Abstract
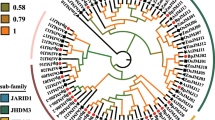
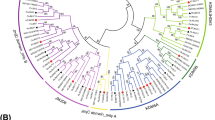
Jumonji (JMJ) genes play major roles in the modulation of chromatin at certain stages of plant development such as flowering, development of androecium and gynoecium, circadian regulation, and brassinosteroid signalling. However, the information on this gene family in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) is limited. In this study, 19 PbrJMJ genes were identified and divided into five groups. Their gene structures and conserved domains shared a resemblance within the same groups. 18 PbrJMJ genes were presented on 8 of the 17 chromosomes in the pear. In the expansion of the PbrJMJ genes family, the whole-genome duplication event played a critical role, and the evolution of the PbrJMJ family was mainly affected by purification selection pressure. Gene expression analysis revealed that PbrJMJ genes were distributed in various tissues of P. bretschneideri. PbrJMJ14 and PbrJMJ29 were highly expressed in the pollen. Inhibition of PbrJMJ14 and PbrJMJ29 expression resulted in reduced pollen tube length, suggesting that they play a role in regulating pollen tube growth. In summary, these results provide evolutionary insight into PbrJMJ genes and lay a foundation for further analysis of their functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13(8):1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2011.07.002
Chen M, Chory J (2011) Phytochrome signaling mechanisms and the control of plant development. Trends Cell Biol 21:664–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2011.07.002
Chowrasia S, Panda AK, Rawal HC, Kaur H, Mondal TK (2018) Identification of jumonjiC domain containing gene family among the Oryza species and their expression analysis in FL478, a salt tolerant rice genotype. Plant Physiol Biochem 130:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.06.031
Clissold PM, Ponting CP (2001) JmjC: cupin metalloenzyme-like domains in jumonji, hairless and phospholipase A2β. Trends Biochem Sci 26:7–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01700-X
Crevillén P (2020) Histone demethylases as counterbalance to H3K27me3 silencing in plants. Iscience 23:101715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101715
De Bodt S, Maere S, Van de Peer Y (2005) Genome duplication and the origin of angiosperms. Trends Ecol Evol 20(11):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2005.07.008
De Graaf BH, Rudd JJ, Wheeler MJ, Perry RM, Bell EM, Osman K, Franklin-Tong VE (2006) Self-incompatibility in Papaver targets soluble inorganic pyrophosphatases in pollen. Nature 444(7118):490–493. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05311
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195
Fan S, Wang J, Lei C, Gao C, Yang Y, Li Y, An N, Zhang D, Han M (2018) Identification and characterization of histone modification gene family reveal their critical responses to flower induction in apple. BMC Plant Biol 18:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1388-0
Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2009) Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in plants. New Phytol 183:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02923.x
Gan ES, Xu Y, Wong JY, Goh JG, Sun B, Wee WY, Huang J, Ito T (2014) Jumonji demethylases moderate precocious flowering at elevated temperature via regulation of FLC in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6098
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: The proteomics protocols handbook, pp 571–607. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-890-0:571
Gu T, Ren S, Wang Y, Han Y, Li Y (2016) Characterization of DNA methyltransferase and demethylase genes in Fragaria vesca. Mol Genet Genomics 291:1333–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1187-y
Han Y, Li X, Cheng L, Liu Y, Wang H, Ke D, Yuan H, Zhang L, Wang L (2016) Genome-wide analysis of soybean JmjC domain-containing proteins suggests evolutionary conservation following whole-genome duplication. Front Plant Sci 7:1800. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01800
Hong EH, Jeong YM, Ryu JY, Amasino RM, Noh B, Noh YS (2009) Temporal and spatial expression patterns of nine Arabidopsis genes encoding Jumonji C-domain proteins. Mol Cells 27:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0054-7
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang Y, Dennehey B, Shi X (2017) Histone lysine methylation, demethylation, and hormonal gene regulation. In: Gene Regulation, Epigenetics and Hormone Signaling, p 1
Inagaki S, Miura-Kamio A, Nakamura Ya LF, Cui X, Cao X, Kimura H, Saze H, Kakutani T (2010) Autocatalytic differentiation of epigenetic modifications within the Arabidopsis genome. EMBO J 29:3496–3506. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.227
