Abstract
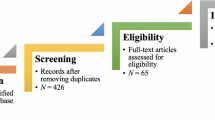
This study provides a detailed analysis of the "green gap" as it is presented in existing literature. It covers the definition of the gap, the reasons behind it, and the proposed solutions. Using a systematic literature review approach, the researchers refined their search criteria and selected 151 relevant articles for further analysis. The causes of the green gap were classified into four categories: psychological, demographic, social and cultural, and elements of the marketing mix. The study also explored different strategies to address each of these categories. The discussion and conclusion sections of the study provide insightful observations about the green gap, its implications, and future research directions. This comprehensive analysis contributes to furthering our understanding of the green gap and provides a foundation for future interventions aimed at bridging this divide.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Since this paper is a review paper, no specific data has been used. All the referred papers are given as references.
References
Adrita UW, Mohiuddin MF (2020) Impact of opportunity and ability to translate environmental attitude into ecologically conscious consumer behavior. J Mark Theory Pract 28(2):173–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/10696679.2020.1716629
Agag G, Brown A, Hassanein A, Shaalan A (2020) Decoding travellers’ willingness to pay more for green travel products: closing the intention–behaviour gap. J Sustain Tour 28(10):1551–1575. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1745215
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Org Behav Hum Decis Process 50(2):179–211
Akehurst G, Afonso C, Gonçalves HM (2012) Re-examining green purchase behaviour and the green consumer profile: new evidences. Manag Decis 50(5):972–988. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251741211227726
Alagarsamy S, Mehrolia S, Mathew S (2021) How green consumption value affects green consumer behaviour: the mediating role of consumer attitudes towards sustainable food logistics practices. Vision 25(1):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972262920977986
Albayrak T, Aksoy Ş, Caber M (2011) The effect of environmental concern and scepticism on green purchase behaviour. Mark Intell Plan 31(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634501311292902
Al-Majali MM, Tarabieh SMZA (2020) Effect of internal green marketing mix elements on customers’ satisfaction in Jordan: Mu’tah University students. Jordan J Bus Adm 16(2):411–434. https://doi.org/10.35516/0338-016-002-004
Ames DL, Fiske ST (2013) Intentional harms are worse, even when they’re not. Psychol Sci 24(9):1755–1762. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613480507
Amin S, Tarun MT (2021) Effect of consumption values on customers’ green purchase intention: a mediating role of green trust. Soc Responsib J 17(8):1320–1336. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-05-2020-0191
Ammendolia J, Saturno J, Brooks AL, Jacobs S, Jambeck JR (2021) An emerging source of plastic pollution: Environmental presence of plastic personal protective equipment (PPE) debris related to COVID-19 in a metropolitan city. Environ Pollut 269:116160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116160
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, Echebarria C, Barrutia JM (2017) Organic label’s halo effect on sensory and hedonic experience of wine: a pilot study. J Sens Stud 32(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/joss.12243
Apipuchayakul N, Vassanadumrongdee S (2020) Factors affecting the consumption of energy-efficient lighting products: exploring purchase behaviors of Thai consumers. Sustainability (switzerland) 12(12):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12124887
Arifin MR, Raharja BS, Nugroho A (2023) Do young Muslim choose differently? Identifying consumer behavior in Halal industry. J Islamic Mark 14(4):1032–1057. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-02-2021-0049
Ballester ED, Manuera-Aleman JL (2001) Brand trust in the context of consumer loyalty. Euro J Mark 35(12):309–0566
Bamberg S (2003) How does environmental concern influence specific environmentally related behaviors? A new answer to an old question. J Environ Psychol 23(1):21–32
Bamberg S (2013) Changing environmentally harmful behaviors: a stage model of self-regulated behavioral change. J Environ Psychol 34:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.01.002
Barbarossa C, Pastore A (2015) Why environmentally conscious consumers do not purchase green products: a cognitive mapping approach. Qual Mark Res 18(2):188–209. https://doi.org/10.1108/QMR-06-2012-0030
Basha MB, Lal D (2019) Indian consumers’ attitudes towards purchasing organically produced foods: an empirical study. J Clean Prod 215:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.098
Berenguer J (2010) The effect of empathy in environmental moral reasoning. Environ Behav 42(1):110–134
Berkowitz L, Lutterman KG (1968) The traditional socially responsible personality. Public Opin Q 32(2):169–185
Bernardes JP, Ferreira F, Marques AD, Nogueira M (2018) “ Do as i say, not as i do”—a systematic literature review on the attitude-behaviour gap towards sustainable consumption of Generation y. IOP Conf Series Mater Sci Eng 459(1):5–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/459/1/012089
