Abstract
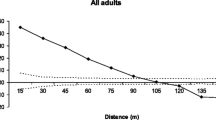
Cedrus brevifolia is a narrowly distributed conifer species, currently limited to a single mountain in Cyprus, growing in restricted habitats on sites of different densities and sizes. This study assessed the influence of seed and pollen dispersal, as well as the effect of demographic and genetic features on the magnitude of fine-scale spatial genetic structure (SGS). Sampling was performed in 11 plots where 50 neighboring adult trees were sampled from each plot, while biparentally and paternally inherited genomes were used for analysis with microsatellites. Fine-scale SGS was significant but showed contrasting patterns among plots. Although the magnitude of SGS in C. brevifolia mainly results from restricted seed dispersal, short-distance pollen dispersal could also explain fine-scale SGS in some plots, which is rather uncommon in wind-pollinated conifer species. The lack of a general and consistent trend of SGS among plots and between genomes indicates that pollen and seed dispersal varies at plot level. The complex SGS patterns in C. brevifolia may result from the unequal ratio of male and female strobilies of trees within the same plots, at different reproductive periods. Demographic features such as habitat fragmentation did not influence the magnitude of SGS in C. brevifolia, whereas low tree aggregation reduced it. Further, the significant correlation observed between linkage disequilibrium (LD) and plots with significant SGS supports the assumption that under specific conditions, LD is likely to be caused by the magnitude of SGS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asuka Y, Tomaru N, Nisimura N, Tsumura Y, Yamamoto S (2004) Heterogeneous genetic structure in a Fagus crenata population in an old-growth beech forest revealed by microsatellite markers. Mol Ecol 13:1241–1250
Bou Dagher-Kharrat M, Mariette S, Lefèvre F, Fady B, Grenier-de March G, Plomion C, Savouré A (2007) Geographical diversity and genetic relationships among Cedrus species estimated by AFLP. Tree Genet Genomes 3(3):275–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-006-0065-x
Chaib J, Danan S, Jouaud L, Hagen S, Lefèvre F, Fady B (2006) Identification and characterization of nuclear microsatellite in Mediterranean cedar (Cedrus sp.) Mol Ecol Notes 6(3):840–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01364.x
Chapuis MP and Estoup A (2007) Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24: 621–631
Chung MY, Chung GM, Chung MG (1998) Spatial genetic structure in population of Cymbidium goeringii (Orchidaceae). Gen Gen Syst 73(5):281–285. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.73.281
Chybicki IJ, Dzialuk A, Trojankiewicz M, Slawski M, Burczyki J (2008) Spatial genetic structure within two contrasting stands of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) Silvae Genet 57:193–202
Chybicki IJ, Dering M, Iszkuło G, Meyza K, Suszka J (2016) Relative strength of fine-scale spatial genetic structure in paternally vs biparentally inherited DNA in a dioecious plant depends on both sex proportions and pollen-to-seed dispersal ratio. Heredity 117:449–459
Clark PJ, Evans FC (1954) Distance to nearest neighbor as a measure of spatial relationships in populations. Ecol 35(4):445–453. https://doi.org/10.2307/1931034
Crawford TJ (1984) The estimation of neighbourhood parameters for plant populations. Heredity 52:273–283
Cyprus Department of Forests (2000) Inventory of forest vegetation and regeneration in the Trypilos nature reserve area. Sector of management and data processing service. Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment, Nicosia, Cyprus [in Greek ]
Degen B, Petit R, Kremer A (2001) SGS-Spatial Genetic Software: a computer program for analysis of spatial genetic and phenotypic structures of individuals and populations. J Hered 92:447–448
Doligez A, Baril C, Joly HI (1998) Fine-scale spatial genetic structure with non-uniform distribution of individuals. Genetics 148:905–920
Dounavi A, Koutsias N, Ziehe M, Hattemer HH (2010) Spatial patterns and genetic structures within beech populations (Fagus sylvatica L.) of forked and non-forked individuals. Eur J Forest Res 129(6):1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-010-0409-9
Eliades N-G, Gailing O, Leinemann L, Fady B, Finkeldey R (2011) High genetic diversity and significant population structure in Cedrus brevifolia Henry, a narrow Mediterranean endemic tree from Cyprus. Pl Syst Evol 294(3-4):185–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-011-0453-z