Jeong JH, Song HR, Ko JH, Jeong YM, Kwon YE, Seol JH, Amasino RM, Noh B, Noh YS (2009) Repression of FLOWERING LOCUS T chromatin by functionally redundant histone H3 lysine 4 demethylases in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 4:e8033. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008033
Juanzi W, Qin Y Zhao J (2008) Pollen tube growth is affected by exogenous hormones and correlated with hormone changes in styles in Torenia fournieri L. Plant Growth Regul 55;137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9268-5
Katoh M, Katoh M (2004) Identification and characterization of JMJD2 family genes in silico. Int J Oncol 24:1623–1628. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.24.6.1623
Kim JD, Lee A, Choi J, Park Y, Kang H, Chang W, Lee MS, Kim J (2015) Epigenetic modulation as a therapeutic approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Exp Mol Med 47:e175. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2015.45
Klose RJ, Bird AP (2006) Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci 31:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2005.12.008
Koch MA, Haubold B, Mitchell-Olds T (2000) Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in Arabidopsis, Arabis, and related genera (Brassicaceae). Mol Biol Evol 17(10):1483–1498. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026248
Kong H, Landherr LL, Frohlich MW, Leebens-Mack J, Ma H, DePamphilis CW (2007) Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J 50:873–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03097.x
Kou X, Xiong C, Wang D, Sun Y, Wang P, Wu J, Zhang S (2020) Comparative analysis of bHLH transcription factors in five Rosaceae species, and expression analysis of PbbHLHs in response to drought stress in pear. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-78164/v1
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lee SH, Kim T, Cho E, Jeon J (2020) B-9: MoJMJD2, a JMJD2 family histone demethylase regulates the development and pathogenicity in rice blast fungus. 균학회소식 32:112–112
Letunic I, Bork P (2018) 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D493–D496. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx922
Liu C, Lu F, Cui X, Cao X (2010) Histone methylation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:395–420. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.091939
Lu F, Li G, Cui X, Liu C, Wang XJ, Cao X (2008) Comparative analysis of JmjC domain-containing proteins reveals the potential histone demethylases in Arabidopsis and rice. J Integr Plant Biol 50:886–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00692.x
Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Geer LY, Bryant SH (2015) CDD: NCBI's conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 43(D1):D222–D226. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1221
Ning YQ, Ma ZY, Huang HW, Mo H, Tt Z, Li L, Cai T, Chen S, Ma L, He XJ (2015) Two novel NAC transcription factors regulate gene expression and flowering time by associating with the histone demethylase JMJ14. Nucleic Acids Res 43:1469–1484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1382
Ojolo SP, Cao S, Priyadarshani S, Li W, Yan M, Aslam M, Zhao H, Qin Y (2018) Regulation of plant growth and development: a review from a chromatin remodeling perspective. Front Plant Sci 9:1232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01232
Panchy NL, Azodi CB, Winship EF, O’Malley RC, Shiu SH (2019) Expression and regulatory asymmetry of retained Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor genes derived from whole genome duplication. BMC Evol Biol 19:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-019-1398-z
Pleskot R, Potocký M, Pejchar P, Linek J, Bezvoda R, Martinec J, Žárský V (2010) Mutual regulation of plant phospholipase D and the actin cytoskeleton. Plant J 62(3):494–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04168.x
Potter D, Eriksson T, Evans RC, Oh S, Smedmark JEE, Morgan DR, Campbell CS (2007) Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant Syst Evol 266(1):5–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0539-9
Qian S, Wang Y, Ma H, Zhang L (2015) Expansion and functional divergence of Jumonji C-containing histone demethylases: significance of duplications in ancestral angiosperms and vertebrates. Plant Physiol 168:1321–1337. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00520
Qian Y, Chen C, Jiang L, Zhang J, Ren Q (2019) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in maize. BMC Genomics 20:256. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5633-1
Qiao X, Li Q, Yin H, Qi K, Li L, Wang R, Paterson AH (2019) Gene duplication and evolution in recurring polyploidization–diploidization cycles in plants. Genome Biol 20(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1650-2
