Abstract
Objectives
Hyoid expansion is a novel procedure that was developed to widen and stabilize the lateral walls of the hypopharynx in order to improve obstructive sleep apnea. This study was conducted to evaluate the safety, efficacy and feasibility of hyoid expansion.
Study design
A prospective, non-randomized multicenter pilot study with a follow-up of 6 months was conducted.
Method
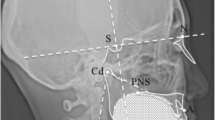
An implantable device (the Air-Frame system) was used to surgically expand the hyoid bone. Subjective and objective outcome measures were evaluated.
Results
The procedure was successfully performed in all patients without technical adverse events. There were three clinical adverse events, and tolerance was good. Although there was a significant improvement in snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness, there was no objective improvement of the apnea–hypopnea index as measured by polysomnography.
Conclusion
Hyoid expansion did not provide objective improvement of obstructive outcome measures in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Naegele B, Pepin J, Lévy P, Bonnet C, Pellat J, Feuerstein C (1998) Cognitive executive dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) after CPAP treatment. Sleep 21:392–397
Pichel F, Zamarron C, Magan F, Rodriguez J (2006) Sustained attention measurements in obstructive sleep apnea and risk of traffic accidents. Respir Med 100:1020–1027
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2005) International classification of sleep disorders. In: Diagnostic and Coding Manual, Second Ed. AASM, Westchester
Yaggi K, Concato J, Kernan W, Lichtman J, Brass L, Mohsenin V (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med 353:2034–2041
Marin J, Carrizo S, Vincente E, Agusti A (2005) Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea with or without treatment with continuous airway pressure: an observational study. Lancet 365:1046–1053
American Sleep Disorders Association (1996) An American Sleep Disorders Association report. Practice parameters for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults: the efficacy of surgical modifications of the upper airway. Sleep 19:152–155
Kribbs N, Pack A, Kline L, Smith P, Schwartz A, Schubert N, Redline S, Henry J, Getsy G, Dinges D (1993) Objective measurement of patterns of nasal CPAP use by patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am Rev Respir Dis 147:887–895
Santamaria J, Iranzo A, Ma Montserrat J, de Pablo J (2007) Persistent sleepiness in CPAP treated obstructive sleep apnea patients: evaluation and treatment. Sleep Med Rev 11:195–207
Sher A, Schechtman K, Piccirillo J (1996) The effect of surgical modifications of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 19:156–177
Kezirian E, Goldberg A (2006) Hypopharyngeal surgery in obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:206–213
Schwab R, Gupta K, Gefter W, Metzger L, Hoffman E, Pack A (1995) Upper airway and soft tissue anatomy in normal subjects and patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Significance of the lateral pharyngeal walls. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1673–1689
Iwanaga K, Hasegawa K, Shibata N, Kawakatsu K, Akita Y, Suzuki K, Yagisawa M, Nishimura T (2003) Endoscopic examination of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients during drug-induced sleep. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 550:36–40
Patton T, Thawley S, Waters R, Vandermeer P, Ogura J (1983) Expansion hyoidplasty: a potential surgical procedure designed for selected patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Experimental canine results. Laryngoscope 93:1387–1396
Croft C, Pringle M (1991) Sleep nasendoscopy: a technique of assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 16:504–509
Gliklich R, Wang P (2002) Validation of the Snore Outcomes Survey for patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:819–824
Johns M (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Ahmadi N, Shapiro G, Chung S, Shapiro C (2009) Clinical diagnosis of sleep apnea based on single night of polysomnography vs. 2 nights of polysomnography. Sleep Breath 13:221–226
Hessel N, Vries N (2004) Increase in apnea-hypopnea index after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: analysis of failure. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:682–685
Rombaux P, Hamoir M, Bertrand B, Aubert G, Liistro G, Rodenstein D (2003) Postoperative pain and side effects after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty, and radiofrequency tissue volume reduction in primary snoring. Laryngoscope 113:2169–2173
Li K, Guilleminault C, Riley R, Powell N (2002) Obstructive sleep apnea and maxillomandibular advancement: an assessment of airway changes using radiographic and nasopharyngoscopic examinations. J Oral Maxillo Surg 60:526–530
Villa M, Rizzoli A, Miano S, Malagola C (2011) Efficacy of rapid maxillary expansion in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: 36 months of follow-up. Sleep Breath 15:179–184
Chervin RD, Aldrich MS (1999) The Epworth Sleepiness Scale may not reflect objective measures of sleepiness or sleep apnea. Neurology 52:125–131
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by Aspire Medical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, and was presented at the 6th European Congress of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Vienna, June 30, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamans, E., Stuck, B.A., de Vries, N. et al. Hyoid expansion as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea: a pilot study. Sleep Breath 17, 195–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0673-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0673-7