Epperson BK (1989) Spatial patterns of genetic variation within plant populations. In: Brown AHD , Clegg MT, Cahler AL, Weir BS (eds) Plant populations genetics, breeding, and genetic resources. Sinauer, Sunderland. pp. 229–253
Epperson BK (1992) Spatial structure of genetic variation within populations of forest trees. New For 6(1-4):257–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120648
Epperson BK (2003) Geographical genetics. Princetor University Press, New Jersey, USA
Epperson BK, Allard RW (1989) Spatial autocorrelation analysis of the distribution of genotypes within populations lodgepole pine. Genetics 121(2):369–377
Epperson BK, Alvarez-Buylla E (1997) Spatial autocorrelation analysis of family structure in multiple life stages of Cecropia obtusifolia. Evolution 51(1):275–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1997.tb02409.x
Epperson BK, Chung MG (2001) Spatial genetic structure of allozyme polymorphisms within population of Pinus strobes (Pinaceae). Amer J Bot 88(6):1006–1010. https://doi.org/10.2307/2657081
Fady B, Lefèvre F, Reynaud M, Vendramin GG, Bou Dagher-Kharrat M, Anzidei M, Pastorelli R, Savouré A, Bariteau M (2003) Gene flow among different taxonomic units: evidence from nuclear and cytoplasmic markers in Cedrus plantation forests. Theor Applied Genetics 107(6):1132–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1323-z
Farjón A (1990) Pinaceae: drawings and description of the genera Abies, Cedrus, Pseudolarix, Keteleeria, Nothotsuga, Tsuga, Cathaya, Pseudotsuga, Larix and Picea. Regnum Begerabile Vol. 121. Königstein: Koeltz Scientific Books, Germany
Fenster CB, Vekemans X, Hardy OJ (2003) Quantifying gene flow from spatial genetic structure data in a metapopulation of Chamaecrista fasciculate (Leguminosae). Evolution 57(5):995–1007. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00311.x
Flint-Garcia S, Thornsberry J, Buckler E (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Frankham R (1995) Effective population-size adult-population size ratios in wildlife—a review. Genet Res 66(02):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016672300034455
Grivet D, Robledo-Arnuncio JJ, Smouse PE, Sork VL (2009) Relative contribution of contemporary pollen and seed dispersal to the effective parental size of seedling population of California valley oak (Quercus lobata, Née). Mol Ecol 18(19):3967–3979. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04326.x
Hamilton MB, Miller J (2002) Comparing relative rates of pollen and seed gene flow in the island model using nuclear and organelle measures of population structure. Genetics 162(4):1897–1909
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (1999) Isolation by distance in a continuous population: reconciliation between spatial autocorrelation and population genetics models. Heredity 83(2):145–154. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.1999.00558.x
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SPAGeDi: a versatile computer programme to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2(4):618–620. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00305.x
Hardy OJ, Maggia L, Breyne P, Caron H, Doligez A et al (2006) Fine-scale genetic structure and gene dispersal inferences in 10 Neotropical tree species. Mol Ecol 15:559–571
Heuertz M, Vekemans X, Hausman JF, Palada M, Hardy OJ (2003) Estimated seed vs pollen dispersal from spatial genetic structure in the common ash. Mol Ecol 12:2483–2495
Heywood JS (1991) Spatial analysis of genetic variation in plant populations. Annu Rev Ecol System 22(1):335–355. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.22.110191.002003
Jump AS, Peñuelas J (2007) Extensive spatial genetic structure revealed by AFLP but not SSR molecular markers in the wind-pollinated tree, Fagus sylvatica. Mol Ecol 16(5):925–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.03203.x
Jump AS, Rico L, Coll M, Peñuelas J (2012) Wide variation in spatial genetic structure between natural populations of the European beech (Fagus sylvatica) and its implications for SGS comparability. Heredity 108(6):633–639. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2012.1
Kalisz S, Nason JD, Hanzawa FM, Tonsor SJ (2001) Spatial population genetic structure in Trillium grandiflorum: the roles of dispersal, mating, history, and selection. Evolution 55(8):1560–1568. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00675.x
Khanduri VP, Sharma CM (2002) Pollen production, microsporangium dehiscence and pollen flow in Himalayan cedar (Cedrus deodara Roxb. Ex D. Don). Ann Bot 89(5):587–593. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf101