Biswas A (2017) A consumption value-gap analysis for sustainable consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(8):7714–7725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8355-9
Bodur HO, Duval KM, Grohmann B (2015) Will you purchase environmentally friendly products? Using prediction requests to increase choice of sustainable products. J Bus Eth 129(1):59–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2143-6
Boncinelli F, Dominici A, Gerini F, Marone E (2021) Insights into organic wine consumption: behaviour, segmentation and attribute non-attendance. Agri Food Econ. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40100-021-00176-6
Cai Z, Xie Y, Aguilar FX (2017) Eco-label credibility and retailer effects on green product purchasing intentions. Forest Pol Econ 80:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2017.04.001
Caliskan A, Celebi D, Pirnar I (2020) Determinants of organic wine consumption behavior from the perspective of the theory of planned behavior. Int J Wine Bus Res 33(3):360–376. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJWBR-05-2020-0017
Carlson J, Rosenberger PJ, Rahman MM (2016) A Hierarchical model of perceived value of group-oriented travel experiences to major events and its influences on satisfaction and future group-travel intentions. J Travel Tour Mark 33(9):1251–1267. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2015.1117407
Carrión Bósquez NG, Arias-Bolzmann LG, Martínez Quiroz AK (2023) The influence of price and availability on university millennials’ organic food product purchase intention. Br Food J 125(2):536–550. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-12-2021-1340
Caruana R (2008) A sociological perspective of consumption morality. J Consum Behav 50(October):35–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.222
Casaló LV, Escario JJ (2018) Heterogeneity in the association between environmental attitudes and pro-environmental behavior: a multilevel regression approach. J Clean Prod 175:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.237
Cerri J, Testa F, Rizzi F (2018) The more I care, the less I will listen to you: how information, environmental concern and ethical production influence consumers ’ attitudes and the purchasing of sustainable products. J Clean Prod 175:343–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.054
Champniss G, Wilson HN, Macdonald EK, Dimitriu R (2016) No I won’t, but yes we will: driving sustainability-related donations through social identity effects. Tech Forecast Soc Change 111(I):317–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.03.002
Chang S, Hu B, He X (2019) Supply chain coordination in the context of green marketing efforts and capacity expansion. Sustainability (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205734
Chawla L (1998) Significant life experiences revisited: A review of research on sources of environmental sensitivity. J Environ Educ 29(3):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958969809599114
Cheah WKA, Aigbogun O (2022) Exploring attitude-behaviour inconsistencies in organic food consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Klang Valley. Malaysia. Clean Respon Consump 7:100077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clrc.2022.100077
Chekima B, Oswald AI, Wafa SAWSK, Chekima K (2017) Narrowing the gap: factors driving organic food consumption. J Clean Prod 166:1438–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.086
Chekima B, Chekima K, Chekima K (2019) Understanding factors underlying actual consumption of organic food: the moderating effect of future orientation. Food Qual Prefer 74:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2018.12.010
Chéron E, Sudbury-Riley L, Kohlbacher F (2022) In pursuit of happiness: disentangling sustainable consumption, consumer alienation, and social desirability. J Consum Policy 45(2):149–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10603-021-09498-w
Cheung MFY, To WM (2019) An extended model of value-attitude-behavior to explain Chinese consumers’ green purchase behavior. J Retail Consum Serv 50(December 2018):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2019.04.006
Chi CGQ, Ouyang Z, Lu L, Zou R (2021) Drinking “green”: what drives organic wine consumption in an emerging wine market. Cornell Hosp Q 62(4):516–534. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965520943193
Chowdhury P, Samuel MS (2014) Artificial neural networks: A tool for understanding green consumer behavior. Mark Intell Plan 32(5):552–566. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-06-2013-0099
Chu KWK (2020) The green gap of high-involvement purchasing decisions: an exploratory study. Asian J Bus Eth 9(2):371–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13520-020-00115-6
Claudy MC, Peterson M, O’Driscoll A (2013) Understanding the attitude-behavior gap for renewable energy systems using behavioral reasoning theory. Journal of Macromarketing 33(4):273–287. https://doi.org/10.1177/0276146713481605
