Abstract
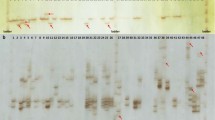
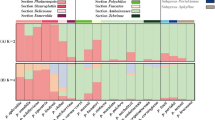
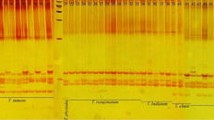
The genus Populus is classified into six different sections, and depending on the declaration of hybrids, the number of species varies between 22 and 85. Species within one section, and sometimes between sections, are crossable to each other, resulting in many naturally but also artificially produced hybrids. Morphological attributes for a clone characterisation are often difficult to evaluate when different poplar species or even hybrids are crossed; thus, molecular markers are needed to characterise the different species. Taking advantage of the large microsatellite resource developed for Populus trichocarpa, however, amplification of these microsatellite markers in other Populus species either often fails, or in the case of amplification, unrelated genomic regions are amplified. To meet this obvious problem of the species transferability of microsatellite markers, in total, 305 microsatellite loci, mainly from P. trichocarpa but also few from Populus tremuloides and Populus nigra, were tested for their transferability to diverse genotypes of six species belonging to three sections of the genus Populus. Ultimately, 209 microsatellite loci could be amplified with varying sizes in the different species. The PCR products of selected loci were separated in a polyacrylamide gel and sequenced to assure that the expected loci were derived from the database genome of P. trichocarpa. The present results constitute a large study for microsatellite transferability for Populus species. The documented microsatellite loci can be applied to species-, hybrid- and clone-specific diagnostic approaches or as universal markers for comprehensive ecological studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2012) Die Pappel - Klone, Klonmischungen und Familieneltern. Bundesanstalt für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung
Bradshaw HD Jr, Ceulemans R, Davis J, Stettler R (2000) Emerging model systems in plant biology: poplar (Populus) as a model forest tree. J Plant Growth Regul 19:306–313
Cervera M, Storme V, Ivens B, Gusmao J, Liu B, Hostyn V, Van Slycken J, Van Montagu M, Boerjan W (2001) Dense genetic linkage maps of three Populus species (Populus deltoides, P. nigra and P. trichocarpa) based on AFLP and microsatellite markers. Genet 158:787–809
Cervera MT, Sewell MM, Faivre-Rampant P, Storme V, Boerjan W (2004) Genome mapping in Populus. In: Kumar S, Fladung M (eds) Molecular genetics and breeding of forest trees. Food Products Press, New York, pp 387–410
Cervera MT, Storme V, Soto A, Ivens B, Van Montagu M, Rajora OP, Boerjan W (2005) Intraspecific and interspecific genetic and phylogenetic relationships in the genus Populus based on AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 111:1440–1456
Cole CT (2005) Allelic and population variation of microsatellite loci in aspen (P. tremuloides). New Phytol 167:155–164
Dayanandan S, Rajora O, Bawa K (1998) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides). Theor Appl Genet 96:950–956
Deutsch F, Kumlehn J, Ziegenhagen B, Fladung M (2004) Stable haploid poplar callus lines from immature pollen culture. Physiol Plant 120:613–622
Dumolin S, Demesure B, Petit RJ (1995) Inheritance of chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes on pedunculate oak investigated with an efficient PCR method. Theor Appl Genet 91:1253–1256
Eckenwalder JE (1996) Systematics and evolution of Populus. In: Stettler RF, Bradshaw HD, Heilman PE et al (eds) Biology of Populus and its implications for management and conservation. NRC Research Press, Ottawa, pp 7–32
Floate KD (2004) Extent and patterns of hybridization among the three species of Populus that constitute the riparian forest of southern Alberta, Canada. Can J Bot 82:253–264
Fossati T, Grassi F, Sala F, Castiglione S (2003) Molecular analysis of natural populations of Populus nigra L. intermingled with cultivated hybrids. Mol Ecol 12:2033–2043
Fossati T, Patrignani G, Zapelli I, Sabatti M, Sala F, Castiglione S (2004) Development of molecular markers to assess the level of introgression of Populus tremula into P. alba natural populations. Plant Breeding 123:382–385
Fossati T, Zapelli I, Bisoffi S, Micheletti A, Vietto L, Sala F, Castiglione S (2005) Genetic relationships and clonal identity in a collection of commercially relevant poplar cultivars assessed by AFLP and SSR. Tree Genet Genomes 1:11–19
Gaudet M, Jorge V, Paolucci I, Beritognolo I, Scarascia Mugnozza G, Sabatti M (2007) Genetic linkage maps of Populus nigra L. including AFLPs, SSRs, SNPs, and sex trait. Tree Genet Genomes 4:25–36
Gomez A, Manzanera JA, Aguiriano E, Grau JM, Bueno MA (2003) SSR markers for monitoring an in vitro core collection of Populus tremula. Silvae Genet 52:5–6
Grattapaglia D, Resende MDV (2011) Genomic selection in forest tree breeding. Tree Genet Genomes 7:241–255
Hamzeh M, Dayanandan S (2004) Phylogeny of Populus (Salicaceae) based on nucleotide sequences of chloroplast TRNT-TRNF region and nuclear rDNA. Am J Bot 91:1398–1408
Hancock JM (1999) Microsatellites and other simple sequences: genomic context and mutational mechanisms. In: Goldstein DB, Schlötterer C (eds) Microsatellites—evolution and applications, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–9
