Abstract
A life threatening medical condition occurs when arteries that supplies blood to the brain gets blocked resulting in Ischemic Stroke. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays major role in diagnosis of brain stroke at early stages. Manual detection of stroke lesions by medical experts is time-consuming, expensive, and susceptible to intra- and inter-observer variability. Accurate detection of stroke lesions from brain MRI, the challenging task requires development of automated computer aided diagnostic techniques. This paper aims at reviewing the state of art techniques currently available fulfilling the above objectives, their merits and limitation. Through this review we figure out the modifications that need to be carried out in future to develop best automated diagnostic tool which performs better and mitigates all the pitfalls in current literatures.

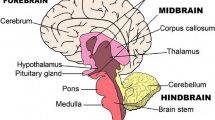
(Courtesy Mayo Clinic)



[courtesy from reference 22]

[courtesy from reference 26]

[courtesy from reference 33]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Institutes of Health. (2011). Brain basics: Preventing stroke. Brain basics: Preventing stroke.
Benjamin, E. J., Virani, S. S., Callaway, C. W., Chamberlain, A. M., Chang, A. R., Cheng, S., & de Ferranti, S. D. (2018). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
Pandian, J. D., & Sudhan, P. (2013). Stroke epidemiology and stroke care services in India. Journal of Stroke, 15(3), 128.
Prasad, K., Vibha, D., & Meenakshi, (2012). Cerebrovascular disease in South Asia-Part I: A burning problem. JRSM Cardiovascular Disease, 1(7), 1–7.
Towfighi, A., & Saver, J. L. (2011). Stroke declines from third to fourth leading cause of death in the United States: Historical perspective and challenges ahead. Stroke, 42(8), 2351–2355.
Feigin, V. L., Lawes, C. M., Bennett, D. A., Barker-Collo, S. L., & Parag, V. (2009). Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. The Lancet Neurology, 8(4), 355–369.
World Health Organization. Cerebrovascular disorders. A Clinical and Research Classification, offset publication 43. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Bamford, J., Sandercock, P., Dennis, M., Warlow, C., & Burn, J. J. T. L. (1991). Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. The Lancet, 337(8756), 1521–1526.
Fisher, M. (1999). Antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke. Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis, 7(2), 165–169.
Barber, P. A., Darby, D. G., Desmond, P. M., Gerraty, R. P., Yang, Q., Li, T., et al. (1999). Identification of major ischemic change: Diffusion-weighted imaging versus computed tomography. Stroke, 30(10), 2059–2065.
Petrick, N., Sahiner, B., Armato, S. G., III, Bert, A., Correale, L., Delsanto, S., et al. (2013). Evaluation of computer-aided detection and diagnosis systems a. Medica Physics, 40(8), 087001.
Wong, K. P. (2005). Medical image segmentation: Methods and applications in functional imaging. In Handbook of biomedical image analysis (pp. 111–182). Boston, MA: Springer.
Norouzi, A., Rahim, M. S. M., Altameem, A., Saba, T., Rad, A. E., Rehman, A., et al. (2014). Medical image segmentation methods, algorithms, and applications. IETE Technical Review, 31(3), 199–213.
Carey, L. M., Seitz, R. J., Parsons, M., Levi, C., Farquharson, S., Tournier, J. D., et al. (2013). Beyond the lesion: neuroimaging foundations for post-stroke recovery. Future Neurology, 8(5), 507–527.
Knight, R. A., Dereski, M. O., Helpern, J. A., Ordidge, R. J., & Chopp, M. (1994). Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of evolving focal cerebral ischemia. Comparison with histopathology in rats. Stroke, 25(6), 1252–1261.
Baird, A. E., & Warach, S. (1998). Magnetic resonance imaging of acute stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 18(6), 583–609.
Rivers, C. S., Wardlaw, J. M., Armitage, P. A., Bastin, M. E., Hand, P. J., & Dennis, M. S. (2007). Acute ischemic stroke lesion measurement on diffusion-weighted imaging—Important considerations in designing acute stroke trials with magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 16(2), 64–70.
Xavier, A. R., Qureshi, A. I., Kirmani, J. F., Yahia, A. M., & Bakshi, R. (2003). Neuroimaging of stroke: A review. Southern Medical Journal, 96(4), 367–379.
Cavalieri, M., Enzinger, C., Petrovic, K., Pluta-Fuerst, A., Homayoon, N., Schmidt, H., et al. (2010). Vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease—Are we in a dead-end road? Neurodegenerative Diseases, 7(1–3), 122–126.
Debette, S., & Markus, H. S. (2010). The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ, 341, c3666.
Mitra, J., Bourgeat, P., Fripp, J., Ghose, S., Rose, S., Salvado, O., et al. (2014). Lesion segmentation from multimodal MRI using random forest following Ischemic stroke. NeuroImage, 98, 324–335.