Costa Pinto D, Nique WM, Maurer Herter M, Borges A (2016) Green consumers and their identities: how identities change the motivation for green consumption. Int J Consum Stud 40(6):742–753. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12282
D’amico M, Di Vita G, Chinnici G, Pappalardo G, Pecorino B.(2014) Short food supply chain and locally produced wines: factors affecting consumer behavior. Ital J Food Sci 26(3)
de Barcellos MD, Krystallis A, de Melo Saab MS, Kügler JO, Grunert KG (2011) Investigating the gap between citizens’ sustainability attitudes and food purchasing behaviour: empirical evidence from Brazilian pork consumers. Int J Consum Stud 35(4):391–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2010.00978.x
De Medeiros JF, Ribeiro JLD, Cortimiglia MN (2016) Influence of perceived value on purchasing decisions of green products in Brazil. J Clean Prod 110:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.100
Deliana Y, Rum IA (2019) How does perception on green environment across generations affect consumer behaviour? A neural network process. Int J Consum Stud 43(4):358–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12515
Dhir A, Sadiq M, Talwar S, Sakashita M, Kaur P (2021) Why do retail consumers buy green appare? A knowledge-attitude-behaviour-context perspective. J Retail Consum Serv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102398
Dhir A, Talwar S, Sadiq M, Sakashita M, Kaur P (2021b) Green apparel buying behaviour: a stimulus–organism–behaviour–consequence (SOBC) perspective on sustainability-oriented consumption in Japan. Bus Strateg Environ 30(8):3589–3605. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2821
Diamantopoulos A, Schlegelmilch BB, Sinkovics RR, Bohlen GM (2003) Can socio-demographics still play a role in profiling green consumers? A review of the evidence and an empirical investigation. J Bus Res 56(6):465–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-2963(01)00241-7
Dickson MA (2000) Personal values, beliefs, knowledge, and attitudes relating to intentions to purchase apparel from socially responsible businesses. Cloth Text Res J 18(1):19–30
Dubois MV, Benjamin M, Magalie D, Schlich P (2023) Hedonic valence of descriptive sensory terms as an indirect measure of liking: A preliminary study with red wines. Food Quality and Preference. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2023.104861
Duong CD (2021) Big Five personality traits and green consumption: bridging the attitude-intention-behavior gap. Asia Pacific J Market Log. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-04-2021-0276
Durif F, Roy J, Boivin C (2012) Could perceived risks explain the “green gap” in green product consumption? Electron Green J. https://doi.org/10.5070/g313310923
Echegaray F, Hansstein FV (2017) Assessing the intention-behavior gap in electronic waste recycling: the case of Brazil. J Clean Prod 142:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.064
ElHaffar G, Durif F, Dubé L (2020) Towards closing the attitude-intention-behavior gap in green consumption: a narrative review of the literature and an overview of future research directions. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122556
Elsantil Y (2021) Antecedents of green purchasing behavior in the Arabic gulf. Social Marketing Quarterly 27(2):133–149
Essiz O, Yurteri S, Mandrik C, Senyuz A (2023) Exploring the value-action gap in green consumption: roles of risk aversion, subjective knowledge, and gender differences. J Glob Mark 36(1):67–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/08911762.2022.2116376
Fahy F (2005) The right to refuse: Public attitudes and behaviour towards waste in the west of Ireland. Local Environ 10(6):551–569. https://doi.org/10.1080/13549830500321618
Farjam M, Nikolaychuk O, Bravo G (2019) Experimental evidence of an environmental attitude-behavior gap in high-cost situations. Ecol Econ 166(March):106434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106434
Fauzi N, Yakob R (2019) The influence of demographic and herbal characteristics on purchase decisions of zingiberacea familia: an exploration in kota bharu, kelantan society. Int J Recent Technol Eng 8(9):1058–1062. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijrte.B1139.0982S919
Fraj-Andrés E, Herrando C, Lucia-Palacios L, Pérez-López R (2023) Intention versus behaviour: integration of theories to help curb food waste among young Spanish consumers. Br Food J 125(2):570–586. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-09-2021-1042
Fu L, Sun Z, Zha L, Liu F, He L, Sun X, Jing X (2020) Environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior within China’s road freight transportation industry: moderating role of perceived policy effectiveness. J Clean Prod 252:119796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119796
Fukukawa K, Shafer WE, Lee GM (2007) Values and attitudes toward social and environmental accountability: a study of MBA students Kyoko Fukukawa. J Bus Eth. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-005-3893-y
Gahlot Sarkar J, Sarkar A, Yadav R (2019) Brand it green: young consumers’ brand attitudes and purchase intentions toward green brand advertising appeals. Young Consum 20(3):190–207. https://doi.org/10.1108/YC-08-2018-0840
Gan C, Wee HY, Ozanne L, Kao TH (2008) Consumers' purchasing behavior towards green products in New Zealand. Innovative Marketing. 4(1).
