulation 118:1080–1111
Arias MA, Garcia-Rio F, Alonso-Fernandez A, Mediano O, Martinez I, Villamor J (2005) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome affects left ventricular diastolic function: effects of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in men. Circulation 112:375–383
Altekin RE, Yanikoglu A, Karakas MS et al (2012) Assessment of left atrial dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea patients with the two dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. Clin Res Cardiol 101:403–413
Dimitradis Z, Wiemer M, Scholtz W et al (2013) Sleep-disordered breathing in patients undergoing transfemoral aortic valve implantation for severe aortic stenosis. Clin Res Cardiol 102:895–903
Nakamura S, Asai K, Kubota Y et al (2014) Impact of sleep-disordered breathing and efficacy of positive airway pressure on mortality in patients with chronic heart failure and sleep disordered breathing: a meta-analysis. Clin Res Cardiol 103:805–815
Utriainen KT, Airaksinen JK, Polo O et al (2014) Unrecognised obstructive sleep apnoea is common in severe peripheral arterial disease. Eur Respir J 41:616–620
Hammerstingl C, Schueler R, Wiesen M et al (2012) Effects of untreated obstructive sleep apnoea on left and right ventricular myocardial function. Int J Cardiol 155:465–469
Hammerstingl C, Schueler R, Wiesen M et al (2013) Impact of untreated obstructive sleep apnoea on left- and right ventricular myocardial function and effects of CPAP therapy. PLoS One 8:e76352
Hein H, Raschke F, Kohler D, Mayer G, Peter JH, Ruhle KH (2001) Guideline on diagnostics and treatment of sleep-related respiratory disorders in adults. Pneumologie 55:339–342
Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ Jr et al (2009) Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnoea in adults. J Clin Sleep Med 5:263–276
Berry RB, Budhiraja R, Gottlieb DJ et al (2012) Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med 8:597–619
Tendera M, Aboyans V, Bartelink ML et al (2011) ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries: the Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 32:2851–2906
Katakam R, Townsend RR (2006) What’s in a pulse? J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 8:140–141
Criqui MH (2001) Peripheral arterial disease-epidemiological aspects. Vasc Med 6:3–7
Diehm C, Schuster A, Allenberg JR et al (2004) High prevalence of peripheral arterial disease and co-morbidity in 6880 primary care patients: cross-sectional study. Atherosclerosis 172:95–105
Utriainen KT, Airaksinen JK, Polo O et al (2014) Sleep apnoea is associated with major cardiac events in peripheral arterial disease. Eur Respir J 43:1652–1660
Phillips BG, Narkiewicz K, Pesek CA, Haynes WG, Dyken ME, Somers VK (1999) Effects of obstructive sleep apnea on endothelin-1 and blood pressure. J Hypertens 17:61–66
Kraiczi H, Caidahl K, Samuelsson A, Peker Y, Hedner J (2001) Impairment of vascular endothelial function and left ventricular filling: association with the severity of apnea-induced hypoxemia during sleep. Chest 119:1085–1091
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Dyugovskaya L, Lavie P, Lavie L (2002) Increased adhesion molecules expression and production of reactive oxygen species in leukocytes of sleep apnea patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:934–939
El Solh AA, Akinnusi ME, Baddoura FH, Mankowski CR (2007) Endothelial cell apoptosis in obstructive sleep apnea: a link to endothelial dysfunction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:1186–1191
Nieto FJ, Herrington DM, Redline S, Benjamin EJ, Robbins JA (2004) Sleep apnea and markers of vascular endothelial function in a large community sample of older adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:354–360
Smith SC Jr, Milani RV, Arnett DK et al (2004) Atherosclerotic vascular disease conference: writing group II: risk factors. Circulation 109:2613–2616
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1318–1327
Seetho IW, Parker RJ, Craig S, Duffy N, Hardy KJ, Wilding JP (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with increased arterial stiffness in severe obesity. J Sleep Res 23(6):700–708
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the help of Karin Springmann for her excellent technical support and Sonotechnik Austria for providing us with the AngE Pro8®.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. A. Schaefer, L. Adam, C. Pizarro, and D. Skowasch contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaefer, C.A., Adam, L., Weisser-Thomas, J. et al. High prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin Res Cardiol 104, 719–726 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0834-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0834-3