Qiao X, Yin H, Li L, Wang R, Wu J, Wu J, Zhang S (2018) Different modes of gene duplication show divergent evolutionary patterns and contribute differently to the expansion of gene families involved in important fruit traits in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Front Plant Sci 9:161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00161
Shi T, Rahmani RS, Gugger PF, Wang M, Li H, Zhang Y, Li Z, Wang Q, Van de Peer Y, Marchal K (2020) Distinct expression and methylation patterns for genes with different fates following a single whole-genome duplication in flowering plant. Mol Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa105
Sun Q, Zhou DX (2008) Rice jmjC domain-containing gene JMJ706 encodes H3K9 demethylase required for floral organ development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:13679–13684. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805901105
Vogler F, Schmalzl C, Englhart M, Bircheneder M, Sprunck S (2014) Brassinosteroids promote Arabidopsis pollen germination and growth. Plant Reprod 27:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-014-0247-x
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J (2010) KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 8:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wu J, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang S, Ming ZS, Khan MA, Tao S, Korban SS, Wang H (2013) The genome of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Genome Res 23:396–408 http://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.144311.112
Xu G, Liu G, Xiong S, Liu H, Chen X, Zheng B (2015) The histone methyltransferase Smyd2 is a negative regulator of macrophage activation by suppressing interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) production. J Biol Chem 290(9):5414–5423. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.610345
Yang W, Jiang D, Jiang J, He Y (2010) A plant-specific histone H3 lysine 4 demethylase represses the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 62:663–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04182.x
Yang Z, Qiu Q, Chen W, Jia B, Chen X, Hu H, He K, Deng X, Li S, Tao WA (2018) Structure of the Arabidopsis JMJ14-H3K4me3 complex provides insight into the substrate specificity of KDM5 subfamily histone demethylases. Plant Cell 30:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00666
Yu X, Li L, Li L, Guo M, Chory J, Yin Y (2008) Modulation of brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression by Jumonji domain-containing proteins ELF6 and REF6 in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:7618–7623. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0802254105
Zhang L, Wu S, Chang X, Wang X, Zhao Y, Xia Y, Trigiano RN, Jiao Y, Chen F (2020) The ancient wave of polyploidization events in flowering plants and their facilitated adaptation to environmental stress. Plant Cell Environ 43(12):2847–2856. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13898
Zheng S, Hu H, Ren H, Yang Z, Qiu Q, Qi W, Liu X, Chen X, Cui X, Li S (2019) The Arabidopsis H3K27me3 demethylase JUMONJI 13 is a temperature and photoperiod dependent flowering repressor. Nat Commun 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09310-x
Zhou H, Yin H, Chen J, Liu X, Gao Y, Wu J, Zhang S (2016) Gene-expression profile of developing pollen tube of Pyrus bretschneideri. Gene Expr Patterns 20:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gep.2015.10.004
Zong W, Zhong X, You J, Xiong L (2013) Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K4-tri-methylation and gene expression in rice under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 81:175–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9990-2
Acknowledgements
The usage of the microscope was guided by Yuehua Ma.
Data archiving statement
All PbrJMJ-related sequences were available from the Pear Genome Project (peargenome.njau.edu.cn) (Wu et al. 2013). The protein sequences of JMJ members including apple, peach, strawberry, sweet cherry, Rosa chinensis, rice, maize, and soybean were searched and downloaded from the Phytozome (http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/) database.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFE0202900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172543), Outstanding Talent for Agricultural Research Project (13210324), the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-28), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. Bioinformatic analysis was supported by the Bioinformatics Center of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by C. Chen
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, W., Liu, W., Liu, Z. et al. Genome-wide identification, expression analysis, and functional verification of the JMJ (Jumonji) histone demethylase gene family in pear (Pyrus bretchneideri). Tree Genetics & Genomes 19, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01586-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-023-01586-x