Gao J, Zhao J, Wang J, Wang J (2021) The influence mechanism of environmental anxiety on pro-environmental behaviour: The role of self-discrepancy. Int J Consum Stud 45(1):54–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12604
Gatersleben B, Murtagh N, Abrahamse W (2014) Values, identity and pro-environmental behaviour. Contemp Soc Sci 9(4):374–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/21582041.2012.682086
Gleim M, Lawson SJ (2014) Spanning the gap: An examination of the factors leading to the green gap. J Consum Mark 31(6–7):503–514. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-05-2014-0988
Gleim MR, Smith JS, Andrews D, Cronin JJ (2013) Against the green: a multi-method examination of the barriers to green consumption. J Retail 89(1):44–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2012.10.001
Goodarzi S, Masini A, Aflaki S, Fahimnia B (2021) Right information at the right time: reevaluating the attitude—behavior gap in environmental technology adoption. Int J Prod Econ 242(August):108278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108278
Gordon R, Carrigan M, Hastings G (2011) A framework for sustainable marketing. Mark Theory 11(2):143–163. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470593111403218
Gough D (2007) Weight of evidence: a framework for the appraisal of the quality and relevance of evidence. Appl Pr Based Res 22(2):213–228
Grimmer M, Miles MP (2017) With the best of intentions: a large sample test of the intention-behaviour gap in pro-environmental consumer behaviour. Int J Consum Stud 41(1):15
Grimmer M, Kilburn AP, Miles MP (2016) The effect of purchase situation on realized pro-environmental consumer behavior. J Bus Res 69(5):1582–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.10.021
Gruber V, Schlegelmilch BB (2014) How techniques of neutralization legitimize norm- and attitude-inconsistent consumer behavior. J Bus Ethics 121(1):29–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-013-1667-5
Gupta S, Ogden DT (2009) To buy or not to buy? A social dilemma perspective on green buying. J Consum Mark 26(6):378–393. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363760910988201
Gupta K, Singh N (2020) Consumer attitude towards sustainable living in India. Soc Responsib J 17(3):301–320. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-03-2018-0081
Haj-Salem N, Muhammad Ishtiaq I, Ali R (2022) How anticipated pride and guilt influence green consumption in the Middle East: the moderating role of environmental consciousness. J Retail Consum Serv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103062
Hartanto BW, Triastianti RD (2022) Eco-friendly masks preferences during COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. Clean Responsib Consum 4(December 2021):100044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clrc.2021.100044
Haq G, Paul A (2013) Environmentalism since 1945. In: Environmentalism since 1945. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203803875
He Z, Zhou Y, Wang J, Li C, Wang M, Li W (2021) The impact of motivation, intention, and contextual factors on green purchasing behavior: new energy vehicles as an example. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1249–1269. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2682
Hesse E, Mikulan E, Decety J, Sigman M, Del Carmen Garcia M, Silva W, Ciraolo C, Vaucheret E, Baglivo F, Huepe D, Lopez V, Manes F, Bekinschtein TA, Ibanez A (2016) Early detection of intentional harm in the human amygdala. Brain 139(1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv336
Higgins J, Green S (2008) Chapter 22: overview of reviews. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.fmatter/summary
Hossain I, Nekmahmud M, Fekete-Farkas M (2022) How do environmental knowledge, eco-label knowledge, and green trust impact consumers’ pro-environmental behaviour for energy-efficient household appliances? Sustainability 14(11):6513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116513
Huddart E, Beckley TM, Mcfarlane BL, Kennedy EH, Beckley TM, Mcfarlane BL (2009) Society for human ecology why we don’t " walk the talk ": understanding the environmental values/behaviour gap in Canada published by : society for human ecology stable URL : http://www.jstor.org/stable/24707539 Why We Don ’ t " walk the talk ": under. Res Hum Ecol 16(2):151–160
Hustvedt G, Dickson MA (2009) Consumer likelihood of purchasing organic cotton apparel: Influence of attitudes and self-identity. J Fash Mark Manag 13(1):49–65. https://doi.org/10.1108/13612020910939879
Hyun J, Fairhurst A (2018) Understanding consumers’ purchasing behavior of ethnically disparate products. J Consum Behav 17(1):e114–e126. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1691
Inzlicht M, Bartholow BD, Hirsh JB (2015) Emotional foundations of cognitive control. Trends Cogn Sci 19(3):126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2015.01.004
Jaini A, Quoquab F, Mohammad J, Hussin N (2020) “I buy green products, do you…?”: The moderating effect of eWOM on green purchase behavior in Malaysian cosmetics industry. Int J Pharm Healthcare Mark 14(1):89–112. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPHM-02-2019-0017
Jamal FN, Othman NA, Nizam NZ, Jelita A, Rohmah W, Dzakiyullah NR (2022) Green marketing: reviewing aspect of communication tools. Int J Sustain Dev Plann 17(4):1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijsdp.170405
Joshi Y, Rahman Z (2016) Predictors of young consumer’s green purchase behaviour. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal 27(4):452–472. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-05-2015-0091
Khan K, Hameed I, Akram U, Hussainy SK (2023) Do normative triggers and motivations influence the intention to purchase organic food? an application of the goal-framing theory. Bri Food J 125(3):886–906. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-11-2021-1194