Kimura M, Weiss GH (1964) The stepping stone model of population structure and the decrease of genetic correlation with distance. Genetics 49(4):561–576
Knowles P (1991) Spatial genetic structure within two natural stands of black spruce (Picea mariana (Mill) B.S.P). Silvae Genet 40:13–19
Knowles P, Perry DJ, Foster HA (1992) Spatial genetic structure in two tamarack [Larix laricina (Du Roi) K. Koch] populations with differing establishment histories. Evolution 46(2):572–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1992.tb02062.x
Krouchi F, Derridja A, Lefèvre F (2004) Year and tree effect on reproductive organisation of Cedrus atlantica in a natural forest. For Ecol Man 197:181–189
Latouche-Hallé C, Ramboer A, Bandou E, Caron1 H, Kremer A (2003) Nuclear and chloroplast genetic structure indicate fine-scale spatial dynamics in a neotropical tree population. Heredity 91:181–190
Latta RG, Linhart YB, Fleck D, Elliot M (1998) Direct and indirect estimates of seed versus pollen movement within a population of ponderosa pine. Evolution 52(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1998.tb05138.x
Leonardi S, Raddi S, Borghetti M (1996) Spatial autocorrelation of allozyme traits in a Norway Spruce (Picea abies) population. Canad J For Res 26:63–71
Loiselle AB, Sork LV, Nason S, Graham C (1995) Spatial genetic structure of a tropical understory shrub, Psychotria officinalis (Rubiaceae). Am J Bot 82(11):1420–1425. https://doi.org/10.2307/2445869
de-Lucas AI, González-Martínez SC, Vendramin GG, Hidalgo E, Heuertz M (2009) Spatial genetic structure in continuous and fragmented populations of Pinus pinaster Aiton. Mol Ecol 18(22):4564–4576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04372.x
Marquardt PE, Epperson BK (2004) Spatial and population genetic structure of microsatellite in white pine. Mol Ecol 13(11):3305–3315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02341.x
Meikle RD (1977) Flora of Cyprus, vol 1. The Bentham-Moxon Trust, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp 21–23
Mitton JB, Grant MC (1984) Association among protein heterozygosity, growth rate, and developmental homeostasis. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 15(1):479–499. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.15.110184.002403
Neel MC, McKelvey K, Ryman N, Lloyd MW, Short Bull R, Allendorf FW, Schwartz MK, Waples RS (2013) Estimation of effective population size in continuously distributed populations: there goes the neighborhood. Heredity 111(3):189–199. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2013.37
Oddou-Muratorio S, Vendramin GG, Buiteveld J, Fady B (2009) Population estimators or progeny tests: what is the best method to assess null allele frequencies at SSR loci? Conserv Genet 10(5):1343–1347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-008-9648-4
Oden NL (1984) Assessing the significance of a spacial correlogram. Geogr Anal 16:1–16
Ouborg NJ, Piquet Y, Van Groenendael JM (1999) Population genetics, molecular markers and the study of dispersal in plants. J Ecol 87:551–568
Pandey M, Rajora OP (2012) Higher fine-scale genetic structure in peripheral than in core populations of a long-lived and mixed-mating conifer—eastern white cedar (Thuja occidentalis L.) BMC Evol Biol 12(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-12-48
Panetsos KP, Christou A, Scaltsoyiannes A (1992) First analysis on allozyme variation in cedar species (Cedrus sp.) Silvae Genet 41:339–342
Pattichis K, Kyriakou E (2013) Assessment of fertility and variation of cones’ and seeds’ traits of the endemic species Cedrus brevifolia (A. Henry). Dissertation, Faculty of Agriculture, Forest Science & Natural Environment, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. [in Greek]
Pijut PM (2000) Cedrus—the true cedars. J Arboriculture 26:218–224
Piotti A, Leonardi S, Heuertz M, Buiteveld J, Geburek T, Gerber S, Kramer K, Vettori C, Vendramin GG (2013) Within-population genetic structure in beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) stands characterized by different disturbance histories: does forest management simplify population substructure? PLoS One 8(9):e73391. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073391
Rousset F (2000) Genetic differentiation between individuals. J Evol Biol 13(1):58–62. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1420-9101.2000.00137.x
Rousset F (2008) Genepop’007: a complete reimplementation of the Genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol Ecol Res 8(1):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01931.x