Van Leemput, K., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., Colchester, A., & Suetens, P. (2001). Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions by model outlier detection. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20(8), 677–688.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Stone, C. J., & Olshen, R. A. (1984). Classification and regression trees. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Yi, Z., Criminisi, A., Shotton, J., & Blake, A. (2009). Discriminative, semantic segmentation of brain tissue in MR images. In International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 558–565). Springer: Berlin.
Criminisi, A., Shotton, J., & Konukoglu, E. (2011). Decision forests for classification, regression, density estimation, manifold learning and semi-supervised learning. Microsoft Research Cambridge, Tech. Rep. MSRTR-2011-114, 5(6), 12.
Chyzhyk, D., Dacosta-Aguayo, R., Mataró, M., & Graña, M. (2015). An active learning approach for stroke lesion segmentation on multimodal MRI data. Neurocomputing, 150, 26–36.
Yu-Feng, Z., Yong, H., Chao-Zhe, Z., Qing-Jiu, C., Man-Qiu, S., Meng, L., et al. (2007). Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development, 29(2), 83–91.
Zou, Q. H., Zhu, C. Z., Yang, Y., Zuo, X. N., Long, X. Y., Cao, Q. J., et al. (2008). An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: Fractional ALFF. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 172(1), 137–141.
Zang, Y., Jiang, T., Lu, Y., He, Y., & Tian, L. (2004). Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage, 22(1), 394–400.
Kendall, M., & Gibbons, J. D. (1990). Rank correlation methods (5th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Cohn, D., Atlas, L., & Ladner, R. (1994). Improving generalization with active learning. Machine Learning, 15(2), 201–221.
Tuia, D., Pasolli, E., & Emery, W. J. (2011). Using active learning to adapt remote sensing image classifiers. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115(9), 2232–2242.
Maier, O., Wilms, M., von der Gablentz, J., Krämer, U. M., Münte, T. F., & Handels, H. (2015). Extra tree forests for sub-acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in MR sequences. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 240, 89–100.
Shamonin, D. P., Bron, E. E., Lelieveldt, B. P., Smits, M., Klein, S., & Staring, M. (2014). Fast parallel image registration on CPU and GPU for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 50.
Klein, S., Staring, M., Murphy, K., Viergever, M. A., & Pluim, J. P. (2009). Elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(1), 196–205.
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155.
Likar, B., Viergever, M. A., & Pernus, F. (2001). Retrospective correction of MR intensity inhomogeneity by information minimization. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20(12), 1398–1410.
Nyúl, L. G., Udupa, J. K., & Zhang, X. (2000). New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 19(2), 143–150.
Geurts, P., Ernst, D., & Wehenkel, L. (2006). Extremely randomized trees. Machine Learning, 63(1), 3–42.
Maier, O., Schröder, C., Forkert, N. D., Martinetz, T., & Handels, H. (2015). Classifiers for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation: a comparison study. PLoS ONE, 10(12), e0145118.
Zhang, H. (2004). IThe optimality of Naive Bayes. In Proceedings of seventeenth international Florida artificial intelligence research society conference FLAIRS 2004 (Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 1–6).
Rish, I. (2001). An empirical study of the naive Bayes classifier. In IJCAI 2001 workshop on empirical methods in artificial intelligence (Vol. 3, No. 22, pp. 41–46).
Cover, T., & Hart, P. (1967). Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13(1), 21–27.
Friedman, J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 29, 1189–1232.
Freund, Y., & Schapire, R. E. (1997). A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 55(1), 119–139.
LeCun, Y., Boser, B., Denker, J. S., Henderson, D., Howard, R. E., Hubbard, W., et al. (1989). Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Computation, 1(4), 541–551.
Jia, Y., Shelhamer, E., Donahue, J., Karayev, S., Long, J., Girshick, R., & Darrell, T. (2014). Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 675–678).
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the facts and materials reviewed throughout this article are derived from cited external sources and does not include author’s personal research work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiyagarajan, S.K., Murugan, K. A Systematic Review on Techniques Adapted for Segmentation and Classification of Ischemic Stroke Lesions from Brain MR Images. Wireless Pers Commun 118, 1225–1244 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08069-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08069-z