Abstract
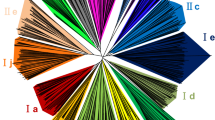
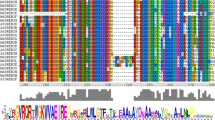
As plant-specific transcription factors, ovate family proteins (OFP) were involved in the regulation of plant growth, development, and stress response. Although OFP proteins have been reported in some species, little is known about their evolution, structure, expression levels under biological and abiotic stress, and interactions among OFP members in apple. In this study, 26 apple MdOFP genes were identified. Gene structure analysis showed that the main characteristics of the OFP genes of monocots and dicots were intron-free. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the OFP proteins of monocots and dicots could be divided into 15 subgroups, of which Ia, Ib, Ic, Id, Ie, If, Ig, Ih, Ii, and Ij subgroups were dicots, while IIa, IIb, IIc, IId, and IIe subgroups were monocots. Chromosomal localization analysis showed that 26 MdOFP genes were unevenly distributed on 13 chromosomes. Twelve MdOFP genes were cloned by RT-PCR method and found to be expressed in the tested tissues in different degrees. Under osmotic stress treatment, MdOFP11, MdOFP14, and MdOFP20 responded to NaCl treatment; MdOFP6 and MdOFP14 responded to mannitol treatment. The results of Y2H showed that MdOFP13, MdOFP16, MdOFP20, and MdOFP22 could form heterodimers with multiple MdOFP proteins, while MdOFP16 and MdOFP16 could form homodimers. These results provide valuable references for analyzing the biological function of MdOFP transcription factors in the growth, development, and stress conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Daccord N, Celton JM, Linsmith G, Becker C, Choisne N, Schijlen E, van de Geest H, Bianco L, Micheletti D, Velasco R, Di Pierro EA, Gouzy J, Rees DJG, Guérif P, Muranty H, Durel CE, Laurens F, Lespinasse Y, Gaillard S, Aubourg S, Quesneville H, Weigel D, van de Weg E, Troggio M, Bucher E (2017) High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat Genet 49:1099–1106
Dong QL, Liu DD, An XH, Hu DG, Yao YX, Hao YJ (2011) MdVHP1 encodes an apple vacuolar H+-PPase and enhances stress tolerance in transgenic apple callus and tomato. J Plant Physiol 168:2124–2133
Dong Q, Duan D, Zhao S, Xu B, Luo J, Wang Q, Huang D, Liu C, Li C, Gong X, Mao K, Ma F (2018a) Genome-wide analysis and cloning of the apple stress-associated protein gene family reveals MdSAP15, which confers tolerance to drought and osmotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 19:2478
Dong Q, Mao K, Duan D, Zhao S, Wang Y, Wang Q, Huang D, Li C, Liu C, Gong X, Ma F (2018b) Genome-wide analyses of genes encoding FK506-bindingproteins reveal their involvement in abiotic stress responses in apple. BMC Genomics 19:707
Dong Q, Zhao S, Duan D, Tian Y, Wang Y, Mao K, Zhou Z, Ma F (2018c) Structural and functional analyses of genes encoding VQ proteins in apple. Plant Sci 272:208–219
Gong SY, Huang GQ, Sun X, Qin LX, Li Y, Zhou L, Li XB (2014) Cotton KNL1, encoding a class II KNOX transcription factor, is involved in regulation of fibre development. J Exp Bot 65:4133–4147
Gu Y, Ji Z, Chi F, Qiao Z, Xu C, Zhang J, Dong Q, Zhou Z (2015) Bioinformatics and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in apple. Sci Agric Sin 48:3221–3238
Hackbusch J, Richter K, Muller J, Salamini F, Uhrig JF (2005) A central role of Arabidopsis thaliana ovate family proteins in networking and subcellular localization of 3-aa loop extension homeodomain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4908–4912
Hu DG, Li M, Luo H, Dong QL, Yao YX, You CX, Hao YJ (2012) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MdSOS2 reveals its involvement in salt tolerance in apple callus and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31:713–722
Huang Z, Van Houten J, Gonzalez G, Xiao H, van der Knaap E (2013) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of SUN, OFP and YABBY gene family in tomato. Mol Gen Genomics 288:111–129