Kim SS, Timothy DJ, Hwang J (2011) Understanding Japanese tourists’ shopping preferences using the Decision Tree Analysis method. Tour Manag 32(3):544–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2010.04.008
Koksal MH (2019) Food choice motives for consumers in Lebanon: a descriptive study. Br Food J 121(11):2607–2619. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-09-2018-0580
Kollmuss A, Agyeman J (2002) Mind the Gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ Educ Res 8(3):239–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504620220145401
Kumar B, Manrai AK, Manrai LA (2017) Purchasing behaviour for environmentally sustainable products: a conceptual framework and empirical study. J Retail Consum Serv 34(September 2016):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2016.09.004
Lan G, Ma Z, Cao J, Zhang H (2009) A comparison of personal values of chinese accounting practitioners and students. J Bus Ethics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-008-9829-6
Langenbach BP, Berger S, Baumgartner T, Knoch D (2020) Cognitive resources moderate the relationship between pro-environmental attitudes and green behavior. Environ Behav 52(9):979–995. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013916519843127
Laroche M, Bergeron J, Barbaro-forleo G (2001) Targetting Consumers Who Are Likely To Pay More for Ethical Products. Journal of Consumer Marketing 18(6):503–520
Lee H, Cheon H (2018) Exploring Korean Consumers’ Attitudes Toward Ethical Consumption Behavior in the Light of Affect and Cognition. Journal of International Consumer Marketing 30(2):98–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/08961530.2017.1376241
Lehner M (2015) Retail store influence on sustainable consumption behaviour. Int J Qual Serv Sci 7(4):404–423. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJQSS-05-2014-0031
Li CY, Fang YH (2022) Go green, go social: exploring the antecedents of pro-environmental behaviors in social networking sites beyond norm activation theory. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114265
Liu H, McCarthy B (2023) Sustainable lifestyles, eating out habits and the green gap: a study of food waste segments. Asia Pac J Mark Logist 35(4):920–943. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-07-2021-0538
Liu P, Teng M, Han C (2020) How does environmental knowledge translate into pro-environmental behaviors?: The mediating role of environmental attitudes and behavioral intentions. Sci Total Environ 728:138126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138126
Lower-Hoppe LM, Aicher TJ, Baker BJ (2023) ntention–behaviour relationship within community running clubs: examining the moderating influence of leisure constraints and facilitators within the environment}, author={}, journal={. World Leisure J 65(1):3–27
Lu L, Chi CGQ, Zou R (2019) Determinants of Chinese consumers’ organic wine purchase. Int J Contemp Hospital Manag 31(9):3761–3778. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-02-2019-0118
Lund TB, Andersen LM, O’Doherty Jensen K (2013) The emergence of diverse organic consumers: Does a mature market undermine the search for alternative products? Soc Rural 53(4):454–478. https://doi.org/10.1111/soru.12022
Luo B, Sun Y, Shen J, Xia L (2020) How does green advertising skepticism on social media affect consumer intention to purchase green products? J Consum Behav 19(4):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1818
Mai R, Hoffmann S, Lasarov W, Buhs A (2019) Ethical products = less strong: how explicit and implicit reliance on the lay theory affects consumption behaviors. J Bus Ethics 158(3):659–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-017-3669-1
Mann S, Ferjani A, Reissig L (2012) What matters to consumers of organic wine? Br Food J 114(2):272–284. https://doi.org/10.1108/00070701211202430
Marcon A, Ribeiro JLD, Dangelico RM, de Medeiros JF, Marcon É (2022) Exploring green product attributes and their effect on consumer behaviour: a systematic review. Sustain Prod Consum 32:76–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.04.012
Marian L, Chrysochou P, Krystallis A, Thøgersen J (2014) The role of price as a product attribute in the organic food context: an exploration based on actual purchase data. Food Qual Prefer 37:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2014.05.001
Martenson R (2018) When is green a purchase motive? Different answers from different selves. Int J Retail Distrib Manag 46(1):21–33. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJRDM-11-2016-0228
Martínez P (2015) Customer loyalty: exploring its antecedents from a green marketing perspective. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 27(5):896–917. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-03-2014-0115
McDonald S, Oates CJ, Thyne M, Timmis AJ, Carlile C (2015) Flying in the face of environmental concern: why green consumers continue to fly. J Market Manag 31(13–14):1503–1528. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257X.2015.1059352
Mehmet A, Gül B (2014) Demographic characteristics of consumer buying behavior effects of environmentally friendly products and an application in Gaziantep. The Business & Management Review 5(1):72–82
Mohd Suki N, Majeed A, Mohd Suki N (2022) Impact of consumption values on consumers’ purchase of organic food and green environmental concerns. Soc Respons J 18(6):1128–1141. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-01-2021-0026
Moisander J (2007) Motivational complexity of green consumerism. Int J Consum Stud 31(4):404–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2007.00586.x
Mol A (2000) The environmental movement in an era of ecological modernisation. Geoforum 31(4):257–292