Rousset F, Billiard S (2000) A theoretical basis for measures of kin selection in subdivided populations: finite populations and localized dispersal. J Evol Biol 13(5):814–825. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1420-9101.2000.00219.x
Rudolf PO (1974) Cedrus. In: Schopmeyer CS (ed) Seeds of woody plants in the United States, agriculture handbook. USDA Forest Service, Washington, DC
Sagnard F, Oddou-Muratorio S, Pichot C, Vendramin GG, Fady B (2011) Effect of seed dispersal, adult tree and seedling density on the spatial genetic structure of regeneration at fine temporal and spatial scales. Tree Genet Genomes 7(1):37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0313-y
Shapcott A (1995) The spatial genetic structure in natural populations of the Australian temperate rainforest tree Atherosperma moschatum (Labill.) (Monimiaceae). Heredity 74(1):28–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.4
Smouse PE, Peakall R (1999) Spatial autocorrelation analysis of individual multiallele and multilocus genetic structure. Heredity 82(5):561–573. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6885180
Troupin D, Nathan R, Vendramin GG (2006) Analysis of spatial genetic structure in an expanding Pinus halepensis population reveals development of fine-scale genetic clustering over time. Mol Ecol 15:3617–3630
Tsintides T, Hadjikyriakos GN, Christodoulou CS (2002) Trees and shrubs in Cyprus. Cyprus Forest Association, Nicosia, Cyprus
Vekemans X, Hardy OJ (2004) New insights from fine-scale spatial genetic structure analyses in plants populations. Mol Ecol 13(4):921–935. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2004.02076.x
Vendramin GG, Lelli L, Rossi P, Morgante M (1996) A set of primers for the amplification of 20 chloroplast microsatellites in Pinaceae. Mol Ecol 5(4):595–598. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.1996.tb00353.x
Wang R, Compton SG, Shi Stephen Y-S, Chen X-Y (2012) Fragmentation reduces regional-scale spatial genetic structure in a wind-pollinated tree because genetic barriers are removed. Ecol and Evol 2:2250–2261
Wells GP, Young AG (2002) Effects of seed dispersal on spatial genetic structure in populations of Rutidosis leptorrhychoides with different levels of correlated paternity. Genet Res 79(3):219–226
Wild AE (1987) Report on the forest in the south and west of the island of the Cyprus (Cyprus no. 10). Harrison and Sons, London
Wright S (1943) Isolation by distance. Genetics 28(2):114–138
Young AG, Merriam HG (1994) Effects of forest fragmentation on the spatial genetic structure of Acer saccharum Marsh. (sugar maple) populations. Heredity 72(2):201–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1994.27
Young AG, Merriam HG, Warwick SI (1993) The effect of forest fragmentation on genetic variation in Acer saccharum Marsh. (sugar maple) populations. Heredity 71(3):277–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1993.136
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Cyprus Department of Forests for providing the basic data for the map design and also for the valuable help in sampling. Many thanks to Dr. S. Oddou-Muratorio, Dr. F. Lefèvre, and Dr. K. Csillery (INRA Avignon) for their comments on this manuscript. Warm gratitude is extended to Dr. M. Heuertz for her support in using the C++ code kindly provided by Dr. O. Hardy. Writing of the manuscript was made possible by financial support to Nicolas-George Eliades from the Mobility Center of the European Network of Excellence EVOLTREE (EVOLution of TREEs as drivers of terrestrial biodiversity, http://www.evoltree.org/) while visiting INRA Avignon. The comments of five reviewers and the associate editor in charge significantly improved the manuscript.
Data archiving statement
Genotypes of the individuals analyzed are available from the Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.163968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N-GE and RF conceived the study. N-GE completed the sampling in the field. N-GE and OG carried out the molecular analyses. N-GE and BF analyzed the data. N-GE, BF, OG, LL and RF wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. G. Vendramin
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Distribution of the sampled trees within each sampling plot of C. brevifolia; distances among trees are given in meters. (EPS 9642 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eliades, NG.H., Fady, B., Gailing, O. et al. Significant patterns of fine-scale spatial genetic structure in a narrow endemic wind-dispersed tree species, Cedrus brevifolia Henry. Tree Genetics & Genomes 14, 15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1231-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1231-7