Lazzaro MD, Wu S, Snouffer A, Wang Y, van der Knaap E (2018) Plant organ shapes are regulated by protein interactions and associations with microtubules. Front Plant Sci 9:1766
Li E, Wang S, Liu Y, Chen JG, Douglas CJ (2011) OVATE FAMILY PROTEIN4 (OFP4) interaction with KNAT7 regulates secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 67:328–341
Li HF, Dong QL, Li GX, Ran K (2018a) Identification and expression analysis of 11 MADS-box genes in peach (Prunus persica var. nectarina ‘Luxing’). J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 93:232–243
Li HF, Dong QL, Jia HZ, Li GX, Ran K (2018b) Isolation and expression analysis of eight MADS-box genes in peach (Prunus persica var. nectarina ‘Luxing’). J Plant Biochem Biot 27:435–442
Liu Y, Douglas CJ (2015) A role for OVATE FAMILY PROTEIN1 (OFP1) and OFP4 in a BLH6-KNAT7 multi-protein complex regulating secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 10:e1033126
Liu J, Van Eck J, Cong B, Tanksley SD (2002) A new class of regulatory genes underlying the cause of pearshaped tomato fruit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13302–13306
Liu D, Sun W, Yuan Y, Zhang N, Hayward A, Liu Y, Wang Y (2014) Phylogenetic analyses provide the first insights into the evolution of OVATE family proteins in land plants. Ann Bot 113:1219–1233
Liu J, Zhang J, Hu W, Miao H, Zhang J, Jia C, Wang Z, Xu B, Jin Z (2015) Banana ovate family protein MaOFP1 and MADS-box protein MuMADS1 antagonistically regulated banana fruit ripening. PLoS One 10:e0123870
Liu J, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang J, Miao H, Jia C, Wang Z, Xu B, Jin Z (2018) MuMADS1 and MaOFP1 regulate fruit quality in a tomato ovate mutant. Plant Biotechnol J 16:989–1001
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma QJ, Sun MH, Liu YJ, Lu J, Hu DG, Hao YJ (2016) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the apple sucrose transporter gene MdSUT2. Plant Physiol Biochem 109:442–451
Ma Y, Yang C, He Y, Tian Z, Li J (2017) Rice OVATE family protein 6 regulates plant development and confers resistance to drought and cold stresses. J Exp Bot 68:4885–4898
Pagnussat GC, Yu HJ, Sundaresan V (2007) Cell-fate switch of synergid to egg cell in Arabidopsis eostre mutant embryo sacs arises from misexpression of the BEL1-like homeodomain gene BLH1. Plant Cell 19:3578–3592
Perini P, Pasquali G, Margis-Pinheiro M, de Oliviera PRD, Revers LF (2014) Reference genes for transcriptional analysis of flowering and fruit ripening stages in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Mol Breeding 34:829–842
Proost S, Van Bel M, Vaneechoutte D, Van de Peer Y, Inzé D, Mueller-Roeber B, Vandepoele K (2015) PLAZA 3.0: an access point for plant comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D974–D981
Rodríguez GR, Muños S, Anderson C, Sim SC, Michel A, Causse M, Garderner BB, Francis D, van der Knaap E (2011) Distribution of SUN, OVATE, LC, and FAS in the tomato germplasm and the relationship to fruit shape diversity. Plant Physiol 156:275–285
Schmitz AJ, Begcy K, SaratG H, Walia H (2015) Rice ovate family protein 2 (OFP2) alters hormonal homeostasis and vasculature development. Plant Sci 241:177–188
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tian Y, Dong Q, Ji Z, Chi F, Cong P, Zhou Z (2015) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-box gene family in apple. Gene 555:277–290
Tsaballa A, Pasentsis K, Darzentas N, Tsaftaris AS (2011) Multiple evidence for the role of an ovate-like gene in determining fruit shape in pepper. BMC Plant Biol 11:46