Moraes C, Carrigan M, Szmigin I (2012) The coherence of inconsistencies: attitude-behaviour gaps and new consumption communities. J Mark Manag 28(1–2):103–128. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257X.2011.615482
Moser AK (2015) Thinking green, buying green? Drivers of pro—Environmental purchasing behavior. J Consum Mark 32(3):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-10-2014-1179
Moser AK (2016) Buying organic—decision-making heuristics and empirical evidence from Germany. J Consum Mark 33(7):552–561. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-04-2016-1790
Mostafa MM (2007) Gender differences in Egyptian consumers’ green purchase behaviour: the effects of environmental knowledge, concern and attitude. International Journal of Consumer Studies 31:220–229
Namkung Y, Jang S (2017) Are consumers willing to pay more for green practices at restaurants? J Hospital Tour Res 41(3):329–356
Nekmahmud M, Ramkissoon H, Fekete-Farkas M (2022) Green purchase and sustainable consumption: a comparative study between European and non-European tourists. Tour Manag Perspect 43(June):100980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2022.100980
Nidumolu R., CK P, & MR R (2014) Sustainability is the key driver of innovation. 71st World Foundry Congress: Advanced Sustainable Foundry, WFC 2014, September, pp 57–64
Nguyen HV, Nguyen CH, Hoang TTB (2019) Green consumption: closing the intention-behavior gap. Sustain Dev 27(1):118–129. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1875
Nguyen C, Faulkner M, Yang S, Williams J, Tong L (2022) Mind the gap: understanding the gap between intentions and behaviour in the charity context. J Bus Res 148(November 2021):216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.04.044
Nguyen ND, Le AT, Do DT (2022) Splitting energy of transmit power serving grouping users in full-duplex networks under imperfect hardware. Wirel Commun Mobile Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9932652
Nguyen-Viet B (2023) The impact of green marketing mix elements on green customer based brand equity in an emerging market. Asia Pac J Bus Adm 15(1):96–116. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJBA-08-2021-0398
Nielsen KS (2017) From prediction to process: a self-regulation account of environmental behavior change. J Environ Psychol 51:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2017.04.002
Nygaard A, Silkoset R (2023) Sustainable development and greenwashing: how blockchain technology information can empower green consumers. Bus Strateg Environ 32(6):3801–3813. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3338
Ottman JA, Stafford ER, Hartman CL (2006) Avoiding green marketing myopia: ways to improve consumer appeal for environmentally preferable products. Environment 48(5):22–36. https://doi.org/10.3200/ENVT.48.5.22-36
Park J, Ha S (2014) Understanding consumer recycling behavior: combining the theory of planned behavior and the norm activation model. Fam Consum Sci Res J 42(3):278–291. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcsr.12061
Peattie K (2001) Towards sustainability: the third age of green marketing. Mark Rev 3(2):129–146
Pop RA, Saplacan Z, Alt MA (2020) Social media goes green-the impact of social media on green cosmetics purchase motivation and intention. Inform (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/INFO11090447
Qi X, Yu H, Ploeger A (2020) Exploring influential factors including COVID-19 on green food purchase intentions and the intention–behaviour gap: a qualitative study among consumers in a Chinese context. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(19):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197106
Rausch TM, Kopplin CS (2021) Bridge the gap: consumers’ purchase intention and behavior regarding sustainable clothing. J Clean Prod 278:123882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123882
Reimers V, Magnuson B, Chao F (2017) Happiness, altruism and the Prius effect: how do they influence consumer attitudes towards environmentally responsible clothing? J Fash Mark Manag 21(1):115–132. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFMM-07-2016-0053
Ritter ÁM, Borchardt M, Vaccaro GLR, Pereira GM, Almeida F (2015) Motivations for promoting the consumption of green products in an emerging country: exploring attitudes of Brazilian consumers. J Clean Prod 106:507–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.066
Rojas-Méndez JI, Le Nestour M, Rod M (2015) Understanding attitude and behavior of canadian consumers toward organic wine. J Food Prod Market 21(4):375–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454446.2014.885869
Sadiq M, Adil M, Paul J (2022) Eco-friendly hotel stay and environmental attitude: a value-attitude-behaviour perspective. Int J Hospital Manag 100:103094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2021
Saeed M, Shafique I (2021) Green customer-based brand equity and green purchase consumption behaviour: the moderating role of religious commitment. Environ Dev Sustain 23(9):13284–13303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01210-1
Schäufele I, Hamm U (2018) Organic wine purchase behaviour in Germany: exploring the attitude-behaviour-gap with data from a household panel. Food Qual Prefer 63:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2017.07.010
Severo EA, de Guimarães JCF, Henri Dorion EC (2018) Cleaner production, social responsibility and eco-innovation: Generations’ perception for a sustainable future. J Clean Prod 186:91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.129
Sh Ahmad F, Rosli NT, Quoquab F (2022) Environmental quality awareness, green trust, green self-efficacy and environmental attitude in influencing green purchase behaviour. Int J Ethics Syst 38(1):68–90. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOES-05-2020-0072