Hofmann M (1998) Bewirtschaftung schnellwachsender Baumarten auf landwirtschaftlichen Flächen im Kurzumtrieb. Forschungsinstitut für schnellwachsender Baumarten Hann. Münden, Merkblatt 11
Isabel N, Lamothe M, Thompson SL (2013) A second-generation diagnostic single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based assay, optimized to distinguish among eight poplar (Populus L.) species and their early hybrids. Tree Genet Genomes 9:621–626
Khasa D, Pollefeys P, Navarro-Quezada A, Perinet P, Bousquet J (2005) Species-specific microsatellite markers to monitor gene flow between exotic poplars and their natural relatives in eastern North America. Mol Ecol Notes 5:920–923
Kibbe WA (2007) OligoCalc: an online oligonucleotide properties calculator. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server Issue):W43–W46
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Nevo E (2004) Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21:991–1007
Liesebach H, Schneck V, Ewald E (2009) Clonal fingerprinting in the genus Populus L. by nuclear microsatellite loci regarding differences between sections, species and hybrids. Tree Genet Genomes 6:259–269
Liesebach M (2012) Anbauerfahrung aus einem 35-jährigen Versuch mit Populus deltoides in Norddeutschland und deren künftige Nutzung als Kreuzungselter. Forstarchiv 83:66–70
Meilan R, Sabatti M, Kuzminsky E (2004) An early-flowering genotype of Populus. J Plant Biol 47:52–56
Orlovic S, Galovic V, Zoric M, Kovacevic B, Pilipovic A, Zoran G (2009) Evaluation of interspecific DNA variability in poplars using AFLP and SSR markers. Afr J Biotechnol 8:5241–5247
Pakull B, Groppe K, Meyer M, Markussen T, Fladung M (2009) Genetic linkage mapping in aspen (Populus tremula L. and Populus tremuloides Michx.). Tree Genet Genomes 5:505–515
Pakull B (2010) Genetische Kartierung und Untersuchungen zur Geschlechtsdeterminierung in Espen (P. tremula L./P. tremuloides Michx.). Dissertation, University of Hamburg, Germany
Rahman MH, Dayanandan S, Rajora OP (2000) Microsatellite DNA markers in Populus tremuloides. Genome 43:293–297
Rathmacher G, Niggemann M, Wypukol H, Gebhardt K, Ziegenhagen B, Bialozyt R (2009) Allelic ladders and reference genotypes for a rigorous standardization of poplar microsatellite data. Trees 23:573–583
Schroeder H, Fladung M (2010) SSR and SNP markers for the identification of clones, hybrids and species within the genus Populus. Silvae Genet 59:257–263
Schroeder H, Hoeltken AM, Fladung M (2012) Differentiation of Populus species using chloroplast single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers—essential for comprehensible and reliable poplar breeding. Plant Biol 14:374–381
Smith RL, Sytsma KJ (1990) Evolution of Populus nigra (sect. Aigeiros): introgressive hybridization and the chloroplast contribution of Populus alba (sect. Populus). Amer J Bot 77:1176–1187
Smulders MJM, Van Der Schoot J, Arens P, Vosman B (2001) Trinucleotide repeat microsatellite markers for black poplar (Populus nigra L.). Mol Ecol Notes 1:188–190
Suvanto LI, Latva-Karjanmaa TB (2005) Clone identification and clonal structure of the European aspen (Populus tremula). Mol Ecol 14:2851–2860
Talbot P, Thompson SL, Schroeder W, Isabel N (2011) An efficient single nucleotide polymorphism assay to diagnose the genomic identity of poplar species and hybrids on the Canadian prairies. Can J For Res 41:1102–1111
Tuskan GA, Gunter LE, Yang ZK, Yin TM, Sewell MM, DiFazio SP (2004) Characterization of microsatellites revealed by genomic sequencing of Populus trichocarpa. Can J For Res 34:85–93
Tuskan GA, DiFazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N et al (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 313:1596–1604
van der Schoot J, Pospiskova M, Vosman B, Smulders MJM (2000) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in black poplar (Populus nigra L.). Theor Appl Genet 101:317–322
Willing RR, Pryor LD (1976) Interspecific hybridisation in poplar. Theor Appl Genet 47:141–151
Yin TM, Zhang XY, Huang MR, Wang MX, Zhuge Q, Zhu LH, Wu RL (2002) Molecular linkage maps of the Populus genome. Genome 45:541–555
Acknowledgements
We like to thank our technical assistants Katrin Groppe for the in silico analyses and Caren Heitmann for the realisation of the PAA gels as well as Dr. Mirko Liesebach, Dr. Georg von Wühlisch and our other colleagues for the collection of different poplar material. Further, we are grateful to Dr. Birgit Kersten (Thünen-Institute of Forest Genetics Grosshansdorf) and Doreen Pahlke (MPI for Molecular Plant Physiology, Potsdam, Germany) for data integration into GabiPD (www.gabipd.org) and sequence submission to the NCBI GenBank database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Ingvarsson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruegmann, T., Fladung, M. Potentials and limitations of the cross-species transfer of nuclear microsatellite marker in six species belonging to three sections of the genus Populus L.. Tree Genetics & Genomes 9, 1413–1421 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-013-0647-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-013-0647-3