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D, Salvi S, Pindo M, Baldi P, Castelletti S, Cavaiuolo M, Coppola G, Costa F, Cova V, Dal Ri A, Goremykin V, Komjanc M, Longhi S, Magnago P, Malacarne G, Malnoy M, Micheletti D, Moretto M, Perazzolli M, Si-Ammour A, Vezzulli S, Zini E, Eldredge G, Fitzgerald LM, Gutin N, Lanchbury J, Macalma T, Mitchell JT, Reid J, Wardell B, Kodira C, Chen Z, Desany B, Niazi F, Palmer M, Koepke T, Jiwan D, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Wu C, Chu VT, King ST, Vick J, Tao Q, Mraz A, Stormo A, Stormo K, Bogden R, Ederle D, Stella A, Vecchietti A, Kater MM, Masiero S, Lasserre P, Lespinasse Y, Allan AC, Bus V, Chagné D, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Lavezzo E, Fawcett JA, Proost S, Rouzé P, Sterck L, Toppo S, Lazzari B, Hellens RP, Durel CE, Gutin A, Bumgarner RE, Gardiner SE, Skolnick M, Egholm M, van de Peer Y, Salamini F, Viola R (2010) The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Nat Genet 42:833–839
Wang S, Chang Y, Guo J, Chen JG (2007) Arabidopsis ovate family protein 1 is a transcriptional repressor that suppresses cell elongation. Plant J 50:858–872
Wang YK, Chang WC, Liu PF, Hsiao MK, Lin CT, Lin SM, Pan RL (2010) Ovate family protein 1 as a plant Ku70 interacting protein involving in DNA double-strand break repair. Plant Mol Biol 74:453–466
Wang S, Chang Y, Guo J, Zeng Q, Ellis BE, Chen JG (2011) Arabidopsis ovate family proteins, a novel transcriptional repressor family, control multiple aspects of plant growth and development. PLoS One 6:e23896
Wang S, Chang Y, Ellis B (2016) Overview of OVATE FAMILY PROTEINS, a novel class of plant-specific growth regulators. Front Plant Sci 7:417
Wu S, Zhang B, Keyhaninejad N, Rodríguez GR, Kim HJ, Chakrabarti M, Illa-Berenguer E, Taitano NK, Gonzalo MJ, Díaz A, Pan Y, Leisner CP, Halterman D, Buell CR, Weng Y, Jansky SH, van Eck H, Willemsen J, Monforte AJ, Meulia T, van der Knaap E (2018) A common genetic mechanism underlies morphological diversity in fruits and other plant organs. Nat Commun 9:4734
Yang C, Shen W, He Y, Tian Z, Li J (2016) OVATE family protein 8 positively mediates brassinosteroid signaling through interacting with the GSK3-like kinase in rice. PLoS Genet 12:e1006118
Yang C, Ma Y, He Y, Tian Z, Li J (2018) OsOFP19 modulates plant architecture by integrating cell division pattern and brassinosteroid signaling. Plant J 93:489–501
Yu H, Jiang W, Liu Q, Zhang H, Piao M, Chen Z, Bian M (2015) Expression pattern and subcellular localization of the ovate protein family in rice. PLoS One 10:e0118966
Zhang L, Zhang X, Ju H, Chen J, Wang S, Wang H, Zhao Y, Chang Y (2016) Ovate family protein1 interaction with BLH3 regulates transition timing from vegetative to reproductive phase in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 470:492–497
Zhao DS, Li QF, Zhang CQ, Zhang C, Yang QQ, Pan LX, Ren XY, Lu J, Gu MH, Liu QQ (2018) GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat Commun 9:1240
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Thomas Alan Gavin, Cornell University, and XuYi for their help in revising our English composition.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31501742), Shandong Agricultural Good Cultivar Project (Grant No. 2016LZGC034), and Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of SAAS (CXGC2016A03 and CXGC2018F03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL and KR collected the public dataset, performed bioinformatics analysis, and drafted the manuscript. QD contributed to the bioinformatics analysis and preparation of all figures and tables. QZ conducted the experiments. HL and KR conceived this study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Data archiving statement
All cloned OFP gene sequences of Malus domestica were deposited into the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The accession numbers were listed in Table 1. Details of the cloned OFP gene sequences were listed in supplementary data file 2.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Troggio
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Dong, Q., Zhao, Q. et al. Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and protein-protein interaction properties of ovate family proteins in apple. Tree Genetics & Genomes 15, 45 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1354-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1354-5