Sharma N, Paço A (2021) Moral disengagement: a guilt free mechanism for non-green buying behavior. J Clean Prod 297:126649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126649
Shatnawi Y, Al-Faouri EH, Al-Hayari M (2019) Examining the direct and moderation effect of psychographic and demographic factors on green purchasing behaviour. Global Business Econ Rev 21(5):556–582
Shepherd R, Magnusson M, Sjödén P (2005) Determinants of consumer behavior related to organic foods. J Hum Environ 34(4):352–359
Sheth JN, Newman BI, Gross BL (1991) Why we buy what we buy: a theory of consumption values. J Bus Res 22(2):159–170
Silvia PJ (2002) Self-awareness and emotional intensity. Cogn Emot 16(2):195–216. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930143000310
Sinnappan P, Rahman A (2011) Antecedents of green purchasing behavior among Malaysian consumers. International Business Management 5(3):129–1139
Skodienė M, Dagiliūtė R, Liobikienė G (2020) Do general pro-environmental behaviour, attitude, and knowledge contribute to energy savings and climate change mitigation in the residential sector? Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116784
Sorensen H, Bogomolova S, Anderson K, Trinh G, Sharp A, Kennedy R, Page B, Wright M (2017) Fundamental patterns of in-store shopper behavior. J Retail Consum Serv 37(February):182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.02.003
Sreen N, Purbey S, Sadarangani P (2018) Impact of culture, behavior and gender on green purchase intention. J Retail Consum Serv 41(July 2017):177–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.12.002
Stolz J, Molina H, Ramírez J, Mohr N (2013) Consumers’ perception of the environmental performance in retail stores: an analysis of the German and the Spanish consumer. Int J Consum Stud 37(4):394–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12028
Suki NM (2013) Young consumer ecological behaviour: The effects of environmental knowledge, healthy food, and healthy way of life with the moderation of gender and age. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal 24(6):726–737. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-02-2013-0010
Sun Y, Wang S (2020) Understanding consumers’ intentions to purchase green products in the social media marketing context. Asia Pac J Mark Logist 32(4):860–878. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-03-2019-0178
Sun Y, Wang S, Gao L, Li J (2018) attitude and intention to buy green products. Nat Hazards 93(1):299–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3301-4
Sun X, Su W, Guo X, Tian Z (2021) The impact of awe induced by covid-19 pandemic on green consumption behavior in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(2):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020543
Taghikhah F, Voinov A, Shukla N, Filatova T (2021) Shifts in consumer behavior towards organic products: theory-driven data analytics. J Retail Cons Ser 61(January):102516
Tan TM, Makkonen H, Kaur P, Salo J (2022) How do ethical consumers utilize sharing economy platforms as part of their sustainable resale behavior? The role of consumers’ green consumption values. Tech Forecast Social Change 176(December 2021):121432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121432
Taufique KMR, Islam S (2020) Green marketing in emerging Asia: antecedents of green consumer behavior among younger millennials. J Asia Bus Stud 15(4):541–558. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABS-03-2020-0094
Tawde S, Kamath R, ShabbirHusain RV (2023) ‘Mind will not mind’—Decoding consumers’ green intention-green purchase behavior gap via moderated mediation effects of implementation intentions and self-efficacy. J Clean Prod 383(October 2022):135506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135506
Testa F, Iraldo F, Tessitore S, Frey M (2011) Strategies and approaches green advertising: an empirical analysis of the Italian context. Int J Environ Sustain Dev 10(4):375–395. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESD.2011.047772
Thøgersen J (2004) A cognitive dissonance interpretation of consistencies and inconsistencies in environmentally responsible behavior. J Environ Psychol 24(1):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-4944(03)00039-2
Thøgersen J (2006) Norms for environmentally responsible behaviour: an extended taxonomy. J Environ Psychol 26(4):247–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2006.09.004
Thogersen J, Jorgensen A-K, Sandager S (2012) Consumer decision making regarding a “green” everyday product. Psychol Mark 29(4):187–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar
Tohidi A, Mousavi S, Dourandish A, Alizadeh P (2022) Organic food market segmentation based on the neobehavioristic theory of consumer behavior. Bri Food J. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-12-2021-1269
Tong X, Su J (2018) Exploring young consumers’ trust and purchase intention of organic cotton apparel. J Consum Mark 35(5):522–532. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-04-2017-2176
Tripathi A, Pandey N (2018) Does impact of price endings differ for the non-green and green products? Role of product categories and price levels. J Consum Mark 35(2):143–156. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-06-2016-1838
Tung SJ, Shih CC, Wei S, Chen YH (2012) Attitudinal inconsistency toward organic food in relation to purchasing intention and behavior: an illustration of Taiwan consumers. Bri Food J 114(7):997–1015. https://doi.org/10.1108/00070701211241581
Uyan U, Anal M (2023) Uncovering the gap between intention and behaviour towards knowledge sharing: evidence from a hybrid healthcare institution. Int J Knowl Manag Stud 14(3):244–282
Venciute D, Kazukauskaite M, Correia RF, Kuslys M, Vaiciukynas E (2023) The effect of cause-related marketing on the green consumption attitude–behaviour gap in the cosmetics industry. J Contemp Mark Sci 6(1):22–45. https://doi.org/10.1108/jcmars-08-2022-0019
Vermeir I, Verbeke W (2006) Sustainable food consumption: exploring the consumer “attitude—Behavioral intention” gap. J Agric Environ Ethics 19(2):169–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10806-005-5485-3
Vilà I, Valor C, Redondo R (2023) Can implementation intentions increase fibre intake? An examination of the effect of planning and educational information. Int Rev Public Nonprofit Mark 20(1):65–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-021-00329-9
Wang L, Wong PPW (2021) Marketing of environmentally friendly hotels in China through religious segmentation: a theory of planned behaviour approach. Tour Rev 76(5):1164–1180. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-08-2019-0327
Wang S, Wang J, Wang Y, Yan J, Li J (2018) Environmental knowledge and consumers’ intentions to visit green hotels: the mediating role of consumption values. J Travel Tour Mark 35(9):1261–1271. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2018.1490234
Wang L, Weng Wong PP, Elangkovan NA (2020) The influence of religiosity on consumer’s green purchase intention towards green hotel selection in China. J China Tourism Res 16(3):319–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/19388160.2019.1637318
Wang D, Weisstein FL, Duan S, Choi P (2022) Impact of ambivalent attitudes on green purchase intentions: the role of negative moods. Int J Consum Stud 46(1):182–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12663
Weisstein FL, Asgari M, Siew SW (2014) Price presentation effects on green purchase intentions. J Prod Brand Manag 23(3):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1108/JPBM-06-2013-0324
Wiederhold M, Martinez LF (2018) Ethical consumer behaviour in Germany: the attitude-behaviour gap in the green apparel industry. Int J Consum Stud 42(4):419–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12435
Wiedmann KP, Hennigs N, Behrens SH, Klarmann C (2014) Tasting green: an experimental design for investigating consumer perception of organic wine. Br Food J 116(2):197–211. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-04-2012-0090
William Y, Kumju H, Seonaidh M, Caroline JO (2009) Sustainable consumption: green consumer behaviour when purchasing products. Sustain Dev 18(March 2009):20–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.394
Wyss AM, Knoch D, Berger S (2022) When and how pro-environmental attitudes turn into behavior: the role of costs, benefits, and self-control. J Environ Psychol 79(December 2021):101748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2021.101748
Xu X, Wang S, Yu Y (2020) Consumer’s intention to purchase green furniture: Do health consciousness and environmental awareness matter? In: Science of the Total Environment, vol 704, Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135275
Yang M, Chen H, Long R, Yang J (2022) The impact of different regulation policies on promoting green consumption behavior based on social network modeling. Sustain Prod Consum 32:468–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.05.007
Zabkar V, Hosta M (2013) Willingness to act and environmentally conscious consumer behaviour: can prosocial status perceptions help overcome the gap? Int J Consum Stud 37(3):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2012.01134.x
Zaikauskaitė L, Butler G, Helmi NFS, Robinson CL, Treglown L, Tsivrikos D, Devlin JT (2022) Hunt–Vitell’s general theory of marketing ethics predicts “attitude-behaviour” gap in pro-environmental domain. Front Psychol 13(March):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.732661
Zeynalova Z, Namazova N (2022) Revealing Consumer Behavior toward Green Consumption. Sustainability (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105806
Zhang Y, Bai X, Mills FP, Pezzey JCV (2021) Examining the attitude-behavior gap in residential energy use: empirical evidence from a large-scale survey in Beijing. China J Clean Prod 295:126510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126510
Zhao R, Zhong S (2015) Carbon labelling influences on consumers’ behaviour: a system dynamics approach. Ecol Ind 51:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.030
Zhao HH, Gao Q, Wu YP, Wang Y, Zhu XD (2014) What affects green consumer behavior in China? A case study from Qingdao. J Clean Prod 63:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.05.021
Zhao Z, Gong Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Sun Y (2021) Gender-related beliefs, norms, and the link with green consumption. Front Psychol 12(December):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.710239
Zsóka Á, Szerényi ZM, Széchy A, Kocsis T (2013) Greening due to environmental education ? Environmental knowledge, attitudes, consumer behavior and everyday pro-environmental activities of Hungarian high school and university students. J Clean Prod 48:126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.11.030
Funding
No financial aid was received for the completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors would like to confirm that there are no conflicts of interest related to this manuscript. This manuscript has been written giving due respect to intellectual property rights and is the original work of the authors. We also confirm that this manuscript has not been submitted to any other journal for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sukumaran, L., Majhi, R. Not all who proclaim to be green are really green: analysis of intention behavior gap through a systematic review of literature. Manag Rev Q (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-024-00415-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-024-00415-2